
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: Coaching Days & Ways
Author: E. D. (Edward William Dirom) Cuming
Release Date: February 10, 2014 [eBook #44864]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
***START OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK COACHING DAYS & WAYS***
| Note: | Images of the original pages are available through Internet Archive. See https://archive.org/details/coachingdaysways00cumi |


BY
E. D. CUMING
WITH ILLUSTRATIONS BY
G. DENHOLM ARMOUR
THE BRITISH SPORT SERIES
HODDER AND STOUGHTON
The many boons conferred by Mr. John Palmer upon his generation faded before the advance of the railways; but he has deserved well of posterity, if only for that he altered the coach team from three horses to four. Until that enterprising man undertook to demonstrate that the coach could carry letters more rapidly and safely than could the post-boy, our ancestors had been content with the unicorn team; but after Palmer had astonished the world by making the journey from Bath to London, in 1784, at the rate of nearly seven miles an hour, the team of four horses gradually but steadily supplanted that of three in the stages on almost every road in the country.
The Stage Coach: Old Times
Painting by G. D. Armour.

It is generally assumed that fast coaching only came into existence after the macadamisation of the roads; but this is not quite the case. Under favourable conditions the speed attained in pre-[Pg 6]Macadam days was nearly as great as it became later. The Sporting Magazine of June 1807 says: ‘Lately one of the stage coaches on the North road ran from London to Stamford, a distance of 90 miles, in 9 hours 4 minutes. The passengers, four in number, breakfasted and dined on the road, so it must have run at the rate of 12 miles an hour all the time it was travelling.’
The ‘old heavies’ discarded under Palmer's drastic rule worked out their lives as ordinary stage coaches, and some of these remained on the road until well on in the nineteenth century.
Nimrod's description of the old-time coachman is worth giving:—
‘The old-fashioned coachman to a heavy coach—and they were all heavy down to very recent times—bore some analogy with the prize-fighter, for he stood highest who could hit hardest. He was generally a man of large frame, made larger by indulgence, and of great bodily power—which was useful to him. To the button-hole of his coat were appended several whipcord points, which he was sure to have occasion for on the road, for his horses were whipped till whipping was as necessary[Pg 7] to them as their harness. In fair play to him, however, he was not solely answerable for this; the spirit of his cattle was broken by the task they were called to perform—for in those days twenty-mile stages were in fashion—and what was the consequence? Why, the four-horse whip and the Nottingham whipcord were of no avail over the latter part of the ground, and something like a cat-o'-nine-tails was produced out of the boot, which was jocularly called the “apprentice”; and a shrewd apprentice it was to the art of torturing which was inflicted on the wheelers without stint or measure, but without which the coach might have been often left on the road. One circumstance alone saved these horses from destruction; this was the frequency of ale-houses on the road, not one of which could then be passed without a call.
‘Still, our old-fashioned coachman was a scientific man in his calling—more so, perhaps, than by far the greater part of his brethren of the present day, inasmuch as his energies and skill were more frequently put to the test. He had heavy loads, bad roads, and weary horses to deal with, neither was any part of his harness to be depended on, upon[Pg 8] a pinch. Then the box he sat upon was worse than Pandora's, with all the evils it contained, for even hope appeared to have deserted it. It rested on the bed of the axletree, and shook the frame to atoms; but when prayers were put up to have it altered, the proprietors said, “No; the rascal will always be asleep if we place his box on the springs.” If among all these difficulties, then, he, by degrees, became a drunkard, who can wonder at his becoming so? But he was a coachman. He could fetch the last ounce out of a wheel-horse by the use of his double thong or his “apprentice,” and the point of his lash told terribly upon his leaders. He likewise applied it scientifically, it was directed under the bar to the flank, and after the third hit he brought it up to his hand by the draw, so that it never got entangled in the pole-chains, or in any part of the harness. He could untie a knot with his teeth and tie another with his tongue, as well as he could with his hands; and if his thong broke off in the middle, he could splice it with dexterity and even with neatness as his coach was proceeding on its journey. It short, he could do what coachmen of the present day cannot do, because[Pg 9] they have not been called upon to do it; and he likewise could do what they never tried to do—namely, he could drive when he was drunk nearly as well as when he was sober. He was very frequently a faithful servant to his employers; considered trustworthy by bankers and others in the country through which he passed; and as humane to his horses, perhaps, as the adverse circumstances he was placed in by his masters would admit.’
Time has dealt kindly with the reputation of the old stage coachman, and popular tradition holds him, as Nimrod portrayed him, a whip of unrivalled skill. That there were such men is perfectly true;[1] but not every stage coachman was an expert: not all were skilful or even careful, and not all were civil: and if, as Nimrod says, they could drive as well when drunk as when sober, the cold light of contemporary record shows that there was ample room for improvement. Take the following:—On the 18th of May 1808 the coachman of the Portsmouth coach to London was intoxicated, and “when he came to the foot of the hill on Wimbledon[Pg 10] Common, instead of keeping straight on turned to the left and found himself in Putney Lane, where turning the corner of Mr. Kensington's wall in order to get again into the road to Wandsworth, the coach was overturned.” He appears to have driven on to the bank by the roadside. The ten outside passengers were all more or less hurt, one dying from her injuries, and the coachman himself had both legs broken. Accidents due to reckless driving and racing were very common, despite the law[2] of 1790 which made a coachman who, by furious driving or careless, overturned his coach, liable to a fine not over five pounds. The following is typical:—
‘Last night occurred one of those dreadful catastrophes, the result of driving opposition coaches, which has so stunned the country with horror that sober people for a time will not hazard their lives in these vehicles of fury and madness.
‘Two coaches that run daily from Hinckley to Leicester had set out together. The first having descended the hill leading to Leicester was obliged to stop to repair the harness. The other coachman[Pg 11] saw the accident and seized the moment to give his antagonist the go by, flogging the horses into a gallop down the hill. The horses contrived to keep on their legs, but took fright at something on the road, and became so unmanageable in the hands of a drunken coachman, that in their sweep to avoid the object of their alarm, the driver could not recover them so as to clear the post of the turnpike gate at the bottom of the hill. The velocity was so great that the coach was split in two; three persons were dashed to pieces and instantly killed, two others survived but a few hours in the greatest agony; four were conveyed away for surgical aid with fractured limbs, and two in the dickey were thrown with that part of the coach to a considerable distance, and not much hurt as they fell on a hedge. The coachman fell a victim to his fury and madness. It is time the Magistrates put a stop to these outrageous proceedings that have existed too long in this part of the country.’ (St. James's Chronicle, 15th July 1815).
The frequency of upsets is suggested by a letter which appeared in the papers in 1785. The writer, who signs himself ‘A Sufferer,’ begs coach pro[Pg 12]prietors to direct their servants, when the coach has been overturned, ‘not to drag the passengers out at the window, but to replace the coach on its wheels first, provided it can be accomplished with the strength they have with them.’
After coaches began to carry the mails, accidents grew more numerous. We can trace many to the greater speed maintained, others to defective workmanship which resulted in broken axles or lost wheels, many to top-heaviness, and not a few to carelessness. The short stage drivers, on the whole, were the worst offenders. For sheer recklessness this would be hard to beat:—
‘During the dense fog on Wednesday last, as a Woolwich coach full of inside and outside passengers was driving at a furious rate, just after it had passed the Six Bells on its way to town, the coachman ran against a heavy country cart. The stage was upset, and those on the roof were pitched violently against an empty coal waggon; two of them fell on the shafts, one of whom had a shoulder badly dislocated; the other had his jawbone broken, with the loss of his front teeth. A Greenwich pensioner, with a wooden leg, had an arm broken, [Pg 15]and some contusions on the head.’ (Bell's Life, 15th December 1882).
It would be easy to compile a list of accidents due to causes unforseen, each one, illustrating a different danger of the road. Here are a few:—
‘Tuesday afternoon, as one of the Brighton stages was leaving London at a rapid pace, the pole broke in Lambeth, and the coach was upset. Several passengers had limbs broken and others were injured.’ (Bell's Life, 25th August 1822).
‘A fatal accident befel the Woolwich Tally Ho opposition stage on Tuesday. Coming down the hill from the Green Man the horses became restive, the coachman lost his command, and immediately the whole set off at full speed. In turning a corner the coach upset, being heavily laden outside. Out of sixteen persons only one escaped without a leg or arm broken, and four are not expected to survive. The coach was literally dashed to pieces. The inside passengers were more lacerated than those outside, owing to the coach being shattered to pieces and their being dragged along the road for fifty yards. But little hopes are entertained of a Major M'Leod—a very fine young man; not a vestige of[Pg 16] his face is left except his eyes.’ (Bell's Life, 22nd September 1822).
‘A fatal accident happened to Gamble, coachman of the Yeovil mail, on Wednesday, caused by the leaders shying at an old oak tree. The coachman was killed on the spot, and the guard escaped with bruises. The horses started off and galloped into Andover at the rate of 20 miles an hour. The single inside passenger was not aware of anything amiss until two gentlemen, who saw the horses going at a furious rate without a driver, succeeded in stopping them just as they were turning into the George gateway.’ (Times, 21st February 1838).
Coachmen and guards were apt to leave too much to the honour of the horses when stopping, and it was not at all uncommon for the team to start on its journey with nobody on the box. An old coachman told Lord Algernon St. Maur that on one night's drive he met two coaches without any driver! In 1806 (46 Geo. III., c. 36) it was made an offence punishable by fine to leave the team without a proper person in charge while the coach stopped.
Organised races between public coaches were[Pg 17] very popular: the coachmen did not spare the horses on these occasions. This race took place in 1808:—
‘On Sunday, August 7th, a coach called the “Patriot,” belonging to the master of the “Bell,” Leicester, drawn by four horses, started against another coach called the “Defiance,” from Leicester to Nottingham, a distance of 26 miles, both coaches changing horses at Loughborough. Thousands of people from all parts assembled to witness the event, and bets to a considerable amount were depending. Both coaches started exactly at 8 o'clock, and after the severest contest ever remembered, the “Patriot” arrived at Nottingham first by two minutes only, performing the distance of 26 miles in 2 hrs. 10 mins., carrying twelve passengers.’

Mail Coaches Racing: Something Wrong with the Opposition Coach
Painting by G. D. Armour.
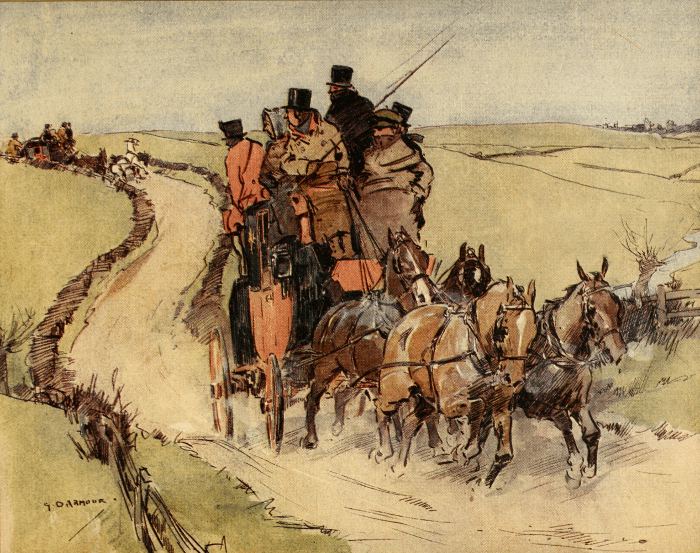

Mishaps were so frequent and productive of so many fatalities, to say nothing of broken limbs, that at last general outcry arose for more stringent repressive measures: and in 1820 a law (1 Geo. IV., c. 4) was passed, making coachmen who might be guilty of ‘wanton or furious driving or racing’ liable to imprisonment as well as to fine, even though their proceedings were not brought to a[Pg 18] close by overturning the coach. The new law did not make an end of accidents: on the whole there were fewer as the result of racing, but the records of time bear ample witness to lack of ordinary caution.
For many years Macadam and Telford had been devoting their ingenuity to the task of solving the secret of road-making; it was not until 1818 that the Macadam system was finally approved and adopted. Then the work of remaking the roads of the kingdom was taken in hand, and the new highways, when constructed, ushered in the brief ‘golden age’ of coaching—say 1825 to 1838, the mails having been transferred to the railways in the latter year.
Nimrod's famous essay, written in 1835, shows in convincing fashion the difference between coaching in the olden days and at its best:—
‘May we be permitted, since we have mentioned the Arabian Nights, to make a little demand on our readers' fancy, and suppose it possible that a worthy old gentleman of this said year—1742—had fallen comfortably asleep à la Dodswell, and never awoke till Monday morning in Piccadilly? “What coach, your honour?” says a ruffianly-looking fellow, much[Pg 19] like what he might have been had he lived a hundred years back. “I wish to go home to Exeter,” replies the old gentleman, mildly. “Just in time, your honour, here she comes—them there grey horses; where's your luggage?” “Don't be in a hurry,” observed the stranger; “that's a gentleman's carriage.” “It ain't! I tell you,” says the cad; “it's the Comet, and you must be as quick as lightning.” Nolens volens, the remonstrating old gentleman is shoved into the Comet, by a cad at each elbow, having been three times assured his luggage is in the hind boot, and twice three times denied having ocular demonstration of the fact.
‘However, he is now seated; and “What gentleman is going to drive us?” is his first question to his fellow-passengers. “He is no gentleman, sir,” says a person who sits opposite to him, and who happens to be a proprietor of the coach. “He has been on the Comet ever since she started, and is a very steady young man.” “Pardon my ignorance,” replies the regenerated; “from the cleanliness of his person, the neatness of his apparel, and the language he made use of, I mistook him for some enthusiastic bachelor of arts, wishing to[Pg 20] become a charioteer after the manner of the illustrious ancients.”[3] “You must have been long in foreign parts, sir,” observes the proprietor. In five minutes, or less, after the parley commenced, the wheels went round, and in another five the coach arrived at Hyde Park gate; but long before it got there, the worthy gentleman of 1742 (set down by his fellow-travellers for either a little cracked or an emigrant from the backwoods of America) exclaimed, “What! off the stones already?” “You have never been on the stones,” observes his neighbour on his right; “no stones in London now, sir.”[4]
‘In five minutes under the hour the Comet arrives at Hounslow, to the great delight of our friend, who by this time waxed hungry, not having broken[Pg 21] his fast before starting. “Just fifty-five minutes and thirty-seven seconds,” says he, “from the time we left London!—wonderful travelling, gentlemen, to be sure, but much too fast to be safe. However, thank heaven, we are arrived at a good-looking house; and now, waiter, I hope you have got breakf——” Before the last syllable, however, of the word could be pronounced, the worthy old gentleman's head struck the back of the coach by a jerk, which he could not account for (the fact was, three of the four fresh horses were bolters), and the waiter, the inn, and indeed Hounslow itself (terraeque urbesque recedunt) disappeared in the twinkling of an eye. Never did such a succession of doors, windows, and window-shutters pass so quickly in his review before—and he hoped they might never do so again. Recovering, however, a little from his surprise—“My dear sir,” said he, “you told me we were to change horses at Hounslow? Surely they are not so inhuman as to drive these poor animals another stage at this unmerciful rate!” “Change horses, sir!” says the proprietor; “why, we changed them whilst you were putting on your spectacles, and looking at[Pg 22] your watch. Only one minute allowed for it at Hounslow, and it is often done in fifty seconds by those nimble-fingered horse-keepers.” “You astonish me—but really I do not like to go so fast.” “Oh, sir! we always spring them over these six miles. It is what we call the hospital ground.” This alarming phrase is presently interpreted: it intimates that horses whose “backs are getting down instead of up in their work”—some “that won't hold an ounce down hill, or draw an ounce up”—others “that kick over the pole one day and over the bars the next”—in short, all the reprobates, styled in the road slang bo-kickers, are sent to work these six miles, because here they have nothing to do but gallop—not a pebble as big as a nutmeg on the road; and so even, that it would not disturb the equilibrium of a spirit-level.
‘The coach, however, goes faster and faster over the hospital ground, as the bo-kickers feel their legs and the collars get warm to their shoulders; and having ten outsides, the luggage of the said ten, and a few extra packages besides on the roof, she rolls rather more than is pleasant, although the centre of gravity is pretty well kept down by four not[Pg 23] slender insides, two well-laden boots, and three huge trunks in the slide. The gentleman of the last century, however, becomes alarmed—is sure the horses are running away with the coach—declares he perceives by the shadow that there is nobody on the box, and can see the reins dangling about the horses' heels. He attempts to look out of the window, but his fellow-traveller dissuades him from doing so: “You may get a shot in your eye from the wheel. Keep your head in the coach, it's all right, depend on 't. We always spring 'em over this stage.” Persuasion is useless; for the horses increase their speed and the worthy old gentleman looks out. But what does he see? Death and destruction before his eyes? No: to his surprise he finds the coachman firm at his post, and in the act of taking a pinch of snuff from the gentleman who sits beside him on the bench, his horses going at the rate of a mile in three minutes at the time. “But suppose anything should break, or a linchpin should give way and let a wheel loose?” is the next appeal to the communicative but not very consoling proprietor. “Nothing can break, sir,” is the reply; “all of the very best stuff; axletrees of the[Pg 24] best K.Q. iron, faggotted edgeways, well bedded in the timbers; and as for linchpins, we have not one about the coach. We use the best patent boxes that are manufactured. In short, sir, you are as safe in it as if you were in your bed.” “Bless me,” exclaims the old man, “what improvements! And the roads!!!” “They are at perfection, sir,” says the proprietor. “No horse walks a yard in this coach between London and Exeter—all trotting ground now.” “A little galloping ground, I fear,” whispers the senior to himself! “But who has effected all this improvement in your paving?” “An American of the name of Macadam,”[5] was the reply, “but coachmen call him the Colossus of Roads. Great things have likewise been done in cutting through hills and altering the course of roads: and it is no uncommon thing now-a-days to see four horses trotting away merrily down hill on that very ground where they formerly were seen walking up hill.”
‘“And pray, my good sir, what sort of horses may you have over the next stage?” “Oh, sir, no[Pg 25] more bo-kickers. It is hilly and severe ground, and requires cattle strong and staid. You'll see four as fine horses put to the coach at Staines as you ever saw in a nobleman's carriage in your life.” “Then we shall have no more galloping—no more springing them as you term it?” “Not quite so fast over the next ground,” replied the proprietor; “but he will make good play over some part of it: for example, when he gets three parts down a hill he lets them loose, and cheats them out of half the one they have to ascend from the bottom of it. In short, they are half-way up it before a horse touches his collar; and we must take every advantage with such a fast coach as this, and one that loads so well, or we should never keep our time. We are now to a minute; in fact the country people no longer look at the sun when they want to set their clocks—they look only to the Comet. But, depend upon it, you are quite safe; we have nothing but first-rate artists on this coach.” “Artist! artist!” grumbles the old gentleman, “we had no such term as that.”
‘“I should like to see this artist change horses at the next stage,” resumes our ancient; “for at the last it had the appearance of magic—‘Presto, Jack,[Pg 26] and begone!’” “By all means; you will be much gratified. It is done with a quickness and ease almost incredible to anyone who has only read or heard of it; not a buckle or a rein is touched twice, and still all is made secure; but use becomes second nature with us. Even in my younger days it was always half an hour's work—sometimes more. There was—‘Now, ladies and gentlemen, what would you like to take? There's plenty of time, while the horses are changing, for tea, coffee, or supper; and the coachman will wait for you—won't you, Mr. Smith?’ Then Mr. Smith himself was in no hurry; he had a lamb about his coach for one butcher in the town, and perhaps half a calf for another, a barrel of oysters for the lawyer, and a basket of game for the parson, all on his own account. In short, the best wheel of the coach was his, and he could not be otherwise than accommodating.”
‘The coach arrives at Staines, and the ancient gentleman puts his intentions into effect, though he was near being again too late; for by the time he could extract his hat from the netting that suspended it over his head, the leaders had been taken from their bars, and were walking up the yard towards[Pg 27] their stables. On perceiving a fine thorough-bred horse led toward the coach with a twitch fastened tightly to his nose, he exclaimed, “Holloa, Mr. Horse-keeper! You are going to put an unruly horse in the coach.” “What! this here 'oss?” growls the man; “the quietest hanimal alive, sir!” as he shoves him to the near side of the pole. At this moment, however, the coachman is heard to say in somewhat of an undertone, “Mind what you are about, Bob; don't let him touch the roller-bolt.” In thirty seconds more they are off—“the staid and steady team,” so styled by the proprietor of the coach. “Let 'em go! and take care of yourselves,” says the artist, so soon as he is firmly seated upon his box; and this is the way they start. The near leader rears right on end; and if the rein had not been yielded to him at the instant, he would have fallen backwards on the head of the pole. The moment the twitch was taken from the nose of the thorough-bred near-wheeler, he drew himself back to the extent of his pole-chain—his forelegs stretched out before him—and then, like a lion loosened from his toil, made a snatch at the coach that would have broken two pairs of traces of 1742. A steady and[Pg 28] good-whipped horse, however, his partner, started the coach himself, with a gentle touch of the thong, and away they went off together. But the thorough-bred was very far from being comfortable; it was in vain that the coachman tried to soothe him with his voice, or stroked him with the crop of his whip. He drew three parts of the coach, and cantered for the first mile, and when he did settle down to his trot, his snorting could be heard by the passengers, being as much as to say, “I was not born to be a slave.” In fact, as the proprietor now observed, “he had been a fair plate horse in his time, but his temper was always queer.”
‘After the first shock was over, the Conservative of the eighteenth century felt comfortable. The pace was considerably slower than it had been over the last stage, but he was unconscious of the reason for its being diminished. It was to accommodate the queer temper of the race-horse,[6] who, if he had not been humoured at starting, would never have[Pg 29] settled down to his trot, but have ruffled all the rest of the team. He was also surprised, if not pleased, at the quick rate at which they were ascending hills which, in his time, he should have been asked by the coachman to have walked up—but his pleasure was short-lived; the third hill they descended produced a return of his agony. This was what is termed on the road a long fall of ground, and the coach rather pressed upon the horses. The temper of the race-horse became exhausted: breaking into a canter, he was of little use as a wheeler, and there was then nothing for it but a gallop. The leaders only wanted the signal; and the point of the thong being thrown lightly over their backs, they were off like an arrow out of a bow: but the rocking of the coach was awful, and more particularly so to the passengers on the roof. Nevertheless, she was not in danger: the master-hand of the artist kept her in a direct line; and meeting the opposing ground, she steadied, and all was right. The newly-awakened gentleman, however, begins to grumble again. “Pray, my good sir,” says he anxiously, “do use your authority over your coachman, and insist upon his putting the drag-chain on the wheel when descending the next hill.[Pg 30]” “I have no such authority,” replies the proprietor. “It is true, we are now drawn by my horses, but I cannot interfere with the driving of them.” “But is he not your servant?” “He is, sir; but I contract to work the coach so many miles in so many hours, and he engages to drive it, and each is subject to a fine if the time be not kept on the road. On so fast a coach as this every advantage must be taken; and if we were to drag down such hills as these, we should never reach Exeter to-day.”
‘Our friend, however, will have no more of it. He quits the coach at Bagshot, congratulating himself on the safety of his limbs. Yet he takes one more peep at the change, which is done with the same despatch as before; three greys and a pie-bald replacing three chestnuts and a bay—the harness beautifully clean, and the ornaments bright as the sun. Not a word is spoken by the passengers, who merely look their admiration; but the laconic address of the coachman is not lost on the bystanders. “Put the bay mare near wheel this evening, and the stallion up to the cheek,” said he to his horse-keeper as he placed his right foot on the roller-bolt—i.e. the last step but one to the box. “How is Paddy's leg?” [Pg 33]“It's all right, sir,” replied the horse-keeper. “Let 'em go, then,” quoth the artist, “and take care of yourselves.”
‘The worthy old gentleman is now shown into a room, and after warming his hands at the fire, rings the bell for the waiter. A well-dressed person appears, whom he of course takes for the landlord. “Pray, sir,” says he, “have you any slow coach down this road to-day?” “Why, yes, sir,” replies John; “we shall have the Regulator down in an hour.” “Just right,” said our friend; “it will enable me to break my fast, which I have not done to-day.” “Oh, sir,” observes John, “these here fast drags be the ruin of us.” 'Tis all hurry scurry, and no gentleman has time to have nothing on the road. “What will you take, sir? Mutton-chops, veal-cutlets, beef-steaks, or a fowl (to kill?)”
‘At the appointed time, the Regulator appears at the door. It is a strong, well-built drag, painted what is called chocolate colour, bedaubed all over with gilt letters—a bull's head on the doors, a Saracen's head on the hind boot, and drawn by four strapping horses; but it wants the neatness of the other. The passengers may be, by a shade[Pg 34] or two, of a lower order than those who had gone forward with the Comet; nor, perhaps, is the coachman quite so refined as the one we have just taken leave of. He has not the neat white hat, the clean doeskin gloves, the well-cut trousers, and dapper frock; but still his appearance is respectable, and perhaps, in the eyes of many, more in character with his calling. Neither has he the agility of the artist on the Comet, for he is nearly double his size; but he is a strong powerful man, and might be called a pattern card of the heavy coachman of the present day—in other words, of a man who drives a coach which carries sixteen passengers instead of fourteen, and is rated at eight miles an hour instead of ten. “What room in the Regulator?” says our friend to the waiter, as he comes to announce its arrival. “Full inside, sir, and in front; but you'll have the gammon board all to yourself, and your luggage is in the hind boot.” “Gammon board! Pray, what's that? Do you not mean the basket?”[7] “Oh no, sir,” says John, smiling; “no such thing on the road now. It is the hind-dickey, as some call it; where you'll[Pg 35] be as comfortable as possible, and can sit with your back or your face to the coach, or both, if you like.” “Ah, ah,” continues the old gentleman; “something new again, I presume.” However, the mystery is cleared up; the ladder is reared to the hind wheel and the gentleman safely seated on the gammon board.
‘Before ascending to his place our friend has cast his eye on the team that is about to convey him to Hartford Bridge, the next stage on the great western road, and he perceives it to be of a different stamp from that which he had seen taken from the coach at Bagshot. It consisted of four moderate-sized horses, full of power, and still fuller of condition, but with a fair sprinkling of blood; in short, the eye of a judge would have discovered something about them not very unlike galloping. “All right!” cried the guard, taking his key-bugle[8] in his hand; and they proceeded up the village, at a steady pace, to the tune of “Scots wha hae wi' Wallace bled,” and continued at that pace for the first five miles. “I am landed,” thinks our friend to himself. Unluckily, however,[Pg 36] for the humane and cautious old gentleman, even the Regulator was about to show tricks. Although what now is called a slow coach, she is timed at eight miles in the hour through a great extent of country, and must, of course, make play where she can, being strongly opposed by hills lower down the country, trifling as these hills are, no doubt, to what they once were. The Regulator, moreover, loads well, not only with passengers, but with luggage; and the last five miles of this stage, called the Bridge Flat, have the reputation of being the best five miles for a coach to be found at this time in England. The ground is firm; the surface undulating, and therefore favourable to draught; always dry, not a shrub being near it; nor is there a stone upon it much larger than a marble. These advantages, then, are not lost to the Regulator, or made use of without sore discomposure to the solitary tenant of her gammon board.
‘Any one that has looked into books will very readily account for the lateral motion, or rocking, as it is termed, of a coach, being greatest at the greatest distance from the horses (as the tail of a paper kite is in motion whilst the body remains[Pg 37] at rest); and more especially when laden as this coach was—the greater part of the weight being forward. The situation of our friend, then, was once more deplorable. The Regulator takes but twenty-three minutes for these celebrated five miles, which cannot be done without “springing the cattle” now and then; and it was in one of the very best of their gallops of that day, that they were met by the coachman of the Comet, who was returning with his up-coach. When coming out of rival yards, coachmen never fail to cast an eye to the loading of their opponents on the road, and now that of the natty artist of the Comet experienced a high treat. He had a full view of his quondam passenger, and thus described his situation.
‘He was seated with his back to the horses—his teeth set grim as death—his eyes cast down towards the ground, thinking the less he saw of his danger the better. There was what is called a top-heavy load—perhaps a ton of luggage on the roof, and it may be not quite in obedience to the Act of Parliament standard.[9] There were also two[Pg 38] horses at wheel, whose strides were of rather unequal length, and this operated powerfully on the coach. In short, the lurches of the Regulator were awful at the moment of the Comet meeting her. A tyro in mechanics would have exclaimed, “The centre of gravity must be lost, the centrifugal force will have the better of it—over she must go!”
‘The centre of gravity having been preserved, the coach arrived safe at Hartford Bridge; but the old gentleman has again had enough of it. “I will walk into Devonshire,” said he, as he descended from his perilous exaltation. “What did that rascally waiter mean by telling me this was a slow coach? and moreover, look at the luggage on the roof!” “Only regulation height, sir,” says the coachman; “we aren't allowed to have it an inch higher; sorry we can't please you, sir, but we will try and make room for you in front.” “Fronti nulla fides,” mutters the worthy to himself, as he walks tremblingly into the house—adding, “I shall not give this fellow a shilling; he is dangerous.”
‘The Regulator being off, the waiter is again applied to. [Pg 39]“What do you charge per mile posting?” “One and sixpence, sir.” “Bless me! just double! Let me see—two hundred miles, at two shillings per mile, postboys, turnpikes, etc., £20. This will never do. Have you no coach that does not carry luggage on the top?” “Oh yes, sir,” replies the waiter, “we shall have one to-night that is not allowed to carry a band-box on the roof.”[10] “That's the coach for me; pray what do you call it?” “The Quicksilver mail, sir; one of the best out of London—Jack White and Tom Brown, picked coachmen, over this ground—Jack White down to-night.” “Guarded and lighted?” “Both, sir; blunderbuss and pistols in the sword-case;[11] a lamp[Pg 40] each side the coach, and one under the foot-board—see to pick up a pin the darkest night of the year.” “Very fast?” “Oh no, sir, just keeps time, and that's all.” “That's the coach for me, then,” repeats our hero; “and I am sure I shall feel at my ease in it. I suppose it is what used to be called the Old Mercury.”
‘Unfortunately, the Devonport (commonly called the Quicksilver) mail is half a mile in the hour faster than most in England, and is, indeed, one of the miracles of the road. Let us then picture to ourselves our anti-reformer snugly seated in this mail, on a pitch-dark night in November. It is true she has no luggage on the roof, nor much to incommode her elsewhere; but she is a mile in the hour faster than the Comet, at least three miles quicker than the Regulator; and she performs more than half her journey by lamplight. It is needless to say, then, our senior soon finds out his mistake; but there is no remedy at hand, for it is the dead of the night, and all the inns are shut up. He must proceed, or be left behind in a stable. The climax of his misfortunes then approaches.
‘Nature being exhausted, sleep comes to his aid,[Pg 41] and he awakes on a stage which is called the fastest on the journey—four miles of ground, and twelve minutes the time! The old gentleman starts from his seat, having dreamed the horses were running away with the coach, and so, no doubt, they might be. He is determined to convince himself of the fact, though the passengers assure him “all's right.” “Don't put your head out of the window,” says one of them, “you will lose your hat to a certainty”: but advice is seldom listened to by a terrified man, and next moment a stentorian voice is heard, crying, “Stop, coachman, stop—I have lost my hat and wig!” The coachman hears him not—and in another second the broad wheels of a road waggon have for ever demolished the lost headgear.’
That was the Road at its best: the poetic side we have in mind when we speak of the good old days of coaching. The following passages refer equally to the ‘golden age’; their very baldness has an eloquence of its own. It is true that the winter of 1836-37 is conspicuous in history for the exceptionally heavy snowfall; but as Nimrod has shown coaching at its best, there is no injustice in[Pg 42] presenting these glimpses of coach travel at its worst:—
‘Tabor, guard of the Devonport, who left London with the mail on Sunday and returned on Wednesday, reports that a mile and a half from Amesbury they got completely blocked. The leaders dropped down, but rose again; the near wheel-horse fell and could not be got up. The coachman procured a pair of post horses, but they could only get the wheel-horse out of the snow; it was impossible to get him on his legs. Four more post horses and four waggon horses were requisitioned, and with their assistance the mail was extricated by daylight. Then they travelled with the six post horses across the Downs. They were again blocked near Mere. About a hundred men were at this time employed a little distance off in digging out the Subscription and Defiance coaches. After being extricated by some labourers they resumed their progress from Mere with four fresh mail-horses and two posters. Between Ilchester and Ilminster the post horse leaders fell in a snow drift, and were run upon by the mail leaders.’ (Bell's Life, January 1837).
‘The Estafette coach from Manchester on Sunday[Pg 43] morning did not reach London until Tuesday night, having been dug out of the snow twelve times. It was the first coach from Manchester of the same day that arrived in town. The guard attributes his success to the exertions of four sailors, outside passengers, who lent a hand at every casualty.’
‘A gentleman who left Sheffield by the Hope coach of Sunday week reports that the coach did not complete its journey until Saturday afternoon. Between Nottingham and Mansfield, close to the Forest, they came upon three coaches blocked in the snow, which was lying 9 feet deep. The Hope left Mansfield with eight horses and was driven into Nottingham with ten. They picked up a poor boy nearly perished with cold. The boy was got by a gentleman jumping down while the coach was in motion, for the coachman declared that if he came to a dead stop he would not be able to get the wheels in motion again.’ (Bell's Life, 8th January 1837).
Highway robbery was still practised at this time, but the armed horseman with crape mask and pistols had gone out of fashion, and thefts were accomplished by craft.[Pg 44] ‘The Stirling mail has been robbed of notes to the value of £13,000 in the following manner:—A man took his seat at Stirling as an outside passenger. The mail was followed closely from Stirling by a gig containing two men. When the mail arrived at Kirkliston the guard stopped to take out the customary bags to leave there. The gig also stopped there, and the two men in it went into the house. The guard had left the mail box open, in which the parcels were, and the outside passenger easily abstracted the one containing the notes. He then left the coach. The gig with the two men took the Queensferry Road. The parcels were not missed until the mail reached Edinburgh. On the Queensferry Road the two men were joined by their accomplice, the outside passenger. They left the gig and took a post chaise for Edinburgh. They discharged the chaise before entering the city and gave the post-boy £3.’ (Bell's Life, 2nd January 1825).
Great improvements in all matters connected with coaching were made during the first two decades of the nineteenth century: these were due to the rage for driving that prevailed about this time.[Pg 45] The King was deeply interested in coaching, was himself no mean whip, and he set the fashion. It did not last very long. Nimrod, writing in 1835, remarks that about 1825 ‘thirty to forty four-in-hand equipages were constantly to be seen about town: one is stared at now.’
The driving clubs held ‘meets’ in George the Third's time much as they do at present, but the vehicles used were ‘barouche landaus,’ and the drive taken was much longer than that in vogue to-day. Bedfont beyond Hounslow, and Windsor were favourite places whither the coaches—‘barouche landaus’—drove in procession to dine. Very particular attention was paid to dress. This was the costume in which members of the Whip Club, founded in 1808 as a rival to the Benson, mounted their boxes on 6th June 1808, in Park Lane, to drive to Harrow:—
‘A light, drab-colour cloth coat made full, single breast with three tier of pockets, the skirt reaching to the ancles; a mother of pearl button the size of a crown piece; waistcoat blue and yellow stripe, each stripe an inch in depth; small clothes corded silk plush made to button over the calf of[Pg 46] the leg, with sixteen strings and rosettes to each knee. The boots very short and finished with very broad straps which hang over the tops and down to the ancle. A hat three inches and a half deep in the crown only, and the same depth in the brim exactly. Each wore a large bouquet at the breast, thus resembling the coachmen of our nobility who, on His Majesty's birthday, appear in that respect so peculiarly distinguished.’[12]
Grimaldi the clown, then at the zenith of his fame, burlesqued this get-up so mercilessly that a less conspicuous garb was adopted.
The fifteen barouche landaus which turned out on this occasion, driven by ‘men of known skill in the science of charioteering,’ were well calculated to set off the somewhat conspicuous attire of the members: they were ‘Yellow-bodied carriages with whip springs and dickey boxes; cattle of a [Pg 49]bright bay colour with silver plate ornaments on the harness and rosettes to the ears.’
The meets of the driving clubs appear to have roused a spirit of ribaldry in unregenerate youth. One day in March 1809 a young Etonian made his appearance in a low phaeton with a four-in-hand of donkeys, with which he brought up the rear of the procession as it drove round Grosvenor and Berkeley Squares.
The Driving Club was the Benson, which had been founded in 1807. Sir Henry Peyton was the last survivor of the ‘noble, honourable, and respectable’ drivers who composed it. Thackeray described him in the last of his papers on The Four Georges as he appeared driving the ‘one solitary four-in-hand’ to be seen in the London parks. He was then (1851) very old, and attracted attention as much by his dress, which was of the fashion of 1825, as by his then unique turn-out.
The Benson Club came to an end in 1853. The Whip Club, otherwise the Four Horse Club, came to an end in 1838. The Defiance Club, for members who had been ‘lately permitted to retire’ from the other two, was projected in 1809, but[Pg 50] it does not appear to have come to anything. The Richmond Drag Club was founded in 1838, but it did not survive for many years; the members to the number of fifteen or sixteen used to meet at Lord Chesterfield's house. These were the principal clubs.
Some of the amateur whips of a century ago were addicted to coach matches. Here is the account of such a race from the Sporting Magazine of 1802:—
‘Mail Coach Match.—On Thursday, May 20th, the London Mail, horsed by Mr. Laud, of the New London Inn, Exeter, with four beautiful grey horses, and driven by Mr. Cave Browne, of the Inniskilling Dragoons, started (at the sound of the bugle) from St. Sydwell's for a bet of Five Hundred Guineas against the Plymouth Mail, horsed by Mr. Phillipps, of the Hotel, with four capital blacks, and driven by Mr. Chichester, of Arlington House, which got the mail first to the Post Office in Honiton. The bet was won easy by Mr. Browne. A very great concourse of people assembled on this occasion.’
In 1811 Mr. George Seward undertook to drive a four-in-hand fifteen miles in fifty minutes. He[Pg 51] selected the road from Hyde Park Corner to Staines, and started at six in the morning. He failed to accomplish his undertaking, but only by three minutes twenty seconds.
There was more originality about the competition arranged in May 1805 between Mr. Charles Buxton, inventor of the bit known by his name and one of the founders of the Whip Club, and a horse-dealer:—
‘One of our most celebrated whips Charles Buxton, Esq., has concluded a bet of 500 Guineas with Mr. Thomas Hall, the dealer in horses. The object of the wager is to decide which of the two is the best driver of four unruly horses. The wager is to be decided by two friends of the parties, who are to pick out eight horses from Spencer's, Marsden's, and White's. Lords Barrymore and Cranley are chosen as the umpires. The horses selected are only to be those which have not been broken in. The friend of each charioteer is to pick the horses alternately until the number agreed on is selected. The parties are then to mount the box and proceed to decide the wager. The bettings already are said to be considerable. Neither the scene of action nor the day when the[Pg 52] contest is to take place are yet determined on. Mr. Buxton is said to be so certain of success that he has offered to double the bet.’
Though the law of 1820 made racing a criminal offence, the practice was one which could not be wholly put down, and on May-day the law was set at naught by popular consent, rival coaches on that day racing one another without disguise: the May-day race became an institution of the road, and seems to have been winked at by the authorities. Some wonderful records were made in these contests on the macadam. Thus, on 1st May 1830, the Independent Tally Ho ran from London to Birmingham, 109 miles, in 7 hours 39 minutes. It was not rare for a coach to perform its journey at a rate of fifteen miles an hour on May-day. We may compare this with the time made in the Leicester-Nottingham race of 1808 mentioned on page 17.
It is seventy years since the carriage of the mails was transferred from coach to railway train, and there are yet living men who can remember the last journeys of the mail-coaches, some carrying little flags at half-mast, some displaying a miniature[Pg 53] coffin, emblematic of the death of a great institution. Yet the mail-coach survived until a much later date in some districts, where the line was slow to penetrate. Mr. S. A. Kinglake, in Baily's Magazine of 1906, gave an account of the Oxford and Cheltenham coach, which only began to carry the mails in 1848, and made its last trip in 1862, when the opening of a new branch line ousted this lingerer on the roads.
The interregnum between the last of the old coaches and the modern era was not a very long one: indeed, taking the country as a whole, and accepting the coach as subsidiary to the railway, the old and the new overlap. Modern road coaching dates from the later 'sixties, when the late Duke of Beaufort, with some others, started the Brighton coach. This was the first of several private ventures of the same kind: their primary object was to enable the owners to enjoy the pleasure of driving a team, and the financial side of the business was not much regarded. The subscription coach was a later development, with the same object in view, pleasure rather than money-making, and the large majority of the coaches which run from London to Brighton,[Pg 54] St. Albans, Guildford, and other places within an easy day's journey are maintained by small syndicates of subscribers, who take turns on the box. American visitors patronise these vehicles extensively, and no doubt to their support may be traced Mr. Vanderbilt's venture on the Brighton road.
The modern coach travels quite as fast as its predecessor when required: as witness James Selby's famous performance on 13th July 1888. He left the White Horse Cellar at 10 A.M.; arrived at the Old Ship, Brighton, 1.56 P.M.; turned and reached town at 5.50; the journey out and home again being accomplished in 7 hours 50 minutes; part of the way between Earlswood and Horley he travelled at a rate of twenty miles an hour.

Modern Coaching: In the Show Ring
Painting by G. D. Armour.

Nor are modern horse-keepers less ‘nimble fingered’ than those of whom Nimrod wrote. At the International Horse Show of 1908 Miss Brocklebank's grooms won the Hon. Adam Beck's prize for ‘Best coach and appointments and quickest change of teams’: the change was accomplished in forty-eight seconds. During James Selby's Brighton drive horses were changed at Streatham in forty-seven seconds.[Pg 55] The road coachmen of the present day do not aim at lightning changes of team: the work is done in leisurely fashion, and passengers enjoy the opportunity afforded them to get down for a few minutes.
The Four-in-Hand Club, founded in 1856, for many years used to meet in the Park at quarter to five in the afternoon, but the hour was changed to half-past twelve in order to avoid the inconvenience inseparable from meeting at the time when carriages are most numerous.
The Coaching Club was founded in 1870, and held its first meet at the Marble Arch in June the following year.
SONG OF THE B.D.C.[13]
[1] Robert Poynter drove the Lewes stage for thirty years without an accident.
[2] 30 Geo. III., c. 36.
[3] The old gentleman's conjecture was not far wrong. At this time, 1835, it is true fewer men of good birth occupied the box than had been the case a few years before—if we rightly interpret Nimrod's own remarks on the point. When the box had been set on springs or made an integral part of the coach-body, when the roads had been made worthy of the name and fast work the rule, coach-driving became popular among men of social position. Some drove for pleasure, horsing the coaches themselves, others took up driving as a profession and made good incomes thereby. These gentlemen coachmen did much to raise the standard of conduct among the professionals of humble origin. Lord Algernon St. Maur (Driving, Badminton Library) says that Mr. Stevenson, who was driving the Brighton Age in 1830, was ‘the great reformer who set a good example as regards punctuality, neatness, and sobriety.’
[4] Until Macadam was adopted the streets in London were cobbled or paved.
[5] John Loudon Macadam was a Scotsman by birth. In 1770, when fourteen years old, he was sent to the care of an uncle in New York, whence he did not return till he was twenty-six years of age; hence the mistake in describing him as ‘an American.’
[6] It was not unusual for retired race-horses to end their days ‘on the road.’ A notable instance is that of Mendoza by Javelin. Mendoza won eight races at Newmarket in his three seasons on the turf, 1791-2-3; then the Duke of Leeds bought him as a hunter; and after a few seasons with hounds he made one of a team in the Catterick and Greta Bridge mail-coach. Mendoza was still at work in 1807, but had become blind.
[7] The early coaches were equipped with a huge basket slung over the hind axle wherein passengers were carried at lower fares.
[8] Only the mail-coach guard carried a horn; stage-coach guards used the key-bugle, and some were very clever performers on it.
[9] 50 Geo. III., c. 48 came into operation in 1810. This enacted that on a four-horse coach baggage might be piled to a height of 2 feet. To encourage low-hung coaches this law allowed baggage to be piled to a height of 10 ft. 9 in. from the ground.
[10] The conveyance of ‘trunks, parcels, and other packages’ on the roof of a mail-coach was prohibited in the Postmaster-General's circular to mail contractors of 29th June, 1807. As the mails increased it became impossible to enforce this regulation, and the bags were carried wherever they could be stowed. ‘The Druid’ says of the Edinburgh mail-coach: ‘The heaviest night as regards correspondence was when the American mail had come in. On those occasions the bags have been known to weigh above 16 cwt. They were contained in sacks seven feet long and were laid in three tiers across the top, so high that no guard unless he were a Chang in stature could look over them ... and the waist (the seat behind the coachman) and the hind boot were filled as well.’
[11] It must be remembered that the old gentleman speaks by the light of his knowledge of nearly a century earlier, when highway robbery was very common, and it was not usual for coaches to run at night. At the period to which Nimrod refers highwaymen had not entirely disappeared from the roads (William Rea was hanged for this offence, 4th July, 1828), and not every stage-coach carried a guard. Mail-coaches, all of which carried guards, were, of course, unknown to Nimrod's old gentleman.
[12] This refers to the ‘mail-coach parade,’ which was first held in 1799 and for the last time in 1835. The coaches, to the number of about twenty-five, were either new or newly painted with the Royal Arms on the door, the stars of each of the four Orders of Knighthood on the upper panel, and the name of the town whither the coach ran on the small panel over each door. Coachmen and guards wore new uniforms and gentlemen used to lend their best teams—often also their coachmen, as appears from the passage quoted. A horseman rode behind each coach to make the procession longer. The ‘meet’ took place in Lincoln's Inn Fields and the coaches drove to St. James's, there turning to come back to the General Post Office, then in Lombard Street.
[13] Benson Driving Club.
Tandem
Painting by G. D. Armour.

It is said, but I must confess failure to trace authority for the statement, that tandem driving was invented as a convenient and sporting method of taking the hunter to the meet. History has not handed down to fame the name of the man who first hit upon the idea of driving tandem; it was in vogue over a century ago, and at Cambridge ranked as a grave offence: witness the following edict dated 10th March 1807:—
‘We, the Vice-Chancellor and Heads of Colleges, do hereby order and decree that if any person or persons in statu pupillari shall be found driving any tandem and shall be duly convicted thereof before the Vice-Chancellor, such person or persons so offending shall for the first offence be suspended from taking his degree for one whole year, or be rusticated, according to the circumstances of the case; and for the second offence be liable to such further punishment as it may appear to deserve, or be expelled the university.’
Extravagantly high gigs were much in favour among the ‘bloods’ of the day, and these were[Pg 59] often used for tandem driving, a purpose for which they were by no means unsuitable, always provided the road was fairly level.
As a matter of course, when tandems became numerous and drivers clever in handling them, races against time came into fashion. Matches on the road, whether trotting in saddle or driving, were usually ‘against time’ for obvious reasons. On April 14th 1819 the famous whip, Mr. Buxton, backed himself to drive tandem without letting his horses break their trot, from Hounslow to Hare Hatch, distance twenty-four miles, in two hours. His horses, however, were not well matched, and ‘broke’ before they had gone six miles. As breaking involved the penalty of turning the equipage round and starting afresh, and breaks were frequent, Mr. Buxton occupied over an hour in going ten miles and gave up, forfeiting the hundred guineas he had staked on the task.
On 19th May 1824 a match was thus recorded in the Sporting Magazine:—
‘Captain Swann undertook a tandem match from Ilford, seven miles over a part of Epping Forest. He engaged to drive 12 miles at a trot and to[Pg 60] back his wheels if he broke into a gallop. This happened only once in the seventh mile, which he nevertheless completed in 33 minutes. On his return the pacing of the horses was a picture. The match was won fairly with two minutes and six seconds to spare.’
A Mr. Houlston in the same year drove his tandem twelve miles on the Winchester Road in one minute thirty-nine seconds under the hour allowed. By this time tandem drivers had come to the reasonable conclusion that the turning penalty (proper enough in trotting matches, whether in shafts or saddle) was excessive for their sport, and ‘backing’ had been substituted therefor. Any one who has had occasion to turn a tandem on the road without assistance will admit that the abolition was wise.
Long journeys against time were sometimes undertaken. In 1824
‘Captain Bethel Ramsden undertook to drive tandem from Theale to London, 43 miles, in 3 hours and 40 minutes. The start took place at four o'clock in the morning, and in the first hour the captain did 12½ miles to between Twyford and Hare Hatch. He did in the next hour 12 miles[Pg 61] and upwards, and got the horses' mouths cleaned at Slough. He had 5½ miles to do in the last forty minutes, and performed it easily with eleven minutes to spare.’
The cult of the trotting horse stood high in those days when so much travelling was done in the saddle: there are innumerable records of trotters doing their fifteen and sixteen miles on the road within the hour, sometimes under very heavy weights. Mr. Charles Herbert's horse, in 1791, trotted 17 miles in 58 minutes 40 seconds on the Highgate Road, starting from St. Giles' Church. The road is by no means a level one, and the only advantage the horse had was the hour selected—between six and seven in the morning, when the traffic was not heavy.
A famous whip of the 'thirties was Mr. Burke of Hereford—he was also an amateur pugilist of renown, but that does not concern us here. In June 1839 he made his thirty-fifth trotting match, whereby he undertook to drive tandem forty-five miles in three hours. The course was from the Staines end of Sinebury Common to the fifth milestone towards Hampton: he did it with four and a half minutes[Pg 62] to spare. The horses used in this match were both extraordinary trotters: the wheeler, Tommy, had covered 20 miles in 1 hour 18 minutes two months earlier, and the leader, Gustavus, twenty-four years old, had done his 20 miles in 1 hour 14 minutes.
Though not a tandem performance in the strict sense of the term, Mr. Thanes' feat on 12th July 1819 is worth mention. He undertook 'to drive three horses in a gig, tandem fashion, eleven miles within the hour on the trot, and to turn if either horse broke.' Fortunately none of the three did break, and he did the eleven miles, on the road near Maidenhead, with three minutes to spare.
Tandem driving seems to have gone out of fashion to a certain extent about 1840, though some young men ‘still delighted in it.’ The re-establishment of the Tandem Club, soon after the close of the Crimean War, marked a revival which made itself felt at Cambridge; for on 22nd February 1866 the Senate passed another edict, this time forbidding livery-stable keepers to let out on hire tandems or four-in-hands to undergraduates. This was confirmed in 1870.
The illustrations which were plates in the book have been moved near to the text they illustrate.
Footnotes in the Coaching chapter have been moved to the end of the chapter.
This book contains inconsistent hyphenations. No spellings have been changed, but apparent printers' errors have been corrected.
Changes that have been made are:
***END OF THE PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK COACHING DAYS & WAYS***
******* This file should be named 44864-h.txt or 44864-h.zip *******
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/4/4/8/6/44864
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is subject to the trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work (or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at www.gutenberg.org/license.
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property (trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary, compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying, performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided that
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at www.gutenberg.org
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit 501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S. Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations ($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm, including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.