
Project Gutenberg's Florida Caverns State Park, by Robert O. Vernon
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: Florida Caverns State Park
Marianna, Florida
Author: Robert O. Vernon
Release Date: July 2, 2014 [EBook #46171]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK FLORIDA CAVERNS STATE PARK ***
Produced by Stephen Hutcheson and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net


The stone administration building, which has been erected near the entrance to the caverns, was built by hand from the solid rock foundation to the hand-riven cypress shake roof. The walls are built of beautifully weathered native limestone and the shelter roof is supported by hand-hewn timbers prepared on the ground. Parties, who tour the caverns, join guides here and return after the tour.

Here we behold most wondrous sights
No mortal understands,
Of stalactites and stalagmites,
A house not made with hands.
Here Nature set to work her hands
In ages long since gone,
That man might quit his work on lands
To see and ponder on.
What means these fluted columns tall,—
These pendants from the dome?
These sculptured figures large and small,
Excelling Greece and Rome?
This drapery striped with Nature’s hues,
In regular spaces wrought?
These scenes man’s pride at once subdues—
They are beyond his thought.
The brute would look and turn away
To seek his fill of food;
’Tis ours to seek while here we stay,
The Great Creative Good.
The Architect within whose mind
The wonders of the sea,
The land, the sky, and all their kind,
Has wrought for you and me.
That we may look upon His deeds
And make our own expand,
For we alone best serve all needs
As tools within His hand.
—Charles Cottingham
Marianna, Florida
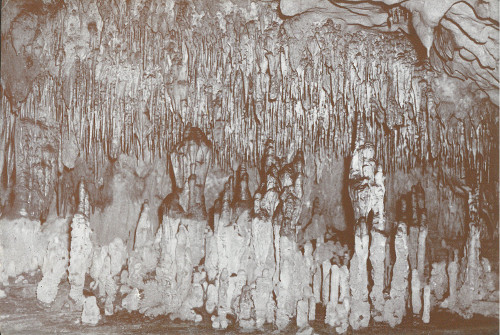
The stalagmite on the right is almost joined with a stalactite. If it does, it will make a column. The grape-like clusters in the upper foreground result when the flow of water is so slow that all of it evaporates from the ceilings and deposits its mineral load there.
By Robert O. Vernon
Assistant Director, Florida Geological Survey
Florida is truly a child of the sea, since all the rocks composing its land were formed directly on the ocean bottoms or by streams emptying along the shores. From the record of these rocks we know that Florida has been alternately above and below the sea many times in the geologic past. In fact, the rocks visible in the park area at Florida Caverns, near Marianna, Florida, and in the caves were formed from the hard shells of animals that lived in one of these seas. As the animals died, their shells accumulated on the sea bottoms, where they were covered by other shells and hardened into lime rock.
These shells, called “fossils” by the geologist, are remains representing cemeteries of the past. Along most of our coastal areas and sea bottoms these shells are accumulating and forming limestone today. Such limestone has formed also in the areas many miles removed from the present seas, as in Iowa and other middle western states, telling us where seas have been in the past.

As visitors explore the well-lighted trails and passageways, they notice the icicle-like formations that hang from the ceilings and the heavier ones that project from the floor. They study the columns that seem to help support the rock above and the small passages that extend in many directions. They notice sea shells imbedded in walls and ceilings.
How do we know that these limestones were formed in the sea? The next time you go through the caves at Florida Caverns look closely at the walls and you will be able to find the shells of Scollops and other clams. These animals lived only in shallow seas. The most common shell that you will notice will be many small coiled flat shells about the size of barley seed and flat thin disks about the size of dimes and quarters. The animals that formed these shells are known as Foraminifera and have the fancy names of Operculinoides and Lepidocyclina. They are one celled animals (our most primitive) and are related to some of the parasites that cause disease. These particular animals are extinct and are known only from these rocks. From their association with other shells they are known to have lived in shallow salt-water seas, and by means of them the geologist is able to recognize this particular limestone, even when it has been taken from a well drilled many feet below the ground surface, for these small shells are recognizable even when the limestone has been broken into fine fragments.
The limestone in which the caves of Florida Caverns were carved is known from geologic studies made throughout the state to have been raised from the sea by land movements after being formed and to have been extensively eroded, following which it was again submerged under the sea and other limestones deposited over the eroded surface. These limestones were subsequently raised out of the sea to be eroded. Over this second eroded surface a delta deposit of sand, clay and gravel was formed by streams that emptied into the Gulf of Mexico.
The limestone that you will see in the caves is known as the Ocala limestone, named from deposits near Ocala, Florida. In the region about the Florida Caverns, limestones named the Suwannee limestone and the Marianna limestone overlie the Ocala limestone. These limestones were named for deposits recognized along the Suwannee river and at Marianna, Florida. The sand, clay and gravel overlying all of these limestones are not named but are believed to be the same age as deposits of the geologic period popularly known as the “ice age.”
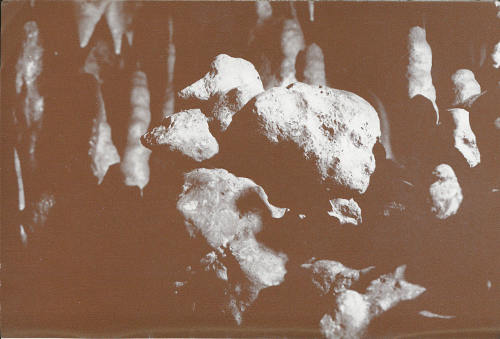
The “duck” results from irregular resistance of the limestone to solution by ground water. These nodular masses were more resistant and the less-resistant, usually softer limestone has been removed from about them, leaving the form resembling a duck. Several stalagmites are in the background. These are younger than the “duck.”
Since emerging from the sea for the last time, this part of Florida about the state park area has been undergoing changes constantly. The rocks have been continuously attacked by elements of the weather, and disintegrated where exposed. Running streams carry away much of these products of weathering, but the work of water under the ground is the major factor in the creation of these caves and the deposits in them. This underground water, running through the pores in the limestone, has been and is now wearing away portions of the land. These water channels are isolated along fractures, bedding planes and other structural weaknesses, or along poorly consolidated rock. The water dissolves the limestone and carries it out into surface streams and on to the sea, and as this material is carried away the rock, through which the water flowed to the surface, is being worn away an equal amount. The amount of this material being carried away is illustrated at Silver Springs, one of our larger springs, where each day about 450 tons of rock is carried away dissolved in water. When it is realized that this is only one of thousands of springs in Florida, you can readily see what a large amount of rock is being dissolved from beneath the ground and just how cavernous the rock must be.
All forms of wildlife are protected in Florida’s State Parks. Hunting, trapping, or shooting are not permitted. These State Parks belong to you. Help protect them.
For further information on specific parks and historic memorials write: Director, Florida Board of Parks and Historic Memorials, Tallahassee, Florida.
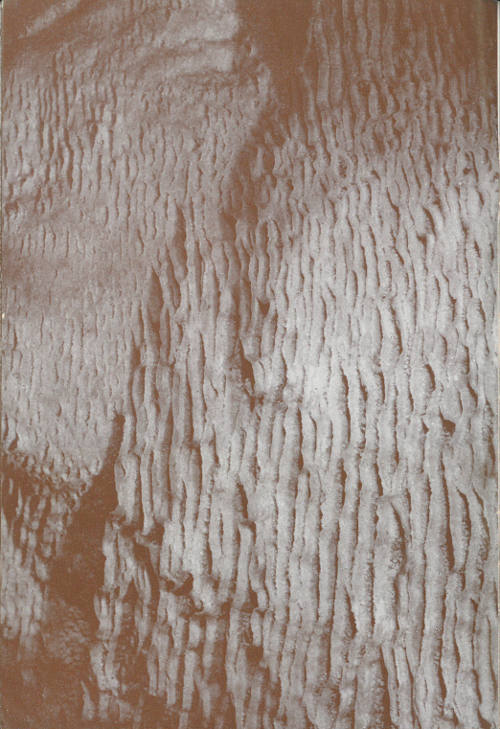

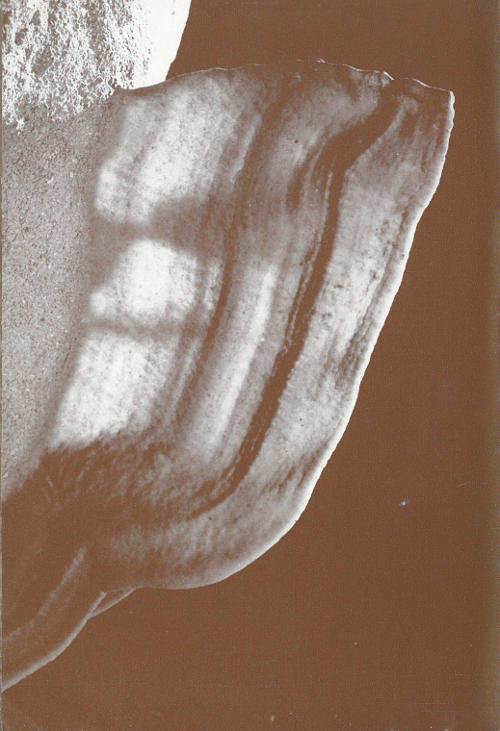
Ground water cascading down a gentle limestone face was ponded irregularly and the evaporation of the water along the outer edges formed small terraces.
The rocks in which the caves of the Florida Caverns State Park were formed are limestone. This rock is made of the mineral calcite, calcium carbonate, and it is soluble in pure water under conditions of favorable structure, a continuous supply of moving water and time. However, in the water of Florida this limestone is readily dissolved, because the humid climate and prolific vegetation contribute organic and mineral acids to water and make it a highly potent solvent that is capable of dissolving large amounts of this rock.
Limestone is as a rule jointed vertically and bedded horizontally. Openings along these joints and beds provide easy avenues of travel for water. The ultimate source of all of Florida’s ground water is from the rain and precipitates from the air. As this rain water falls through the air it becomes charged with carbon dioxide gas which combines with water to form carbonic acid. On the ground humic acids from rotting vegetation is added. These are the common natural solvents of limestone. A good portion of this acid charged water soaks into the ground, and as it descends through lime rock small portions of the rock are dissolved. However, relatively little solution occurs until sufficient water enters the rock to fill completely all the available pores. In this portion of the rock, saturated with water and bathed with weak acids, solution is most active. Because of the pressure of water entering the rock, ground water tends to move horizontally along bedding planes which offer the easiest exit. Thus, cave systems generally are developed horizontally and one system may lie over another and they may be connected by vertical tubes and rooms.

Weird vistas and eerie silhouettes meet the eyes of visitors who explore the amazing networks of trails in Florida Caverns. Droplets of mineral water, dripping through the ages, formed these underground caves into a natural, but highly artistic wonderland.
Any rain water entering the rock from the surface makes its way downward to fill completely all the pores of the rock at some depth. At it moves downward and then into the saturated rock through pores and open spaces it acts as a slow solvent to increase the size of the openings and to connect them to form a continuous system of channels through which streams filling the cavities may run.
As large caverns are formed, solution cavities of irregular shape are gradually cut out and enlarged. Some of these may be expanded to a point near the surface where surface deposits (largely sand in Florida) will collapse into the cavern and a sink is formed. The larger part of Florida’s natural lakes, sinks, depressions and ponds are the result of solution of the underlying limestone. These features range from small pits a few feet in diameter to large depressions several miles broad. Many are perfectly round, others are highly irregular. Some are cone-shaped with rocky bottoms, some have broadly developed flat bottoms and are known as prairies. Still others are vertical tubes, only a few inches in diameter in some cases, that extend as much as one hundred feet down into the limestones. These are “natural wells.”
Florida’s State Parks include miles of white sand beaches, fine streams, beautiful springs, excellent fishing waters, floral displays, wooded ravines and outstanding recreational areas. It is the Florida in which the Indians hunted, fished and lived in original surroundings of great natural charm and wildlife profusion ... where yet remains the memory and imprint of Spanish conquistadores, French crusaders and Anglo-Saxon colonizers. Phenomena such as disappearing rivers, vanishing lakes, historic shrines, virgin country, strange subterranean landscapes are all to be seen inside the parks.
“Fresh crisp bacon” formed by water flowing originally from a crack or elongate hole and cascading down the face of the limestone. The deposit formed as a small ridge that then acted as the course of subsequent water which added additional deposits. The dark bands contain some impurity to give a color to the ordinarily white calcite.
If these caves, we see in the Florida Caverns Park area, were formed under water, how is it possible to walk through them today? This is an obvious question which requires an answer. If rocks formed under marine waters are exposed on the land surface today it is obvious that the land has been raised out of the sea, or the sea has lowered. From geologic evidence it is known that Florida has been rising since late geologic time. This elevation is believed to be caused by downwarping at the mouth of the Mississippi River, where many thousands of box car loads of sediment are dumped each day, accompanied by adjustments in the earth’s crust and the elevation of land areas surrounding the delta of the Mississippi River.
Then there is a second cause by which these caves are made dry. Everyone has heard that ice caps the North and South poles of the earth, but few people realize that, if all this ice melted, the level of the sea as it is known today would be higher by about 110 feet. If all polar ice melted, the Chipola River at Florida Caverns, would become a salt bay, Marianna a seaport town, and a bay beach would be located near the park area. However, do not sell your present beach property too quickly since this polar ice is known to be melting only a few inches a century.

Well-lighted, underground trails make accessible Florida’s amazing network of underground passageways. The temperature remains at about 63 degrees, F. throughout the year. In addition, natural rock gardens, wildlife, historical values and recreational facilities make Florida Caverns one of the South’s outstanding State Parks.
Considering the sub-tropical climate of Florida, isn’t it peculiar that ice had so much to do in shaping our land surface? As a matter of record all of the surficial deposits making up the large part of the land surface of Florida were created and shaped during the geologic past (one to ten million years ago) when ice piled up on the poles and moved down over lower latitudes or when this ice was being melted. In the United States as this ice piled up on the North Pole and moved down over most of the middle western states, the water forming this ice came from ocean basins and the water in them was lowered as much as three to four hundred feet. At this time much of the Gulf and Atlantic bottoms was uncovered, land streams cut their valleys much deeper, ground water circulated much more vigorously and rocks through which it passed were dissolved faster. Later as this ice was melted the lower parts of stream valleys were filled with salt water and the streams became sluggish and deposited sediment in their valleys to make their flood-plains. Ground-water circulation was retarded and the bottoms of the Gulf and Atlantic were again covered. This uncovering of the bottoms of the Gulf and Atlantic followed by covering constitutes a cycle. Five of these cycles have been recognized in Florida, and the red sands, clay and gravel that make up the surface of most of Florida represent former bottoms of the Gulf and Atlantic, now raised out of these seas by land movements.
Today we are living in a period following a time the northern and southern extremes of the earth were covered by ice, and this ice is still melting off of these areas.
In 71,000 acres of parks, valued at approximately $50,000,000, Florida offers the vacationer a natural wonderland he can explore. Within these park areas the visitor can discover for himself the “true” Florida by car, along foot trails, navigating tropical rivers and streams—or by following elevated boardwalks through hauntingly beautiful swamps.

Stalagmites resulting from varied origins. The center one was formed from the intergrowth of several stalagmites. The deposit on the left was developed as a series of flat basin-like parts, over which water splashed and cascaded to the floor, the basins being inclined in various directions. The right stalagmite began as did the left one but the basins were soon eliminated and the growth was made more regularly.
We have seen then in the preceding discussion how caves are formed largely in rocks saturated with water, and how by land movements and changes of sea level the caves and pores formed in this rock are moved above permanent water levels and exposed to air. It then becomes possible to deposit rock in the pores and caves rather than to increase their size by solution. As you go through the caves you will notice that the walls are wet and that water is oozing out of the pores of the rock.
This water has just passed through limestone and has dissolved parts of the rock. The reader undoubtedly knows that water will dissolve a substance in large quantities and more rapidly if it is hot, and that it can hold more gases to make stronger acids if it is under pressure. So, having been released from a relatively warm rock in which it was under some pressure and where there was little air circulating, into a large cave where rapidly circulating air cools the cave and evaporates the water, this water can no longer hold all the limestone it has dissolved and it releases part of it.
Small drops of water emerging from the lime rock on cave walls are evaporated and calcite and other rock minerals are deposited along these walls. Where these drops cascade along the walls a continuous elongated ridge is deposited. If the water oozes out in an extremely fine coating of water, the entire ceiling, walls and floor may be paved with calcite.

These deposits combine a rather even and general flow of water and possible intergrowth of the stalactites to make the thickened deposit. The ground water issued more rapidly and was concentrated at one point to make the long tubular deposits, the tube being made by rapid evaporation along the outer margins of the drops of water as they hang on the stalactite before the large part of the water falls to the floor.
Where individual drops collect on the cave ceilings, a thin deposit may be formed on the ceiling after which the remaining water may drop to the cave floor where more calcite is deposited. Continuous dripping results in paired deposits extending down from the ceiling and up from the floor. The deposit on the floor is commonly thicker and more columnar, whereas that on the ceiling is thin and tapering much like an icicle. Those hanging from the ceiling are called stalactites and those on the floor are stalagmites. Where these two deposits are joined they are known as a column.
These cave formations are all composed of the mineral calcite, which forms all lime rock. If you will notice in the cave this mineral is crystalline, and it is remarkable that as calcite crystallizes from the many individual drops of water it is arranged always in a particular pattern. These crystal faces reflect light and form the many unusual and beautiful arrangements which you will see in a visit to the caves.
Since early time, Florida Caverns have had interest. They were first mentioned in writings by Friar Barreda, who was with the first overland expedition made by the Spaniards to Pensacola Bay. The following paragraph is in the Friar’s own words, written 256 years ago:
“On June 12 (1693) we continued northwest and after we had journeyed a little more than three leagues ... we reached an abandoned village of the Choctaw tribe called San Nicholas where I came to preach the holy gospel in the year 1674. Here we spent the night in the hollow of such a beautiful and unusual rock that I can state positively that more than 200 men could be lodged most comfortably in it. Inside, there is a brook which gushes from the living rock.”
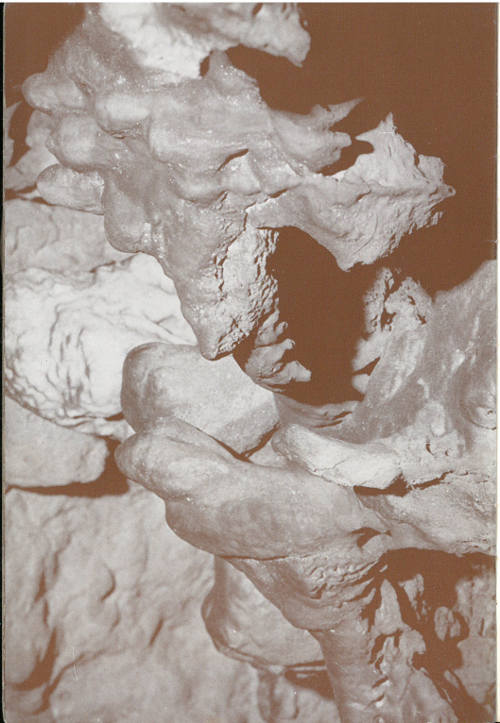
This form is the result of the irregular etching of the limestone by ground water at the time the caves were formed, combined with the later development of stalagmites and a pavement of calcite “drip-stone” upon the irregular surface. Dust and small debris have been incorporated in the crystals of calcite which form the stalagmites. Visitors like to make a game of finding formations in the cave that resemble animals and other things. Note the wolf head to the right and the Dachshund head to the left center of the photograph.
Experts, who know how to read stories told in the designs on Indian pottery, state that the caves were known to the Indians of this section long before the coming of the Spaniards. There is considerable evidence that Indians, even prior to 1693, had been in the habit of using Florida Caverns and caves in the vicinity for shelter during their hunting trips into the region and for refuge from their enemies. In some of the smaller and dry caves there have been found potsherds, or small broken pieces of Indian pottery. According to the archaeologist, all of the sherds so far discovered are of a late post-Columbian type. Ashes from fires, dead for many years, flint arrowheads, and animal bones have also been found.
Several times in history, Florida Caverns—a nature-made shelter—was used as a refuge from armed forces. During Andrew Jackson’s punitive expedition against the Indians in 1818, a large band of Indians escaped from his soldiers by concealing themselves within the underground caves. Again, during the War Between the States, an outfit of Union soldiers en route to Pensacola was resisted by a home guard unit from Marianna, composed of men too young or too old to fight in the armies of the Confederacy. While the battle was raging, women, children and slaves took refuge in Florida Caverns.

Nestled ’midst hundreds of pines, hickories, sweetgum and oak trees, Florida Caverns golf course is one of the most scenic in the United States. It was laid out after the design of the famous St. Andrews Golf Course of Scotland.
A clear spring, which in reality is a subterranean river, rising out of the lime rock, sends its lovely azure stream down through the park over a mile before it enters the Chipola River. The Chipola Natural Bridge, located in the park, is a fourth-mile long and has been restored to its original interesting geological condition with the removal of logs and lumber which had jammed into it in bygone days when the river was used to float them down to a mill.
Open the year round, Florida Caverns State Park is comparable in interest to Carlsbad Caverns, N. M., Mammoth Caves, Ky., and Luray Caverns, Va.
In addition to its geological attractions, the area in which Florida Caverns is located is of peculiar interest biologically. In it are found many species of both plants and animals that are not expected so far south, as well as a large number of typically southern forms.
The State Park system of Florida has been developed as a coordinated group of Parks, each one of which stands upon its own merits and each one possessing as many as possible of the following values: Outstanding historic, scenic and scientific attractions. Florida Caverns is richly endowed with them all.
I hope that you have found this discussion of the creation of lime rock, the formation of caves under water, the elevation of these caves above permanent water levels and the subsequent deposition in them, of interest.... We of the Florida Geological Survey and Florida Park Service hope that you enjoy your visit to the Florida Caverns State Park.
This booklet published by The Florida Park Service, Tallahassee; photography by Monte de Oca, F.S. N.B., and William Z. Harmon; designed and printed by Rose Printing Co., Inc., Tallahassee.
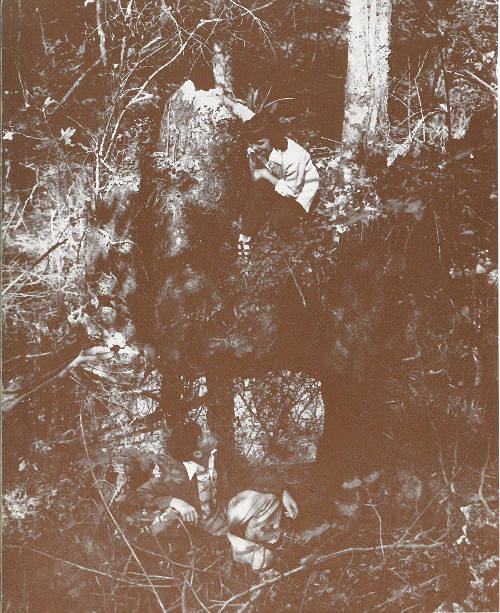

Overhanging rock projection caused by erosion of ancient river. Note large tree growing in rock behind upper visitor. This feature may be all that remains of a large cave, the surrounding limestone having been removed. If the overhanging portion were connected to land a perfect natural bridge would be formed.
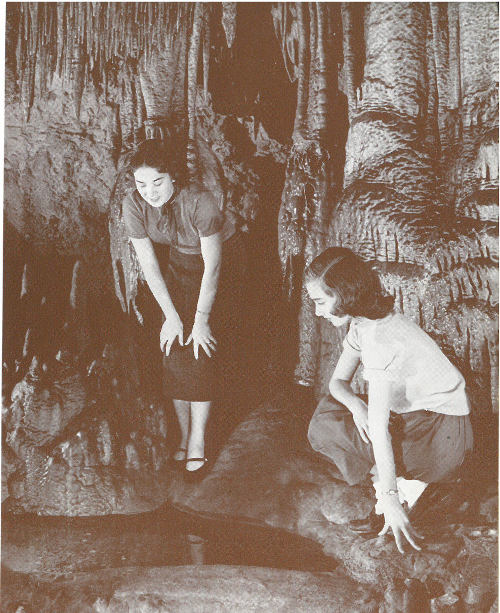

Who would expect to find this cavern scene in Florida? Icicle-like formations and a mirror pool are features of one of the state’s most unexpected attractions at Florida Caverns State Park.
Marianna is located in the northwest section of Florida, approximately twenty miles from both the Georgia and the Alabama state lines. The Gulf of Mexico lies forty-five miles to the south, the Apalachicola River fifteen miles to the east, and Port St. Joe only seventy miles southeast of Marianna. It is relatively easy to travel to the various population centers of the southeast because of Marianna’s centralized location.
Airline Service—The city is served by National Airlines, with three flights daily, with direct service to Mobile, New Orleans, and Jacksonville, and good connections to all major cities. Also available is charter service through local flying agencies.
Bus Service—Marianna is a terminal station for Greyhound and Trailway Bus Lines, and approximately 2,000 passengers daily are handled through this station. Thirty-six regular bus schedules serve the city each twenty-four hours. Lee’s Coach Lines, a Jackson County bus system, regularly serves surrounding communities.
Rail Transportation—Marianna is served by the Louisville and Nashville Railroad, and by the Marianna and Blountstown Railroad. The Atlanta and St. Andrews Railroad traverses Jackson County, serving Cottondale, nine miles west of Marianna, and gives direct connections from Panama City and the Gulf of Mexico to Atlanta and other points.
Hotels, Motels and Restaurants—Marianna is a first-class hotel and motel city, boasting three hotels, the largest of which has 125 rooms, as well as a number of outstanding modern, air-conditioned motels. A number of restaurants and dining rooms serve the traveling and working public. Also rating first-class are several tourist homes along U. S. Highway 90.
Highways—Marianna is served by U. S. Highway 90, and by State Highways 276, 73, 167, and 71. U. S. Highway 231 connects with U. S. 90 only a few miles outside Marianna. An excellent system of hard surfaced highways and roads serve the county.
For further or definite information write Marianna-Jackson County Chamber of Commerce, Marianna, Florida.
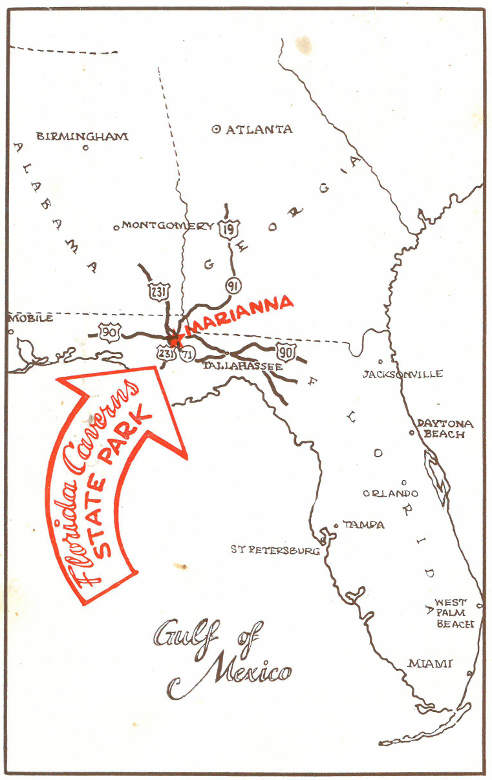
Map showing principal highways leading to Marianna, home of Florida Caverns State Park.
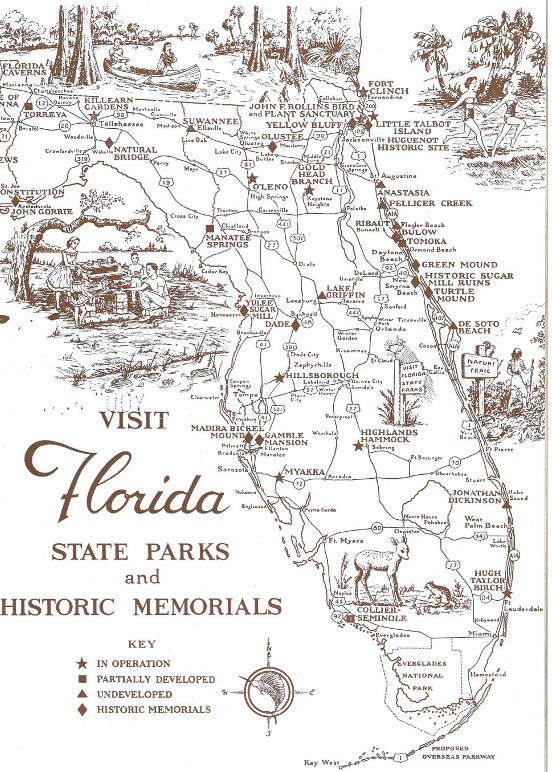
Whether you are a visitor or a resident, you will want to know more about Florida’s State Park System which preserves the tropic lure of primitive Florida and perpetuates memorials of Florida’s absorbing history.
This system of parks and historic memorials, in areas ranging from a few hundred to 26,000 acres, embraces more than 71,000 acres of the most wonderful land in Florida.
These parks in their varied appeals offer recreation possibilities extending from a few hours diversion to extended vacations.


End of Project Gutenberg's Florida Caverns State Park, by Robert O. Vernon
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK FLORIDA CAVERNS STATE PARK ***
***** This file should be named 46171-h.htm or 46171-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/4/6/1/7/46171/
Produced by Stephen Hutcheson and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation information page at www.gutenberg.org
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at 809
North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email
contact links and up to date contact information can be found at the
Foundation's web site and official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For forty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.