
Title: Wagner
Author: John F. Runciman
Release date: December 24, 2004 [eBook #14441]
Most recently updated: December 6, 2024
Language: English
Other information and formats: www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/14441
Credits: Produced by Steven Gibbs and the PG Online Distributed Proofreading Team
HIS YOUTH 1813-1834.
The old world is very remote from us now, but it is worth while making a small attempt to realize how it stood to Wagner. When he was born, in 1813, Bach had been dead only a little over sixty years; Mozart had been dead about twenty years, and Haydn about ten; Beethoven was in the full splendour of his tremendous powers; Weber and Schubert had still their finest work to do. To grasp all that this means, let us consider our relation to Mendelssohn. He died nearly sixty years ago; yet, whatever we may think of him as a composer, we can scarcely call him old-fashioned: he remains indisputably one of the moderns. Now, Wagner can never have looked upon Bach as a modern. He spoke of him and his old periwig almost as one might allude to an extinct race of animals. The history of an art cannot be measured off in years: in some periods it moves slowly, in others with startling rapidity. Since Mendelssohn's day composers have sought rather to develop old resources and forms than to find and create new ones, whereas in the sixty years that lie between Bach's death and Wagner's birth the whole form and content, the very stuff, of music was changed. In 1750 he would have been a daring and extraordinarily sapient being who prophesied that within forty years Mozart's G minor Symphony would be written. Between Bach and Wagner is a great gulf set, a gulf bridged by Emanuel Bach, Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven; between ourselves and Mendelssohn there is no such chasm and certainly no such list of mighty names. It was in the period of swift transition from Bach's fugues to Beethoven's Choral Symphony that Wagner was born, a period when musical Germany was in a state of tumultuous ebullition. Later we shall see for how much this counted in the growth of Wagner's genius. In the meantime it may be observed that in externals the world of 1813 was not so far removed from the world of 1750. All the men on whose work Wagner was fed and brought up had their roots in a past that is now dead and buried. Had he been born a few years earlier he might have worn a wig; the stock was not to depart for many a year to come. A man might still, without causing remark, wear coats, waistcoats and trousers of many hues. The old world was going fast, but it had not gone. The fires of the French Revolution had cast strange lights amongst the peoples and struck a deadly chill into the hearts of kings and governors. Napoleon had shown what the will, brain and energy of a man could do, and all the forces of reaction were gathering together to crush him at Waterloo; the heads of men were seething with new ideas, destined to bring about the strangest results a few years afterwards; but the old order still prevailed, had not yet yielded to the new. Let us remember how short a time had passed since Haydn retired, after a life spent at a pig-tail German Court in the service of a princeling whose position was about as lofty as that of an English country squire, though it must be admitted that his tastes were a little more elevated. Railways had not defiled the landscapes of Europe, nor gas robbed her cities of all romance by night. The watchman blew his horn and called the hour, and told all those abed that it rained or snowed. Most of the blessings of civilization, which were to do so much for humanity and have done so little, had yet to come. Fair fields and forests, fresh, unpolluted rivers, cities of great-gabled houses, old-world narrow streets and beautiful gardens, and, excepting in England, few noisy smoking factories and foul chemical works—this was the Europe into which Richard Wagner was born on May 22, 1813.
He was born in Leipzig. His father, a police official of some vague sort, died when he was a few months old, and his mother went to Dresden and married Ludwig Geyer, an actor. Richard, however, had no great luck in the matter of fathers, for six years later Geyer also died. Dresden was, as things were in those days—ninety years ago—a fairly musical city; it had Weber at the opera and musicians of various degrees of celebrity, deserved or undeserved. This, however, cannot have much affected Wagner as a child. Rather, it is worth while glancing for a moment at the artistic life which went on at his home. Whatever else it may have been, it was not specially musical. Geyer was an actor, Wagner's sister became an actress, and the atmosphere of the theatre must have pervaded the family circle. This accounts somewhat for Wagner's earlier artistic attempts. He showed none of the preternatural musical precocity of Bach, Mozart and Beethoven, who in their very cradles were steeped in music. While his musical powers lay a long time latent, his thoughts and energies were from babyhood directed to the theatre. At the age of ten he probably knew a great deal more about the drama of the day than he did of its music; probably he knew better when a play was well represented than when a symphony was well played. Yet, while his theatrical tendencies were encouraged, he must have been far from being indifferent to music. He realized that Weber was a very great man, and used to watch him passing in the street. This is significant, for Weber remained to him throughout his life as a demigod; from Die Feen, his boyish opera, until after Lohengrin he used freely the Weber phraseology and melodic contours, and when Weber's remains were transported from London to be reinterred in Germany it was Wagner who pronounced the inevitable discourse.
Still, the theatre was his first love, a love rather intensified than otherwise when his mother removed back again to Leipzig and Richard was sent to Nicolai Lyceum. How the family lived at this time is hard to say, but probably it was done through the help of his sister and other relatives. Anyhow, it was not till later that Wagner learnt the meaning of the word poverty, and then it entered like iron into his soul; and in the meantime he got a good general education. Leipzig was then hardly more musical than Dresden. Bach had worked and died there; Mozart, not so long before Wagner's birth, had visited it and got to know some of Bach's motets by the astounding process of memorizing the separate parts and putting them together mentally. It was far from being the busy, if somewhat philistine, musical centre we know to-day. It had its Gewandhaus concerts, but their state may be inferred from a report written by Mendelssohn long afterwards, in which he spoke of dismissing the incompetents of the band, who went away as men who had lost their bread. It had its opera, which was doubtless as good as the average German opera of the time. But without a conservatoire, without musicians of the first rank, with its middling orchestra, it cannot be compared with, say, Vienna, where the very air breathed music and great musical traditions and memories abounded. Bach, the poor organist and schoolmaster, was little more than a name to all save his pupils and their pupils. His Matthew Passion lay there untouched, with the dust thick on it, and there it remained until Mendelssohn had it sung a century after its first and only previous performance.
Here Wagner took lessons on the pianoforte from Gottlieb Müller, and never learnt to play. Later he worked at counterpoint with Weinlig. But at first the drama and not music continued to hold his attention. He studied Greek plays and Shakespeare, and his highest ambition was to achieve a stupendous drama which in the matter of sensations and murders should eclipse anything yet done. But it dawned upon him that without music his play could not make its full and proper effect, so into music he went, and was at once caught in the impetuous torrent of the time. He could not play, but he could read scores, and soon all Beethoven was as well known to him as his mother's face. Accounts, more or less trustworthy, are given of his singing and whistling the chamber works; and it is an undoubted fact that he made a pianoforte transcription—one would much like to see it—of the Choral Symphony. He tried his hand at composition, and wrote some things that are without value; he sketched one opera which came to nothing, and in 1833 completed another, The Fairies (Die Feen), which was not produced till more than fifty years afterwards. The following year he was appointed conductor of the Magdeburg Theatre, and with this appointment may be said to end his apprenticeship to the trade he was to follow for some years.
The trade he had chosen was that of operatic conductor. It was not until eight years later that he made a serious début as an operatic composer. The Forbidden Love (Das Liebesverbot) is entirely unknown to me; but it may be doubted whether Wagner, with his head full of confused ideas, and as yet no definite and distinctive plan or method, could at this time produce a great work of art. He had to pass through his Rienzi period first. But two points may be remarked. Already he had determined to make his own librettos; and his early association with the theatre enabled him to judge much better than any of the libretto-makers of that or any other time as to what would prove effective on the stage. In the second place, in the music of The Fairies, we see to what an extent he had assimilated Weber; the themes are Weberesque in outline, and the whole colour—colour of harmony and orchestration—is also Weberesque. He went on planning and writing operas, but his daily bread-earning work was rehearsing his company and conducting. The experience must have been invaluable to him; but there is nothing especially remarkable to record of the period. He himself left an account of the failure of The Forbidden Love, which was produced in 1836. The company went to pieces immediately after, and he was glad to find a position at Königsberg. This, however, came to nothing, or next to nothing, owing to the director's failure, and again Wagner had to remove, this time to Riga.
The Riga period is one of the most important of his life. He had married Minna Planer, who is said to have been a very pretty woman and quite incapable of understanding her husband and his artistic aspirations; and he began, slowly and tentatively, to shape a course through life for himself. He continued to gain experience in the production of other composers' operas; he studied incessantly, and at last he hit upon the idea of writing a grand opera in the Meyerbeer style, and going to Paris with it, in the hope of getting it produced at the opera there. He was harassed by creditors; and with the daring and energy characteristic of the man whom Fate had destined to build Bayreuth, he determined to try by one bold stroke to retrieve his fortunes. He was still a young man when he went to Riga in 1837, but he was in such a feverish hurry for fame and glory, not to say money, that no obstacle was allowed to stand in his way. During the last few years he had composed a number of occasional things—which we need not stop to consider—but nothing on the sumptuous scale of Rienzi. Heroic personages, dramatic or melodramatic situations, opportunities for huge gaily-dressed crowds and scenic display—these were what the young man was after; and in the story of Rienzi he found plenty to fire an imagination always prone to flame and flare at the slightest suggestion. The libretto was written; the music was partly written; and in 1839 Wagner took one of the most momentous steps in all his stormy career—he sailed from Riga, accompanied by his wife and dog, with the intention of reaching Paris by way of London.
The voyage itself bore noteworthy artistic fruit; for within three years the roar and scream of the tempest, the smashing of heavy seas upon the ship's sides and deck, and (I dare say) the captain's curses, were to be translated into tone and take artistic shape in The Flying Dutchman. London reached in safety, Wagner stayed first near the Tower and then in Soho. He lost his dog, found it, and crossed the Channel to Boulogne. Here he met Meyerbeer, who gave him an introduction to a bankrupt theatre, the Renaissance, in Paris. In Paris he met many well-known people, amongst them Heine, who clasped his hands and looked heavenwards when he heard of a penniless German coming to such a city to seek his fortune, with nothing save an unfinished opera and an introduction from Meyerbeer. The late Sir Charles Hallé met him at this time, and left some amusing reminiscences in his Autobiography. Heine's view of the situation was speedily justified. Not by any efforts could Rienzi be unloaded upon an opera director, and Wagner began to experience the bitterness of poverty. To earn a bare living, he thought himself lucky to be entrusted with the making of transcriptions of popular airs and the writing of articles for the press.
The three years' stay in Paris did Wagner no particular harm that I have been able to trace beyond implanting in him that deadly fear of being hard up which haunted him all his life thenceforward, and is an offensive and yet pathetic feature of his letters to all his friends. On the other hand, he heard opera performances on a scale outside and beyond his past experience; he heard Habenek direct the Choral Symphony at the Conservatoire, and learnt much, not only about that mighty work—which he must already have known by heart—but also of the art of conducting; he finished Rienzi and sent it off to Dresden, where it was accepted; and he planned and completed The Flying Dutchman, which was accepted for production at Berlin. He had also written the Faust Overture in its first form. And probably also he had acquired that almost fatal fluency of the pen which was to make so many enemies for him afterwards, and yet to lead to the realization of his life's dream in Bayreuth. A bare list of the names of the friends and opponents he gained at this time would take up more space than is available in so brief a study as this, and I must pass over many interesting incidents. The most important is that connected with The Flying Dutchman libretto. Wagner submitted his sketches to the opera, where they were placed at the disposal of another composer, and he was offered (I think) £20 or nothing for them. He took the £20, and then, his artistic conscience happily triumphing over his commercial conscience, he used the money to live upon until he had completed his own opera on the same subject. The French Dutchman (music by Dietsch) was produced. It failed and is forgotten. How Wagner's fared all the world knows.
Rienzi was now getting ready at Dresden, and thither Wagner went in April, 1842. The opera was produced in October, with enormous success, and the name of Wagner became famous throughout Germany. Nowadays so much of the music appears so very cheap and tawdry that it is only after a severe mental struggle one can understand the enthusiasm the work aroused. We must put away all thought of the later Wagner; we must forget that when Rienzi was produced the Dutchman had already been some time finished. We must remember the sort of music the Dresden public had suffered under: dull, workmanlike operas, without an original touch, without the breath of life in them—in a word, kapellmeister music. The pomp and outward show of that remarkable heavy-weight Spontini must have come as a relief after the Dresden opera-goer's ordinary fare; but Spontini, though he lays on his colours with a barbarian regal hand, never sparkles; he is altogether lacking in vivacity, elasticity; he had no gift for gracious or piquant melody. Of the operas of Marschner much the same must be said; in them we find the tricks of the Romantics without the best Romantics' sense of beauty, all the horrors of Weber without Weber's passion. Black woods, supernatural fireworks by night, enchantments, vampires, guns that went off by themselves—all this jugglery was fast being done to death, and what at first had been a nerve-shaking novelty was becoming a mere tedium. In opera The Castle of Otranto was played out. Into this region of inspissated gloom Richard burst with Rienzi, the brilliant, the fearless, the tragic hero; all was blazing light and colour; it sparkled; if the champagne of it was of an inferior quality—often, indeed, poor goose-berry—yet it bubbled and frothed gaily. Besides, there were great sweeping tunes—such as the hackneyed prayer—and plenty of really dainty, if very Weberesque, melodies. All that Meyerbeer had to teach was there, and the stolid Dresdener gazed with delight on the brilliance of the latest Parisian musical fashions. So Wagner gained his first success, and deserved it. It was not the Paris success he had dreamed of a few years before, when fame, money and all worldly things desirable were to be his. But it meant bread-and-butter without drudging for the publishers or the press; it meant the means of living while he wrote masterpieces which were to set half the world against him and eventually make him immeasurably the greatest musical figure of his time. He was appointed Court kapellmeister, and there he remained until 1849. Before proceeding to this next period of seven years we must consider The Flying Dutchman.
This is his first music drama. He called it a romantic opera; but here for the first time the drama grows out of an idea and the music out of the drama. The thing suggested itself to him during that stormy trip to London: the roaring waves, the whistling of the salt winds, the loneliness of the bitter North Sea—these set his imagination aworking on the old legend of the mariner doomed to sail the ocean until the Day of Judgment. In this there was colour and atmosphere enough, but no drama. The dramatic idea he took from Heine's sentimental version. In this the Dutchman's lot is softened and mitigated by a possibility of salvation. He can go ashore once in seven years, and if he can find a maiden who will love him and be faithful unto death he will be released from the necessity to wander. That is to say, his chances of redemption depend upon constancy of some unknown young lady. All the Dutchman has to do is to find her, make himself agreeable, and trust to luck. A more childish notion never occurred to an intellectual man, nor a more selfish one. The lady might have done nothing wrong; she was to be punished for loving not wisely but too well; and there is nothing in the old legend or in the Wagner-Heine form of it to show the Dutchman to have been a deserving person. Yet, on the other hand, Wagner, with still vivid memories of the agonies he had endured during his voyage, may have thought the punishment excessive for a momentary loss of temper in trying circumstances and a passing swear-word; and the girl was to find the fullest joy her nature was capable of in sacrificing herself. But there is no fundamental verity inherent in the idea: the Dutchman's salvation might as well depend on a throw of dice; and all this early nineteenth-century romantic sentimentalism, with one of its main notions—that a woman cannot be better occupied than in "saving" a man—this, grafted on to the stern, relentless old story, makes a compound that is always unreal and sometimes ludicrous. But it gave Wagner three opportunities: of painting the stormy sea, of depicting the hopeless misery of the Dutchman Vanderdecken, and of expressing in music woman's most passionate and unselfish love.
No one need be afraid of "not understanding" the Dutchman. The story is simplicity itself. Wagner knew the theatre and every stagey device by heart, and in none of his dramas is there anything half so hard to follow as the plots, say, of Rigoletto and Aïda and most Italian operas. Nor, again, does the music present any difficulty. In spite of the use of the leit-motif which I shall discuss presently, the separate numbers are as clean cut as those of any Mozart opera. He joins his different items, it is true, but it is impossible to avoid knowing where one leaves off and the next begins. The play opens with the raging tempest on a rocky coast; the ship of one Daland is driven there, and Daland goes ashore to see if there is any likelihood of the storm ceasing—a proceeding at which any land-lubber, not to mention experienced tars, might well laugh. Finding himself far from his port and no probability of the wind and sea falling immediately, he goes on board again to take a little rest, and descends to his cabin, leaving a sailor as watchman, to see, I suppose, that the vessel does not batter itself to pieces on the cliffs. The watchman sings himself to sleep with a most beautiful ballad. The sky darkens, the sea boils more furiously than ever, and the phantom ship arrives. With a prodigious uproar her anchor takes ground—another evidence of Wagner's seamanship—and Vanderdecken comes ashore in his turn. His seven years are up; now he has another chance of finding the faithful maiden. The opening of this scene is as fine as anything Wagner ever wrote; the later portions are fine, too, but quite old-fashioned. The storm ceases, and Vanderdecken having expressed his hopes and fears, Daland comes on deck, enters into conversation with the stranger, and in a few minutes it is arranged that the two shall go together, and if the Dutchman can win Senta's heart, she shall be his.
Now, it will be noted here that the whole thing is ridiculously stagey and artificial. In spite of the new ideas fermenting in Wagner's brain, he had not yet got away from the stage-trickiness of Scribe. Unreality and artificiality face you at every step. The music is a different matter. No one, not even Mendelssohn in his Hebrides overture, has ever given us the sea, the noise and colour of it, its violence and ruthlessness, as Wagner has here. It is the sea that pervades the whole of the act; but imposed on its ceaseless sound there are very splendid things—some worn a little threadbare by now, but many still fresh. In the next act the prima donna has her opportunity. Senta, the heroine, sits at her spinning-wheel amidst a number of maidens. After a conventional spinning chorus, Senta sings the ballad of the Flying Dutchman, whose picture hangs on the wall, and ends up with an ecstatic appeal to Heaven, Fate—everyone in general and no one in particular—to give her the chance of saving him. Daland and Vanderdecken enter, and the drama begins to approach its climax. The spinning chorus is pretty; but nothing in the act—nor, in fact, in the whole opera—matches the glorious passage where Senta takes her fate in both hands and avows her resolution to follow the Dutchman to death or whatever else may befall.
The essence of the last act may be given in a few words. It begins as if Wagner had felt that he had not made sufficient use of the uncanny effects to be got out of the phantom ship, and we get a long string of choruses not necessary to the drama. At the last Vanderdecken, he, too, rises to the full height of his character, and, determining that he will not sacrifice Senta, renounces her and goes on board his boat to sail off. But Senta throws herself into the water after him; the phantom vessel falls to pieces, and the glorified forms of the two are seen mounting towards the sky. But Vanderdecken's sudden resolve has the air of an afterthought, and counts for little beside the fact that throughout the drama the sacrifice of Senta has been insisted on as the price of his redemption. It is the Senta theme, also, that is played as the pair mount.
The Dutchman must stand amongst Wagner's great works. More beautiful music for the theatre had been written, but never had such energy been put into it as we find in the Dutchman's damnation theme or the tumult of the bitter, angry sea. Any lazy man can, in time, fill up a score with sufficient notes for the trumpets, trombones and drums to produce a deafening uproar, but it took all the native force of a Wagner to fill, to inform, the thought itself with such energy that, looking at the score, the passages seem almost to leap out from the page, and, played on even a small piano, their effect is still overwhelming. When the opera was produced the effect on the audience was certainly overwhelming, almost stupefying. The Dutchman had been accepted at Berlin on Meyerbeer's recommendation, but that recommendation Wagner probably thought of no great value, and after the success of Rienzi he determined to have it also played at Dresden, and the first performance took place at the beginning of 1843. The noise of the storm rolled far outside the theatre, and from that time forward Wagner and his music were subjects of discussion throughout Europe. His originality was not doubted; the din of his orchestra was no louder than that of Spontini's or Marschner's, but the harmony seemed bold to those who had never known Bach and had already forgotten Beethoven, and people were puzzled by the lack of full-stops at the end of each number. Things that seem old-fashioned to us now were then new, while Wagner's own genuine inventions could at first hardly be grasped. However, Wagner had no reason to be dissatisfied. He had already his admirers, he was secure in an important post, and he could cheerfully set forth in search of fresh woods and pastures new, or, to use a more appropriate figure, fresh seas to cross in search of new continents.
He was now thirty, and although he had written two long works, one of them a great one, they constituted the merest prelude to the gigantic achievements of the next forty years. He was busily engaged at the opera, but set to work at once on an endless number and variety of projects. Tannhäuser was finished by 1845, Lohengrin by 1847, and his brain was occupied with The Mastersingers of Nuremberg (Die Meistersinger) and The Nibelung's Ring, both to be completed long afterwards. During this period he also composed the Love-feast of the Apostles, and did a bit of mending to Gluck's Iphigenia in Aulis. But, though scheming many things, he seemed by no means sure of his road at first. With Schröder-Devrient, the singer, and others, he discussed lengthily the question of whether he should attempt another Rienzi or go on from the Dutchman. If to realize his artistic dreams was dear to Wagner, so were immediate success, fame and money. Of the last he could never have enough, for he spent it faster than he gained it—spent it on himself, needy artists, on any object which suggested itself to him. However, the creative artist in him had the victory. The notion of a second Rienzi was abandoned and Tannhäuser commenced. He had come across the legend of an illicit passion and its punishment somewhere, and he set to work on the book of words. Of course he sentimentalized the story—it was a trick he was always given to, especially during these, his younger, years—and, of course, he made a woman sacrifice herself for a man. In the older form of the tale Tannhäuser lived goodness knows how long with Venus; then he forsook her, and she vowed to take vengeance on him. He returned to his friends, and entered for a competition in minstrelsy. While in the middle of his song, which would have gained him the prize, Venus visited him with sudden madness, and throwing away all cant about pure platonic love, he chanted the praise of foul carnal lust and the joy of living with the Goddess of Love in the heart of the hills. Coming to himself, he went on a pilgrimage to Rome, and asked and was refused the Pope's forgiveness. Then he returned to Venus, and so the story ends with the eternal damnation of Tannhäuser, just as the ancient legend of the Flying Dutchman ends with the eternal damnation of Vanderdecken.
It need hardly be said that this did not satisfy Wagner. He did not like to see people eternally damned; drab, hopeless tragedy was not for him. In nearly every opera we find peace and hope at the close, or even ecstasy in death, as in the Dusk of the Gods (Götterdämmerung) and Tristan. So he promptly made use of Elisabeth in TANNHÄUSER, though, as we shall see, the redeeming act is not so sharply defined as in the Dutchman. In the first scene Tannhäuser is sleeping in the arms of Venus, while bacchanals indulge in riotous dances. Tannhäuser suddenly starts from sleep: he has dreamed of his home as it was before his fall—of the village chime, the birds, the flowers, the sweet air; and he asks permission to return from this hot, steaming cave of vice to the fair clean earth. Venus in vain plays upon him with all her arts and wiles; he sings his magnificent song in praise of her and her beauty, but insists that he must go, and ends with a frenzied appeal to the Virgin. In a moment the illusion is broken: Venus, her luxurious cavern, her nymphs and satyrs, all disappear. There is a minute's blackness, then the light returns, and Tannhäuser is lying in the roadside before a cross. The sky is blue and the trees and grass are green, and a shepherd-boy is carolling a fresh, merry spring song. Tannhäuser remains with his face to earth while a band of pilgrims passes on its way to Rome. Then his old companions come up, recognise him, tell him Elisabeth has patiently awaited his return, and so induce him to go with them.
The second act opens on the Hall of Song. Elisabeth thinks over her grief and longing during Tannhäuser's absence, and sings her delight now that he has come back to her. He comes in, and there follows a most beautiful and touching scene, Elisabeth expressing her love and joy and recounting her past sorrow, while in Tannhäuser's utterances are mingled joy, regret, gratitude, and a sense of rapturous repose on finding himself at peace once again, after being so long tossed on seas of stormy passion. The tournament of song commences. Various minstrels sing the pure pleasures of a love in which the flesh has no part; Tannhäuser, Elisabeth approving, praises an honest, natural love. The others oppose him, until, goaded to madness, he loses all self-control. He hears the voice of Venus and calls upon her; in confusion the women rush from the hall, the men draw their swords, and in a moment the hero would be stabbed did not Elisabeth dash between him and the infuriated knights. She pleads for him, and at last, the voice of pilgrims being heard in the distance, Tannhäuser's life is spared on condition that he joins them and goes to Rome to ask forgiveness. The curtain in the last act rises on the scene of the first, but where all was young and fresh, now the leaves are withered and the tints of autumn are everywhere. Elisabeth watches the pilgrims pass on their return from Rome—Tannhäuser is not amongst them. She sings her prayer to the Virgin and goes home, as it proves, to die. Wolfram, Tannhäuser's friend, who also loves Elisabeth, sings his song of resignation; and then Tannhäuser enters, to the sinister theme of the Pope's curse. He tells Wolfram how he has been to Rome, how he has suffered, how he asked the Pope's pardon, and how the Pope declared that he should never be forgiven until the staff in his hand blossomed. So now he is on his way back to Venus. Venus calls him; he struggles with Wolfram, and is about to break away when the body of Elisabeth is carried by. Tannhäuser falls by the side of the bier; the Pope's staff, which has burgeoned, is brought on; and so the opera ends, Tannhäuser being redeemed.
It is necessary to rehearse in this way the dramatic bases of Tannhäuser and Wagner's succeeding operas for two reasons. First, the drama, which played a big enough part in the Dutchman, now becomes more important, more essential, than ever. Many an old Italian opera may be heard without the hearer knowing in the least what it is about; indeed, in many cases the less one knows of the plot, the more one enjoys the music. But the reverse is true of Wagner. Certain portions of Tannhäuser, for example, can be listened to with pleasure simply as noble or beautiful music: the overture, Tannhäuser's Song to Venus, the Pilgrims' Marching Chorus, Wolfram's "O Star of Eve," Elisabeth's Prayer, and so on. On the other hand, without an acquaintance with the story, and each stage of the story as it progresses, much of Venus's music in the first act loses its significance; the duet of Elisabeth and Tannhäuser in the second act loses its pathos, and the huge finale is meaningless, even as music; and the greater portion of the third act is simply bewildering. When we know what is being sung or done, the music is as clear as the day. Wagner knew this better than anyone, and, as I pointed out in commenting on the Dutchman, he brought his whole theatrical experience and training to help him to make the drama as simple and comprehensible as possible. When the Wagner battle was raging in the seventies and eighties, the sages pointed to the necessity of understanding the drama for the purpose of understanding the music as a defect of the Wagner music-drama, and a proof of Wagner's inferiority as a composer. But one would like to ask the sages how many songs are there which do not afford a finer artistic enjoyment when the words are understood?
A second reason for thoroughly knowing the drama of the later Wagner operas is that without that knowledge the leit-motif, which now becomes a formidable element, is likely to be wholly misunderstood and its artistic value missed. Nine-tenths of the absurdities written and talked about the leit-motif are due to ignorance of the nature of the dramatic situations in which it is used, and in consequence the purposes for which it is used. The leit-motif (leading theme) had very humble beginnings. Who was the first to employ it I really don't know. It was simply a theme which made its first appearance with one of the personages of the opera, and afterwards was used whenever that personage came on again or was referred to. Or it was connected with some thought, someone's destiny, someone's plans, and either because it expressed truly the right emotion, or because it acted by association of ideas, whenever it sounded from the orchestra the thing desired was recalled to one's mind. So used it was a useful father than a highly artistic device. Wagner constantly used it so for matters which did not demand lengthy treatment, such as Lohengrin's warning to Elsa or the curse on the gold in the Ring. But while continuing to make this elementary application of it, rather for dramatic than for musical purposes, he at the same time developed it until it ceased to be merely a leading motive, but became the very stuff of the music itself. Much of the music of the later operas is spun out of what appear at first nothing more than the old leading motives. The process by which this is done will be discussed later; for the present let us see how far Wagner goes with it in Tannhäuser.
In the Dutchman there are two principal themes, the first—
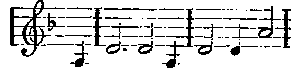
standing for Vanderdecken, the curse laid on him, and the whole idea of the phantom ship; the second—
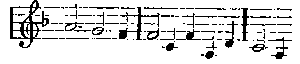
for Senta. They are short and clean-cut; they recur when wanted, and are subjected to little modification. There is not a single theme of this description in Tannhäuser. The first act is perfectly easy to follow. There are no leit-motifs. The Venus and bacchantic music will be heard again in the second and third acts; but the rest consists of numbers almost as completely detached as those that make up the Dutchman, though the joinings are not only more skilful, but are real music and not mere padding. Wagner had not by any means yet arrived at the continuous music of his later work; in spite of his desire to sweep on from the beginning to the end of each scene, he was still forced to take frequent breath and disguise the stoppage as cleverly as he could. The first scene contains many of Wagner's most inspired melodies, notably the despairing song of Venus towards the end, a tune that might have come from Schubert. The old Weber influence is to be seen in the contours of many of the themes, as well as their orchestral colour; and the steadfast four-bar rhythm reminds one, in spite of the difference of subject, irresistibly of Euryanthe. It was not until the Tristan period that Wagner got rid of this. In the second scene of the first act we find all the musical machinery of old-fashioned opera, but used with a mastery that leaves the Dutchman far behind. There is first the shepherd's delightfully fresh song, in wonderful contrast to the scents and stifling heat of the Venus cave music; then comes the Pilgrims' Chorus; then come Tannhäuser's friends with at least one number, Wolfram's appeal, which is distinct and separate from the rest of the music as a goldfish is from the water it swims in. The act ends with a regular set finale, altogether on the old models.
The second act opens with Elisabeth's scena; then follow her duet with Tannhäuser, the march and chorus as the company troop in to hear the contest of minstrels, the various songs, Tannhäuser's fatal mistake, Elisabeth's intercession for him, the voices of the pilgrims setting out for Rome, and Tannhäuser's rush to overtake them. No use is made of the leit-motif; only when Tannhäuser loses his wits and sings in praise of Venus do we get reminiscences of the Venusberg music. In the third act the structure is the same. Number flows into number, it is true, without full-closes—without full-stops, so to speak; but those who have never before heard a note of Wagner can follow as easily as they could a Gluck or Mozart opera. The Pilgrims' Chorus occurs again, and again we have the Venus music, when Tannhäuser, demented, sees her in the heart of the mountain and hears her calling him.
In 1845 Tannhäuser was produced. When the score was published—those quaint lithographed scores: I believe some of them still exist in the British Museum—Schumann got it, and seemed to like it, since he showed it as a treasure to Hanslick, a musical critic of Vienna. Mendelssohn also liked a canon in the second act—Mendelssohn, who ought to have understood and loved the picturesque in it better than anyone. All fantastic dreams of another Rienzi and a huge popular success had long since melted away: the creative instinct in Wagner was master of the situation; never again did he plan anything to please the public, save, comical to relate, when he began on the story of Tristan.
In The Flying Dutchman Wagner had exploited the uncanny, the terror and mystery of gray winter seas; in Tannhäuser he turned to the conflict between the gross, lurid passions of man and the sane, pure side of his nature; and now, in Lohengrin, he was to give us an opera which for sheer sustained loveliness has only one parallel in his works—the Mastersingers. It is the most delicately beautiful thing he wrote; its freshness is the freshness that seems unlikely to fade with the passage of time. Curiously, too, while full of the spirit of Weber—it is the most Weberesque of all his operas—of Weber who loved darksome woods, haunted ruins and all the machinery of the romantics, it is full of sweet sunlight and cool morning winds: the atmosphere of Montsalvat, the land where it is always dawn, pervades it. As a painter in music of landscape, seascape, of storm, rain amongst the leaves, spring mornings, and calm sunny woodland scenes, Wagner has no equal. There is nothing theatrical on this side of his art: the footlights and back-cloths disappear, and the very thing itself is before us.
In or about 1847 Lohengrin was finished. The tale is of the simplest. Elsa is in distress. She is the daughter of the late Duke, and her brother, the heir to the title and lands, has been changed into a swan by the enchantments of Ortruda, wife of Frederick, who says that Elsa has murdered him. Ortruda's tale is believed and Elsa is charged with the crime before the King, Henry the Fowler. Frederick brings the charge and claims the possessions and everything as the rightful heir. Henry asks whether she is willing that some champion should fight on her behalf. She consents. The herald calls for the champion; no one appears, and the case is about to be decided against her when a knight is seen in a magic boat on the river drawn by a swan. He offers to fight for her on one condition: that she will never ask his name or whence he comes. She promises, and in a few minutes Frederick is overcome and, with his wife, disgraced, and the act ends with a regular opera finale. Next, Ortruda comes as a suppliant in the night to Elsa, gains admittance, and poisons her mind with doubts about Lohengrin. However, the wedding arrangements go forward, and at the very church door Frederick interrupts the procession, and accuses Lohengrin of witchcraft and what not. He is put aside; but in the next act we see the poison at work in Elsa's mind. She and her unknown husband are left alone, and, as Nietzsche observed, they sit up too late. Elsa, with all the exasperating pertinacity of an illogical, curious woman, persists in questioning Lohengrin, getting nearer and nearer to the vital matter, until at last she can restrain herself no longer. In fancy she sees the swan returning to carry off her lover; and, wholly terrified, she asks, "Who are you and where do you come from?" At the moment Frederick rushes in with some confederates, only to be slain by Lohengrin. Sadly Lohengrin says that all now is ended; his hopes are shattered because his bride could not subdue her inquisitiveness for a year. In the next act he appears before the King and nobles; he relates what has happened, says that he comes from Montsalvat, where his father, Parcival, is King, and now he must return. Ortruda breaks through the crowd, and in malicious triumph confesses her crime. Lohengrin prays to Heaven; the swan is changed back to Elsa's brother, a dove descends and is attached to the boat, and Lohengrin sails away up the shining river, while all give a cry of distress.
We have here a simple fairy story. It is the only opera in which character, a personal idiosyncrasy as distinct from an overwhelming passion, produces the dramatic action. It has been urged that Lohengrin's stipulation is monstrous; but seeing that he is bound—we do not know how—and that if Elsa had not agreed her fate had been quickly settled, it seems to me that (accepting the magical and supernatural elements on which the whole thing rests) it was perfectly reasonable. I fancy that Wagner, after some years with his very stupid wife, Minna, was getting thoroughly angry with the irrational curiosity of women and the idiotic demands which they make on their life-mates. Anyhow, though he gives Elsa some very beautiful music to sing, he does not spare her in drawing her character. It is one of the few characters he did attempt to draw, and by far the most important of them. In the Mastersingers Walther and Eva are sketched, and Hans Sachs is worked out in some detail; but nothing in their nature especially affects the drama. In Lohengrin the tragedy is directly produced by Elsa's weakness and curiosity. The characterization is by no means profound or microscopic. It is, indeed, a question whether music is capable of anything of the sort, whether it can render anything save bold, simple outlines. In Figaro and Don Giovanni Mozart was content with this, and yet his characterization appears subtle in comparison with that of every other composer, with the exception of Wagner with his Elsa. Music can express things that lie outside the range of literature; and perhaps fine and delicate portrait and character painting are things that lie outside the range of music.
In the Dutchman, I have said, we have the North Sea for a background, in Tannhäuser the sultry, scented cave of Venus. In Lohengrin it is the broad, shining river, flowing ceaselessly from far-away lands to the distant sea, and on it the swan floats—the swan which throughout is used as the symbol of the river. In the first act it gives the pervading atmosphere and colour; in the third it recurs with amazing effect in the midst of one of Elsa's paroxysms. Here is the simple phrase by which such magic is wrought:
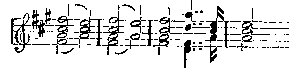
No changes are made in this theme. It occurs again and again, without wearying the ear; it keeps the atmosphere charged with mystery and suggestions of that far-away land where it is always dawn. It is the calm, refreshing, gently-rippling river; the cool, placid water sliding through many countries, with the swan as symbol and token of all that is strange and beautiful where it has its source. It is less a theme capable of purely musical development to form pattern after pattern of entrancing beauty, like the Grail or Montsalvat theme, than the equivalent in music of tender colour. It never sings out from the orchestra without carrying the imagination for a moment from the scene before one's eyes to the fernem Land. It blends the actual with the dream, and imbues all the drama with a delicious romantic mysticism. I dwell on it because without this prevailing colour and atmosphere the story of Lohengrin is a plain prosaic fairy-tale to amuse children. Further, in the most important musical theme in the opera it is there also—the Montsalvat theme:
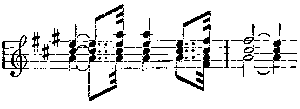
The characteristic chords in the second bar cannot escape notice. This motive, one of the sweetest Wagner invented, is long, and less of the nature of a leit-motif—as I have explained the leit-motif—than a passage like the Venus music in Tannhäuser. Just as Senta's ballad of the Flying Dutchman is the germ of that opera, so this is the germ of Lohengrin. It is worked out at great length when Lohengrin's narrative arrives, and he declares his name, parentage, and country. The Swan or River theme can scarcely be called a leit-motif in the elementary meaning of the phrase. For a fair example of this we must go to the passage used by Lohengrin when he warns Elsa that she must ask no questions:
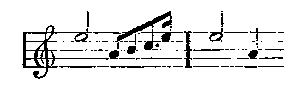
This is never developed at all. It recurs only when Elsa's pertinacious inquisitiveness threatens to rupture their somewhat hastily arranged alliance. Then it sounds out sinister, menacing, and the effect, both dramatic and musical, is overwhelming. Another example is the phrase representing Lohengrin simply as a heroic knight. Save in the finale of the first act, no great use is made of it.
It is unnecessary for me to describe in further detail an opera which is so well known, and can be followed at a first hearing very much more easily than Tannhäuser. While there is a great deal of recitative, there are also many numbers merely joined together in the Tannhäuser manner. Such numbers as the Prayer and Finale of the first act, Elsa's Song and the Processional March in the second, the Wedding Chorus in the last, are simply placed there; they do not grow out of themes, as they would have grown had the opera been written when Wagner was ten years older. The love duet which takes place after the marriage is a series of his most generously inspired melodies. There are enough beautiful and passionate tunes there to make the fortune of half a dozen Italian operas.
After Lohengrin the composer wrote nothing more for some years, though we may be sure he was eternally planning. He was intensely interested in politics. Revolution was in the air, and Wagner had to have his say on that as on every other topic. He made speeches and published pamphlets; and just as his musical schemes seemed wild to such contemporaries as the late Charles Hallé, so his ideas of social regeneration must have seemed Utopian to the point of sheer lunacy to the very comrades with whom he was acting. The explosion came; barricades were thrown up in the Dresden streets, and Wagner sought to bring about a quiet ending to the crisis by appealing to the Imperial soldiers to join with, and not to fight against, their own countrymen. Whether he actually shouldered a musket or not it is hard to say. This much is certain, however: that Wagner did take part in the rising, and that a warrant was issued for his arrest. The fiasco resulted in a great gain to music, and, as far as Wagner was concerned, there was no political loss. Had the insurgents by some unthinkable chance succeeded, he would soon have been on worse terms with them than ever he was with Kings and Imperial personages. They tried revolt because they wished to alter all the conditions under which men lived. Wagner, too, wanted to alter the conditions of life, but mainly with a view of carrying out his operatic reforms. Look where we will in his writings, we see that to be the secret of all his incursions into practical politics. Passionate—a bursting volcano of elemental energy—he was always a man of one idea at a time, and that idea always involved Richard Wagner playing an important rôle, for he was one of the most splendid egoists to be met in history.
He was now, indeed, in a pretty pickle. At Dresden he had an assured livelihood and time to write operas; and, despite his former experience of hunger and want, he threw away his position for the sake of an idea. He afterwards was wont to complain that he only wished to be kept alive in reasonable comfort, and he would in return present the world with masterpieces. Yet he was not content when he was, for a comparatively slight return in daily labour, kept comfortably alive. But, after all, what appears at first to have been an act of madness turned out anything but disastrous in the long-run. It is true that without the generous help of Liszt, Wesendonek and others he could not have lived as he did in Zurich, and, as it was, constant apprehensions of approaching poverty harassed him. The old fear of an empty belly which got into his very blood and bones in the Riga—Paris period now began to show itself in those appealing letters written to his friends when there appears to have been no necessity whatever. He had exaggerated hopes and exaggerated fears. The hopes were realized—as well as anything can be realized in this imperfect world—at Bayreuth; the fears found expression in the begging letters of which advantage was taken by every mean and cowardly spirit without the intelligence to understand his real greatness. Mendelssohn, we are reminded, wrote no such letters; but Mendelssohn, it may be remarked, was always rich, and has no such record of charitable deeds as stands to Wagner's credit. The nearest parallel to the case of Wagner is that of Beethoven in his old age. He, although perfectly well off, scared himself almost to death with his dread of poverty. Wagner's letters written about this time are well worth reading. There is no need to discuss them; they should be read and carefully weighed. Nor do I propose to spend any great space on the prose writings of the period. They are full of theories which were no sooner formulated than they had to be discarded in practice. At a time when Wagner was quite thoroughly misunderstood, the notion—perhaps naturally—became prevalent that he was simply completing a work commenced by Gluck. Now, no two men ever had more widely different aims than Wagner and Gluck. True, both wrote for the theatre, both employed singers and orchestra; and there the likenesses terminate. Gluck never sought to change the musical forms in use in opera. He retained the old recitatives, airs, concerted numbers, and choruses; not Handel himself clung more firmly to the old forms and formalities than Gluck did in Orpheus and Iphigenia. He sought, in the first place, to substitute worthy and dignified subjects for the ancient frivolities which had inspired composers since opera became popular; he wanted those subjects treated in a sufficiently dignified way, and, above all, in a reasonable way; he resolved that his music should be worthy of the drama. No concessions were to be made to the prima donna or vain tenor: the music had to be dramatically appropriate. He got magnificent results; and when the leaven of Wagnerism has ceased to work and froth and bubble in the public brain—in a word, when Wagner's music is no longer mere exciting new wine, and we are as accustomed to it as we are to the music of Beethoven—then we shall turn back to Gluck (and also to Mozart) and find them as young and fresh as ever.
Wagner's aim was totally different. First, music, he held, was played out: one must have the spoken word with it. He went to the myth for subjects, and gave plentiful reasons, which need not detain us, for the choice. Then—and here the effect of his early association with the theatre shows itself—the music was in nowise to hinder the actor; therefore all formal set numbers must be discarded and replaced by his "speech-singing" expressive recitative which should be beautiful as sheer music, and not hinder the actors from playing their parts as well as singing them. And, finally, he came to the conclusion that in his music-drama he could effect a synthesis of all the arts. Music and acting were the basis; there had to be scenery, and the scenery must form pictures, with the figures always properly placed, according to what I suppose painters would call, or refuse to call, the laws of composition. But each of the figures, or groups of figures, on the stage had also to be regarded as an entity, and as sculpture had not to be excluded from the synthesis, the poses must always be sculpturesque.
Here was a programme indeed! Very fine it seemed to his young followers; when new it seemed wholly admirable. Unfortunately, as Wagner found, the moment it was tried it proved impracticable and useless. Take sculpture, for example. Sculpture, I take it, has reached a fairly high point when the marble figure gives one the sense of life and of motion. Wagner, with his sculpturesque poses, instead of letting the living figure give us directly the impression of life and of motion, sought (always theoretically) to attain the end by an imitation of an imitation. Moreover, no moving figure ever did or can suggest sculpture—even if we wanted such a suggestion, which we don't. Even the Commandatore in Don Giovanni, with the aid of stiff gestures and plentiful whitewash, ceases to look like a statue as soon as he opens his mouth to sing. Consider, too, the notion of making, so to speak, set pictures—of dealing, that is, with his puppets and scenery in exactly the opposite spirit to that in which he wished to deal with vocal music. A realistic picture suggests Nature, and if the figures are well done they suggest human figures; a well-arranged scene does the same. There was no reason for getting indirectly, again by an imitation of an imitation, an effect that can be got directly. As for producing a series of "composed" pictures, it was practically impossible and highly undesirable. A carefully-composed picture needs time for its appreciation, and no one could, or would, try to judge or be affected by an ever-changing series of pictures. Besides, if one did try, the attention would be hopelessly withdrawn from the main things—the drama that is going forward and the music. The picture plan is still tried at Bayreuth, with disastrous results. With the most beautiful scenery it would fail; and the Wagner family appear to be colour-blind, the magic garden, for instance, in Parsifal looking like a cheap bed-hanging.
Then take, again, the set forms. Wagner eliminated the double bars and full stops, even as Beethoven had done, to an extent, in the "Heroic" Symphony, where theme leads into theme without a break; but his music is full of form, and also of forms, and the more he wrote the more careless he became about keeping up an appearance of continuity when vital continuity there was none. Wagner's forms were vaster than those of his predecessors; but for all that they are there.
Wagner's essays are worth reading by those who have the time and the physical and mental strength, if only because they reveal a man thinking on wrong lines while he is doing on right ones; but they are terribly long-winded, and many weary pages are devoted to demonstrations of the obvious or the actually fallacious. Mr. W. Ashton Ellis has given many years of a valuable life to translating them into something which is not English and not German. For the ordinary music-lover I believe the above summary will be sufficient to enable him to understand Wagner's aims at this period, and we shall presently see how far he was able to attain them, and to what extent they refused to be, and could not be, attained. The most valuable of his writings are those on conducting and on Beethoven. The latter has some bumptious and comical allusions to "world conquerors," the Germans suffering badly at the time from an attack of swelled head, subsequent to their defeat of the unhappy, unprepared French.
At Zurich Wagner was occupied with a multiplicity of other pamphlets, with conducting concerts, with his librettos, and so on. Hans von Bülow came to him as a pupil, and proved a devoted friend, afterwards letting him take his wife, Cosima, of whom he, Bülow, it is true, stood in no particular need. Wagner had sent the score of Lohengrin to Liszt, and it was produced at Weimar in 1850. It presently went from opera-house to opera-house, and everywhere triumphed, so that a few years later Wagner could complain that he was probably the only German who had not heard it. In 1853 he published the words of The Nibelung's Ring, which aroused the premature ire of those who did not know how he intended to treat it musically.
I may here say that my ear is not sufficiently attuned nor my mind accustomed to the subtleties of German for me to offer any judgment on the prosody of Wagner's librettos. So far as I can understand them, they are uncouth enough. On the other hand, dramatically they are admirably constructed; and when we compare the words with the completed musical setting we can see how the drama was, so to speak, always latent; the words are as an invisible writing, on which the music is poured like a liquid, and out starts the drama, unmistakable and irresistible.
In 1855 Wagner went to London to conduct a season of the Philharmonic Society. That body invited him on the recommendation of Sainton, the violinist, and the season was one of its most successful. The feuds that arose, and the newspaper and other squabblings, have small interest for us now; but it is certain that the finer spirits appreciated, or partly appreciated, him, and Royalty flattered him. Into this period comes the Paris performance of Tannhäuser, which was a disgraceful failure—I mean disgraceful to the Parisians, and especially to their Jockey Club, which resolutely went to work to prevent the music being heard by cat-calls and shoutings. The event was not of any great artistic importance—indeed, it is hardly worth calling an event; it was only one more sin on the soul of a musically benighted people.
Wagner's prospects were still of the poorest; he was still living mainly on charity; but in 1859 he had finished Tristan, and much of the Ring was sketched or actually written. He was amnestied and free to return to Germany, and he could do little good there. Tristan was accepted at Vienna, but the production was put off. He was busy on the Mastersingers—busy with all manner of impracticable dreams, and could not earn a livelihood. His concert tours brought him little or no profit; in Paris a series of concerts cost him 10,000 francs, and where on earth he found the money I do not pretend to know. He was fifty-one years of age; his fortunes seemed at their very worst, the outlook was of the blackest, when of a sudden all was changed. King Ludwig of Bavaria sent for him, and promised to help him in every possible way. He had many rebuffs to face, but from this time (1864) his ultimate victory was assured.
From the outset squabbles and intrigues made Wagner's life bitter. He did not do things by halves, and when he had succeeded in getting the music school of Munich re-organized to suit his wishes, with Bülow as chief director, the local musicians felt they had little cause to love him. Bülow was appointed kapellmeister of the Court Theatre; reforms, peculiarly disagreeable to those reformed, were set on foot; and singers, players, régisseurs, who had anticipated sleeping away their existence in the good old fashion, were violently awakened by this reckless adventurer, charlatan, and what not, who had won the King's ear. The invertebrate flunkeys attached to every Court were jealous of his influence over the King, and did what they could to hinder the execution of his plans. But Wagner was not the man to be hindered, and if these backboneless crawling things made life at Munich so loathsome to him that he sought peace to complete his work at Triebschen, near Lucerne, nevertheless his plans were carried out. Tristan and Isolda was produced in 1865 and The Mastersingers of Nuremberg three years later. If I had space, it would be amusing to quote the contemporary criticisms passed on the first. Tristan was hopelessly misunderstood at the time, and even now it is misunderstood by many professed Wagnerites. It created an uproar in Germany; in England our sires were too busy singing the oratorios of Handel, Haydn and Mendelssohn to pay any attention.
Tristan was the first opera to be finished after Wagner had published his many theories, and it was their completest refutation. He himself wrote afterwards that in composing it he found how far he had gone ahead of his doctrines; but, as a matter of fact, he had not gone ahead of them at all: he simply forgot all about them, and composed as if they had no existence. In no opera in the world is there such an entire absence of the calculation that working to a theory would have involved. It is the most intense and, to use Wordsworth's word, the most inevitable opera ever written. Words, music and action seem to have originated simultaneously in the creator's brain. Writing to Liszt, Wagner said he meant to express a love such as he had never experienced. It was as well that he never experienced it: no human creature could endure the strain for twenty-four hours. Here we have the elemental passion of man for woman and woman for man in a degree of intensity that is nothing less than delirium. The action is simple, the story is simple. Isolda has nursed Tristan when he was picked up wounded; she has loved him and he has loved her. He has killed her betrothed, Morold, and she conceives it to be her duty to kill him, but she cannot. Tristan dare not aspire to win her, and when she is claimed by his uncle, King Mark of Cornwall, he is sent to bring her. At this point the opera opens.
The prelude begins with one of the love themes; other themes are worked in; the parts weave and interweave with each other, swelling and mounting until a shattering climax is reached; then all subsides, and an effect of terrible suspense is produced by the last subdued phrase in the bass as the curtain rises, and we feel that something tragic is to come. Here we have Wagner the full and ripe musician. As a technical achievement this prelude is marvellous; the polyphony is as intricate and yet as sure as anything in Bach or Mozart, part winding round part, and each going its way steadily to the climax; and the white-hot passion expressed by this means makes the thing a miracle. There is nothing like it in Tannhäuser and Lohengrin. Here we are entirely free of the Weberesque four-bar phrases; the rhythms are subtle and complex, though to the ear they sound clear and simple enough. When the curtain goes up we see a sort of tent arranged on the deck of a ship. From aloft a sailor chants a wild sea-song, unlike any sea-song ever chanted off the stage and yet redolent of the sea and salt winds.
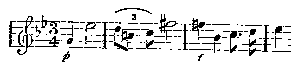
Isolda is lying on a couch, her face buried in her hands; Brangaena stands by. In the sailor's song she has fancied some gibe at herself, for she is being carried off against her will by the man she loves to wed an old man she has never seen. She starts up in rage, and then, realizing her position, asks Brangaena where they are. Now, Wagner, if he scarcely considered the prima donna, took great pains with the lesser characters, and Brangaena never opens her mouth without giving us something of magical beauty and tenderness. Quite unconscious of the impending tragedy, she remarks that they are drawing near Cornwall, and that before evening they will land there. The gently-rolling sea is kept before us by an accompaniment made out of a phrase of the sailor's song. "They will land"—that means to Isolda that she will become the property of the old man she has never seen, and lose for ever the man she has no hope of gaining, the man whom she has every good reason to hate and despise. This is a drama of passion pitted against reason—against everything excepting passion, and Wagner loses no chance of making the situation clear. Here, as in every other opera, he is, if not first a dramatist, yet always a dramatist. "Never!" screams Isolda, and curses the vessel and all that it holds. Astounded, Brangaena tries to comfort her; but Isolda is a woman, and means to have her way. There must be plenty of air in such a deck-tent, but Wagner, with a spite that is itself somewhat feminine, makes her, in feminine fashion, complain of a want of it; so one of the curtains is drawn aside, and she can see what she wants to see: Tristan standing on what seems to be the prow, but is really the stern, of the vessel. There he stands, the man she hates and loves, and shows no sign of discomposure, although the helmsman invariably holds the tiller at such an angle that the ship must be gyrating like a teetotum, thus offering a simple, if coarse, explanation of Isolda's qualms. The music up till now has been made up of the fragment last quoted of the sailor's song, and one of the love themes—a simple phrase of four notes, out of which lengthy passages are woven. When the curtain is drawn a fragment of the sea-song is again heard, and then this love phrase is taken up by the orchestra and filled with sinister, smouldering passion. Isolda's anger gathers and mounts against Tristan, and when this theme arrives
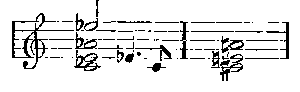
it is the announcement of her determination that death for both of them shall end an impossible situation. This, however, we do not learn until later; for the moment the theme conveys little special meaning to us. It is when we hear the drama a second time that its appalling tragic force is felt. Isolda tells Brangaena to command Tristan to come to the pavilion. Kurvenal, his servant, sings a scoffing song, in which all the sailors join, in spite of Tristan's endeavour to stop them. Brangaena rushes back and hurriedly closes the curtains. Isolda, half-crazed, tells the whole story as it occurred previous to the rising of the curtain—how she nursed the wounded Tristan, found him to be the slayer of her betrothed, took his sword and was about to kill him, when he opened his eyes, and the sword dropped from her listless fingers. Brangaena is sufficiently astonished; Isolda works herself up into a paroxysm of fury; and now the drama is indeed on foot. Brangaena has a long, lovely, soothing passage to sing, and in her over-anxiety to serve her mistress she accidentally suggests to Isolda the very means of revenging herself on Tristan, and terminating at the same time her own misery. "You remember your mother's art," says Brangaena: "do you think she would have sent me over-seas with you without a means of helping you?" Isolda knows it is the love-potion she means. She has only to drink the contents of a small flask, and old King Mark will become at least tolerable to her. The flask is in a casket, and another is there, as Isolda knows, full of a deadly poison. She commands Brangaena to pour out the poison. Brangaena, terrified, beseeches, implores; but Isolda insists; and in the midst of the dispute the sailors suddenly roar out their "Yo-heave-ho!" The sea had ceased, as it will in moments of preoccupation or intense emotion, to haunt our ears for a time; now it breaks in again, and we feel as if it had really never ceased. Kurvenal enters, and tells them to get ready to land. Isolda tells him point-blank that she will not stir until Tristan has come to demand her pardon for a sin he has committed. Brusquely, Kurvenal says he will convey the message; Brangaena again prays to her mistress to spare her. "Wilt thou be true?" replies Isolda; and the voice of Kurvenal is heard: "Sir Tristan!"
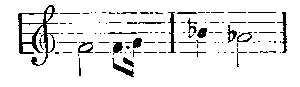
A minute of frightful suspense occurs while Isolda is waiting for Tristan; and, as the situation is to be one of the most poignant in the drama, it is only fitting that Wagner should prelude it with one of his most tremendous passages. Isolda tells Tristan what is his crime, and how she had meant to slay him. He offers her his sword to carry out her old purpose, and she laughs at him. "A pretty thing," she says, "it would be for me to go to King Mark as his bride with his nephew's blood on my hands. We must drink together to our friendship, that all may be forgotten." Brangaena has been tremblingly preparing the potion, and, not knowing what to do—not daring to give the poison, not daring to disobey her mistress—she has poured out the elixir of love. Isolda hands it to Tristan, who fully understands Isolda's meaning and half of her intention—if, indeed, there is another half, for Wagner has given Isolda a true touch of womanly character in leaving it uncertain whether or not she really means to poison herself. He takes the cup and drinks; she, with a cry of "Betrayed, even here!" snatches it from him and drinks also.
Here we have got many leagues away from Lohengrin, with its scene between a man and a jealous, ungenerous, querulous woman, and TANNHÄUSER, with its contest between an impossible platonic affection and piggish lust. There is not a touch of staginess about Isolda; she was not born in the green-room. In her we have two elemental passions in conflict—her love for a man, and her hatred for the same man after he has shown manly gratitude by preparing her a lot that is loathsome to her. The character of Tristan is not so transparent or simple. He had loved Isolda—so much is certain; but whether he gave her up to curry favour with the King (he himself says as much afterwards), whether he dares not ask for her for himself, whether he does not know that Isolda loves him—about all this we know nothing.
What we do know is that standing there on the deck of the ship are two very tragic figures. They have drunk poison; they are consumed with passion one for the other; death is close at hand, and there is nothing to prevent them confessing their love and dying in each other's arms. If Wagner meant us to accept the love elixir as the genuine spring of the immediate drama, he might have saved himself the trouble. It is the imminent presence of death that brings their love to light, as it is their love that takes them to death. They gaze upon one another, and rush into each other's arms. Brangaena, turning round, is horrified to see what her officiousness has accomplished. The music rolls on in a torrent of almost unendurable sweetness; the ship reaches land, and the curtain drops as Tristan and Isolda, oblivious of all but themselves and their passion, stagger in one another's arms, and the trumpets sound without as the King approaches to claim his bride.
I hope I have succeeded in setting forth clearly the forces at work and the nature of the two people on whom they are working. Writers have indulged in grotesque pages of explanation and speculation, from which they might have been saved by a careful reading of the libretto, supplemented by a slight acquaintance with the music. The subject might easily have become intricate—in fact, hopelessly involved and entangled—but Wagner's consummate dramatic art, stage-craft, and knowledge of stage effect have combined to make all as clear as the day. The end of each act sees the lovers in a situation which is at heart the same, though in externals different. Rapt in each other, they care nothing about the sailors, attendants, approaching crowds, and the rest, at the end of the first act; at the end of the second they scarcely understand Mark's passionate affection—they only know it is an enemy of their love; and, finally, they are glad when death frees them from life, which means an incessant trouble and interruption to them. The tragedy deepens and grows more intense with each successive scene; each separates them more widely from life and all that life means, until in the last act the divorce is complete. This is the purpose of the drama; this is the drama, and those who do not like it must turn to another opera.
If the drama is clear, so is the music. Wagner's powers were now at their fullest and ripest; in invention, technical skill, mastery of the colours of the orchestra, he towers far above every composer born in the nineteenth century. Nietzsche, in one of his many quarrelsome diatribes, says Wagner determined to be a musician and made himself one by sheer will-power. But not by taking much thought, nor by determination, nor by exercise of will-power, does any man become an artistic inventor, as Nietzsche would have perceived had he himself been capable of more than spasmodic, fragmentary thought. Tristan is full of great melodies: gigantic themes, like that which is played while Isolda awaits Tristan's entrance; tender ones, like the music given to Brangaena; passionate and intolerably sweet, like the duet of the pair after the drinking of the philtre. The other acts contain even more amazing things, and to them we shall come in due time. First let us note how Wagner sustains his background and atmosphere throughout the first act. At times, when our attention has to be concentrated on the personages on the opening stage, the sea song theme, with its smell of the pungent, salt sea air, disappears; then, as I have remarked, it gradually creeps in again, so that we do not realize that it has ever been absent; or, again, as during the conversation between Isolda and Brangaena, it breaks in abruptly, with the roar of the seamen's voices and Kurvenal's savage orders. It is managed with the most consummate skill. Though the tent blots out a view of the ocean, yet the mast and bellying sail (which ought to be visible), and the miraculous music, preserve an ever-present sense of the sea, and in that atmosphere of keen freshness and ozone the characters begin to work out their destiny. To understand Wagner's real greatness and the personal quality that differentiates his art from the art of all other musicians, let us try to realize what this means. Weber and Mendelssohn had written picturesque music; they gave us landscapes, the rolling sea, black woods, moaning winds; and having done that, they were satisfied. But where they left off Wagner began; their completed picture was for him nothing more than a background. Against it he placed his characters, with their different thoughts and emotions fully expressed. Now, in music you cannot express two or more conflicting emotions, even if you have two themes, each of which shows its own emotion when played separately, and set them going together. However many parts a piece of music may be written in, it is the mass of tone reaching our ears, it is the ensemble, that makes the effect. It is obvious, then, that when Wagner puts a shrieking female on the deck of a ship which is shouldering its way through a gently-rolling sea, the same music must serve for the lady and the sea: it must suggest the sea and express the lady's emotions. He could not give picturesque music to the orchestra and let the female indulge in real screams, or even musical imitations of real screams. That would be to step beyond the boundaries of art; for neither real screams nor their imitations are beautiful, and—if a truism may be pardoned to complete a nice sentence—without beauty there can be no art. In spite of much nonsense that has been written and talked, Wagner never sacrificed beauty. Those foolish tales which I used to read in my youth—of how Wagner appropriately, if daringly, sustained discords through long discordant situations—what are they but the blatherskite of long-tongued persons who could talk faster than they could think? Wagner would not sacrifice beauty. He made the characters say, in notes as well as words, what they had to say; he always got the colour and atmosphere of the scenic surroundings into the music. By inspiration and marvellous workmanship he made each phrase serve a double purpose: it expresses the emotion of the person who sings, it gives the atmosphere in which the person is singing. More than anything else, it is this that gives his music its individual character. Such music is bound to remain for ever fresh. So long as trees and grass, rain and sunshine, running waters and flying cloud-scud are things sweet to man's thought, so long will the music of Wagner's operas remain green, always new and refreshing, full and satisfying. He often achieved the task, or helped himself to achieve it, by showing us Nature in sympathy with the human mood of the moment (see the second scene in Tannhäuser, the last act of Tristan, the whole of the last act of The Valkyrie); but he succeeds equally well without these touches of his unrivalled stage-craft.
Further back I referred to Wagner's earlier and later use of the leit-motif. In its naive, primitive simplicity the device is certainly not highly artistic. When our academic gentry use it in their festival oratorios, they are supposed to show themselves very advanced. But what purpose, musical or other, is subserved by arbitrarily allying a musical phrase to a personage or an idea and blaring it out whenever that personage or idea comes to the front? Wagner early realized the uselessness of the proceeding, and, as I pointed out, in Tannhäuser there are no leit-motifs, though passages and parts of passages are repeated. In Lohengrin it is used rather for a dramatic than a musical purpose. By the time he wrote Tristan he had learnt the splendid artistic uses to which a rather commonplace device could be put. The differences between the leit-motif in Lohengrin and the leit-motif in Tristan are two: in Tristan they are more significant—indeed, they are pregnant to bursting—and more fully charged with energy and colour; also they are not stated and restated in their elementary form as in Lohengrin, but continually subjected to a process of metamorphosis. This last mode of developing a theme he probably learnt from Liszt, and without it both Tristan and the Ring would be very different. But while these are the most striking characteristics of Wagner's later leading themes and mode of using them, it must be remembered that he was now absolute master of every device of operatic art previously known, and of many he invented as he went along. The same theme in Tristan has a dozen functions to fulfil; it may be changed almost out of recognition to suit a particular occasion, and a few minutes later, for a dramatic purpose, it may be stated in all its original plainness. I advise all who wish to understand Tristan not to fret themselves with those rascally and stupid guide books which merely addle the brain with their interminable lists of motives. Throughout the opera new matter is continually introduced, with old themes, changed or unchanged, woven into the tissue; and to go hunting for these old themes, to try to recognise them whenever they crop up, is not only to lose one's enjoyment of the music, but to run a fair risk of misapprehending it altogether, and the drama as well. This jack-fool twaddle about there being not a single phrase in an opera which has not grown out of another is manifestly absurd—for out of what does the first one grow?—and utterly untrue. In every scene of Tristan an enormous amount of new material is added; it is the richest thematically of all the operas. But this labelling of nearly every phrase as the This, That, or the Other motive has confused thousands of people; they fatigue themselves by incessantly trying to remember the significance of a phrase which resembles one that has been heard before; and instead of letting the music make its natural and proper effect, they grow bewildered, and blame Wagner for what is in reality the fault of the analysis-makers. To follow Tristan, one need not know more than the few fragments I have quoted above; in fact, without any knowledge whatever it can be followed. The themes have no arbitrary significance attached to them; they are expressive music and tell their own tale. But, of course, when one has heard the opera many times—and twenty performances, supplemented by a study of Von Bülow's incomparable piano arrangement of the score, are hardly enough to enable us to begin to comprehend the real richness and vastness of Tristan—then gradually new features are found, new lights are thrown by the use of leit-motifs, and slowly the music yields us that multiplicity of complex delights—delights intellectual, emotional, or purely sensuous—that only the greatest works of art can give. Take, for example, the theme which Isolda sings when she perceives death to be the only cure for her woes. Later, when she is compelling Tristan to drink the poison-cup, the sailors break out into "Yo-heave-ho!" and he says, "Where are we?" "Near to the end!" she says, to the accompaniment of this same theme. To one who barely remembers the phrase the effect is marked enough, but to one who knows every phrase and its associations the double meaning is almost horrifying. It is idle to search out such points as this with the aid of a guide, for while you are waiting for them you lose the music in which they are set; the prevailing mood eludes you, and the points themselves fail to make their effect. There is another danger. People easily go leit-motif mad, and their insane imagination creates a leit-motif out of any two phrases that have a superficial and accidental resemblance. Tristan and the Ring are not musical puzzles. The themes are quite able to look after themselves, and to assert themselves at the proper moment. Many of them are not leit-motifs at all. The passage out of the sea-song, which is heard constantly through the first act, is not a leit-motif, nor are many of the other subjects. They receive symphonic development; but, after all, the opening four notes of Beethoven's Fifth Symphony do not form a leit-motif. I have dwelt at length upon this, for misguided people have blinded both themselves and others as to Wagner's true aims and methods and the splendour of the accomplished thing by trying to read into his music a host of trifling and pettifogging allusions which he never intended. There is enough to break our minds upon without troubling about these.
In the second act we are left in the dark as to what has happened since we left Isolda in Tristan's arms on the deck of the ship. Some years ago an excited discussion took place on a very momentous question—"Did Isolda marry King Mark or not?" If not, it was strange that she should have been left free enough apparently to see Tristan whenever she wished, and Mark's expostulations at the end of the act seem rather unwarranted in the mouth of a man whose honour, in the Divorce Court sense, has not been smirched; yet, on the other hand, it is unlikely that a legendary King, with the bride in his palace, would wait so long for the marriage as to allow the many pretty incidents mentioned by Brangaena to happen. Yet again, if they were married, Mark, in the third act, shows a more than heroic willingness and less than cuckold readiness to let Isolda go free. Probably Wagner never gave the problem a moment's consideration, which is hardly surprising when we consider his own multitudinous love affairs. He was not writing a Sunday-school tract, but a drama of passion so intense that purity, prudence and all such considerations were thrown to the winds.
The act opens with a very Proteus of a theme. Its entrance is like a thunder-clap in a cloudless sky. The conductor lifts his stick, and then—
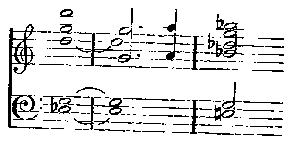
—an unprepared discord which must have pained the ears and grieved the hearts of the ordinary opera-goers and pedants when the opera was first given. This subject is used in connection with the notion of daylight as a nuisance to lovers in the subsequent conversation of Tristan and Isolda—a notion which we shall examine presently. Presently another subject is heard, one of which extensive use is made in the first scene—
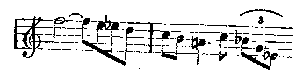
The curtain rises. It is a sultry summer night; the black woods stand round a garden; on the left is the castle of Mark, with a torch blazing at the doorway, making the surrounding night blacker. Sounds of hunting-horns are dying away in the distance. Brangaena and Isolda are there listening, and Brangaena, to music of enchanting beauty, is warning Isolda that the hunters can be no great way off. "Listen to the brook," says Isolda. "How could I hear that if the horns were near?" Then comes one of Wagner's matchless bits of painting—the brook rippling through the silent night. Isolda is now going to extinguish the torch, as a signal to Tristan that he may approach. Brangaena protests, and warns Isolda against Melot, who has arranged this night hunt as a trap to catch Tristan; and she bewails the officiousness which led her to substitute the love-philtre for the poison. The rest of the scene may be passed over. The music is woven out of themes just quoted, and another which will play a big part in the love-duet:
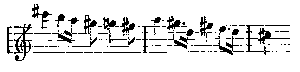
Of course, Isolda prevails. Brangaena is sent to keep watch, and Isolda throws down the torch to the Death motive. Tristan rushes in, and the most passionate love-duet ever written begins.
After the first ecstasies have subsided the lovers converse. They must talk about something—what should it be? As Wagner's thoughts were occupied with Schopenhauer at the time, he makes them talk a sort of pseudo-Schopenhauer. Light is their enemy; only in night—extinction—can perfect joy be found. It was the deceitful phantoms of daylight—worldly ambitions—that betrayed Tristan into acting so basely towards Isolda (before the drama opens); it was the light of the torch that kept him so long from her this night; and now in the darkness they find rapturous peace. This is the substance of what is said. Twice Brangaena warns them that the dawn is at hand, but they do not heed her. Her songs are exquisite enough, surely, but the lovers, steeped in their bliss, have no ears for them. Their own music is far more beautiful:
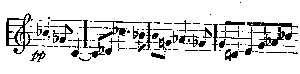
And again:
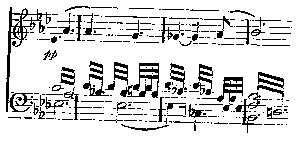
The lovers are presently awakened. At the very climax of a mad, tumultuous passage Brangaena gives a scream; Kurvenal rushes in, and then—enter Mark, Melot and the other hunters. Melot's trap has worked satisfactorily.
The cold red dawn slowly breaks. The phantoms of the daylight have broken in upon the dream of night, which alone is true. It is here that many would have the act terminate. Such an ending would leave the idea of the act half expressed, and shatter the noble architectonical scheme of the whole drama. The idea of the act—that the light is the lovers' enemy, the dark their friend and refuge—has to be worked out to prepare for the last act; the idea of the drama—that the lovers must be seen gradually thrust away from life (which is light) to death (which is eternal night)—must be carried one step further. Mark, in an agony of grief, asks them why they, the two he loves best in the world, dishonour him in so frightful a fashion. He presses home to them their sin and his suffering, his affection and their indifference to it; and he ends up with the question, "Why?" Tristan cannot answer; he perceives only that Mark's love is a more terrible menace for them than any trap laid by Melot. Without their passion they cannot live, and it is not Melot and the general outside world that threaten to sunder them, but their protector and dearest friend. The passion is irresistible, and Tristan faces the inevitable. He asks Isolda if she will follow him where he is now going: she replies that she will; and he, after taunting Melot with his treachery, lets him thrust him through with his sword. The drama has moved a stage further on, and there remains now only the logical completion. Anyone who thinks all this is to read into the opera a meaning that is not there merely accuses me of being greater than Wagner; without this we have only a commonplace Divorce Court episode.
The next act takes place in the courtyard of Tristan's castle in Brittany. It is in a state of decay. In the hot afternoon sun the sea shines like burnished metal, and Tristan, who has been brought there by Kurvenal, lies delirious. Presently one of the saddest songs ever written sounds from a shepherd's pipe without. It half awakens Tristan, and he talks of it—how it has haunted him since his childhood. Kurvenal tells him Isolda has been sent for. He becomes more and more delirious, and at last, after an outburst, he faints; then awakens and sings the sublime passage in which he sees Isolda coming over-seas, the ship covered with sweet-smelling flowers. The accompaniment to this piece of magic is a figure taken from the fourth theme I have quoted in this chapter. It is given at first to the horns, and over it sways a lovely melody, leading to Tristan's cry of "Oh, Isolda!" which occurs again and again until Isolda does come.
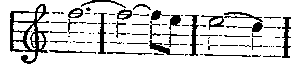
There are few tender and beautiful and pathetic things in music to match it. Presently the horn of the shepherd is heard again; but this time it plays a lively tune, as a signal that the ship is in sight. Tristan goes mad for joy, and tears the bandages from his wounds. As Isolda rushes in he staggers into her arms, and dies there to the phrases in which they had first spoken after drinking the love-philtre. Isolda's plaints are as touching and profound as those of Donna Anna in Don Giovanni after her father has been murdered. There is again tumult; even at the last the lovers cannot be left alone; another ship comes in sight, and Melot and Mark's warriors rush in. Kurvenal fights and kills Melot, and is himself stabbed. He receives the wound, and feels his way to his master's side, and dies groping for his hand. Mark and Brangaena come in. She has confessed to the mistake she made in giving the wrong potion, and he has come to make all well. Isolda pays no attention, but, after a beautiful phrase from Brangaena, rises and sings the wonderful Death song. The drama is now ended; the lovers' passion has led them whither they knew it was leading them from the beginning. Night has come on, and Isolda falls on Tristan's body and dies, fulfilling the promise she had made—that where he went she would follow. And so ends the greatest music-drama ever written, and the greatest likely to be written for centuries to come.
We must pass on now to The Mastersingers, an old idea of Wagner's. The music was completed at Triebschen. Here is nothing of the tension, burning passion, and unfathomable depth of Tristan, but a pretty love-story, with some comedy and more than a little of very broad farce. In it Wagner determined to satirize the musical pedants, and he did so with considerable acerbity. But it is not to see his enemies roughly handled that we go to The Mastersingers: it is to hear one of Wagner's two most beautiful operas. There is no need to go through it closely, as in the case of Tristan. The methods are those of Tristan; we have the themes used as leit-motifs, and also long passages woven out of them and new matter; we have the harmonic freedom of Tristan, the same gorgeous orchestration, and even more than the same marvellous polyphonic writing. But, broadly speaking, the drama counts for comparatively little, and the opera consists of a series of enchanting songs and scenes. The very title tells us that we are not simply to follow the destinies of a hero and heroine. The person mostly in evidence is Hans Sachs, a sort of heavy father, who has some of the most glorious music. The young lover comes along—Walther—and tries to win Eva by gaining the prize in a contest of minstrels; Beckmesser, a pedant, opposes him. Sachs supports him, and he wins. Every note of the music can readily be understood. There are regular set numbers provided for in the structure of the libretto, so as to come in naturally; there is even a sextet—which I have often heard encored—and the opera winds up with a chorus. It disproves Wagner's theory that in the Ninth Symphony Beethoven had said the last word in pure music, and that henceforth words would always be necessary; for here the text is often a mere excuse for using the human voice, and little of the music would be unintelligible without it.
The establishment of a festival theatre where, humanly speaking, ideal performances of all the great operas could be given—this was long a dream of Wagner's. He knew what could be done and how to do it; he knew also that it was not done because managers, conductors, bandsmen and singers had formed careless and slovenly habits, and were blinded by prejudices and traditions surviving from the days of old Italian opera. King Ludwig helped him as far as he could, the good burghers of Bayreuth were ready to give him a site, societies were formed to rake in money; and after apparently interminable preliminary difficulties had been overcome, the business of building the house was begun. It stands high on a hill, away from the centre of Bayreuth—a great structure of red brick and timber, not an imposing piece of architecture by any means, yet not unpleasing to the eye. Inside every seat is arranged so to afford a perfect view of the stage, and the orchestra is in a pit, so as to be unseen, although the singers, wherever they may be placed, can see the conductor. The improvements Wagner made on the stage have themselves been improved on, and in this respect Bayreuth is no better than many other theatres. At the beginning Wagner secured every possible appliance, and then set to work to teach his men how to use them. And it was just in this that he reformed the opera-house: he insisted on everything being done artistically and with the utmost care. Nothing had to be slurred over; every detail had to be carried out as conscientiously as if the fate of empires depended on it. The idea was novel in operatic circles. It aroused opposition; but in the end Wagner got his way, and what was at first declared impossible, then difficult, is now done as a matter of course in all the serious opera-houses. It is in this very matter that Bayreuth has now fallen far behind other German towns, and can no longer be regarded as a serious art centre. In another respect it has departed from the original intention. That was to give model representations of all the fine operas, with the best artists obtainable. But, under the rule of the Wagner family, only Wagner's works are played; while as for the artists, Mr. Siegfried Wagner—Richard's son—often directs, although he is an inferior conductor, and petty intrigues are allowed to prevent some of the greatest singers singing there. Wagner's idea was magnificent, but it needs a Wagner to execute it. However, Bayreuth has done a great service, and now what becomes of it matters to no one.
Bayreuth was opened with performances of the Ring, that enormous music-drama which consists of three huge music-dramas and a shorter one. Now, it was the Ring more than any other of Wagner's works which led to him being misunderstood, and afforded opportunities for misrepresentation. When the libretto was published, long before the music was written, it was called a monstrosity, and one professor implored Wagner not to set it. At first sight it seems so hopelessly involved and intricate, the main dramatic idea works its way so sinuously through such a maze of subsidiary ideas, that intellectually honest and intelligent people can hardly be blamed if they are unable to see at a glance what it is all about. Yet the plot is not more complicated than that of many a novel, and the real trouble is that we won't take the pains over it that we do over a novel, or, perhaps, do not apply our intelligence in the best way. At this time of day no one, I hope, will condemn a work of art because it cannot be grasped in a glance.
There are four music-dramas, or operas (I use the terms indiscriminately, now that there is no danger of the Wagnerian opera being confused with the older forms). Wagner made each self-contained, complete and comprehensible by itself, and yet he carried the main action on from one to the next until the final catastrophe; but he did this at the cost of much repetition, whence another charge brought against the work—that of its interminable tedium. I will therefore first disentangle the main idea, which is simple. Let it be granted that Wotan is ruler of the world—not a first cause, but a god, limited in his powers, conditioned, ruling only so long as he obeys the laws inscribed in Runic characters on his spear. How he arrived in this position we do not know, any more than we know the origin of the Greek gods; indeed, in this respect and others there are parallels between the Greek and the Northern mythology. Wotan goes in fear lest the powers of the nether world usurp his domination, which he wants to make absolute. He makes a pact with the giants—the Titan forces of the earth—that be will give them Freia if they build him a castle, Valhalla, which he intends to fill with slain warriors in sufficient numbers to keep down his foes. This is his primary, essential, fatal blunder; for unless the gods eat of Freia's apples every day they must wither and their powers decay. But Wotan means to cheat the giants, and Loge, the deceitful god of fire, who is ultimately to destroy the whole of the present régime, has been sent off to find a means of doing it. It is when so much has been accomplished that Wagner raises the curtain on the first scene of the first drama. The Rhinegold is entirely devoted to an exposition of the main drama.
The gold lies in the Rhine. The Rhine maidens play about it. It is only a pretty plaything for them. The Nibelung comes and steals it. Meanwhile, far above, Wotan and his wife Fricka awake and find Valhalla built, and now Wotan has to pay the giants. They arrive; Loge has not arrived. Loge does arrive and makes his excuses—no man will give up a beautiful woman, for no matter what sum. But he tells of the Rhinegold, and the giants agree to accept it in lieu of Freia. Wotan and Loge go off and get it by a trick. But Alberick has shaped part of it into a magic ring, which gives its possessor absolute power over the whole world. When they come back to conclude the bargain with the giants, it is found necessary that Wotan should give up the ring also. He does so, after resolving on his grand idea, which will appear presently; and the gods enter Valhalla while the Rhine maidens below are heard bewailing the loss of their plaything.
The ring is cursed, and no sooner do the giants begin to share their treasure than they fall to disputing about it. Fafner kills his brother, and making off with all, buries it in a cave—"Hate Hole"—and changing himself into a dragon, by virtue of the Tarnhelm which is amongst the treasure, he settles down to guard it. At any moment now Wotan's empire may be taken from him; the ring he must gain somehow, but by the laws written on his staff he may not perpetrate such an act of injustice as taking it himself. His position is more tragic than he knows. His brilliant idea is the sword, and here is its theme, one of the most important in the work:
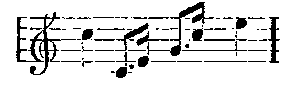
He will raise up a breed of heroes, let them fend for themselves in the world—even heap pains and trials upon them; and in the end a fearless hero will arise, find this sword, and of his own absolute free-will slay the dragon and take the ring. He is trying to jump out of his own shadow, as we see immediately in The Valkyrie. Siegmund, his son, the hero, takes the sword, and then commits adultery and incest with Sieglinda, his sister, the wife of Hunding. Fricka, the punisher of matrimonial crimes, compels Wotan to let Hunding slay Siegmund. This is done, though Brunnhilde, the incarnation of love, tries to save the hero. She has to be punished—the laws that bind Wotan are inexorable—and he has to put away love; in order to rule, love must have no place in his thoughts nor influence his actions. Brunnhilde is put to sleep, and a hedge of fire set blazing round her. There she must sleep until a hero arrives who has no fear of Wotan or his spear, and will pass through the fire and take her for bride.
The hero is the son of Sieglinda and Siegmund; he kills the dragon, takes the ring, shatters Wotan's spear, passes the fiery hedge, and weds Brunnhilde. The details we shall examine when we deal with the drama of Siegfried. Wotan's part is now ended; he retires to Valhalla to await the inevitable dénouement. He willingly abdicates, and wills his own destruction and the destruction of Valhalla and all that existed under his rule. If power involves the compulsion to renounce himself, to destroy all that he loves and all that makes life sweet, then he rather renounces life. So he awaits during the Dusk of the Gods, until Siegfried has been slain and the ring restored to the Rhine. His own power being broken, and the power that lay in the ring being again in the hands of the innocent Rhine-maidens, there is nothing to control Loge, who blazes up in sheets of fire, and Valhalla is consumed, while the Rhine maidens swim joyfully about in the bubbling, roaring Rhine.
I have tried to trace as clearly as possible this main story as it pursues its course through the tangle of subsidiary stories. In dealing with a drama so richly stored with material, where every rift is loaded with ore, much has necessarily to be left untouched; in such a sketch as this one cannot do more than indicate the broad masses. There is no philosophic idea, no exposition of a philosophy. Wagner was no philosopher, though he found in Schopenhauer's Will to Live, and its Renunciation, material which he could use for poetic and dramatic purposes. The "lessons" which many ingenious persons find here are not lessons at all, but the ground-facts on which the drama is based. That the power of gold—signified by the ring—carries with it the curse of gold is not a thing to be inferred from the drama; it is assumed as the starting-point of the drama. That a man cannot by many subterfuges hold power in this world without incidentally committing acts which revolt the better part of his nature—this, again, is no lesson, but a fact taken for granted. I will not waste space on the thousand odd "meanings," "lessons" and so on found by the enthusiastic in Wagner. His ideas were at once the substance and the inspiration of his music-dramas; but he never dreamed of writing copybook headings. He had in language to make his characters talk about these ideas for two reasons, each sufficient in itself. First, excepting in melodrama and rough-and-tumble farces, the audience must know the motives actuating the personages of the drama—their situation, their emotions, ambitions, fears and what not. Without that all drama would be an incomprehensible jabbering and gesticulating of mummers, fit only to be put on the London stage at the present moment. Second, if Wagner spread himself in the expression of certain things where an ordinary dramatist would have dealt with them more briefly, it must be remembered that he was writing words to set to music. An animadversion on the length of the speeches would be perfectly just if the drama were meant to be spoken; as the drama is meant to be sung, it is irrelevant and silly. Now, it is idle to say, in answer to all this, that Wagner proves the truth of his premisses by the deductions he draws in the drama, as in Euclid a proposition is stated to be a truth and then proved to be a truth. In Wagner nothing is proved. Accept his premisses, and you understand the subsequent drama; wait for the premisses to be proved true, and there is no drama for you to understand—no drama, but a series of incoherent, unrelated and inconsequent incidents. Finally, we all know that when a man tumbles over a high precipice he is killed. Suppose that in a melodrama the villain tumbled and is killed. Would some wise commentator write, "The master here proves the wickedness of villainy, and shows conclusively how it always meets with its just punishment, for the villain tumbles over a precipice and is, if we mistake not, killed. It is true the same fate unfortunately overtakes the hero, but the circumstances and the moral are different. The villain met his just reward; an unlucky accident befell the hero. Underlying this is the profounder truth that when men—and we will even say women—fall off high places, they get killed or seriously hurt"? This is on a par with the "truths" and "morals" found in the Ring.
Throughout the Ring Wagner fairly let himself go in the matter of gorgeous, riotous colour in depicting Nature—the earth, the waters, clouds, and the working of the elements. He had ampler opportunities than any of his previous works afforded. He had not, as before, to place his characters in a scene, to arrange a background for them. Many of the characters are the elements typified—the water-nymphs, the giants, Donner, Loge, Erda. Wotan himself rides on the tempest, surrounded with fearful lightnings; the Valkyrie maidens ride through the air on supernatural horses amidst thunder and wind and rain. The whole action takes place in the open air, or in the bowels of the earth, or the depths of the Rhine; mountain and storm-lashed woods, dismal caverns and chasms, the broad river, are always before us. Two scenes take place under a man-made roof: in the first act of The Valkyrie we have Hunding's rough hut, built round an ash-tree, which penetrates the top, and its branches sway and dash together above the actors' heads; in the Dusk of the Gods there is Gunther's hall, completely open on one side. Undefiled Nature, healthy and wild and sweet, is always present, and always in sympathy with the character of every scene. Besides being magically picturesque, the music is also continuously in a high degree dramatic, and it has yet another quality: it is charged with a sense of a strange, remote past—a past that never existed. No archaic chords or progressions occur, but by a series of miraculous touches the atmosphere of a far-away past is kept before us. To save coming back to this again, I will mention such instances as the Rhine-maidens' wail, heard far down in the valley as the gods march triumphantly to Valhalla; the passage in which Siegmund recounts how on coming home one day he found the house in ashes, his sister and father gone, and only a wolf-skin lying on the ground; the Fate theme, and the haunting song of the Rhine-maidens in the last act of the Dusk of the Gods.
Now, though one would regret the loss of some of the music I have mentioned, the Rhinegold is tedious, long in proportion to the significance—musical and dramatic—of its content, and on the whole a bore. I never go to see it. The Fricka music in the second scene is as effective on the piano as in the theatre, and the last scene is as effective on a concert orchestra as in the theatre; in fact, in the theatre the device of a pasteboard rainbow, coloured to suit German taste, detracts from the effect. Only a fool would dare to say that Wagner should have done this, that or the other; but I venture to say that if he had not suffered from that very German malady, a desire to work back to the beginning of things, and to embody the result in his art, Wagner would have found a better means than a two-hour long "fore-evening" to prepare for the real drama of the Ring.
That drama opens in earnest with The Valkyrie—the story of how, in pursuing his ambitious plan, Wotan is forced to sacrifice first his own son, then his daughter Brunnhilde, who is the incarnation of all that is sweet and beautiful in his own nature. She shares, it is true, his curiously limited immortality—an immortality that may be, and finally is, curtailed—but she can suffer a punishment worse to her than extinction. The prelude opens with the roar and hoarse scream of the storm as it dashes through the forest—- the plash of the rain, the flashing of lightning and the roll of the thunder. The musical idea was obviously suggested by Schubert's "Erl-king." In each we have the same rapidly-reiterated notes in the upper part, and Wagner's bars are simply a variant of Schubert's. The curtain rises on Hunding's hut; the door is burst open, and Siegmund tumbles in exhausted, and falls before the fire. Sieglinda gives him mead, and one sees it is a case of love at first sight. Hunding enters, and, finding Siegmund to be an enemy of his, gives him until morning, and tells him that then he must fight. Sieglinda drugs her husband's night-draught, and, while he is sleeping, tells Siegmund of how, when she was abducted, and compelled against her will to marry Hunding, a gray-bearded stranger came in, with his hat drawn over one eye—Wotan had but one eye—and wearing a dark-blue cloak marked with stars, suggested by the deep-blue star-pierced sky by night. He drove a sword into the ash trunk, and, declaring that only a man strong enough to draw it out should wield it, went his way. Many have tried, and none succeeded. Siegmund at once draws it, and the pair fly. There has been some of Wagner's finest and freshest love-music, and one entrancing effect is got when a puff of wind suddenly blows the door open. The storm has ceased, and there we see the forest bathed in a spring moonlight, the raindrops on the young leaves dancing and gleaming. It is at this moment Siegmund sings the wonderful spring song.
In the next act Wotan tells Brunnhilda she must protect Siegmund in the coming fight; but Fricka seeks him out in this rocky place amongst the hills, and compels him to promise on oath that Siegmund shall die to atone for his violation of the sacred rite of marriage. Brunnhilda reenters, and then occurs a scene which has caused much debate. At enormous length Wotan recounts to her practically all we have already seen and heard before. It may be, as I have said, that Wagner wanted to make each opera comprehensible in itself, without reference to the others; it may be that his artistic sense forced him to make it clearer and ever clearer that each tragedy as it happens is Wotan's tragedy; but, in any case, I, for one, never regret when the scene is somewhat shorn. Wotan is defeated in this attempt to observe the word of the law, but break the spirit. He cannot wield the sword himself, but he made it and placed it where and so that the hero alone could take it. The hero is of the seed of his loins, and the fact that Wotan has made life bitter for him counts for nothing against that fact; and, finally, though he could not himself aid Siegmund, he ordered his daughter to do so. He wished Siegmund to act of his own free-will, and yet to do what he, Wotan, wanted. Checked by Fricka, he revokes his command to Brunnhilda, and goes off cursing fate. Siegmund and Sieglinda enter, flying before Hunding; Sieglinda faints, and at last sleeps; and then Brunnhilda steps forward from among the rocks in the gloomy half-light—a stern, imposing, indeed an awful, figure, the herald of death, seen only by warriors about to die. The Fate theme sounds from the orchestra, and another melody, out of which nearly the whole scene is woven, is heard, and then, to a simple chord—supernatural, ghostly in its effect—she calls Siegmund. She tells him he is to die and go with her to Valhalla. He pleads in vain; she (simply, be it remembered, a part of her father's will) cannot understand why he should refuse to go where his father and so many famous warriors have already gone. "So young and fair, and yet so cold and stern!" Siegmund exclaims; and at last he asks whether Sieglinda will also be there. "Siegmund will see Sieglinda no more," she replies to a quiet phrase of unspeakable pathos. Then Siegmund refuses to go with her, and he draws his sword to slay first Sieglinda, then himself. Brunnhilda is overwhelmed by the revelation of a love so devoted, and at last promises to help him. It is her own nature as is revealed to her. Night and storm come on; Hunding's horn is heard as he comes nearer and nearer; Siegmund mounts amongst the rocks to meet him; a flash of lightning reveals them in the act of fighting; Brunnhilda hovers above to strike for him, when Wotan appears in a fiery glare and smashes Siegmund's sword, so that Hunding's spear passes through him. Sieglinda has awakened to see this and collapses; Brunnhilda rapidly descends, and, gathering the fragments of the shattered sword, hurries Sieglinda off to seek shelter from Wotan's wrath. Wotan kills Hunding with a contemptuous gesture, telling him to say to Fricka that her will has been accomplished. He rests there for a moment, then goes off in flaming wrath. The tragedy has gone a step onward; he has killed his son, and now must punish Brunnhilda—put away love from himself to the end that he may enjoy a loveless empire.
The music throughout the act is amongst Wagner's noblest and most beautiful and dramatic. Every phrase given to Fricka proclaims her queenly and overbearing, with right and power on her side, and relentless determination to use them. Then there is the Valkyries' war-whoop—well known from its use in the Valkyries' Ride. Sieglinda has tender, piteous cries. In the scene of pleading and counter-pleading between Siegmund and Brunnhilda we have Wagner at the zenith of his powers: the pleading of the man, the calm, cold majesty of the Valkyrie, awe and pathos and heroic defiance, are all there. From the technical point of view, the scene is equal to Tristan: the continuous sweep of the music, with its ever-changing colours and emotions, is almost supermasterly. The tragedy at the end is a stage rather than a musical effect, and it is made the more powerful by being delayed so long and then arriving with such terrific swiftness.
The last act opens on a high hill, where stands the Valkyries' rock, and amidst thunder, lightning, and rain we get the Ride. Brunnhilda rushes in to her sisters with Sieglinda, tells what she has done, and begs for help. All are aghast and refuse. Sieglinda herself asks no aid; Siegmund is dead, and she has nothing to live for. Brunnhilda tells her she carries within her the seed of the world's mightiest hero, and in a moment her mood changes, and she begs to be sheltered. Her ecstatic outburst is due to a mother's instinctive joy and to the hope of having someone or something to care for, and no more to be utterly forsaken and purposeless. The maidens tell her of the dark wood where the dragon hides, and Brunnhilda, chanting her hymn in praise of the love for which one surrenders all, gives her the fragments of the sword and bids her fly, awaiting with undaunted courage her own punishment. The god comes in bursting with rage, and declares that Brunnhilda shall be left on the mountain to wed the first man who finds her. The other maidens fly in horror; she alone remains to make an appeal to Wotan, as Siegmund had appealed to her. At first he is obdurate, but she begs him to spare her that frightful disgrace, and to surround her with a wall of fire through which only a great hero will dare to pass. He yields, taking her godhood, her limited immortality, away from her, putting her to sleep, calling up the fire, and swearing that only a hero who has no fear of his spear shall pass through, and so the drama ends. Wotan has definitely renounced love. The moment at which he can renounce life rather than endure life without love has not yet come. The old Adam, the biological bias, the will to live, is strong in us all.
When Liszt read the score of The Valkyrie, he wrote to Wagner that he wanted to cry, like the chorus on the miraculous arrival of Lohengrin, "Wunderschön! wunderschön!" No man can cry otherwise to-day when he hears the last act. The summit of artistic achievement seemed to be reached in the second act, but we are now carried still higher. After the Ride, with its unequalled painting of tempest amongst the rocks and pines, there comes Brunnhilda's glorious chant as she sends off Sieglinda, then her long supplication to Wotan, and finally the sleep and fire-music and Wotan's Farewell. The black storm gradually subsides, the deep-blue night comes on, and against it we see the swirling, crackling flames as the fire mounts, forming an impassable barrier that cuts off Brunnhilda from the everyday, busy world. All Brunnhilda's plaint is magnificent in its sweetness and pathos; and the sleep-music, with its caressing, lulling figure, is a thing by which a man's memory might well live for ever.
This, the tragedy of Siegmund and Sieglinda and the punishment of Brunnhilda, is the first of the subsidiary dramas; the second, the finding of Brunnhilda by Siegfried, must now be considered. We hear the clinking of Mime's hammer, and the curtain rises on his home in a cave. All is dark within save for the smouldering smithy fire; but facing it is the hole in the rock which is the entrance, and through it we see the green summer forest. Mime is a malignant dwarf, in whose care Sieglinda, dying in childbirth, has left Siegfried. Years have passed, springs and summers and winters have come and gone; but Nature goes on in her imperturbable way, and Brunnhilda still lies wrapt in slumber on the mountain heights, the subject of awe-struck whispers amongst passing tribes. Mime tries in vain to piece the sherds of the sword together; Siegfried always smashes the new-made weapon at a single blow. The Wanderer, in his blue cloak, enters: it is Wotan, the heart-broken god, going wearily about the world awaiting what may happen. Again we hear the whole history of the Ring, but this time it is wrought into, and becomes an essential part of, the drama. Mime wagers his head that he will answer three questions put to him by the Wanderer, and having triumphed twice, is posed by the third: "Who will make a useful sword of these bits?" The Wanderer laughs at him, tells him it will be he who knows not fear; and he leaves Mime's head to this hero. He goes off, while fantastic lights dance without through the forest, until Mime is in an agony of fear. But on this scene depends the whole subsequent action. Mime tries to frighten Siegfried, and finds it impossible. He wants the Nibelung's ring to rule the world: Siegfried is the only man to get it; and after he has got it, Mime will avert the Wanderer's prophesied disaster by poisoning him. He tells the history of Sieglinda also, and Siegfried knows he is the hero. He will have no patching of the sword: that sword was Wotan's and subject to his will; he grinds it to powder, and makes one of his own, with which he will face either man or god. In the making of it he sings the glorious Sword-song; and when it is made he tests it by splitting the anvil with it. Here the first act ends. There are two Siegfried themes to notice; the first, the Hero, has been heard before:
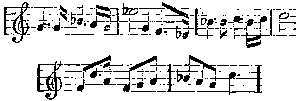
In case I have too much insisted on the storm, passion, and fire in The Valkyrie, it may be pointed out that these play little part in Siegfried. Here we have first the calm summer morning, and if the scene with the Wanderer is filled with that sense of the remote past, and the Wanderer's exit uncanny, spectral—a very nightmare—much of the other music, such as the bit where Siegfried describes himself looking into the brook, and all the tale of Sieglinda, is tender and delicate; the fresh morning wind blows continuously. The same is true of the second act. After the beginning at Hate Hole, the slaying of the dragon—which is always comic—and the squabble of Alberich and Mime, we have scarcely anything but sustained beauty to the end. Having accidentally tasted the dragon's blood, Siegfried knows exactly what Mime means when he comes coaxingly to persuade him to drink the cup of poison; so he passes the sword through him. Then follows the scene where Siegfried lies in the sun and hears the wind murmuring in the trees, and then listens to the bird as it sings of Brunnhilda asleep far away on the mountains, and goes off to find her—all admirably painted in the freshest tints. The last act opens in the mountains. It is dawn, and gray scud is flying; the Wanderer summons Erda and learning nothing from her, tells her, virtually, his determination to struggle no more, but to await the end. Siegfried arrives; the Wanderer bars his way to try him; but Siegfried has no fear of the spear, and the sword was made by his own hands; so the spear is shattered, and he goes on his way. He passes through the fire, which immediately subsides.
The scenery changes to that of the last of The Valkyrie, save that (generally) someone has erected a wall behind Brunnhilda. It is a calm summer afternoon; far away other hills are seen sleeping in the sun; Grani, Brunnhilda's horse, grazes quietly at one side; Brunnhilda, covered by her shield, her spear by her side, slumbers on. Siegfried enters, and after many doubts, wakes her with a kiss. At first she fiercely revolts against the new tyranny, the most terrible consequence of her crime; but she yields in the end, and the drama ends with a love-duet of a curious kind—not so much loving and passionate as heroic and triumphant, with a most elaborate cadenza, as if Wagner had said to himself, "Here's an end to all theories!"
In the prologue of the Dusk of the Gods we find the Norns spinning in the dark near Brunnhilda's cave; the rope they are at work on breaks, and they learn that the end is near. They disappear; day breaks, and Siegfried and Brunnhilda enter. She is sending him to do heroic deeds, quite in the spirit of medieval chivalry; he presents her with the ring and goes, wearing her armour and taking her horse. He arrives at the hall of Gibichungs, where he finds Gunther, his sister Gutruna and Hagen, a son of Alberich. They give Siegfried a draught which takes away his memory; he falls in love with Gutruna, and when they propose that he should take Gunther's shape and win Brunnhilda for him, he agrees at once. In the meantime, Waltraute, a Valkyrie, knowing Wotan's need of the ring, has come and tried in vain to get it; Brunnhilda refuses to part with it. Presently Siegfried, wearing the tarnhelm, comes and claims her, and compels her to share his couch, placing his sword between them to keep faith with Gunther. The ring, however, he tears from her. She is overcome with dismay and grief. When, at the end of The Valkyrie, Wotan had pronounced her doom, it had seemed bad enough; but this is a thousand times worse, and she cannot understand the god's cruelty. Arrived at Gunther's home, she of course recognises Siegfried in his own shape, and knows by the ring that it was he, changed by the tarnhelm, and not Gunther, who had broken through the fire a second time. Her sorrow changes to fierce anger; she denounces him, and says he has not kept faith with Gunther; he does not remember anything that occurred previous to drinking the potion, knows he has been true to Gunther, and goes joyfully off with his new bride. Gunther thinks he has been dishonoured; Brunnhilda is furious at her betrayal; Hagen wants to get the ring; and the three decide that Siegfried must die. There can be no explaining away the draught. In Tristan it is not essential that the philtre is a true love-philtre, but here the case is different. If it symbolizes, as has been suggested, a sudden passion for Gutruna, then Siegfried is an out-and-out blackguard, and not the hero Wagner intended. Besides, if the loss of his memory leads to the sacrifice of Brunnhilda, afterwards its sudden return, due to another potion, leads immediately to his own death. We must accept these potions as part of the machinery. If we do not grumble at talking dragons, tarnhelms, flying horses and fires and magic swords, we need not boggle at a couple of glasses of magical liquid.
In the last act Siegfried, out hunting with the Gibichung tribe, finds himself alone by the riverside. The Rhine-maidens beg the ring from him; he refuses, and they tell him that this day he must die. The other hunters arrive, and Siegfried, drinking the second philtre, tells the story of how he first won Brunnhilda. That is Hagen's opportunity: to avenge Gunther he stabs Siegfried in the back. To the tremendous funeral march the body is carried over the hills. It is brought into the hall of the Gibichungs. Gunther has pangs of remorse, but Hagen, only half-human, has none; the pair fall out, and Gunther is killed. Gutruna wails, as a woman will when she loses her husband and brother within a quarter of an hour; Hagen goes to take the ring from Siegfried's finger, but the corpse raises its hand menacingly and all draw back aghast. Brunnhilda enters; all now has become clear to her, and she resolves that she, like Wotan, will renounce a loveless life—a life based on fraud and tyranny. She tells Gutruna that Siegfried has never belonged to her—is hers, Brunnhilda's; and on receiving this crushing blow, Gutruna creeps to her brother's side and lies there, miserable and hopeless. He is dead; but he was the list of her kin and only friend, and, robbed of even the memory of Siegfried, to be near his dead body seems better than nothing. Then Brunnhilda commands the funeral pyre to be built and the body of Siegfried placed on it; she chants her song in praise of love, mounts her horse Grani, and rides through the fire into the Rhine. Shouting "The ring!" Hagen dashes after her; the ring has returned to the maidens, and Loge, unchained, mounts up and Walhalla is consumed. So ends the third subsidiary drama of the Ring.
The music is the last Wagner wrote in his ripe period; when we get to Parsifal his powers were waning. In point of structure it is the same as that of Siegfried. It has less of springtime freshness than the Valkyrie, and the prevailing colour is sombre and tragic; but there are magnificent things. The Norns scene, the Journey of the Rhine, the Waltrante scene, the funeral march, and Brunnhilda's final speech, are Wagner in the full glory of his strength.
The complete Ring was given for the first time at the opening of the Bayreuth (Wagner) Theatre in 1876. The performance did not pay, and the expenses had to be covered by selling the dresses and scenery. Bayreuth was by no means in those days the fashionable summer resort it has since become. Nevertheless, the immediate effect felt throughout Europe was electric, stupendous. As a mere advertisement, it proved more effective than anything devised for pills and patent soaps. Hundreds who went to Bayreuth to pass the time, or at most in a spirit of intelligent curiosity, came away converted to the new faith; many who went to sponge remained to pay; and all preached the doctrine of Wagnerism wherever they went. Well they might. As I was an infant at the time, my recollections of the first performances and of Wagner's speech are not so vivid as those of some of my younger colleagues, who, like myself, were not there; but, according to all creditable accounts, the representations must have been a nearer approach to perfection in all respects, save the singing, than anything seen before. In one sense Wagner had attempted no revolution in stage-craft; but in another sense it was, perhaps, the best sort of revolution to secure the ablest men, and make them take care, pains, with their work. Anyhow, if tolerable operatic representations can now be seen in every country of Europe save Italy, the credit must go to Wagner, who first taught the impresarios what to aim at and how to achieve their aim, and gave the accursed star system a blow from which it is slowly dying. Carefully nursed though it is in New York and at Covent Garden, its convulsive shudders announce impending death, and already one hears the wail of those who mourn a departing order of things.
This disastrous and evil opera was written in Wagner's old age, under the influence of such a set of disagreeably immoral persons as has seldom if ever been gathered together in so small a town as Bayreuth. The whole drama consists in this: At Montsalvat there was a monastery, and the head became seriously ill because he had been seen with a lady. In the long-run he is saved by a young man—rightly called a "fool"—who cannot tolerate the sight of a woman. What it all means—the grotesque parody of the Last Supper, the death of the last woman in the world, the spear which has caused the Abbot's wound and then cures it—these are not matters to be entered into here. Some of the music is fine.
Wagner died suddenly at Venice February 13, 1883, and a few days later was buried in the garden of Villa Wahnfried, Bayreuth. For a really great composer he had quite a long life, and he lived it out strenuously; and if he struggled and suffered during a great portion of it, at any rate his last years brought him peace, undisturbed by the old nightmare dread of poverty.
His activity manifested itself in three forms: the reforms he effected in the theatre and the concert-room, his own music dramas, and the prose writings, in which he both advocated the reforms and argued for his theories. The prose, I have said, is of very small account now, and, with the exception of the essays mentioned earlier, his essays and articles have only a curious interest. His theatrical reforms consisted in making the artistes sing intelligently and with care, and in demanding realistic scenery. Intelligence and pains—these are the two new elements he introduced into the theatre; and if most operatic performances to-day are not absolutely ridiculous, we owe this miraculous change to Wagner alone. The notion that anything, however slovenly and stupid, is good enough for opera was dissipated by him alone. A book of an interesting gossipy sort might be compiled to show the difference between opera representations before Bayreuth and those of a post-Bayreuth date, but there is no space for any such excursions here. At the risk of turning this sketch into something like an analytical programme, I have concentrated my attention on his operas, and have tried to show how the later Wagner—the Wagner of the Ring, the Mastersingers, and of Tristan—grew out of the earlier Wagner, who composed as everyone else did at the time. He created a new form of art, and no serious composer will ever dream of going back to the ancient form of Gluck, Mozart and Weber. From the historical point of view, it is the creation of this new form that gives him his importance. He did for opera what George Stevenson did for vehicular traffic. The music drama has driven out Italian opera as completely and irrevocably as the steam-engine drove out the stage-coach. As far as his choice of subjects, there is no reason on earth why he should be followed. The myth suited him because he happened to be the Wagner he was, but there are a hundred reasons why present-day composers should leave the myth alone. The myth gave him opportunities to display his passion, keen sympathy with picturesque nature, tremendous sense of a remote past that never existed; but other composers have other mental and artistic qualities, and for them there are fresh fields to be explored. No one need trouble about the myth unless he is prepared to show us something finer than anything in Wagner.
I have been compelled to leave out much interesting matter—Wagner's trips to London, his difficulties in getting his theatre built, the financial failure of Bayreuth at first, its success afterwards. Nor can I say much about the man. He was certainly an overwhelming personality. In his train followed such really great musicians as Liszt, von Bülow, Tansig, and others. Richter was his copyist and disciple. He crushed all originality out of Jensen, and, doubtless, others. Kings and Princes were his very humble servants. And at Bayreuth he had round him a pack of fools to do his bidding, as well as a number of intelligent mediocrities, who wrote books and printed newspapers about him, inspired by the mediocrity's ordinary ambition to become known through attaching one's self to a famous man.
The fighting is over and done; there remain to us the glorious music dramas. After more than twenty years Wagner's fame is still growing, and it seems impossible that it will ever wane or that he will not, in far-off times, be numbered with the greatest of the great. "He sleeps, or wakes, with the enduring dead."