
Title: Ferdinand Vandiveer Hayden and the Founding of the Yellowstone National Park
Author: Geological Survey
Photographer: William Henry Jackson
Release date: January 29, 2015 [eBook #48110]
Most recently updated: October 24, 2024
Language: English
Credits: Produced by Stephen Hutcheson, Dave Morgan, Carol Spears
and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at
http://www.pgdp.net


U.S.
DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR
GEOLOGICAL SURVEY

Ferdinand Vandiveer Hayden and the Founding of the Yellowstone National Park
One of the prime movers among the many explorers of the west who played key roles in establishing the Yellowstone National Park was Ferdinand Vandiveer Hayden of the U. S. Geological and Geographical Survey of the Territories, a predecessor of today’s U. S. Geological Survey. His signal accomplishments, in 1871-72, were among the many highlights of a long and distinguished career in public service.
Hayden’s professional training was as a doctor of medicine. It is a tribute to his determination and energy that he reached this professional status. Born in Westfield, Massachusetts, on September 7, 1829, he was, in his early youth, sent by his widowed mother to live with an uncle on a farm in Rochester, New York. Following an unusually studious childhood, he began teaching school when he was 16 years old. He soon became discontented with what he considered an inadequate education, and made his way to Oberlin, Ohio. There, he persuaded the President of Oberlin College to allow him to enroll in medical school although he was virtually penniless.
Young Hayden proved to be a diligent and dedicated student, and won the respect of classmates and professors alike for his hard-working attitude. None, however, foresaw the great success that he later achieved.
While working his way through college, Hayden formed a close association with a young geologist named John Strong Newberry, who persuaded Hayden to pursue his studies under his own former teacher, James Hall of Albany, New York. Soon after, Hayden enrolled at Albany Medical College, and though he graduated with an M.D. in 1853, it is during this time that his interest in geology was fostered under the influence of Professor Hall.
Shortly after his graduation from medical school, Hayden set out on his first geographical expedition under the sponsorship of Hall. Accompanied by the paleontologist Fielding Bradford Meek, Hayden headed up the Missouri River to explore the Dakota Badlands and to collect fossil specimens. Returning in 1854, he and Meek began to acquire reputations of their own and, as a team, they added significant geological information to what was known about the Nation’s Western frontier.
During the War between the States, Hayden practiced medicine for the only time in his career, serving with the Army as a surgeon. Following the War he received his first formal degree in geology when he was elected Professor of Geology and Mineralogy at the University of Pennsylvania in 1865, a post he held mainly in absentia for 7 years. For the next several years, much of his time was spent studying and reporting on the geology of the Nebraska Territory and Rocky Mountain Region.
In 1869 Hayden’s activities became officially organized under the Department of the Interior, as the United States Geological and Geographical Survey of the Territories. In that same year he completed a highly successful expedition through the western mountains from Denver to Santa Fe. This expedition set the pattern for those to follow, for his team studied not only the geology, but virtually all natural phenomena which they encountered, including wildlife, water resources, and mineral deposits.

Dr. Hayden in Union Officer’s uniform during the Civil War. This was the only time Hayden actually practiced medicine.
Hayden’s historic expedition into the Yellowstone area in 1871, was preceded by two expeditions which fired the imagination of those interested in that largely unknown region. The Folsom-Cook group penetrated the Yellowstone Country in 1869, followed by the Washburn-Langford-Doane Expedition in 1870. Lieutenant Gustavus C. Doane, who served as the leader of the military escort for this latter expedition as well as for the later Hayden Survey, filed a detailed report which was published as a Congressional document and became a landmark of the Yellowstone story. The following is taken from his report:
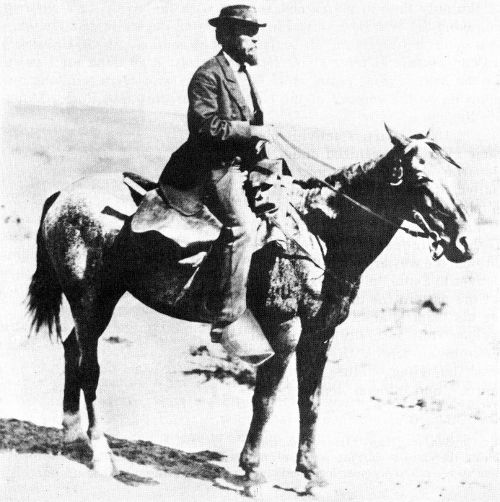

Hayden, mounted here on his horse “Patsy”, maintained a tenuous link with his professor’s chair at Pennsylvania by frequently wearing a frayed dress coat.
“We kept the Yellowstone to our left, and finding the canyon impassable, passed over several high spurs coming down from the mountains, over which the way was much obstructed by fallen timber, and reached, at an elevation of 7,331 feet, an immense rolling plateau extending as far as the eye could reach. This elevated slope of country is about 30 miles in extent, with a general declivity to the northward. Its surface is an undulated prairie dotted with groves of pine and aspen. 5 Numerous lakes are scattered throughout its whole extent, and great numbers of springs, which flow down the slopes and are lost in the volume of the Yellowstone. The river breaks through this plateau in a winding and impassable canyon and trachyte lava over 2,000 feet in depth; the middle canyon of the Yellowstone, rolling over volcanic boulders in some places, and in others forming still pools of seemingly fathomless depth. At one point it dashes here and there, lashed to a white foam, upon its rocky bed; at another it subsides into a crystal mirror wherever a deep basin occurs in the channel. Numerous small cascades are seen tumbling from the lofty summits a mere ribbon of foam in the immeasurable distance below. This huge abyss, through walls of flinty lava, has not been worn away by the waters, for no trace of fluvial agency is left upon the rocks; it is cleft in the strata brought about by volcanic action plainly shown by that irregular structure which gives such a ragged appearance to all such igneous formations. Standing on the brink of the chasm the heavy roaring of the imprisoned river comes to the ear in a sort of hollow, hungry growl, scarcely audible from the depths, and strongly suggestive of demons in torment below. Lofty pines on the bank of the stream ‘dwindle to shrubs in dizziness of distance.’ Everything beneath has a weird and deceptive appearance. The water does not look like water, but like oil. Numerous fishhawks are seen busily plying their vocation, sailing high above the waters, and yet a thousand feet below the spectator. In the clefts of the rocks, hundreds of feet down, bald eagles have their eyries, from which we can see them swooping still further into the depths to rob the ospreys of their hard-earned trout. It is grand, gloomy, and terrible; a solitude peopled with fantastic ideas; and empire of shadows and of turmoil.”
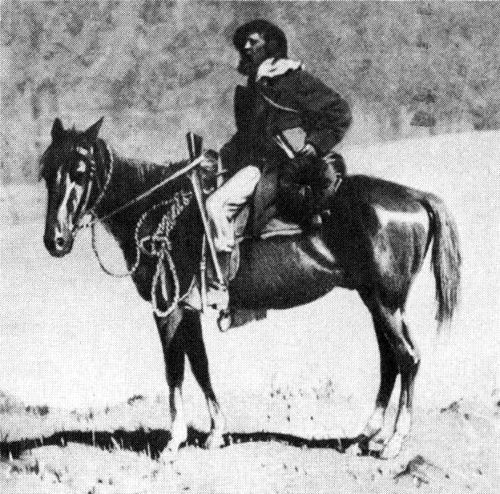

The artist Thomas Moran as he appeared on the 1871 Expedition. W. H. Jackson took this photo as evidence that his seemingly frail friend was actually a durable outdoorsmen.
Spurred on by these reports, Hayden organized his expedition with the support of a $40,000 appropriation from Congress. On June 1, 1871, a team of 34 men and seven wagons, set out from Ogden, Utah. Among the group were geologist and managing director James Stevenson, mineralogist A. C. Peale, topographer Antoine Schoenborn, artists Henry W. Elliott and Thomas Moran, and photographer William H. Jackson. The latter two proved to be invaluable members of the expedition for their work served as dramatic and effective publicity in favor of establishing the park. Moran’s famous landscapes 6 were afterwards hung in the halls of Congress and Jackson’s equally famous photographs portraying the primeval grandeur of the Yellowstone were widely distributed.

William Henry Jackson, self-portrait. Jackson made this exposure while exploring the Tetons in 1872.

The Hayden Survey, led by Lieutenant Gustavus C. Doane, about to enter the Yellowstone area. The two-wheeled vehicle, in the center foreground, is an odometer, a horse-drawn device used to measure distances travelled in the wilds.
After several weeks travel, the Hayden expedition reached Boetler’s Ranch in the Yellowstone River Valley. There they were joined by the Barlow-Heap military party of engineer-explorers who also planned a reconnaissance of the Upper Yellowstone. This latter group intermittently explored with the Hayden expedition during the next several weeks. The results of the Barlow-Heap explorations were published as a modest Senate Document which proved to be of material help in establishing the Yellowstone National Park.
The joint Hayden/Barlow-Heap expeditions departed from Boetler’s on July 20, 1871. The journey through the wilderness was by no means an easy one. The wagons had to be abandoned and the gear packed on mules. Progress was slow, and the difficulty of moving through the dense forest was compounded by the great number of trees felled by fires that periodically swept the region.
The Yellowstone Basin however, proved to be an ideal open-air laboratory for the geologist, and perhaps one of the best places on earth for studying active volcanic processes because of the wide variety of geologic features. Each of the scientists accompanying the expedition found unique opportunities for observation and study.
Hayden recorded his thoughts as his party advanced up the River: “But the objects of the deepest interest in this region are the falls and the Grand Cañon (of the Yellowstone). I will attempt to convey some idea by a description, but it is only through the eye that the mind can gather anything like an adequate conception of them.... But no language can do justice to the wonderful grandeur and beauty of the cañon below the Lower Falls; the very nearly vertical walls, slightly sloping down to the water’s edge on either side, so that from the summit of the river appears like a thread of silver foaming over its rocky bottom; the variegated colors of the sides, yellow, red, brown, white all intermixed and shading into each other; the Gothic columns of every form standing out from the sides of the walls with greater variety and more striking colors than ever adorned a work of human art.”
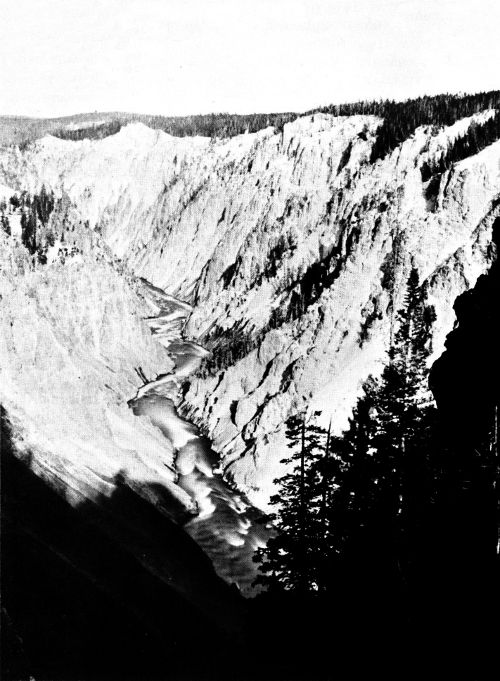

The Grand Canyon, from the Lower Falls.
Hayden continued to describe the falls: “Standing near the margin of the Lower Falls, and looking down the Cañon ... with its sides 1,200 to 1,500 feet high, and decorated with the most brilliant colors that the human eye ever saw, with the rocks weathered into an almost unlimited variety of forms ... the whole presents a picture that would be difficult to surpass in nature.”
“From any point of view, the Upper Falls are most picturesque and striking. The entire volume of water seems to be, as it were, hurled off the precipice with the force which it has accumulated in the rapids above, so that the mass is detached into the most beautiful snow-white, bead-like drops, and as it strikes the rocky basin below, it shoots through the water with a sort of ricochet for the distance of 200 feet.”
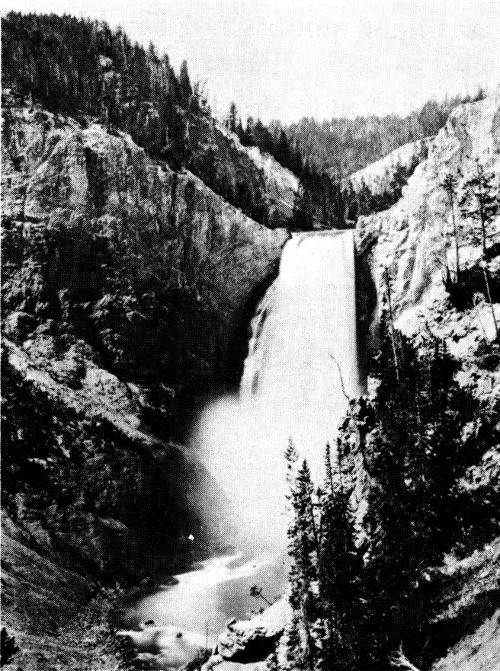

The Lower Falls of the Yellowstone.

The Upper Falls of the Yellowstone.

Crater of the Grotto Geyser.
Of the Yellowstone itself, Hayden said: “The river, by its width, its beautiful curves, and easy flow, moves on down towards its wonderful precipices with a majestic motion that would charm the eye of an artist.”
However, not all was majestic beauty, for there was also the power and mystery of the geysers, and the grotesque forms of the hot mud springs. Hayden described these phenomena, such as one geyser he named the Grotto: “A vast column of steam issues from a cavern in the side of the hill, with an opening about 5 feet in diameter. The roaring of the waters in the cavern, and the noise of the waters as they surge up to the mouth of the opening, are like that of the billows lashing the sea-shore. The water is as clear as crystal, and the steam is so hot that it is only when the breeze wafts it aside for a moment one can venture to take a look at the opening.”
“Located higher up on the side of the hill not far from the Grotto, is the most remarkable mud-spring we have ever seen in the West. It may not improbably be called the Giants Cauldron. It does not boil with an impulse like most of the mud-springs, but with a constant roar which shakes the ground for a considerable distance, and may be heard for half a mile. All the indications around this most remarkable cauldron show it has broken out at a recent period....”
Examining the mud-springs and geysers was hazardous business and could be a painful experience, as Hayden discovered: “The entire surface is perfectly bare of vegetation and hot, yielding in many places to slight pressure. I attempted to walk among these simmering vents, and broke through to my knees, covering myself with hot mud, to my great pain and subsequent inconvenience.”
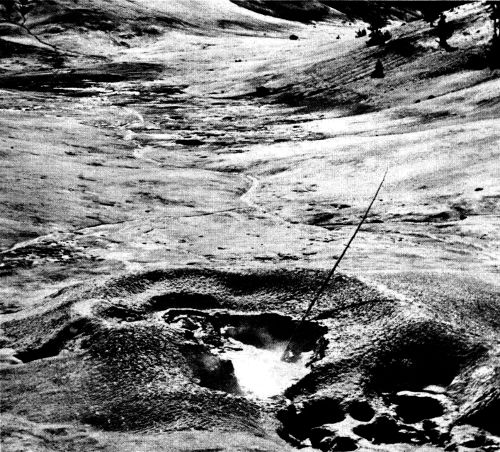
Boiling Mud Springs at Crater Hills near Sulphur Springs.
Finally, the expedition reached Yellowstone Lake, the focal point of their exploration, causing Hayden to remark: “On the 28th of July we arrived at the Lake, and pitched our camp on the northeast shore, in a beautiful grassy meadow or opening among the dense pines. The lake lay before us, a vast sheet of quiet water, of a most delicate ultramarine hue, one of the most beautiful scenes I have ever beheld. The entire party was filled with enthusiasm. The great object of our labors has been reached, and we were amply paid for all our toils. Such a vision is worth a lifetime, and only one of such marvelous beauty will ever greet human eye. From whatever point of view one may behold it, it presents a unique picture.”

The Head of Yellowstone Lake.
Hayden’s party split into groups, with some continuing to explore the perimeter of the lake, while Hayden, Schoenborn and other members of the expedition went on toward the Firehole Geyser Basin. Eventually, the entire party arrived back at Boetler’s Ranch, having spent 38 days in the wilderness.
The most important product of the expedition, in addition to Jackson’s photos, was a 500-page report by Hayden documenting findings 13 of his party. Hayden presented this report and photos to Senators, Congressmen, his superiors in the Interior Department and nearly anyone else who could possibly influence the founding of a park. He also wrote articles in magazines with national circulation, and spent much personal time and effort in trying to convince Congress to establish the park.
On December 18, 1871, a bill was introduced simultaneously in the Senate, by Senator Pomeroy of Kansas, and in the House of Representatives by Congressman Clagett of Montana, for the establishment of a park at the headwaters of the Yellowstone River. The bill in each case was referred to the respective Committees on Public Lands. Upon reporting the bill back to the Senate on January 22, 1872, Senator Pomeroy advised that body, “Professor Hayden and party have been there, and this bill is drawn on the recommendation of that gentleman to consecrate for public uses this country for a public park.”
The original bill, as presented to both Houses, read as follows:
“Be it enacted & c., That the tract of land in the territories of Montana and Wyoming lying near the headwaters of the Yellowstone river, and described as follows, to wit: commencing at the junction of Gardiner’s river with the Yellowstone river, and running east to the meridian passing ten miles to the eastward of the most eastern point of the Yellowstone lake, thence south along said meridian to the parallel of latitude passing ten miles south of the most southern point of Yellowstone lake; thence west along said parallel to the meridian passing fifteen miles west of the most western point of Madison lake; thence north along said meridian of the latitude of the junction of the Yellowstone and Gardiner’s rivers; thence east of the place of beginning, is hereby reserved and withdrawn from settlement, occupancy or sale under the laws of the United States, and dedicated and set apart as a public park or pleasuring-ground for the benefit and enjoyment of the people; and all persons who shall locate, or settle upon or occupy the same, or any part thereof, except as hereinafter provided, shall be considered trespassers, and removed therefrom. Sec. 2 That said public park shall be under the exclusive control of the Secretary of the Interior, whose duty it shall be as soon as practicable to make and publish such rules and regulations as he may deem necessary or proper for the care and management of the same. Such regulations shall provide for the preservation from injury or spoliation of all timber, mineral deposits, natural curiosities, or wonders within said park, and their retention in their natural condition. The Secretary may in his discretion grant leases for building purposes, for terms not exceeding ten years, of small parcels of ground, at such places in said park as shall require the erection of buildings for the accommodation of visitors; all of the proceeds of said leases, and all other revenues that may be derived from any source connected with said park, to be expended under his direction in the management of the same, and the construction of roads and bridle-paths therein. He shall provide against the wanton destruction of the fish and game found within said park, and against their capture of destruction for the purposes of merchandise or profit. He shall also cause all persons trespassing upon the same after the passage of this act to be removed therefrom, and generally shall be authorized to take all such measures as shall be necessary or proper to fully carry out the objects and purposes of this act.”
On January 23, 1872, Senator Pomeroy, in response to questioning during consideration of the bill, stated: “This bill originated as the result of the exploration made by Professor Hayden under an appropriation of Congress, last year. With a party he explored the headwaters of the Yellowstone and found it to be a great natural curiosity, great geysers as they are termed, waterspouts, and hot springs, and having plotted the ground himself, and having given me the dimensions of it, the bill was drawn up, as it was thought best to consecrate and set apart this great place or national resort, as it may be in the future, for the purpose of public enjoyment.”

The Senate, sitting as Committee of the Whole, gave its final consideration to the bill on January 30. There was limited floor discussion, basically concerning whether or not the land was suitable for agricultural development. The bill’s chief supporters convinced their colleagues that the region’s real value was as a park area, to be preserved in its natural state, and the bill passed by a comfortable margin.
The House considered the same bill on February 27. Again, the question was raised as to whether the region should be left open for agricultural development. However, as in the Senate, the obvious value of the region as a scenic preserve made the task of the park’s advocates an easy one. The bill was readily passed with 115 yeas to 65 nays, and 60 not voting.
On March 1, 1872, President Grant signed the bill into law establishing the Yellowstone region as a public park, thus setting a major conservation precedent. The Nation had its first National Park; an area of unique beauty was set aside for the enjoyment of generations to come, and a tradition of preserving other such areas was established.
The photographs in this section of the booklet were selected from those taken by William Henry Jackson during Hayden’s second Yellowstone Expedition in 1872, and reproduced from U. S. Corps of Engineers negatives maintained by the National Archives. Jackson, considered one of the foremost photographers of the early West, was the first man to photograph and publish many of these scenes of the Yellowstone. Jackson’s own captions describe the photographs on the following pages.
Photography in the field was an arduous affair one hundred years ago. On the Yellowstone Expedition, Jackson had to pack by mule both his large, cumbersome cameras and his darkroom—for exposed negatives had to be developed immediately.
Hayden was well aware of the artistic and practical worth of Jackson’s photographs. A series of Jackson photos served to illustrate his report on the Yellowstone Country which sparked the interest of government officials and the Public. The two men continued their association for many years, covering many expeditions.
Perhaps the most fitting testimonial of Jackson’s contributions to the 1871 Yellowstone Expedition was offered by a former Director of the National Park Service, who said:
“It was a singular stroke of fortune that the Hayden Expedition took with it to the Yellowstone land of miracles, the miracle of photography. The camera, in the hands of William H. Jackson, recorded for the first time the phenomena of the Yellowstone in a form that the most skeptical human eye could not dispute. These photographs helped as much as anything to convince Congress that the Yellowstone region should be set aside as a National Park.”

Title page for “Photographs of the Yellowstone National Park, etc.” by W. H. Jackson.
PHOTOGRAPHS
OF THE
YELLOWSTONE NATIONAL PARK
AND
Views in Montana and Wyoming Territories.
DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR.
United States Geological Survey of the Territories.
F V Hayden, United States Geologist-in-charge
W. H. JACKSON, PHOTOGRAPHER.
Washington:
Government Printing Office
1873.

William H. Jackson and an assistant photographing in high places—Tetons.

Camp of U. S. Geological Survey, Ogden, Utah. The camp is located on one of the remarkable lake-terraces which form an interesting feature of the scenery on the Salt Lake Basin. The Wasatch Mountains, in the background, are about five thousand feet above the camp, and nine thousand five hundred and thirty feet above sea level.

Meeting of the U. S. Geological Survey in the Lower Firehole Basin. The two divisions of the Survey met at this locality on the same day, July 17, 1872, starting from this point several hundred miles distant from each other. The locality is near the source of the Madison River, and is within the limits of the National Park, Latitude 44° 34′6″: Longitude 110° 55′15″.
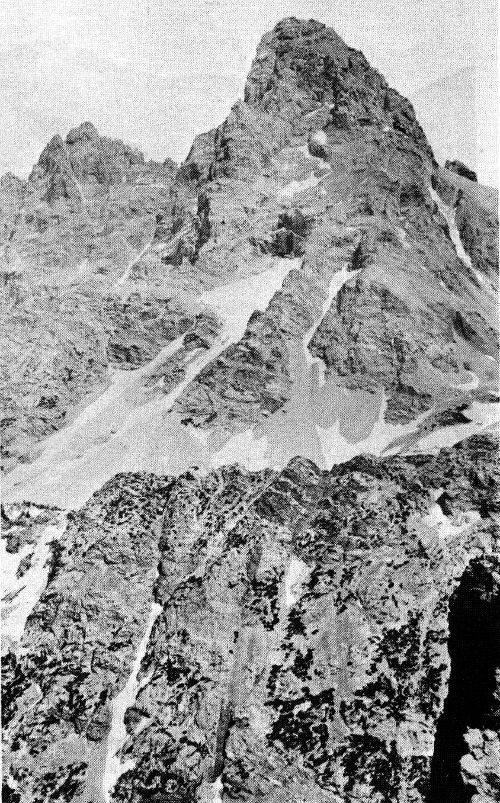

Mt. Hayden, or the Great Teton. This picture represents one of the monarch peaks of the Rocky Mountains. It is visible on a clear day for a radius of one hundred and fifty miles in every direction, thus forming one of the most conspicuous landmarks in the West. It is probable that the only white men that ever reached its summit are Mr. James Stevenson and Hon. N. P. Langford. The elevation is thirteen thousand four hundred feet. It is seen by the traveler on the overland stage-road to Montana, from the Snake River Basin, far to the eastward, rearing its “Bald awful head” far above the limit of perpetual snow.

Panoramic View of the Teton Range. This photo presents a panoramic view of the north portion of the Teton Range. The peaks in the distance are composed of massive granites, while the rocks in the foreground are limestones. For beauty as well as grandeur, no description can convey any adequate idea of it.

Camp at the Mouth of Teton Canyon. This camp is in the Teton Canyon, and West of the Teton Range, just ten miles by Triangulation to the summit of the Grand Teton. The trees are all pines and firs. As the sun rises in the morning immediately back of the peaks, it invests them with remarkable beauty. The scenery along the Teton River is rugged and most attractive. It furnished some of the finest views taken on the Survey.

Crater of the Architectural Geysers, Lower Basins. This picture represents one of the handsomest fountain springs in the Lower Basin. The entire mass of the water is at times most violently agitated, and is thrown up by a succession of impulses forty to sixty feet. The water overflows the borders, producing the wonderful ornamentation which is so clearly shown in the photograph. The peculiar coral-form masses of pearly silica are well brought out. The crater is about twenty-five feet in diameter, and the water when quiet has a temperature of about 180°.

Upper Firehole Basin from the Crater of Old Faithful. Old Faithful derived its name from the regularity of its action, which occurs once in sixty-five minutes. When it is in operation it throws a column of water, by a succession of impulses six feet in diameter, to the height of one-hundred and sixty feet. The paroxysm continues about twelve minutes when the water sinks down in the crater, and all is quiet. The silicious deposits around the crater are marvels of beauty. The Madison River can be seen in the distance and also the geysers in operation.

Hot Springs and Castle Geyser. The spring in the foreground is in all respects the most beautiful one in the National Park. The ornamental rim is nearly circular, being about twenty-two feet. The depth is unknown. When the rays of the sun fall nearly vertically on the almost unnaturally transparent waters, all the colors of the prism are produced. The temperature is about 180°. Just in the background is the Castle Geyser, which is so called from the form of its crater. It is really an old ruin. It seldom plays, but when in operation it is a terrific power, shaking the ground for a considerable distance. It continues with great force for one to two hours.

Mammoth Hot Springs on Gardiner’s River. The peculiar character of the deposits is well shown in this picture. The larger hot springs are located on the terrace above, and, as the heated water flows over the declivity, the beautiful pool-like basins are formed from four to eight feet wide and two to four feet deep. As the water leaves the spring and flows over the sides of the mountain, it loses a portion of its heat, so that the bather may choose any temperature he may desire. These pools are sometimes called Diana’s Baths. The deposit is as white as snow.

Mammoth Hot Springs, Lower Basin. The four succeeding pictures represent the calcareous group. There are two kinds of hot springs in the park, called siliceous and calcareous from the character of their deposits. A large amount of lime is held in solution in the hot water which is precipitated in wonderfully unique architectural forms on the steep sides of the mountains, as shown in the photograph. These springs are located in the valley of the Yellowstone, near the northern boundary of the park, and are named White Mountain Hot Springs on the map. At the present time they are most accessible by the way of Fort Ellis, Montana, and the Yellowstone Valley.
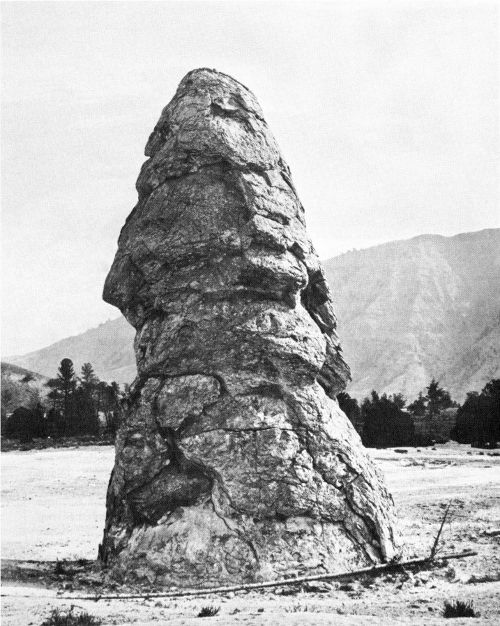

Cap of Liberty Mammoth Hot Springs. This is a fine example of an extinct geyser or fountain spring. It doubtless operates much like one of our artificial fountains, throwing up a column of water several feet, by a succession of impulses, building up a cone by overlapping layers of lime, like the thatch on the roof. The cone is forty-two feet high and about twenty-five feet in diameter at its base. When the hydrostatic force begins to abate, the cone is gradually closed up at the summit, as is shown in the photograph. These dead springs or geysers are a common feature in the park, and are called, in the language of Iceland a “laug.” It is only a calcareous spring that can form so curious and lofty a cone as this.
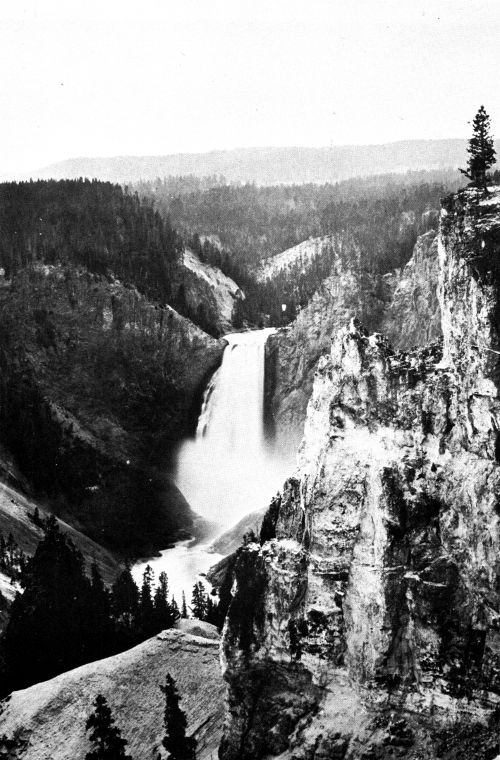

Lower Falls of the Yellowstone. A more distant view of the falls. The photograph however, conveys but a dim conception of the ruggedness of the surroundings.
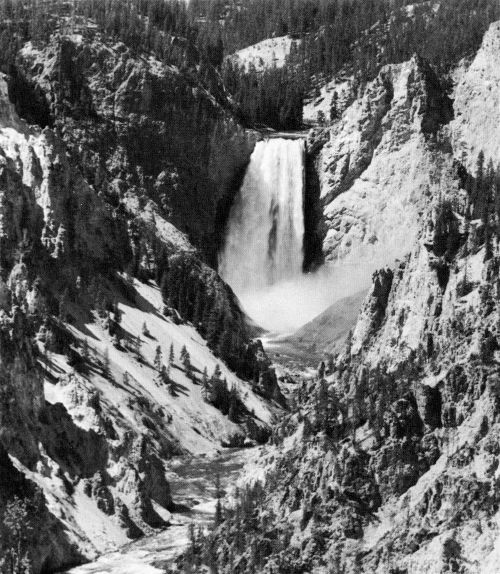

Lower Falls of the Yellowstone. About a fourth of a mile below the upper falls, the waters of the Yellowstone take a much more fearful leap, making a clear descent of three hundred and fifty feet. There is probably not a more beautiful sight in existence than the falls with the Grand Canyon below. The rocks are mostly volcanic.
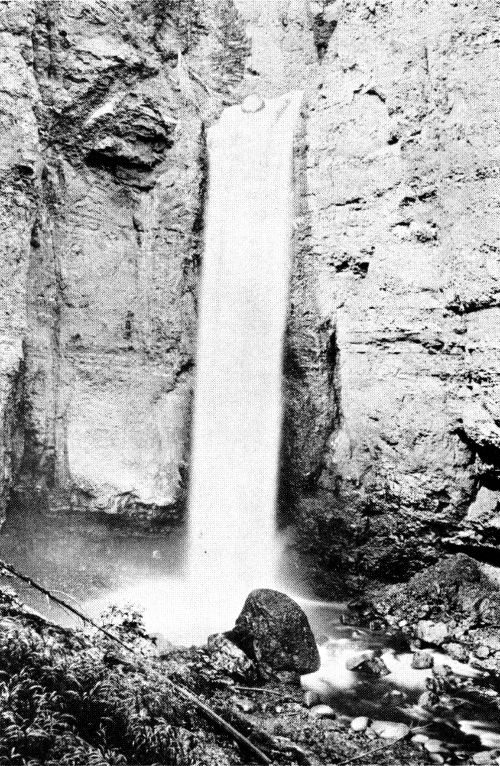

Tower Falls. These beautiful falls are located on a little branch of the Yellowstone, which flows in from the west side, near the lower end of the Grand Canyon. The descent of the water is about one hundred and fifty feet. The rocks are composed of a peculiar conglomerate, which has been weathered into most fantastic, pointed columns resembling the towers of a gothic cathedral. Hence the name.

Panoramic View of the Valley of the Yellowstone. This group of three pictures from a panoramic view of what is regarded by visitors to that region as the most beautiful and symmetrical range of mountains in America. The summits of the peaks are covered with snow more or less the year round, and can be seen for eighty to one hundred miles in every direction.
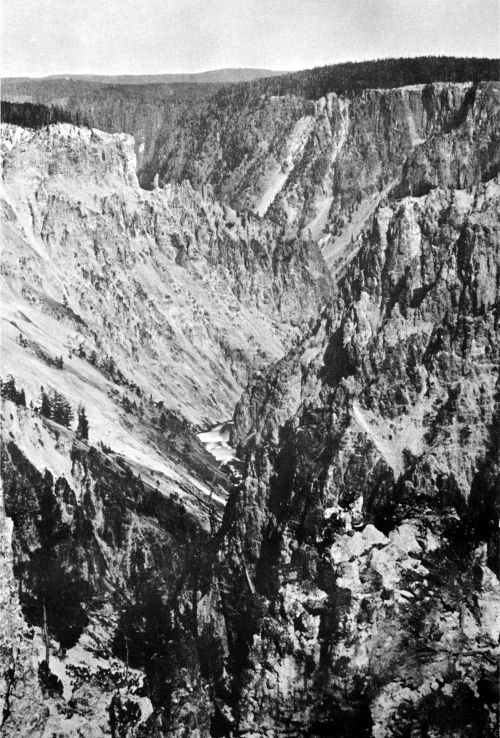

The Grand Canyon, One Mile Below the Falls. This picture is intended to convey to the eye some idea of the depth and remarkable ruggedness of the Canyon. To one standing on the margin of the Canyon, the Yellowstone River fades to a slender thread as it flows along the bottom of the chasm.
As the Nation’s principal conservation agency, the Department of the Interior has basic responsibilities for water, fish, wildlife, mineral, land, park, and recreational resources. Indian and Territorial affairs are other major concerns of America’s “Department of Natural Resources.”
The Department works to assure the wisest choice in managing all our resources so each will make its full contribution to a better United States—now and in the future.
