
The Project Gutenberg EBook of The English Lakes, by W. T. Palmer This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook. Title: The English Lakes Author: W. T. Palmer Illustrator: A. Heaton Cooper Release Date: August 10, 2018 [EBook #57664] Language: English Character set encoding: UTF-8 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE ENGLISH LAKES *** Produced by Donald Cummings, Adrian Mastronardi, Stephen Hutcheson, and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images generously made available by The Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries)


A MISTY MORNING, NEWBY BRIDGE, WINDERMERE

AGENTS IN AMERICA
THE MACMILLAN COMPANY
64 & 66 FIFTH AVENUE, NEW YORK
First Edition July, 1905
Second Edition October, 1908
The Illustrations in this volume have been engraved and printed in England
by the Hentschel Colourtype Ltd.
The present book, it must be understood, treats the English Lakes rather apart from various other elements comprised in what is known as the Lake District. There is so much to say of the waters and their immediate surroundings that no space has remained to describe mountain, pass, and tarn in the manner their beauties merit. Other limits to the book are due to the writer’s promiscuity of taste. I am interested in most things—antiquities, fauna, flora, sports, geology, entomology, and the like; but in not one of these subjects have I that erudite knowledge which might render my work of profit. This book is written to interest those who love out-of-doors without claiming any particular study there. Of the paintings—I can only commend them to notice. In my humblest manner I assert that only an artist who feels the beauty of his environment thoroughly 2 could produce work so stamped with the innate character of our Lakeland.
Of the history of the English Lakes little need be said. We are in a backwater, so to speak, of events; only the outer edges of great affairs have touched us. The mountains have been the last home of the invaded after their defeat in the field and their banishment from the accessible level lands. Druidical, and perhaps more ancient, remains are plentiful, along with relics of Roman, Norseman, and Saxon; but these at best only evidence sparse occupation. So far as history shows, no really great campaign has been fought out in our wilds—the battlefield of Dunmail (and only legend fixes that) is almost the only extensive one within the heart of the fell country. Great religious changes—the Dissolution of Monasteries, the Reformation, the rise of Nonconformity—have been far more striking in their results than ever were the fortunes of war. The mountains of Lakeland and Scotland stand blue on a common horizon, and the alarms and reprisals of Border feud were not unknown. But the hardy warriors from nor’ward did not often risk operations here, where conditions were so unfavourable to their feverish but unsustained method of warfare. The Civil War brought strife between the squires, but no great action was fought, yet in outlying districts the name of Cromwell is not forgotten in weird tale. Though the land of the Lakes has been free from war in the sense of great happenings, it has been far from a peaceful country.
Our lakes are fifteen in number, ranging from the lordly Windermere and Ullswater, ten and a half and nine miles long respectively, to Loweswater and Rydalmere, which hardly exceed the larger tarns in area. Our mountain ranges contain the most elevated ground in England—Scawfell Pike, Scawfell, Helvellyn, and Skiddaw being over three thousand feet in height, and several others approaching that level. About thirty minor waters are scattered over the area known as the Lake District; but I must not make a guidebook of my volume.
My story of the Lakes will be told in the manner it has discovered itself to me. I do not claim originality of method, nor will my reader find much savouring of literary symmetry and style within these covers. My wanderings cover a long series of years, and my recollections are as disconnected as they well can be. I have kept no diary of things seen, and scarcely regret the omission. There is no pile of data to confuse me; trivial impressions have passed away, leaving a harvest of perfect pictures to describe. And if I fail in putting these to paper, my attempt has at least been sincere.
Much has been written of the dalesmen. Some writers deprecate everything we have, from our mountains, the faces of which they hardly know and the mysteries of which they have never dreamt of, down to our social customs, which often they have neither witnessed nor studied. To these nothing need be said, but to our over-laudatory friends I must say 4 that “to gild the lily” is not kind. Dalesman though I am, our faults are quite visible to me, and “don’t pinch us” for them. I meet the dalesman on equal terms. With him at “dipping” eve I have slept, star-embowered, on the open fells. Many curious yarns of the uplands are believed only by the wandering tourist: inner lore of the mountain life is reserved for the home-sanctum. Where, in my wandering story, I feel myself competent to introduce the men of the land, the pictures are as faithful as I can make them. They have a store of stories, yet unprinted, in the wilder glens: stories of weird things, of splendid heroisms among the flocks and fells.
We have two classes of tourists: “The Strenuous Life” and “The Lotos Eaters,” I divide them by their tastes. Others call them “Visitors,” “Tourists” and “Trippers.” The first they adore—they take a “cottage furnished” perhaps, and anyway are profitable in a staid, comfortable manner; the second they tolerate—he is a man of hotels and boarding houses, here to-day, and to-morrow “away ower t’fell,” but, by reason of his plenty, worthy attention; the third they despise; many seem to think that the day-visitor ought to be put down—by violence preferably.
To revert to my own division of our visitors, I feel that my tastes join me in both types. I like the peaceful vales and lakes where the “lotos-eaters” idle the summer hours away, and perhaps the detailed descriptions of so many days of ease may incline the reader to believe that I care nothing for the fells. But I love the breezy uplands, the miles of free moor, the peaks and the crags.

FURNESS ABBEY IN THE VALE OF NIGHTSHADE
A few words about accommodation and routes of travel are unavoidable. There are huge hotels with fashionable prices, smaller ones that are as comfortable or more so, at a fifth of the cost, and boarding houses in large numbers. But sometimes in August there are more tourists than can be comfortably put up even in our village-towns. However, the Lake District is small, and, if Ambleside be thought full, there is Grasmere not far away and Bowness within five miles. All three places are unlikely to suffer from excess of visitors at the same time. Of the remoter dales let me tell you a story. Two young men wandered into a certain dale-head where there are but two homes for tourists. At the first they asked for a couple of rooms. “We haven’t one to spare.” The way had dealt hardly with them, and at the second they moderated their request to “two rooms, but if quite necessary we don’t mind sharing one.”
“Why, bless thee, my lad,” said outspoken old Mother, “ther’s three to ivvery bed, an’ two to ivvery table awreddy. But mappen I can put you up in t’ barn with them others.” The barn across the yard had been pressed into service as a bedroom; but at the prospect these townsmen shivered, thanked the good lady, and walked wearily towards the dale-foot three miles off (where the excess of tourists was still great, though not so marked). The moral is, if you intend to make any place a centre for your journeys 6 engage a room there, but—I was just preparing for repose when a knock came to my door. “Hello,” I answered. “Please, sir, there’s another lady just come in, and will you give up your bedroom for her?” I slept in less comfortable quarters that night, with half a score others who, by chivalry or improvidence, were without rooms.
Three railway systems touch the Lake District. The London and North-Western runs up one side with its main line, and casts a branch from Oxenholme to Windermere, which is a very popular way to reach the Lakes. From its terminus regular lines of coaches run to Coniston, Ullswater, and Keswick, as well as to Bowness, Ambleside, and Grasmere. A new company is putting on more motor-cars to cope with the traffic between the terminus and Ambleside and Grasmere. The main London and North-Western line at Shap is near Haweswater, an area growing in renown among tourists. At Penrith it is near Ullswater, and regular coaches connect with the steamers there. A company has exploited motor-traffic from Penrith to Patterdale, partly for passengers, partly to carry the output of the Glenridding lead mines.
The Furness Railway is the railway of the Lake District. From Carnforth, where it connects with the London and North-Western main line and with the northern arm of the Midland Railway, it sweeps round Morecambe bay to Ulverston. Here it throws branch the first to connect the steam-yachts on 7 Windermere with the outer world. By means of these tourists are poured into Bowness and Ambleside in great numbers. A line of coaches connect Ulverston with the foot of Coniston Lake. The main Furness line passes through warrior Barrow to the Duddon, where branch the second goes off winding through the hills to Coniston. From Coniston there is coach connection with all parts of the Lake Country. The main line has not yet, however, finished with the Lakes. It crosses the Duddon and swerves round the foot of Black Combe to Millom of the hematite beds, then away through a beautiful district between the fells and the sea to Ravenglass and to Seascale, where a good road leads up to Wastwater. At Sellafield another branch is thrown through Egremont, within a few miles of Ennerdale Lake. The London and North-Western comes on to the scene again here, a branch bearing southward from Carlisle and tapping a district rich in iron ore, but fringed with lovely valleys.
The Lake Country is also served by the Cockermouth, Keswick, and Penrith line, as important for the north as the Furness line is to the south. It connects the London and North-Western at Penrith with the Furness at Whitehaven, passing by Derwentwater and Bassenthwaite. At Threlkeld it is nearest Thirlmere, at Troutbeck it is nearest Ullswater, while from Cockermouth the tourist may easily reach Loweswater, Crummock, and Buttermere.
The North-Eastern and Midland Railways both 8 come into Penrith, which is an important junction for the Lakes, and an interesting town in itself.
It is not my intention to give any space to a description of the internal traffic of the country—it is plentiful and good.

WINDERMERE FROM WANSFELL
Sunset
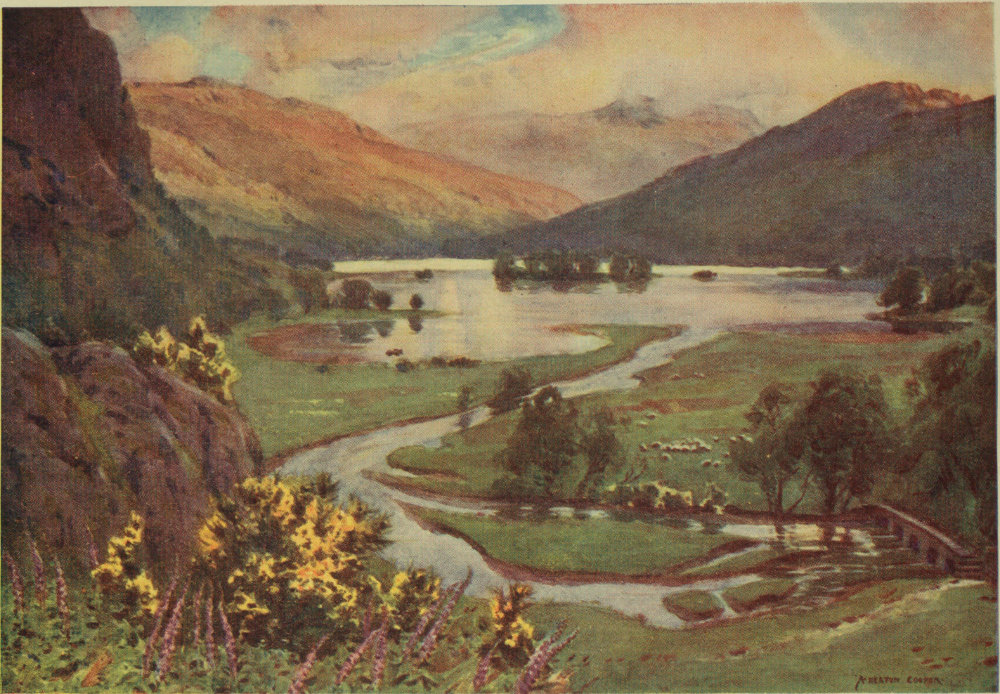
From its foot at Newby Bridge to the circling beach at Waterhead, Windermere, the largest of our Lakes, is full of interest. Not a bay on either bank fails in variety of scene, while from mid-lake the surroundings are ever changing. The ideal way to see Windermere is from a small boat; the journey, coasting every bay and yet not losing the broader views of mid-water, should not take less than two long summer days. Of course few can spare so much time to the pleasant task. By steamer in a short afternoon and at a moderate expense it is possible to make the tour of the lake. The visitor, however, can taste some of the pleasures of the ideal if he spare an evening for boating. From Bowness steer past the corner of Belle Isle; then as you near the Furness shore, turn right or left as fancy directs, coasting under larch-hung bluffs toward the Ferry, with Belle Isle on the left, or passing alder-fringed meadows past Rawlinson’s Nab for Wray. The Furness shore is rather the more diverse, and your rowing there at the close of day does not disturb the many anglers who frequent Millerground. From Lakeside the boat 10 can be turned in any direction. Many wish to see the Leven leaving the lake: it is but a half-mile away. Paddling quietly beneath Gummers Howe is delightful; but the person with a taste for detail in light and shadow may decide that the opposite shore, with its view of the fell across the clear water, has even more charm.
By steamer the great majority see Windermere. The boats are large, and, though at some hours crowded, fairly often carry quite a few passengers. At mid-afternoon I have sailed from Bowness to Ambleside, a solitary passenger,—and that during the height of the touring season. From the deck of the steamer as it lies berthed at Lakeside there is a glorious view. The steep side of Gummers Howe, green in summer with bracken, golden with the young tendrils in spring, and in autumn russet with fading glory, rises opposite. Like a wide river the lake winds further and still further as your eyes turn toward the mountains. Yes, there they are, blue with distance—sharp peaks limning strongly against the sunlit sky. At present the lake is still as a mirror; drippings from the oars of passing boats make little glittering ripples. But though the views are so beauteous, it is well for a contemplative person to sit near the gangway and watch the throng which the latest train has brought from the outside world. There are two tall ladies, evidently school ma’ams, with much luggage and the power of looking after it without fuss; the stout old gentleman there has come this many years for a 11 sojourn by the shore of Windermere. I don’t know his name, but his portly person is frequently seen on board the steamers. ’Cute chap that, say the lakemen; he has a season ticket and takes out full value. Now there is a quiet whirring of the screw; the captain, a white-bearded man with many years’ service on the lake, sounds the whistle for the last time, and the echo dies away among the hazels and coppices around. The water, with a quiet churning sound, parts in front of the boat and we are well away. Don’t look back, unless it be to catch a glimpse of where lake finally narrows into river.
The boat speeds past one or two wooded islets: in spring the undergrowth is blue with wild hyacinths. The afternoon sunlight glints upward from the calm water as from a mirror. By Finsthwaite the woods are rich green. Of cultivated land we see but little: here a cornfield between woods and lake; there, evenly hoed patches of turnips and potatoes, or more often meadows where rich grass is mantled in the white and yellow of ox-eyes and buttercups. Peeping between green bowers of sycamore and ash are one or two farmsteadings. Old and weathered, built of blue-grey stone, they harmonise well with their surroundings. Do our eyes, accustomed to these from birth, feel in this hoariness of theirs a rare beauty which is purely imaginary? We almost hate the sight of a modern-built villa, trim without, healthy and comfortable within. I make no pretension to the artistic temperament: subordinate the villa to its surroundings, and 12 I am content; but stick a horror of brick and red tiles in all its nakedness on a commanding hillside, or right on the edge of a beautiful mere, and the wanderer is above human whose temper is not tried at the sight. Pretty bungalows, for occasional occupation, are springing up on the shores of Windermere; they are welcome, be the woodlands around them sere or green.

SWAN INN, NEWBY BRIDGE, WINDERMERE
When not watching the glorious picture unfolding as the steamer passes bay and creek, headland and rocky cove, there is to me much interest in observing other people on the boat. For the deck of a Windermere lake yacht has often as cosmopolitan a load as a cheap emigrant or “special tour” steamer. True, there is little distinction of nationality in dress; but the voices are often without disguise. Frenchmen, Swiss, and Germans are not unusual, while Americans are frequent. Here let me defend our friends from across the Atlantic. They are seldom the loud, almost vulgar critics of our lake scenery they are popularly supposed to be. Most of our visitors are readers of Wordsworth, of Ruskin, and our other poets in prose and verse, and know what to expect. A Yale man I once accompanied from Windermere to Keswick stated: “It is the breathlessness of Lakeland which surprises me. Here there is a memory of De Quincey or Coleridge: next moment there is a story of Christopher North. I lift mine eyes suddenly from the pastoral scenes of Wordsworth to the blue skies and mountains of Ruskin. Your country-side is breathless with lore: America has no place to compare it with.” I am not a “hail-fellow” person, preferring to be seen, not heard, and as the boat glides along I silently piece together, from external evidence, the little stories of my co-passengers. To-day there is a young man pacing the boat amidships. He is no chance visitor, I judge, by the anxious way he keeps looking ahead. There is some point he evidently does not wish to miss. Presently I hear a movement of his arm: he has drawn out his handkerchief and is waving it. Every eye turns to find out where he is signalling. In a moment we catch an answering flutter: there is a lady in white blouse and dark skirt on the shingles beneath the wood. Something in the message heartens our fellow-passenger; a load of anxiety has left him. Again and again he signals—ever there is an answer. Then a lithe dark figure springs into a path from the shore, and runs out of sight among the bushes. A child is hastening to give some one the news that the desired steamer is passing. Now, from the front of a bungalow, hardly to be seen for larches, another signal begins to jerk. Our passenger answers this also till the yacht sweeps out of the bay.
The promontory of Storrs now pushes out, and here the steamer will stop. The call of the syren, like an enormous flute, rings full and sonorous over the water, and dies in tuneful cadences, each softer and more sweet, through the green ghylls and swelling hills. The road to the pier runs close to 14 the lake: a cyclist is rushing along vieing our boat in speed. The signaller has seen him, and smiles. In a minute we are past the narrow stone embankment with its small summer-house, and are purring alongside the newer wooden pier. The cyclist speeds into sight through an avenue of trees, and dismounts close by. The gangway is thrown aboard—the signaller is the first ashore. The cyclist exchanges a word, and they walk from view together. A story of joy and peace and love is maybe working itself out before us, and the whole while, seated on the opposite seat, a lady has been gloating over the theatricalities of miserable “life” as depicted by Marie Corelli. Better advised is the one who patrols the deck with a volume of the best carefully tucked under his arm. That book will be digested presently when lamps are lit and night like a velvet pall descends over lake and mountain.
Storrs Hall—now an hotel—was occupied a century ago by Mr. Bolton, who, a man of literary tastes, thought noble friendships a boon. He communed with Wordsworth, North, Sir Walter Scott, De Quincey, and many others who were attracted to that great coterie of genius. In these days the poetry of the Lakes school is often sneered at. The men with their simple tastes and pleasures are despised, but, leaving their work aside, never in history has a group of men so able, so high-minded, so far in advance of their day and generation, been so intimately associated. They had their weaknesses, 15 their vices, but conducted their worst hours without impairing the morality of their surroundings. Their influence was wholly for good, wholly for an upward trend of thought.
As the Swift threads through the reefs above Storrs, we enter a new reach of the lake. In front Belle Isle’s tree-shaded level seems to close the water; to our left is the Ferry; on the right green fields and filmy woods, with, beyond and above, the mountains clustering round the vale of Troutbeck. A faint blue ruffle travels along the lake toward us, a catspaw of wind that sends a yacht which, sail-slack, had been drifting, bowing and dancing through the water. At the landing-stage our steamer has to wait till the tank-like cable-boat has completed its journey. Down the hill opposite comes the road from Kendal to Hawkshead, and about this point, from time immemorial, the lake has been crossed. Various sorts of craft have been used: in the time of the Lake poets the conveyance was a large and almost flat-bottomed boat, pulled along by sweeps. Christopher North was wont, on a Saturday morning, to come down from Elleray to steer the market-folk across. On one of these occasions he noticed a flurry in the water, as of a struggling fish. The boat’s course was diverted, and a landing-net used. Two pike, each of about six pounds weight, had been fighting. The victor had seized his antagonist by the head and endeavoured to swallow him whole. But, as an American has sagely commented, “he had bit off more 16 than he could chew.” When North’s landing-net lifted the pair, his jaws were still locked round the victim’s shoulders, though the biter had drowned. Though badly mauled, the other fish was still feebly alive. In his fishing reminiscences of the Borders Sir Walter Scott told a similar story. Near the Tweed one day, seeing a commotion on its banks, he asked a laddie what the matter was. “I dinna ken exactly,” was the reply, “but there’s a muckle fush wi’ twa tails i’ t’ watter.” Anglers—and more veracious folk—have similar stories to tell. The version I have given above of Christopher North’s experience is not, I am aware, the accepted one: it was given me, several years ago, by a dales dweller, one of whose parents had witnessed the incident. There are legends to tell of this Ferry. The most sinister is of an awful voice which on wild nights began to peal across the turmoil—“Boat!” Once a bold ferryman answered the call, put off his boat and rowed into the storm and darkness. Half an hour later he returned, with boat swamping and without a passenger. The boatman’s face was ashen with terror; he was dumb. Next day he died. Stories there were of demons carrying off their spoils of witched souls, and even the bodies of dead saints, across the lake. No boatman, after this incident, could be prevailed to put off in darkness, so a priest was summoned from the Holy Holme. With bell and book he raised the skulking demon—at midday there was the voice of storm in the air, though, mindful of the call of the Master on Galilee, the water fell calm. Voices argued with the priest, whose cross planted firmly by the edge of the lake was surrounded by terror-struck lakemen. At the end of a long altercation the demon released from thrall the soul of the boatman, and craved for mercy. For its peace, the priest laid the evil thing in the depths of Claife, there to remain until “dryshod men walk on Winander, and trot their ponies through the solid crags.”
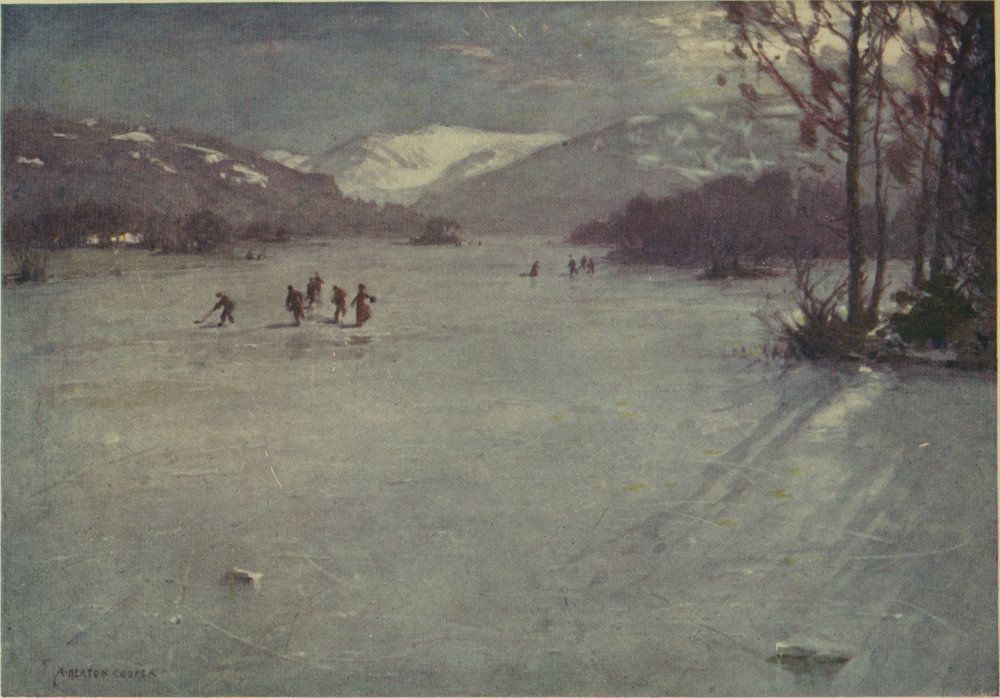

NEAR THE FERRY, WINDERMERE: SKATING BY MOONLIGHT
At least once the ferryboat has been wrecked: the records of Hawkshead Church show that a wedding party was drowned, about a dozen lives in all being lost. The tank-like servant of the cable now against the shingles has shown sea-like jauntiness. One Whit Saturday morning, when laden with strength and beauty going to Kendal hirings, she broke both hawsers and at a majestic pace drifted down the lake. In half an hour she touched one of the islands, from which her passengers were shortly taken off. In these times of watertight compartments, there is little chance of a disaster occurring.
The hotel in front of which our Swift is floating presents a gay appearance on yacht-racing days. The lawns are occupied by a well-dressed throng, and a small but excellent band plays appropriate music. The line of red-flagged buoys marks start and finish: some of the races are round the lake, about twenty miles; others are fought out in the northern or southern basins only. The needs of the racing have developed 18 a special type of boat. The quest for speed dictates no great displacement of water, therefore the craft are built shallow; but the frequent and violent squalls of wind from the mountains make some stability and weight essential to prevent capsize. Windermere yachts carry heavier keels than is usual to their sail area, and there are other minor variations between them and sea-going or conventional river and lake boats. With a good breeze the yachts are very fast: they are handy too, frequently “going about” in narrow quarters. At times, when the air is dead calm, a race may degenerate into a drifting match: the lakemen say that on one occasion the yachts were over ten hours in covering as many miles. The locally developed design is eminently suited to its work. Mr. Fife, the great draughtsman, some years ago built a yacht on the Clyde for this lake. He came to see it compete, but the local boats quickly showed their superiority over the new design.
The engines are now re-starting, and our steamer cleaves toward Curwens’, or Belle Isle, which for long has seemed to close the way. Now, however, narrow channels open to both right and left. The yacht bears right away past two small holmes. One of these, a cluster of trees and a level sward, is ofttimes used for kennels for the puppies of the Windermere harrier pack. Here they are quite at liberty and yet out of mischief, a remarkable circumstance in a puppy’s career. Often I have laid on the oars to watch the little hounds romping and playing, under the blinking 19 superintendence of an elder. Then their game would stop, and a pell-mell of puppydom charge to the shingles and bay its infantile delight. Belle Isle is the only island of Windermere on which a house is now standing. In the long ago a branch of the Philipsons of Calgarth held it. During the Civil War this family was Royalist. One, a major in the king’s Northern army, was shut up in Carlisle by the Roundheads; another was here beleaguered. For several weeks the men of the Parliament tried to carry the island by storm, but failed. The major had been apprised of his brother’s peril, and immediately the siege of the Border city was raised he came south with a troop and dispersed the Roundheads. Now to the daring Robert came the hope of reprisals. The island was fully relieved at Sunday dawn; three hours later Royalist horsemen were on their way to Kendal. Colonel Briggs, the Cromwellian commander, attended divine service regularly. Robert accordingly made straight into Kendal Church. Though the building was crowded, he galloped through the tall doorway and up the aisle. Sword in hand he rode to where his antagonist usually sat, but Briggs was not at church. The townsfolk rose, and Robert was forced to gallop down the other aisle to prevent being overwhelmed by numbers. The doorway to the right is lower than the central: Robert’s head struck the arch, and he was thrown. His steel helmet received most of the concussion, and Robin was on his feet again in a moment. One townsman caught his horse; 20 the saddle girth had broken when the rider had been hurled backward. Robert instantly threw the saddle across his charger’s back and leapt into it. Suddenly and cruelly spurred, the horse reared up and jerked the rein from its detainer’s hand, while the intruder clove him to the chin. Without further interruption, the Cavaliers rode back to their island fortress.
The steamer has been bearing us through the narrow channel to Bowness Bay. The scene here is usually a busy and a pretty one. The public fore-shore is narrow, and rowboats are crowded toward it. The steamer-pier and two long jetties make the narrowness still more emphatic. But Bowness Bay, with the Old England hotel to our left, looks perfect. Beyond the short promenade, laid out in trees and terrace-gardens, the ground rises to rocky Biskey Howe, whence is a glorious view of the lake. Quite close at hand is Windermere parish church, with some stained glass removed here from Cartmel Priory at the Dissolution. The walls were at one time decorated with texts, but the Lutherans rebelled against these and hid them beneath ignoble whitewash. But what the sixteenth century despised, the twentieth reveres, and the old Scripture paintings have been carefully restored. The village of Bowness presents little noteworthy except its attention to visitors: its reputation in this respect is thoroughly justified.

THE OLD FERRY, WINDERMERE
If you take a walk ashore, the various boatmen will embarrass you with offers of craft. “Fishing tackle? oh, I’ll lend you that with pleasure, and bait too.” Now this is all very well for the disciple of Walton who insists on having a competent person on board to select the fishing-ground. But the average man may be fairly warned by the following note: “Hired a boat for the day and set out to fish with six rods, plenty of bait, and a hopeful word of success from the boatman. We cast our lines right and left, back and front, but not a fish did we see. Whether the fish or the bait were enchanted we could not say, but concluded that the lines were lent to make people believe they could catch fish.” In answer I had to point out (my complainant knew sea and a quiet variety of river fishing well) that, under a blazing June sun, perch and trout were not likely to feed. There are times when the fishing is good—out of the tourist season mainly. Some anglers regularly come to Windermere for sport; but these swallows do not make a summer, and Windermere is far from being an angler’s paradise yet. The lapsus linguæ of the boatmen is perhaps excusable: others delude in less satisfactory fashion.
Turning again to the bay, with its view of Belle Isle, and the blue mountains peering over the bluffs of Furness, it strikes every visitor that the landing-place is exceedingly cramped. Thousands use the boats; were the rival proprietors less good-natured traffic would be impossible. Perennially there is a movement afoot to acquire additional frontage for the public use, but as perennially it fails. In the Diamond Jubilee year, many thought that an acquirement was 22 coming at last. Negotiations were opened for land to the south of the bay, but the Vicar of Windermere could not meet the promoters.
Aboard the Swift again, we are borne into the upper basin. On Lady Holme was once a chapel, served by the monks of Segden Abbey, one of the Scotch monasteries. They were in possession so early as 1355, and till the Dissolution maintained two priests here. There is, in some old descriptions, a legend that one of these priests, to mortify his flesh, caused himself to be chained in the crag above Rawlinson’s Nab, and there he remained for thirty years or so, before death released him. Sweet in early May are the islets here with lily of the valley: at any time it is pleasant to land on them, for they are dry, their brakes are not tangled—an ideal place for a quiet afternoon. As the steamer goes on, the scene grows in grandeur. Over a vast plain of water the distant mountains seem to hang. There are misty indications of level meadows and woodlands next the water, but the charm lies in the craggy, shaggy braes and the uprising summits. The woods continue—larch! larch! planted in harsh geometrical lines on the Furness side; the opposite, though really covered with villas, presents a happy, confused forest of oak and ash, sycamore, elm, beech, interspersed with hollies and great patches of underwood. The white foam of hawthorn flecks these hills in early summer; later, patches of gorse, in wild, unconsidered corners, brighten up the heavy green. Then come the heather 23 and the heather bell, empurpling the higher ground; till September’s chilly nights turn the leafage to glories of gold and crimson, the brackens to red and russet. We are now opposite Millerground; the lake near shore is shallow and tempting to the angler.
The hill jutting out above there is Orrest Head—the viewpoint of the Lake County. I have no wish to disparage other of our views: each has its merits. From Orrest you look up and down the river-lake, Winandermere, winding through a long valley. Round the head of its hollow are rugged masses of mountain, cut into by narrow glens and ghylls. The basins of Langdale, of Grasmere, with their tarns and lakes, are hidden in a maze of wildering rocks. Right opposite, the Furness fells, ridge beyond ridge, till, a grand barrier, Coniston Old Man heaves skyward, give no indication of two lakes and wide valleys embosomed beneath. There are two circumstances under which they who climb Orrest are especially well repaid: on a calm June morning, when the lake like a mirror reflects every detail of the hills, when the ruffle of a passing boat or steamer dies away on the dead calm; the other time is when light clouds are drifting across the sky and you can see dappled areas floating over water and wood and fell. There is little to choose between these and when the sun sinks in a bank of vapour behind the Langdale Pikes. Instantly a crimson light filters across the upper basin, picking out bay and islet in a halo of brilliance. For half an hour it becomes more glorious, then to 24 purple and to grey the light declines. Yet, again, climb Orrest when thick snow covers the earth. The scene is awe-inspiring: if in moonlight, you see the terror and majesty of winter; in sunshine the air is filled with chill radiance, and the scene invites you not to despond but to work or play with a will. But this is not of the steam yacht and the lakeside.
Opposite us, with its big round chimneys, is Calgarth, the mansion of the Philipsons. There is nothing now to distinguish it from the Calvegarth it originally was. If the place was ever fortified, all traces of such, save its thick walls, have disappeared. The house has the reputation of being haunted, for the misdeeds of a Naboth. Desiring land in the possession of an old couple, he had them convicted for theft. The old woman, who had occult power, pronounced seven curses against the Philipsons. The couple were duly hung at Appleby, but their skulls came home to Calgarth ere morning light. And at Calgarth they have remained, though men have calcined them with lime, cast them into the lake, and buried them on the mountains. Horrible sounds were heard, groanings and shriekings and wild lament, after any tampering with the uncanny things; so, to prevent further trouble, they were built into the wall—and few now believe in their existence. There are other mysteries hereabout too. When grievous trouble is at hand, a spectral white horse passes over the lake from shore to shore. And occasionally the wanderer’s eye is caught by a faint iris on the water, rivalling in its clear tinges the very rainbow. Both phenomena are said to be well vouched for, which, I presume, has made it not essential for the present writer to witness them.

OLD LABURNUMS AT NEWBY BRIDGE, WINDERMERE
Above Calgarth is the great glen of Troutbeck, where many illustrious personages, from Hugh Bird, a giant of Henry III.’s time, downward, have lived. Hogarth, the weird painter of sordid life, was born here, and at one time the sign of the old Mortal Man inn was held to be his work: a very free drawing it was, of a burly man with vermilion nose, confronted by a thin, white-visaged stranger, with the couplets:
“Oh, Mortal Man, who lives on bread,
How came thy nose to be so red?”
“Thou silly ass, that art so pale,
It is with drinking Birkett’s ale.”
Till within the last half-century Troutbeck was a ’statesman dale, but few of the yeomen are now left. They were not noted fighters, like the men to northward, but in self-defence they manned a fort which an obscure generation had built in Thresthwaite Cove at the head of the valley. The last time was in 1745, when a small band of Scotch rebels were sent back “wi’ a flee in ther lugs.” The grey mansion in the park was built by Bishop Watson, of Llandaff. Westmorland-born, he loved his homeland, and during a forty years’ reign he ruled his bishopric from thence. There is but one mention in his Life and Letters of 26 his going to Wales. Yet he preached strongly to those of his clergy who were absent too much from their livings!
The most prominent building now in sight is Wray Castle. This is not old. In one of his interesting colloquies on angling and things in general, Dr. John Davy, in a book published shortly after the building was completed, remarks:
“Wray Castle is altogether a modern building, and erected by its present proprietor and inhabitant, who has too much knowledge of sanitary conditions to surround himself with stagnant water, making an enemy to health where there is no fear of neighbouring hostility. As to the structure itself we need not criticise it; it is well placed, and at a distance may well pass for what you supposed it to be” (a moated stronghold), “and have the desired effect on the uninformed mind and the careless eye.”
Now the steamer approaches Lowwood, and the coppices of Wansfell sheer up in feathery grandeur as we sail inshore. The view from the hotel attracted Ruskin on his first visit as a child of ten, and in his rhyming diary he speaks of his impatience to be at the windows enjoying the glorious view. The lake is here at its widest and deepest; from shore to shore the distance is considerably over a mile, with a depth approaching two hundred feet. The boats out on the water are fishing for char with the cumbrous implement known as the plumb-line. Char feed at varying depths; to-day the shoal may be 27 within ten feet of the surface, to-morrow near a hundred feet lower. The instrument used is made up of a long central line heavily weighted, to which tiers of smaller lines are attached at intervals. By this means the fish are tempted at all levels, but the implement is for the professional rather than the amateur. The tiers of hooks and baits are sure to foul one another if not dexterously handled.
As the steam yacht gets under way again, Dove Nest, once the abode of Mrs. Hemans, is seen peering through the woods climbing Wansfell. The poetess ever fondly remembered her sojourn here, and the friends she made among the Lakeland poets. Some of the finest contemporary appreciations, both of personalities and work, came from her pen.
Passing Hen Holme, a spine of rock sticking out into the lake—how the waves from the screw lash and dash against its ledges!—the yacht carries us into open lake again. What a panorama of mountains!
Wansfell rises to the right; beyond is the gap of the pass and Kirkstone fell. Red Screes presents its tamer slope, and looks not half so commanding as less lofty Scandale Pike. The long ridge of Fairfield, its ghylls raw with floods and winter storms, comes next, standing above Rydal park. Along this group, a century ago, wild red deer used to range; there was a herd on the Ullswater fells, as now, and also in the wildernesses about Eskdale and Ennerdale. The long slope bending downward to Nab Scar is Great Rigg. You can see only the head of the 28 precipitous Scar, for the bracken-covered heights of Loughrigg climb to the skyline. At square with our course are the Langdale Pikes, their strange knotty summits showing up finely. Great Gable peeps from beyond Borrowdale; Great End, Scawfell Pike, and Scawfell glance through gaps in the rugged chain stretching from Bowfell to Wrynose pass. The country beneath these is the famous Langdales, land of tarns and ghylls, crags and screes. From Wetherlam westward is the Coniston range, haunt of the raven and other wild birds. The head of Windermere is particularly glorious: fir-crowned Fisher Crag sets off the levels where Brathay and Rothay sloom into the lake. The sharp spire of St. Katharine’s, according to Mrs. Hemans, was foundationed for a square tower. Ambleside creeps in rows and terraces up Wansfell, but the grey stone is harmonious and the red ridge-tiles at this distance invisible. To the left Fox Howe stands on its sentry-hill; the views from its lawns are fine: to northward into the heart of the mountains, and the wild forest of Rydal; southerly, green lowland and the silvern mass of Windermere right down to where islands close the view. The level next the river-mouth was at one time a Roman camp, but nothing to prove its name has yet been discovered. Medals and coins are sometimes, after heavy floods, cast up out of the mere. The Rothay was diverted somewhat by the camp builders, that the rectangle they favoured might be preserved. The camp was doubtless used as a caravansery for the traffic between Brougham on the Eamont and the seaport of Ravenglass. Both places are, if mountain roads have not altered for the worse, a good day’s journey away: one over the lofty passes of Wrynose and Hard Knott, the other over the elevated road along High Street. Cultivation has robbed the earthwork of distinctness, but enough remains to show dimly its angles and extent.

WINDERMERE AND LANGDALE PIKES, FROM LOWWOOD
Now the quiet rumble of the screw stops; the yacht sails smoothly and accurately to her berth. Outside the pier a concourse of conveyances is in waiting, and we see our fellow passengers melt away by common ’bus or lordly pair to their respective destinations. The water here is crowded with craft, but there is not the terrible congestion we saw at Bowness bay. A long curve of shingle is open to the public, and forms a favourite promenade.
Even during the height of summer there are dull days sometimes, when dense clouds simply stifle the dales in gloom. This is the more tantalising when one is at Ambleside in the midst of the beauties of Lakeland.
But after two o’clock the day became perceptibly brighter; Loughrigg discovered itself opposite our window, a kindly precipice of damp grey crags rearing through a forest of dwarf oaks and clinging ash, green plumed larches and verdant undergrowth, its long crest crowned with patches of heather and wide, quivering wastes of bracken. There is little to interest us in Ambleside: the sun is bursting his cloudy bonds, and we chafe at streets and houses! Out, then, on the Rydal road, past the old moss-grown mill and the bridge-house Ruskin sketched in his youth, past the Knoll where Harriet Martineau lived. Now we rejoice to see a riven cloud turn to gleaming silver at its edges, and through the gap a shaft of light strikes down to earth. It is lost! No, there it is again, kissing the rugged crest of Nab Scar, and hovering along its flank. The clouds above whirl together, and the welcome gleam is cut off. But the upper heavens are overpent with sunshine; glance after glance of glory dances down and melts away on Loughrigg fell. For half an hour gloom and coming sunshine wage unequal warfare, then the clouds to westward break up their solid phalanx, and wider and more frequent are the wheeling spokes of light. Here one blazons a scree-drifted hillside, there one peers and glances into a rocky ghyll. Broad streams of radiance flow into unseen abysms beyond the nearer mountain curtain, a flash of refreshing brilliance lights up acres of rugged scrub.

A GLIMPSE OF GRASMERE
Evening sun
By the rivulet we see the usual patient angler. Men there are so entranced in seeking to lure the trout, that they brave rain or shine indifferently. Under the hazels, when booming gusts clash walls of rain against mountain and bosky meadow, they still angle on; under the hazels you find them when from a sky of staring blue the sun beats down on a drought-struck land. This brook from happy, lonely Scandale holds many a small brown trout; its bed is bright and shingly, with clean swirling pools and glinting, tinkling rapids. The road now enters Rydal park; miles of rough land stretch toward the lofty ridge from which a cloud is drifting slowly. The sun has now the victory, pouring a flood of joyous light on a scene of unparalleled beauty, and this fleecy, crawling monster is the rearguard of departed gloom.
Near a fir-crowned hillock we see a picturesque 32 group of mountain ponies. The Le Flemings of the Hall have ever been upholders of these useful little animals, going to great trouble and expense to improve the breed. The well-selected Rydal stallions are admired in the dales for miles around. The farmers are not keen to part with their best stock, so the standard, though not yet entirely satisfactory, is creeping upward. Rydal beck hurries beneath the bridge, bank-full, its tiny surges shaking the plumy water-grass, whipping the too-pendant branches. The Rothay, close to our left, is a greater volume, but calmer, clear and shining where the sunlight dapples through the wych-elms, darkling in deep pools in the dense oak shade. The stream carries flakes of foam, and from ahead we hear the water purling down a rocky channel.
A few yards on, at Pelter bridge, a cross-road passes under Loughrigg. Looking up-stream, from the parapet, it is a lovely confusion: the beck, overhung with tall sycamores, ashes, and oaks, is split into tiny currents, each babbling its merry way down through a maze of boulders. Some of these are crowned with grass, over which in due season dangle the dainty blue harebell, the yellow-irised oxeyes, the crimson-spiked foxglove, or the blue-orbed sundew. In the margins goldilocks show dark tufts of leaves; when these are in bloom, the waterside is gay with brilliant yellow. Some of the river-stones are decked with moss—the gurgling, dashing streamlet occasionally tosses a tiny jet of spray to gem the glossy crowns. After a long spell of drought Rothay shrinks almost from view in this labyrinth of pool, wee cascade, and calmer channel. The riverside is almost too beautiful to lift the eyes from, but a sharp crag of Loughrigg sheers against a rosy cloud of eventide to our left, and on our right the great green mass of Nab Scar almost overhangs the cottage in front.

WILD HYACINTHS
A cottage by Rothay! Wordsworth’s Rothay! In far-off climes and dusty, choking cities many pause in their eternal soul-grinding struggle and think of such sweet retirements, even when the scene is merely a figment conjured up by the poet’s craft. To such as know Rothay from its source in the craggy fells to slooming Winander, the feeling of envy is more acute. It is a glorious stretch of country, alike calm and beautiful, stormy and forbidding; in spring tinged with delicate green, in summer wreathed in blossom of pink and white and blue; in autumn shot with crimson and gold of dying leafage; in winter grey and dank with rain, or garmented in dazzling snow. But the cottage!—clung with the bines of creepers and eaved with glossy ivy; the lowly little cot where the tallest hollyhock peeps in at the chamber window; the old-fashioned garden laid out in neat beds of showy or sweet-scented flowers, with gay gladioli spikes of puce and white, and fuchsias red and outbending, with balsam and balm and the sweetest thyme; the rockery with green caressing films of parsley fern, the smooth tongues of scolopendrium, and the broad palmated fronds and upstanding 34 brown “flowers” of the royal fern, with the wiry, graceful forms of oak and more robust-looking holly ferns; the wall-garden where white rocket, yellow musk, and a few hardy plants flourish, with rare mosses garnishing their fountains of bloom, and the half-wild turmoil of king-cups and “cross-buns” in the miniature pool of the Rothay. But the cottage!—with twisty oaken beams in the ceil of the parlour, with dark recesses and low windows, with a wide fireplace, to which, when winter’s roar and rain and snow run riot without, the chairs can be drawn and the many-houred evening drift away in happy talk and song and merriment. “Plain living and high thinking”—one could almost realise the ideal in such a home, where the fare is the humble, wholesome product of our mountain land; where thin haver-bread, tough, sweet cheese, and warm, pure milk might form the staple food; a home where the spinning-wheel might awaken from silence and dusty limbo, and give a perfect employment; where linen and wool might be worked up to thread and yarn in quiet hours. Such a prospect is fair beyond words, but few of us will ever dwell—save in our roseate dreams, by day or night—in a cottage by Wordsworth’s Rothay.
After a time spent beneath the trees and by the gushing waters, where viewpoints ever more fair allure us from one coign to another, we return to the road, here avenued by giant beeches. The western light touches a moving cloud, the damp, coppery leaves below catch the glow and throw it in a myriad little sparkles from twig to branch, and from branch to smooth bole. What is there in Nature more glorious than a group of well-grown trees?
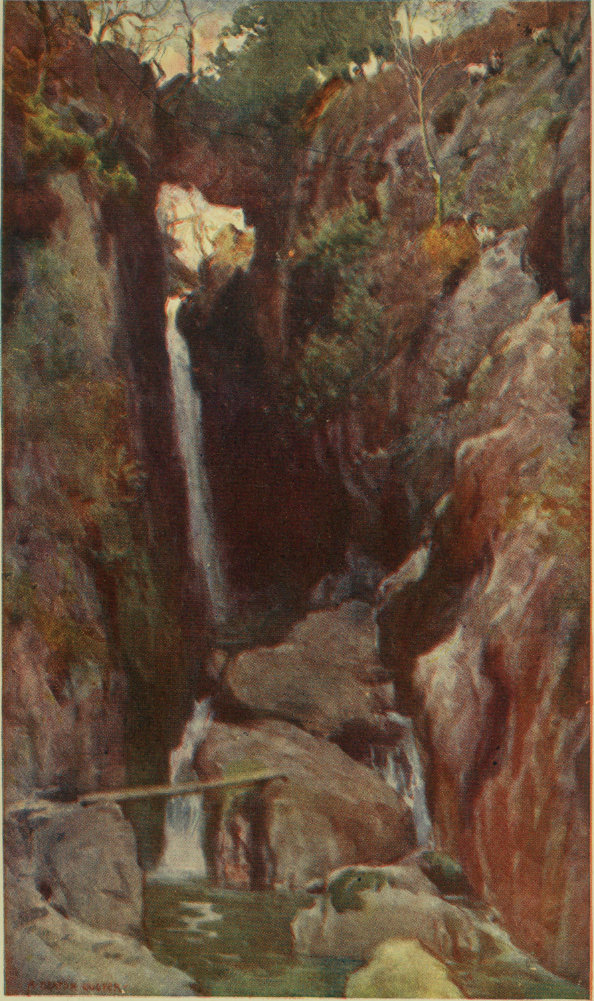

DUNGEON GHYLL FORCE, LANGDALE
Wordsworth’s connection with the hamlet of Rydal is well known. In his pretty cottage on the hill he lived a life apart from the dalesfolk, watching the seasons come and go over the beautiful glen. Through the little knot of houses, we shortly approach the mere. Right up to Silver Howe the basin is brimmed with light; mountain and wood and lake are at “the pride of day.” Evening, sweet and slow, is dropping nearer, its first sign the grey-blue mist hovering beyond the bordering hills. The crag on which the Laureate of the Fells often sat commands a good view of the lake, and of a huge gash in Loughrigg, whence comes the sound of tinkling slate, where the quarry thunders ring. This of course was not so prominent in Wordsworth’s day. The cottage at Nab where Hartley Coleridge lived, loved by the dalesman (as his master was almost shunned), comes next: here De Quincey afterwards resided some opium-cursed years. We wander by the reedy mere, noting the islet on which not so long ago herons used to nest among the tangled trees, then take the road again for home.
It is unfortunate that so many see Lakeland from its main ways only. They realise its narrow bounds, but cannot justly appreciate its rare beauties. For a week or two such travel our macadam roads; they climb the most frequented mountains, visit ghylls and tarns and waterfalls, wander by the favourite lakes: then away they pass, believing doubtless that Lakeland offers nothing further. Could they but come again, and discover our wealth of bypaths! Why I, a native of and dweller upon the soil, have spent the leisure of a dozen years and more in exploring without wearying, and know that many corners remain unvisited. To those who have seen Lakeland in hurried guise, I would say come again, avoid the sights noted in prose and verse, go elsewhere where you will, and at the end you may feel, with me, that less-known scenes make the “cream” look not unlike the watery dregs of the milk-pail.
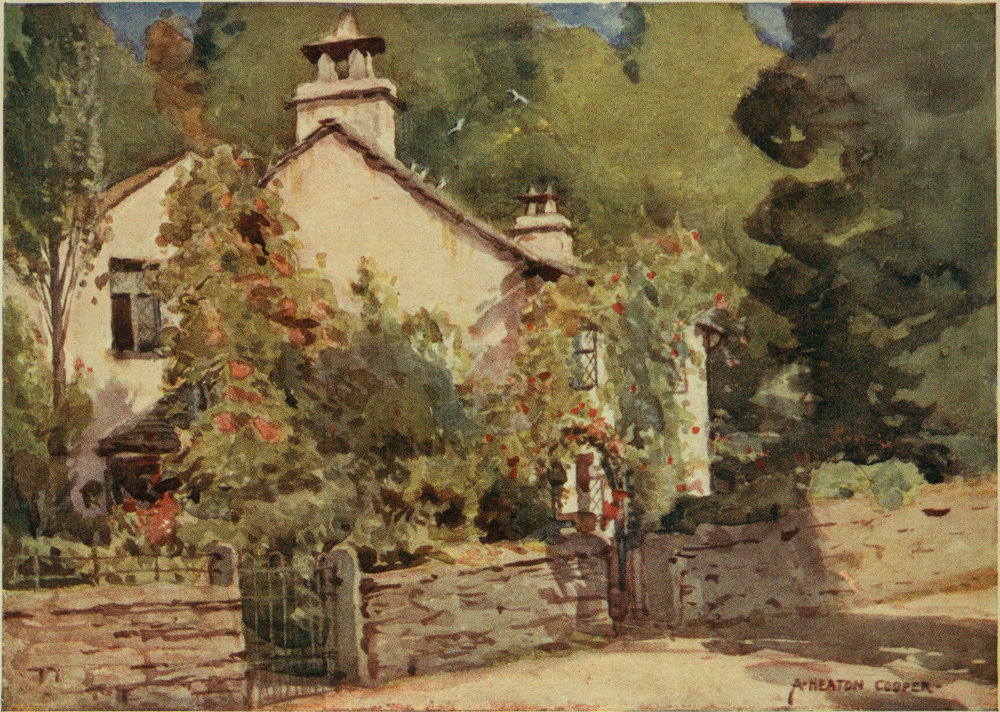
DOVE COTTAGE, GRASMERE
On a cloudy morning we came to Rydal and turned up the road to Wordsworth’s home in old age. At Rydal Mount he produced some of his most characteristic poetry—short pieces such as “The Clouds” and “The Mountain Echo”; at Dove Cottage “The Excursion” and “The Prelude” were penned. In Wordsworth’s day the road in the glen did not send up an almost ceaseless clatter, and seldom did the steam plume by Waterhead pier meet his sight. The poet had an aversion to the larch-tree, an exotic then being planted extensively in the dales, and did not care much for steam and the work of the engineer. The trees in stiff lines and squares make hideous the mountain slopes to-day; but see them growing in romantic irregularity, as by Thirlmere, and you will believe that Wordsworth might have conceded a beauty to the larch. And there are things more hideous than steam—for instance, the petrol motor. Rydal Mount is not a museum: its grounds are kept private. It is a simple dales dwelling in design—round chimneys, lead-glazed windows, grey walls without, low-ceiled, raftered rooms within: its well-planned gardens are the only characteristic to mark it from many other abode of “the bettermer mak” of yeoman folk. Enthusiasts often run up from the road to peep over its shrubs and gate, but most tourists go heedlessly by this retreat of the aged poet. From the garden where the poet composed his verses—“bumming and booing to hissel,” says one who recollects him clearly: “bum—bum—bum—bum, and at every bum he maid a step forrit, mebbe six or sebben steps; then roond he wad whirrel and gang back—bum, bum, bum,—happen just as many times. It didn’t matter to him whether he wor in his ane garden or on t’ fell or on 38 t’ roo-ad,”—there is a grand view. Down the glen to the lake, darkling under the massed clouds, over the woods of Rydal and a corner of the mere, Loughrigg and, dimly seen through rolling mists, Crinkle Crags and Bowfell. Would that a gleam of sunshine would kindle the grey and brown and dull red of dale and fellside to silver and russet, crimson and gold! For it is late September, and the glory of autumn is about us.
I have read many “interviews” with the aged Wordsworth. Some writers have seen him in idealism; others in a matter-of-fact light. A third class, bent on decrying his worth, have conjured up overheated visions of an uncultivated, unmannered man, calling to question his genius, his mode of living, his person. But some humble scribe, long before the poet was removed by death, penned the following. He had no difficulty in reaching the Laureate; a request at the door of Rydal Mount for a short interview was answered by the poet himself. “He took me by the hand in a way that did me good. There was welcome in his words and looks as well as in the shake of his hand, and in less than five minutes he was taking me round his fairy dwelling-place and pointing out to me the most striking objects of the beautiful and glowing scenes around. He was rather tall and thin, with a countenance somewhat pale, and more thoughtful than joyous. Simple and courteous in his demeanour, and frank in his remarks, he made me feel at ease. He was just the man that I had 39 imagined him to be from reading his ‘Excursion.’” The same writer, looking into an ivied and moss-grown unused quarry near White Moss, expressed his pleasure at the sight. “Sir,” was the poet’s response, “all might find these secluded temples of beauty, but all will not give themselves the trouble to seek them.” The path which cuts along the breast of Nab Scar turns to the left just above the poet’s home, between it and Hart Head, name reminiscent of days when its holder was forester on Rydal fells to Le Flemings of old. Looking ahead, we see a rough road climbing up to as wild a piece of fell land as we have. It is another haunt of the shepherd, a land bleak and wild—the ravines of Rydal Head and the great crags of Fairfield, fit home for wild red deer. Fit home too for the half-wild, little Herdwick, that atom of sturdiness fit to live in a land of storm. Two months hence there will be a day of days in wild Rydal, when the shepherds clear their heafs of the flocks. The work begins ere daybreak, and lasts sometimes into the night following. The sheep dogs, obedient to the calls of their masters, range the whole fellsides very completely, driving down the sheep as they are detected in ghyll or by bog. The work is arduous for both men and dogs, the exact equivalent of the work in miles and altitude ascended being often tremendous.
Our way, however, is smoother, easier than this. We skirt the grounds of Rydal Mount: from a higher bank we look over its round chimneys on to the green 40 glen below, on to Windermere, the river-lake, winding away between bluffs bronzed with fading foliage, to be lost at last in the heart of them; we look along the rocky edge of Loughrigg, where the dying bracken shows the approach of autumn. We are walking in a forest of stumpy oak-trees, the twisted heads of which speak eloquently of the power of the winter gales on this exposed fell-end: below us, with its long, narrow, wooded islet almost dividing it into two portions, is Rydalmere. From the outlet in Rothay to swampish White Moss it is in full sight, and of a kindlier hue than was chill Winander, which a corner of Loughrigg has now shut from sight. The breaking mass of cloud over Langdale Pikes is letting in the full day. On the road beneath, even thus early, the mad race of vehicles has begun. No one seems to be able to go slowly by Rydalmere, save the lumbering carrier’s cart. Once all the ordinary passenger traffic of the country was carried on these slow conveyances—I can see a merit in the method now. The coaches sweep you along at a fast trot; one gasps at new things that are gone ere he comprehends their beauty. And now we have motor-traffic, a series of giant ’buses followed by so many pillars of dust as though they held out the rallying signals for a world of traffic; these excel all in soul-destroying haste.

SKELWITH FORCE, LANGDALE
Our path clears the woodlands; there is now an uninterrupted view of the lake. Above the farmstead where De Quincey and Hartley Coleridge lived, the folks are busy making hay. In our glens this, the only harvest, is of great importance: unless it is well secured the supplies of winter forage for the flocks are scant and often much suffering is caused. The flocks are kept on the lowlands till late May, so that the crop is not sufficiently grown to be cut until late August and sometimes September. At that period the weather is so apt to be unsettled that, when once the grass is mown, almost superhuman efforts have to be made to house it. A few hours lost may mean that the farmer has to watch his crop soaking and wasting for a fortnight or more. My Southron reader will hardly believe that not infrequently whole fields of hay cannot be gathered in and are utterly lost on account of foul weather; in wet 1903, the acres of Lakeland meadows which yielded no crops for this reason, to the writer’s knowledge numbered thousands; and instances of carting the hay on sunny days in November, December, and even January were woefully frequent.
A little way ahead the path passes into a wilder scene. The woods close in from below; above, the brackens sway over a maze of broken, downthrown stones. The foot of the cliff is not many feet above, a block of limestone broken into by narrow spits of grass and bleached tongues of scree. Among the rocks a few sheep are feeding; as we approach they rush away, picking their way accurately and neatly over the debris at a great pace. Hereabouts on a winter’s morning you may be fortunate enough to surprise a fox, blinking and slinking away 42 to some deep hold in the mountain after a night’s marauding. Every score yards gives a fresh view, a new angle of vision to the glen, the lake, and Loughrigg scattered o’er with purple waste of stones. Here we come to White Moss of the three roads, from which Dr. Arnold took his famous political allegory. That way twisting up through the boulders, climbing steeply and ruggedly over the top of the hill, well-nigh impossible to wheeled traffic, was his Old Corruption. Here another route swings up the hill, on a level keel certainly, but it climbs a great height and is far from easy—that was his Bit-by-bit Reform. Along a bold terrace a third road sweeps; it surveys the knot in front, passes the foot of Old Corruption with a puzzled glance as to what manner of man prefers such tortuous ways, comes to Bit-by-bit Reform and has half a mind to go that way, then remembers its destiny to carry traffic without labour or danger, and curves into the pass, avoiding the knot altogether—Radical Reform—scotching the hill of Privilege and Abuse. The cottage on the hillside is the home of our most noted trail-hound trainer, Steve Walker. A word as to his craft is not amiss as we near Grasmere, the home of fell-head sports. True lovers of the hound genus, the dalesmen are not content to let them slip out of sight in the summer, so have evolved a mimic fox-chase with a scent of aniseed. The course is laid round a rough daleside, the hounds loosed. It would be impossible for the fleetest horse to live long with them over such terrific ground. A circuit of six miles is often covered in little over the half hour. To train the hounds to so great pace is a recognised craft, and Steve often has half a dozen hounds in his hands for different owners. It is not an unusual sight to see three of his charges running neck and neck for the blue riband of the sport at Grasmere. The training is severe; pace is required and also strength and staying power. The food given is plain and strong; several hours each day are devoted to outdoor exercise. The trainer with his leash of hounds is a frequent sight on the Lake Country byways. Twice or thrice a week the hounds are put over a short trial course and their progress noted with care. The sport has a fascination for the dalesman-born, and I must not dwell too much upon it.

SUNSET, RYDAL WATER
Grasmere Lake will shortly be visible over the tree-tops, but we seek a more striking approach. Therefore, sinking the hillside, we cross White Moss, down to the footbridge spanning the prattling Rothay. It is an angler’s path we tread; this length of water should be famous, for white-headed rodsmen tell legends of mighty trout, up to twenty pounds weight, which used to come from Windermere and Rydalmere to spawn upon the beaches here. Shortly the wood is cleared, the sunlight is touching Helm Crag in steady blaze; it comes forward to Silver Howe, and in a few seconds the rushing rivulet by our side is sending out myriad sparkles of glory. The sky has cleared, and there 44 is prospect of a fairer day. The lake of Grasmere lies in a perfect basin, and, though its sweet retirement is somewhat marred by too many buildings, yet the glen for a greater part of the year remains a pleasant nook. From the shingle we stand upon, the head of the Rothay ravine, there is a beautiful view. In front, Silver Howe, to its right Helm Crag, then Steel fell, the gap of Dunmail, Seat Sandal and the stony backs of Rydal fells; beneath them are many lower hills, cut into by tiny level glens and narrow watercourses. But this sunny autumn morn the eye takes in the atmosphere of the scene even more than its component features. Thus the peaks soaring into the gleaming air become less important than the glorious woods at their feet. Autumn’s gorgeous art is vivid on fell and wood and meadow. The beauty of the scene lies in Nature’s harmonious blendings, and one feels that only the poet’s imagery can describe the scene. Silver Howe is pictured in two-thirds the width of Grasmere; at our feet a feathery cloudlet sails in a second sky. So clear, so perfect, the counterfeit that even the charming mystery of height remains. The summit curving against autumnal blue, the purple crags, the screes, here grey, there blue, there a finer tinge where rock, grass, and heather meet, the turgid flood of colour where the bracken is dying, the solid green of the larch woods, the softer plumes of birch, the fiery oaks, the fading green meadows, are all in this peaceful mirror.
There is a chunking of oars, and shortly across our 45 range of vision there swings a small boat; it grounds a few yards away, a boat from the hotel carrying a visitor to the Loughrigg side. We hail the boatman, and in a few seconds have hired him to take us out on to the lake awhile. What a splendid picture the glen makes from the island! The village church towers above a knot of grey buildings across the meadows; the hills around all seem to be higher; the feast of colour is even finer than that seen from the foot of the lake. Above the eastern shore the woods, a paradise of varied tints, lit up by the bright sun, rise to the Wishing Gate. Then back again we are rowed. There are plenty of brackens here to give a flush to the hillside, but we avoid their tangle. Among the boulders the hardy sheep are grazing; no other animal could nibble and thrive on the short, slippery grass of the uplands. As we turn, the lake seems to have narrowed; really more of the level valley is in sight, and the mountains are discovering themselves in their true magnitude. When Red Bank is reached, the view is at its widest; over the gap of Dunmail is seen a blue portion of Skiddaw forest. As a dalesman, it must be confessed that I am somewhat impatient with our “show” scenes; they tell me few stories, arouse few reminiscences. It is on a foxhunt that my memory pauses, when we streamed off over the rough slopes toward Silver Howe—a grey day of winter, not a morning in full autumn. One sees but little of the lake in descending to Grasmere village, just outside which 46 is Pavement End, reminiscent of our “Sports.” Here for at least thirty years was held our great athletic festival—the “Derby of the Dales.” Here were seen our fell runners, our pole leapers, our trail hounds, our wrestlers in the true mountain style. The course of the old fell race was up the rough hillside, “that precipice,” as our Southron friends call it. Had I space I would say much on this topic; the sports are held on another field now, and—shades of the past, you giant athletes of Cumbria!—the race is now run on less difficult ground across the glen.
At Grasmere, beneath the yews of the kirk-garth, the poet Wordsworth is buried. Rothay murmurs near by. The church is not yet “restored,” and remains simple as in the days of Wordsworth. There is a pretty custom here (and in other dales) known as “the rush-bearing.” Many years ago our chapels were not floored with timber, the earth was merely pressed hard by the use of generations. Damp struck up on wet days, and chill in winter, which rendered worship uncomfortable. Rushes were therefore strewn on the floor at the approach of winter. Time went on, the earthen floor was superseded: instead of the old gathering of rushes for use a festival has been inaugurated. The children of the glen weave rushes into crosses and bouquets, go in procession to the church and lay their offerings by the altar there.

GRASMERE CHURCH
Grasmere is in itself without especial charm to the visitor. It is too busy to grow beautiful; romance has stayed away, commercialism reigns, and I for one do not care a fig for the place outside its connection with the poet, with its great possession, his grave and its grey-towered church. But Grasmere as a centre for rambles is unparalleled.
My last glimpse of Grasmere was in wintry weather, and from the Wishing Gate. No snow had fallen; the frost-rime covered the valley with white, though the southern facets of the uplands, on which the sun had spent its feeble power, were stiff bronze. The lake was partly frozen, the westering light gleamed on ice and the dark patches of water here and there. The woods, last seen glorious with autumn tints, were now sere and thin. The silence was divine: no rumbling car passed on the road beneath, no sound of voice broke the spell. And bending over the frosted bars of the gate I wished Grasmere’s peace and content—and mine own. Turning away at length to pass over to sweet Rydal Water,—oh! banished was the dream from my mind, for a house new-built on the moor-edge peeps curious eyes through the plantations at the sacred corner of the Wishing Gate. Truly it is a commanding site; perhaps the owner is proud of a choice which gives him views of Grasmere and Rydal, Loughrigg and the Wishing Gate—I cannot justly rail at him, but my unreason wishes his dwelling far hence. From the ridge, with the level sunbeams around you, leaving the hollows veiled in misty blue, you look down upon 48 Rydalmere. Skimmed over with ice, except where busy rills keep open a few yards’ space, its levels steely hard, with a few skaters gliding among its islets, with brown coppice and white fields rising around, with the towering front of Nab Scar frowning at the softer slacks of Loughrigg, Rydal was a sight to remember. But its glory was all forgotten as I noticed the frost flowers in the roadside—are Nature’s largest or her smallest forms the loveliest? Is the spreading landscape as full of beauty as the flowers formed by frost rime round a casual sod in the wayside? I know not, nor care.
If, after a complete survey of our Lakes, one is asked which could be spared, there is little doubt that often Esthwaite Water would be the one selected: so uncharacteristic is it, so unlike the rest of the country. It is a lowland mere strayed into a district of crag and brae and foaming rivulet. I don’t wish to agree with such an opinion, for Esthwaite has its real beauties.
Esthwaite mere certainly possesses no bold scenery; its shores are regular, its bays sweep in smooth curves among the meadows. No ridges of rock jut into its waters, its shores are smooth and shingly. Esthwaite is the weediest, reediest of our Lakes, and at places absolutely the quietest, though a great main road runs close beside. But the vale of Esthwaite, with its old village of Hawkshead, is worth of notice. In no other case is there so much to be said about the locality and so little about the lake. High Furness has ever been wild and retired. After Domesday it was given to the Baron of Kendal as a chase for deer—possibly because the country was uninhabitable at that time. Then great Furness 50 Abbey arose, and obtained a wide right over this country-side. The Old Hall at Hawkshead was the home of the monks when they came to collect their tithes and harvests. With the fall of the monastery the Sandys family leapt to ascendancy. One Sandys in King Edward VI.’s time became Archbishop of York, and used his interest to procure a market, by royal charter, for the town, which thereupon began to flourish considerably. This Sandys also gave the old grammar school its foundation. The church on the hillside, standing like a watchtower above the grey roofs, owes much to the Sandys’s beneficence, but its interior is to the casual observer somewhat dull. Its register, giving a list of Burials in Woollen, is very complete, that curious old law passed to aid the woollen industry being rigidly observed for long in these parts.

ESTHWAITE WATER: APPLE BLOSSOM
To deal with present-day Hawkshead, there is the old church on high, its God’s acre now spreading from the narrow promontory on to the swelling hillside behind, the grammar school where Wordsworth was educated, and many an old house built in a fashion now long abandoned. There are curious nooks here and there, particularly near the church. One house, built with its upper story protruding on stone pillars to form a sort of penthouse, tells that here in happier days the “garn” or yarn was displayed, within the hum of the busy spinning-wheels, to the intending purchaser. To picture Hawkshead in its prime of two centuries ago is not easy. Though land was plentiful and even lay waste, the rigours of manorial law made it impossible to spread out environs on the sumptuous scale we are accustomed to to-day, so the little community was herded into the least possible space. Houses were built as near together as possible, with narrow entries not two yards wide passing between the squares; the main street was hardly broad enough to enable a coach to be driven along without fear of fouling some outstanding wall. Sunlight and fresh air were strangers, sanitary arrangements were nil, roadways, of natural earth, had a powerful range of suction assimilating sooner or later the masses of garbage thrown from door and window. Within the houses, ceilings were low: a tall man could not stand erect in the loftiest chamber. Stairways and passages were troublesome things to build, said our forefathers; so, when building the penthouse over the shop, many left the upper portion open, to form a ladder-reached balcony from which the sleeping apartments could be attained. What the huge rounded chimneys were intended for is almost a puzzle. The open fires, with that immense draught at work, could hardly throw off much heat, and firelight was an illuminant not favoured by our forefathers. All cooking was done in pans hanging over the burning fuel. One real attribute the spacious chimney had, and has. Across its throat, from bars, could hang whole sheep to be cured by “smoking.” Hung mutton, from a chamber fed with smoke of wood or peat, is hardly unknown even now in our 52 wilder dales. The roofs without were slated with thin slabs of soft stone, locally quarried, for the hard grey slate was not discovered for the purpose then. Down the streets and across them at various places babbled tiny streams which, in their courses from the hills, alighted on the town. To pass these in time of flood, footbridges were provided for men, but how the great coaches managed to drive across their deep channels is a mystery. Looked at from a distance then, even more than now, Hawkshead would look like a grey blotch in the landscape. Though its population was more than at present, the old town was hardly half the width of the present one. One must have walked through streets with huddled houses on either hand awhile, then at once and completely have emerged into God’s country. The houses were close, mouldy, filthy erections, and the ignorance of the people was so great that these were preferred. The idea that anything could be more healthy than those fœtid rooms, poisonous smells, and filthy drinking-water!

AN OLD STREET IN HAWKSHEAD
In those days, too, hundreds of acres near the lake were swampy and almost impassable: there are many items in the accounts of the old town for maintenance of causeways across. The river was spanned by a wooden bridge, at first for foot passengers only, while the pack-ponies with merchandise ventured the ford. The vale of Esthwaite sweeps quietly down from the rugged hillocks behind Outgate in a wide sweep to the water’s head. The only building of historic merit outside the town is the Old Hall, now being used as an ignoble barn or granary. The walls remaining have been part of the gatehouse; tremendously thick are they, with narrow stairs climbing inside solid columns of stone, and with a fine fourteenth century fireplace in the upper room. The vale of Esthwaite has no story of war: the Scottish raiders never penetrated so far aside into the mountain land, and successive invasions by Romans, Picts, Norsemen, Saxon, and Norman have been without memorable strife, and hardly a legend of such actions remains. Near the head of the lake is the pool known as Priest’s Pot. No streams enter it, none leave, but the oozy ground around carries into it a sufficiency of water. It might, from the name, once have been used as a fish stew; though such a thing is unlikely, for the monks would have more convenient waters. In the Priest’s Pot was for years a floating islet, but there is now pointed out a bunch of sallows on a tuft of mossy grass against the edge of the pool, which has grown part of the mainland. The locals say that the Priest’s Pot is the measure of a certain dead-and-gone parish priest’s appetite for strong ale. Not a hundred yards from the Priest’s Pot is the meeting-house at Colthouse, founded in the early days of Quakerism. In Claife are one or two notable farmhouses, but nothing possessing a story. One of the grey farms on the other side of the glen was for centuries the home of the Sandys.
There are boats available on Esthwaite mere, but 54 the fishing is strictly preserved. For a shilling fee a day you are permitted to take coarse fish only. Pike are plentiful enough at some places, and many a trimmer is set in defiance of regulations. A summer afternoon spent on Esthwaite is a memory of some charm. We pushed off from the shingle near the ruined boathouse, and were soon well away. Then we pulled down to where a streamlet purls into the lake, and at the mouth of this lines were put over for perch, as bait for pike. But no tackle for sinking the baits had been provided, and our flighty thoughts turn meanwhile to the wealth of water-lilies and flowering grasses in a bay just below. So long as open water remained it was easy enough to put the boat along; but in a tangle of stems, when every pull at the oars means fouling and pulling plants up by the roots, it is hard work. The water-lily, with its heart of bright gold and ivory petals lying just awash the clear peaty water, is a queen of flowers. Beyond a profusion of these, tall, straight grasses rise like a brake over the boat, brown flower tufts crowning the straight green stems, a background of meadow tinged white and red and blue with flowers, and a coppice wood glorious with fox-gloves and wild Canterbury bells. The faint sweetness rising from land and water too is a memory to treasure. As we float idly along there is a variety of bird life to notice: the king-fisher and the dipper busy on the shingles and threading the narrow ghylls of the rivulets: further down we pass a heron, standing 55 poised and still in the shallow. Time was when the heron was more plentiful in the Lake Country than to-day; the heronry on the shore of this water, as that of Rydal, has been tenantless for many a year. A few pairs still resort to the firs near Whitestock Hall for breeding, but the only great heronry left is at Dallam Tower, some leagues away. Yet from the hills above Esthwaite you may, during winter, watch the birds rise when evening is falling, and flight away toward their great haunt and home. The woods fringing the lower part of the lake are used for the preserving of the “wild” duck. The sedges are haunted with these, and also with coot and waterhens. Sit still awhile and they will come into sight. Truly to the patient man nature is free with stories and secrets. In ten minutes the shyest brood of ducklings may paddle fearlessly within fifty feet of you, and often birds are daring enough to dive under and about your craft. But keep still! The first movement sends the whole company fluttering into the sedges, and they will be long in coming out again. The water is split into a hundred little wakes as the birds dash along, half flying, half swimming, in terror. In winter perhaps finer things are to be seen. Attracted by the plenty of their kind, ducks from northward, mallard, wigeon, whistlers, come circling down to Esthwaite: wild geese whistle about the dark waters, and the clanging of swans resounds during hard weather from the air above, where in triangular packs they breast southward, or from the lake, where in 56 wary little groups they feed near the other birds. But it is a hard winter that brings swans to Esthwaite. The country about this lake-foot is the only real haunt of the badger in the Lake Country. A gamekeeper of my acquaintance says he has often traced the badger’s prints in snow-time, from his domain at Grisedale to the earth near Esthwaite Lodge. The badger does not provide regular sport for the dalesmen, but only a few seasons since a pack of foxhounds ran a hot scent into a well-known borran here. Terriers were slipped and “found” within. As the “fox” would not bolt, it was decided to dig him out. The fight had rapidly shifted far into the ground, so an attack was delivered on the rear of the piled stones. Ere long a dalesman, outstretched in the narrow tunnel, espied a moving of earth ahead. “Hold hard!” he cried, “this is no fox.” Terriers were still at work, and sounds of their barking with an occasional animal cry came from within. In five minutes Brother Brock prepared to bolt, but a sack was ready for his reception, and as he came with a rush he was caught. Not he alone, but also one of the terriers who still held on to his rear.

SHEEP-SHEARING, ESTHWAITE HALL FARM
Our boat is now pulled up the Sawrey shore: to northward great fells shoulder the sky, and as the wavelets rumble beneath I think of the boy-life of Wordsworth. He was educated under the lee of the old church here, and in this vale began that deep study and appreciation of nature which shows itself in his poetry. Wordsworth is at home with nature: he speaks of birds, of animals of the covert-side, of flowers and trees, and the ever-changing glory of the skies and seasons, in far more convincing manner than of the people he dwelt long years among. In his school days it was customary to adjourn school of a Shrove Tuesday that cock-fighting might be practised. With spurs of sharp steel fastened to their natural weapons, the selected birds fought in pairs, till one was cut down and disabled. The sport was cruel, for the pluck and tenacity of the birds made the contests more often to the death. The winner of the “main,” or rather its owner, was hailed captain of the school till another champion gained victory. Wordsworth ever writes with fondness of his boyish days—of riding across the fells, of skating on this mere, of nutting and bird-nesting expeditions to the unchanging, yet ever-changing woods around. There is no story of his school days save that told in his own work; but he admirably portrays the shy lad he was, his comrades, and his successive schoolmasters.
Here, floating across the water level with ourselves, is a swan: how graceful its progress, how white the half-lifted wings as it keeps pace! Calm idyllic beauty is its charm, and the charm of Esthwaite mere.
One scene characteristic of Lakeland comes before us at the outskirts of the little town. It is the country carrier, a lusty, embrowned, genial man, and his large covered cart within which in picturesque (but safe) confusion are the parcels from a larger town to our vale. Storm or calm, rain, shine, or snow, so regular 58 that events are timed by his appearances, passes the carrier along the roads of this land where are no railways. An old farmer, selling some sheep to a dealer, asked when he would take away his purchase.
“Will it do if I come about the seventh of next month?”
“Oh aye,” but the old man looked puzzled. After the dealer had taken his leave, a reflective voice sounded from the ingle-nook.
“T’ seventh o’ next month! That’ll be——” and for awhile the old farmer counted on his fingers, but without satisfaction to himself.
“That’ll be t’ Tuesday after t’ carrier comes, father,” announced a matron who was washing dishes at the far end of the room.
“Aye,” responded the old man promptly, “that’ll be three weeks to-morn; t’ sheep’ll be ready.”
This is not an extraordinary thing to hear in our dales where the list of “inevitables” is: Rent-day, Candlemas (February 2nd, when all accounts are rendered), and t’ Carrier.
The carrier’s life is an arduous one, yet we have whole families who succeed one another in it without a break. Our oldest “carrier” family is to be traced in manor-rolls far into the pack-horse days. The halting of the railway on the confines of Lakeland has preserved, and indeed given impetus to, his craft. He is a necessity to dales-life, but now he is perhaps doomed to totally disappear. The new traffic companies are hoping to send their motors, humming 59 and throbbing, with loads of parcels into the villages and over the passes. As a rule our carrier is a genial soul—he knows the gossip of a hundred miles of road. “We can neither stir dish nor spoon,” complain the daleswomen (who are keenest to hear his news and give notes of their neighbours), “wi’out the carrier hearin’ on it.”
On a sultry afternoon, the wanderer over High Cross from Hawkshead suddenly sees a gulf beneath, a delectable vision of waters, the ancient Thurston mere; a lake of shining silver, chased with darker lines and patches as faint catspaws play here and there, with calm pools irradiating the sunlight like clusters of diamonds, the glow fining down to a distant wisp of blue threading between hills and woods. The setting is lovely as the gem: fertile, swelling farmlands, with here and there a white-walled home peering through its curtain of sycamore, the venerable grey church behind its yews, and the village straggling around its God’s acre. Often so ethereal seems the beauty and repose that one fears that tree-shaded bays, white beaches, and spreading reaches dotted with a shimmering sail or two, will yet dissolve in the disappointment of a mirage. For the road one walks is a dusty ribbon over a parched moor, the grouse cluck drowsily in the heather, the rabbits lop lazily into the furze—the larks alone sing briskly, for they have climbed to fuller life in the highest heavens, far from the slumbrous world around us; the mountains afar off swim in haze, their scarry sides uncertain seem, but down there is the fruitful valley of the lake, with dancing rills, fields of green corn, and its flowery meadows ready for the mower. Such is the delightful picture unrolled as a hundred yards are passed, then a corner of the hills shuts it from view.

DAWN, CONISTON
Coniston, the third longest of our Lakes, is perhaps the one most intimately associated with our earliest civilisations. On its placid bosom the Britons plied their coracles; they were keen anglers, and built their settlements near the lake-shore. Next came the Roman legions, to whose credit is placed by some the presence in Lakeland of that toothsome fish, the char. And after them, Norsemen raiding from the seaboard for harvests denied to their semi-frozen home-land, yet after awhile remaining permanent settlers on the soil. They built their boats of timbers from the forests around, and on Peel Island one erected a house, the foundations of which have recently been determined by an antiquarian. After the Norseman, the Saxon. And the char were taken up the fells to dark Gateswater, over which the golden eagle screamed and round which roved bear and wolf. The Normans after a couple of centuries of strife found the land comfortable to dwell in, but no baron ousted the native from his hearth. And the char had been carried further, over the pass beyond the haunt of the wild eagles to where the seafowl scream—lonely Seathwaite tarn. With the Norman came the forest laws and rights to fish the 62 lake. Nets were reserved to the lord of Coningstone, and the Le Flemings became a mighty power in the dale. The monks of Furness Abbey, not many miles distant, afterwards obtained great privileges here—a relic of their times is to be found in the shore woods. Down among the roots of the trees, deep beneath accumulations of leaf-soil, are red metal stains and nodules of iron. Trees were converted into charcoal by the industrious monks, and iron ore brought here to be smelted. A thriving trade was this long after it had reverted to the great families, whom it enabled to prosper during dark times. The ore was conveyed by the lake to the neighbourhood of the “bloomery,” and again was so carried to the waiting panniered ponies. Great rafts of forest trees also floated down with the slow current. All this while Coniston Water had been in unsullied purity. But a century ago copper was found among the fells and mines opened. Refuse ran down in muddy streams, tainting the lake from head to foot. Many fish died, for the shingles on which they had previously spawned were fouled, and, though ripe with ova, they could not perpetuate their kind. The damage was not completed in a season, but in thirty years, just as English law began to protect the finny denizens, the lake had been robbed of a great proportion of its fish. Twenty years more the mines continued to send down poisonous offal. Then the copper veins gave out, pollution ceased, and the fishery gradually improved. A few years ago it was gravely propounded as a fact that the lack of size in the angler’s spoils here was due entirely to the overcrowding of the water by the trout and perch! It is not many places where such an accusation can be brought forward. A large number of visitors annually come for the angling alone; and as they are seen year after year, no doubt they find it worth while from the sporting as well as the scenic point of view.

CHARCOAL-BURNERS, CONISTON LAKE
The lake-head is bounded by a mass of mountains of which the Old Man is the chief. On the east of the water too the hills are lofty, their lowest slopes a mass of coppice and larches, their upper braes wild and desolate. It seems odd to look down from these upland farms, where everything is sterile, on the soft, rich-looking lands of the lake-side.
Coniston Water is hardly less famous for the people who have lived on its shores than is Windermere or even Grasmere. To the challenge of Wordsworth and Coleridge and De Quincey, of Christopher North, Hemans and Arnold, it can reply with Tennyson, Linton, and, greatest and nearest of all, John Ruskin. If Grasmere reveres the ashes of Wordsworth, Coniston holds in no less esteem those of Ruskin—and the memory of the great is so much the more living. Every one almost in Coniston remembers Professor Ruskin, but few folks can recall Wordsworth. However, my concern is less with rival celebrities than with the lake and its natural surroundings.
To know Coniston Water well is to be convinced that one’s pen cannot describe it. The greatest master 64 of English descriptive prose, John Ruskin, after years of residence, left the task undone. Duty, however, dictates that some attempt must be made, and I cannot conceive anything more likely to give a fair idea of the lake and its surroundings than notes on a long summer day spent on its waters.
We breakfasted by candlelight—one of our party was a keen angler and had persuaded us to rising before the midsummer sun. Outside the cottage the air came cool and fresh, laden with the fragrance of the morning—honeysuckles over our porch and new mown hay, wild roses of the hedgerows and sweet flowers of our garden, larch woods and white-wreathed fields. The faint light just shows a sea of mist overhanging the lake, shows patches of cloud wandering among delicate grey-blue crag and mountain. Now we near the lakeside: the deep blue sky becomes dimmed by trailers of vapour. The boat engaged by the angler overnight is here; but, as he speaks of remaining hours in his almost motionless craft, and that is not to our taste, we select another, opening, after much labour, a link in the mooring chain and setting it free. The view when first we are afloat is curious: a bank of mist overhangs the lake; we can see the lower meadows around, but the mountains are invisible. Soon, however, we find the mist sweeping away in the dawn-breeze.

BRANTWOOD, CONISTON LAKE: CHAR-FISHING
Day is at hand, the dark hour of the morning watch is ending. One by one the stars fade away: a dark shadow passes up the sky from eastward, and the horizon there is being fringed with kindlier light. A cloud floating high above flushes from pearly grey to pink at its edges, to purple in its densest plume, and, as it floats nearer the day, to crimson, to red, and to glistening gold. And now we rest on the oars to watch the coming of the sun to the mountain tops. The fuller light has revealed a glorious scene: the horizon is a rugged sea of summits, lands of rocky steeps with torrents gushing down—Helvellyn and Seat Sandal, the Pikes and Fairfield, with, nearer at hand, Wetherlam, the Carrs, and Old Man himself. Shortly the coming sunshine touches one after another of these giants: Fairfield’s huge gashes where the foxes dwell secure are picked out in gloom and light before day bends to awake the Old Man from his rest. It is interesting to watch the band of sunshine gradually descend his stony, riven flanks. At first only the cairn has the glow; then shortly, a hundred feet below, shadow divides from light. So day breaks among the mountains. Purple shadows still remain in the hollows, the dark green of woodlands is softly dusked: on Coniston Water it is light, though the sun’s rays still linger aloft. “Come on,” grunts the angler at this juncture—the scene to him is beauteous, no doubt, but for his art most valuable minutes are wasting away. We heed him not, and shortly his oars rattle as he pulls for the bay in which the trout should be on the feed. Awhile we feast our eyes on sunlit mountains and shadowy glens, then our oars are plied to take us further down the lake. Quite close to the 66 shore is the Old Hall, once the home of the great Le Fleming family, but now merely a picturesque farmhouse. To Sir Daniel of that family was due the peaceful succession in the three north-western counties of Charles II. after the Interregnum. In Oliver’s day his house at Rydal was almost demolished by soldiers seeking a hidden treasure. To me Sir Daniel is more interesting as the first man to attempt to solve the life-history of the char of our lakes. In few particulars only are we able to improve his observations to-day. The char is the most mysterious as it is the most beautiful of British fishes. Though for three hundred years “silver” and “gilt” char have been noted, no close observer will say there are two varieties of the fish. Sir Daniel suggested that the two divisions spawn at different periods—November and February respectively—but the information then and now hardly justified the idea. During the midsummer months char are bottom feeders; in April and early May, and again towards the close of the fishing season, they occasionally come near the surface, and odd captures are made with the fly. Char average about nine inches in length and three-quarters of a pound in weight. A two-pound char is a great event among the lakemen. Potted char is quite a Lakeland delicacy, and commands high prices. In former times each inn had its stew into which the fish netted or plumbed were placed till a demand for them came along. West, touring over a century ago, mentions particularly the stews at Waterhead Inn, Coniston, and the Ferry, Windermere, as holding great numbers of char. Char pie was once a favourite dish too; in the Le Fleming house-keeping accounts, dating back nearly three hundred years, mentions are made of the large number of fish so used up. Char pie of those days is said to have been so full of spices that the flavour of the fish was neutralised out of existence. In the papers preserved at Holker Hall, a noble duke orders fish for a char pie to be sent to London without loss of time—in December, when the char would be spawning and far from toothsome!
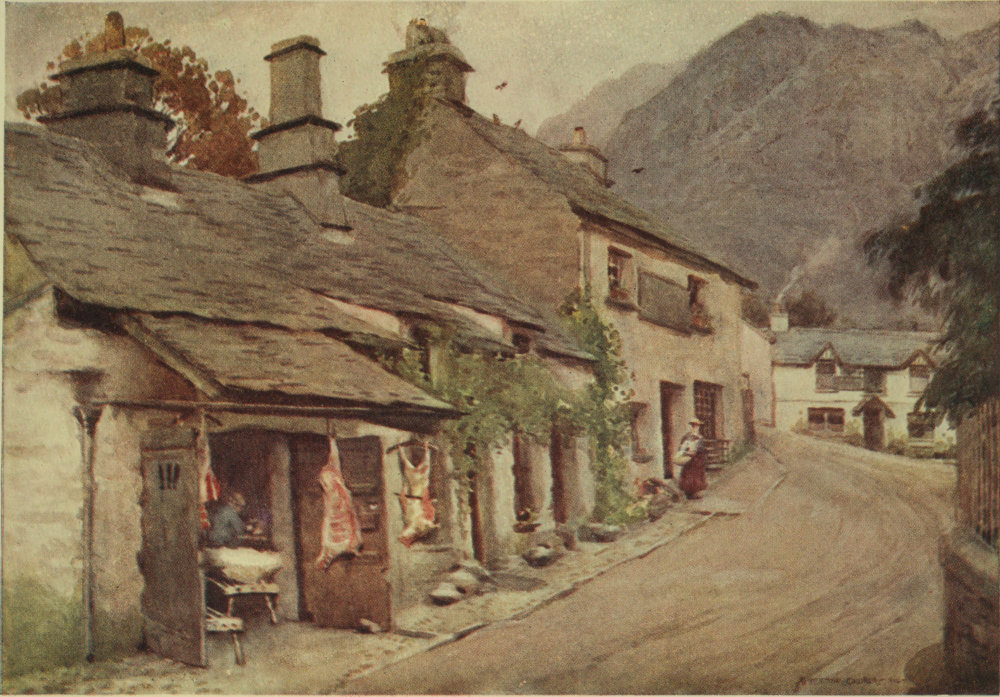

CONISTON VILLAGE: THE OLD BUTCHER’S SHOP
Now the light is falling in a wider riband; it has touched the top of Yewdale crags, the scarred Mines valley is brimming with radiance. How uneven that line where shadow meets sunshine! Still lower bends the light; it is now only minutes before the lake will be flooded in glory. The heights round Torver are in the realm of sunshine, but the larches of Brantwood side are green and unkindled. Not a breath of air disturbs the flat calm. Over the eastern hills the great round sun rolls into sight. Everything is transformed. The subdued grey light is expelled by shimmering gold, green hills and fields alike are suffused with a living blaze. A boat pulled out from the pier near the Old Hall is followed by a wake of pale gold, the oars drip diamonds, the curl of parting waters is like a crystal-crowned sapphire.
To see Coniston Water by broad daylight nothing is better than Felix Hammel’s handsome craft, though the commander will cheerfully admit that we, in our 68 pulling boat, had the best of it at dawn. The Gondola’s landing-stage is in the shade of some mighty oaks, an old cottage astride a shallow waiting-room with a jetty running out a few yards into the lake. The craft is of strange shape; at the stern, where the engines are placed, the draught is a yard and a half, but at bow—“There are few places on Coniston Lake,” says Mr. Hammel, “where I could not put the prow into the green fields while the stern was in deep water,” which, incidentally, shows the paucity of shallows. Mr. Hammel is fond of the engines which drive his taper-keeled craft along. “Fourteen horse-power, yet they drive the boat through the wildest gales betwixt April and September. I have sailed here for twenty-five years, and we have lost time but once. That was the wildest gale that ever smote this water. It blew from sou’-west, and there was a pretty lively water going. Not big rollers, but nasty short things that broke and shook themselves out into a cross-sea that would have made a pulling boat a mighty risky thing to be in. But the Gondola ran within five minutes of normal—the five and a half miles from here to Lake Bank we reckon to do in thirty-five minutes. That wild day it took forty. Only two days in my experience has the steamer not run. During the wet summer of 1903 the lake was so full that for two days the landing-stage was under water, and never a passenger got within two hundred yards of us.”
“I suppose you did a bit of fishing out of your windows those two days,” I commented. Mr. Hammel is an angler—as keen as ever.

MOONLIGHT AND LAMPLIGHT, CONISTON
“Hardly out of the windows, though of course I did do a bit.”
By this time the hands of the clock nearly point to starting-time; passengers are rapidly coming on board, and to hurry up laggards Mr. Hammel sends a flute-like note booming and swelling from the syren. Now there is a quiet rumble as the engines start, a purling of water beneath the stern, and the Gondola backs out into the lake. Tent Lodge, where Tennyson once dwelt, is almost opposite—a square sturdy house standing on a narrow green bank just above the water. The little landing-stage looks decidedly picturesque now; our craft pauses as though regretting to leave so happy a scene, then again the thrumming begins and we are swung round toward the foot of the lake. Far away two green banks contract till the water seems to end: Fir Island narrows the curving lake there. Brantwood is a pretty house beneath the fell, the views from its windows are splendid. Here Ruskin came to spend his latter days, in a house which had been occupied by Linton, the famous wood-engraver. The homelikeness of Brantwood is to me its chief charm: once a dweller in it, no mortal can, I should think, be so dead to natural beauties as not often to picture it, when far away, in memory’s freshest pigments. The eyes of all on board are turned to Brantwood—Mr. Hammel is speaking of it to a bevy of interested young ladies, the other 70 lakemen are pointing it out to those near them; but, seated on the knife-like ridge of iron where his stokehole joins the deck, the engineer is looking intently at the greasy jacket of his boiler! Instantly his posture captures my attention. What meant that strange position? Were we in danger of an explosion? The engineer’s back was eloquent of intent inspection, even of alertness. Nothing happened, however, and as none of the lakemen seemed apprehensive I did not allow that rapt gaze to spoil my pleasure further.
“Brantwood?” says Mr. Hammel, “and Ruskin? Well, of course I knew the Professor well. He wasn’t a man to laugh and talk much, though. For five-and-twenty years I have done odd repairs to Mr. Severn’s yacht at Brantwood, and I often met the old gentleman thereabouts. Mr. Ruskin did not like scrow [upset], I remember, and every year the family used to go down to Lake Bank Hotel till spring cleaning was over. Mr. Ruskin went with them, of course. Mr. Severn used to hire the Gondola, and we ran in to the landing-stage to take servants and luggage on board. Now you know Mr. Ruskin didn’t like our boat at all—I believe he used to write a bit bitter about it; but I remember once (it was in the seventies) when we drew it to the stage, that Mr. Ruskin stood there with Mrs. Severn and the family. I was surprised and some pleased, I can tell you, when he came on board. He went all over the boat, into every corner while we were steaming down, looked at the engines a long while and asked a lot of sharp questions about them—he knew a fair bit about machinery in spite of his old-fashioned ways and ideas. Then when we were nearing Lake Bank he came out of the saloon there, and as he passed me, said with a nice smile, ‘I may like steam after all.’”

AN OLD INN KITCHEN, CONISTON
“Do you remember any others of the big men who lived about here,” I ask my friend.
“Oh yes: there was Mr. Tennyson lived across at Tent Lodge awhile, and in the seventies we had Carlyle here at the Waterhead Hotel two or three weeks. He used to have the steamer nearly every morning for a cruise around. He was a pleasant man to do with, but quiet. They used to say to me that Carlyle never laughed, and Mr. Ruskin but rarely, but I know different. One evening when Carlyle was here, I was across at Brantwood doing some repair to Mr. Severn’s yacht that was drawn up on the slip. While I was working away, down from the house came Mr. Ruskin and Carlyle and sat down on a pile of rough stones beside the slip. I didn’t take much heed of what they were talking about, for I was thrang [busy]; but I remember well that I was surprised to hear a big burst of laughing. I looked up—it was Mr. Ruskin, and before my eyes were fairly clapt on him Carlyle roared out quite as long and loud as he. Then they sat there full a quarter of an hour, talking quite merry, and every now and then there was a crack of laughing as made your heart feel glad.”
At this Mr. Hammel steps away and takes charge 72 of the wheel of the steamer. There is little need of fine steering, for the water is deep and free from reefs.
We move along the crowded promenade deck to get a better view of the grand mountains clustering around. Like a sheet of blue the water stretches far away to meet the multi-shaded greens beneath High Cross. Yewdale crags are prominent, but the soaring ridges culminating in Old Man’s pointed top fill the eye most. Now the eastern shore is crowded with regiments of larches, growing where once the old monks burnt charcoal for their bloomeries by the beckside. On the right is Torver Common where never a wall is to be seen, and the lake-shore is fringed with rocks. Fir Island, a mass of Scotch firs or stone pines, anchored to a narrow rib of rock, has been passed, and now seems like a promontory of green. The woods on the mainland look delightful in this pleasant air, but the stiff lines of their planting is rather an eyesore. The coppice woods next succeed, in wide acres climbing to the skyline. These are allowed to grow fifteen years, then, when the saplings are about six inches thick, all are felled. The best wood is sent down to the mines to use as props; the other portions, after being peeled (for even in these days of chemical tanning bark of ash and oak and sycamore is still put on the market), are placed in neat circular piles in the centre of which a fire is laid. Then by a covering of wet turf the air is excluded. The fire has been sufficiently kindled not to be put out by the short supply of air, and it smoulders away for weeks. Much charcoal burning is done in the winter, and a pleasant scene it is to find on a snow-clad day lines of smoke rising from the barrenness where once was woodland, men moving round the conical patches from which internal heat has melted the white covering, the rough huts, the incipient flicker which has to be immediately quenched else the whole oven of charcoal be spoiled, the thinning smoke which threatens a dead fire there, to which the woodmen hasten to encourage the hidden blaze.

THE SHEPHERD, YEWDALE, CONISTON
Peel Island, alluded to before, is the place when in the time of the Sagas a Norseman dwelt, and a daring man he was to live on so low a rib of rock. In a wild gale the water, lashing its rocky sides, will throw spray right over it. In relief the islet is mitred; two rock ledges face the lake, leaving between a grassy depression some feet in depth. Our old Norseman built walls across this gap, then with poles and twigs from the shore-woods made a roof, and thereby obtained a home sufficient in its humble way to provide shelter in the wildest weather. In spring the glen of the islet is a mass of blue—with wild hyacinths. The lake is now becoming riverine in character, its banks are nearing rapidly, a picnic party seated on the rock-set shore wave and call merrily to the passing craft. The water is still as a pond, the reflections only broken in the wake of the passing steamer. And thus we come to Lake Bank, 74 the end of the lake for steamer purposes, and the point to which coaches drive from Greenodd and Ulverston. It is a change for a good walker to get ashore here, and by the Brantwood shore return—a walk of some eight miles.
At first the road leads down by the rushing Crake, then crosses. The traveller passes through tall-hedged lanes, past old-world farms nestling against sheering hillsides. Once there is a beautiful glimpse—a vista of lake, Fir Island in foreground, and far away the rising fells. Just as the walker feels that Brantwood must be at hand, the woods open a little; here is a point jutting out into the lake to which he can easily pass, a shelf of shingle, overgrown with wych elms and sallows, but from it is a marvellous view. Not too far for detail to be dimmed is Coniston Hall, the church and the village, Mines valley and Yewdale crags, Old Man, Wetherlam and a number of giant hills. In autumn particularly the play of light and shade among the woodlands is glorious. The road passes within a few yards of Brantwood. If the wanderer has time to spare let him leave the road by one of the paths he sees up the hillside. There is little danger of any one complaining of trespass if you should light upon a worn path that is not public. Rising some two hundred feet up you are above coppice woods, and come among the heather, enjoying an excellent view of the lake and its surroundings. How peaceful such a place at sunset! Once I watched the sun set in a haze of blood red: the lake turned like frozen gore beneath my eyes, the hillsides mantled in crimson, the outstanding spurs of rock were wreathed in fire, a purple shadow gradually gathered in the hollows. Then, through a ravishing succession of tints, the scene melted away till I was looking down on a lake with moonlight shimmering on it, edged by blue, rocky mountains.

STEPPING-STONES, SEATHWAITE
One scene more and I have finished. It is of mid-winter—and night. Day was dying ere we left the village; with a parting glish at the snow-covered church tower, the sun left the lower glen. Now the hills were pointed with fire; from the lake a blue vapour rose as the air chilled, to join the helm of feathery smoke gradually spreading from the village. The glen was snowbound indeed; from hedges and plantations came the rustle of slipping snow; a partial thaw after the snowfall passed gave us the roads fairly clear. There were many slippery places, but to the careful and robust there was pleasure in the prospect of a walk. Large flocks of sheep are crowded into the fields lying near the farms we pass; there a weary shepherd is still at work. On the higher farms the shelter of the plantations will have been courted; down here a huge rib of rock lies athwart the wind, and the fields have been but little swept by the storm. Almost the most arduous of a shepherd’s trials is after a long snowstorm. His flock have to be mustered; if the snow has drifted at all a band of ewes are sure to be beneath it, and these have to be got out. Then comes the problem of hand-feeding 76 perhaps a thousand. Hay and roots may be brought by sleigh, but the labour of distribution is great. The soft snow clings so tenaciously to the grass beneath that to walk a hundred yards in the fields is too hard work for any pleasure-seeker. The sheep are nosing down to the hidden grass: even in the hardest weather they forage well for themselves, though the gap between “feed” and “appetite” is often very wide. The lake looks blue and cold under its veil of soft vapour; a skin of ice is forming. There is a loud crack and a rattling echo passes along the frozen surface. Eerie it is so to hear the ice “stretching”: the frostier the night the louder and more frequent the reports. (In 1895 I was on Windermere after dark—it was a moonless night—and the loud and long continued roars which spread about the ice were almost alarming.) Soon we are in the byroad for Tarn Hows. The trees meet overhead, and if it were not for the white flashes of snow between them the way would be bad to find. The road is slippery, and time and again we have to leave the metalled part for the snow-banks to get on at all. The sounds heard in the woods on a frosty night are interesting. A faint rustle in the undergrowth as a small bird hops from one twig to another, a faint rumble and a sissing of snow as a rabbit bolts away, the thud of falling pieces of snow from the branches, the crackling of twigs as the frost nips harder, the blundering rush of a large bird through the curtain of branches, followed by a mimic snowstorm of dislodged particles; from darksome glades, the melancholy hoot of the wood owl and the shriekings of the barn owl, then from far away floats the chime proclaiming the hour, the cadence dying in sweet confusion over the tapering larches.

WINTER SUNSHINE, CONISTON
So far the way has been steep and the footing uncertain; now, however, we rise above the woods to the open hillside. The angle of ascent is less difficult and the snow firm to the tread. Our path forms a terrace above Yewdale. Beneath is a glen cumbered with snow; above, a sky liberally dusted with stars large and small, the gentle light from which is sufficient to kindle the jewels on the frosted snow. The air is chill, but our blood is too warm for us to be more than barely conscious of it. From a corner of the track we have an excellent view backward. The lake is still hidden in its curtain of mist, the dark woods of Brantwood side climb sharply into the white desolations. Coniston Old Man over the way—how truly near it looks!—is gilded by a new light; the moon is rising and the light spreads over summit and upper snowfield, over crag and bield and lower slack of white, finally touching with crystal the fields and houses in the deep dingles around. From one point we look over a wilderness of snow to other dales, but the expected mountain heads are hidden in pearly cloud. The tarn is covered with ice, and some time we spend sliding. Then to return, but first of all notice that grey moving blotch on the shoulder of Wetherlam. The glasses show a family of wild 78 goats. Villagers of Coniston tell of a herd of over thirty observed not many seasons ago, while groups of over a dozen occasionally tempt the keen gunster out on to the chilly wastes.
The goats, I am told, were introduced about a century ago in order to prevent fell-sheep frequenting dangerous cliffs—for a goat is safe where a sheep will turn giddy, and, falling, be dashed to pieces. By nature the sheep is divided from the goat, and will not browse the same pasture. For long it was a custom of the quarrymen of Tilberthwaite to assemble on Good Friday morning, and attempt to hunt the goats haunting the fell near by. But though a kid or so, weaker than the rest, might be taken, I never heard that much success accompanied these chases. The goats from Coniston fells wander in search of toothsome grass to beyond the Duddon, and there is record of an exciting hunt among the rocks of Wallabarrow for a wandering goat. In winter only do these animals approach civilisation; their usual haunts are the crags above sequestered glens. The snow crunches under our feet, and we speedily come down to where we again catch view of Coniston Water. Now it is clear of mist, the whitened fields, blotched with woods, limned with hedges, are in sharp contrast to the grey ice, and to the glittering unfrozen water in mid-lake. A glory almost approaching that of day spreads over the scene: the queen of the heavens is indeed “walking in brightness” here.

DAFFODILS BY THE BANKS OF THE SILVERY DUDDON
I never think of Wastwater without recalling some exciting hours—Wastwater surrounded by crag-set mountains and wide bouldery moorlands where foxes rule wild and strong. Under Tommie Dobson, that genius among fell-land huntsmen, a pack of wiry hounds has been raised in the bordering dales. In pursuit ruthless, untiring, determined; a chase from dawn to night, over country bristling with difficulties, is no unusual thing to them. Screes, miles of frittering mountain rampart, Yewbarrow, ridged like a Napoleon’s hat, Scawfells, impending over great piles of fragments, Gable; about these are benks and earths and borrans innumerable. Never a season do they fail the hunt; never do they fail for redskins to plunder flock and poultry roost. Then the wilds to Ennerdale—I had climbed the slope of Gable before the meet at dawn on a spring day, the crisp air became full of music—what finer sounds than those from a foxhound’s throat!—the turf was springy and dry, the sky flecked with high-sailing clouds. To climb the rocky terraces was delightful; to hunt—the exhilaration needs experience, it is beyond my words to describe. No pink 80 coat was in the knot of men below; and a follower on horseback is seldom seen at a meet by Wastwater. Hounds unkennelled as they left the short lane from the inn, and soon above the babble of eager questers rose the clear peal of a true find. To one line gathered the pack, and away! Not often does Reynard give so good a chance. Over the tall drystone walls surged the hounds, at first in a compact bunch, then, as pace began to tell, dribbling out into a line. Out of the fields, and into the intakes of Mosedale; and ever higher rose the note of the chase, ever smarter the gliding forward of the clan. A check! From Gable’s lofty flank I saw hounds halt at a dark grey patch of stones, circle it almost in silence. Reynard has gone aground; the huntsmen and the fleeter followers come up. The scent drew the pack in and out, over wall and beck, through dead bracken and crackling heather, three or four good miles, but the huntsman, judging the true route, reached the borran in less than a mile. The hounds called away, terriers are put “in” and possibly will have Reynard out ere long. Nowhere but in the fells are terriers really used after foxes—nowhere else, the dalesmen proudly say, are dogs capable of doing such work. After a considerable delay two white dots stray out on to the dark grey stones—Reynard has been killed in the dark recesses.

A FELL FOX-HUNT, HEAD OF ESKDALE AND SCAWFELL
The sun is now high, the cloud flecks are gone, the air has become warm. Long ago foxes ceased to be afoot, and hours of careful work by huntsman and hounds may be necessary to find another fair scent. But even the pattern of all wiliness, like the human votaries at his shrine, sometimes overreaches himself. After a tedious march it is refreshing to hear hounds speak to a piping line. Reynard, lying out in a pile of boulders, has heard the coming pack. He steals away—too late, for a keen-sighted dalesman has viewed him away. Ten minutes of frenzied rushing, and the fox is reached. Ruby in the van seizes him, and over go both at the impact. The hound, aged but plucky, loses his grip and Reynard is free again; down the scree, in the very access of terror, the redskin flies, but with a couple of bounds Chorister has him fast. The iron jaws crunch into the fox’s spine, and though together they roll near twenty yards the grip never falters. There is no “worry” at the death; the hounds, now that their enemy is dead, take little further notice of him. Ofttimes the death is compassed a mile away from the nearest follower, but occasionally a fair number view the finish. And to do this you may have to come pell mell down some rotten “rake.” We saw hounds stream over a patch of snow on a near-by hill: a dalesman pointed out Reynard dead beat a hundred yards in front. “The Gate,” called some one, “who’s going down?” Six of us rushed for the head of that precipitous scree-shoot. The angle of descent was terrible, but, hunting mad, we leapt and slid, stumbled and jolted down. A thousand feet plumb drop, with a hail of loose stones roaring behind us. The rake-foot was narrow, 82 between perpendicular rocks, and in single file we raced down. No one tried to halt; if it were thought of, the gathering pelt of stones decided in favour of forward. Shades of Silver Howe! In the madness of the guide-race you never saw the like of this. But after five minutes of real, tearing life—oh! it’s good to have lived through such a time!—we were running down the smoother grass. The hounds were probably quite close by—running mute for the death—and across the roaring, flooded beck within a score yards came the fox. We halted in silence—back up, tongue lolling, moving stiffly and with evident pain, he was the scourge of the fells, but a respected foe at that. Thrice had he been chased far, now came for him the end. Two outstripping hounds shot across a cove which was bank-high in snow, leapt at him, and all was over.
Wastwater, its bed hewn and filled by Almighty power in the beginning to contrast the silvern temporalities of a level mere with the solid, silent, rugged eternities of rock around. There is always some pleasure to the hale of body and mind in climbing from Wastwater, whether by pony-track, mountain-path, or dangerous puzzle route up the cliffs. In early October I had to cross to Wastwater from Keswick. In the golden glory of afternoon we passed up Borrowdale. One side the glen sloomed in dying bronze of bracken, the other was grey with nude birches below, chocolate with heather above. We left the main road and passed into the desolate mountain land. As the sun declined, clouds, at first mackerel but now dull and heavy with rain and night, floated majestically from behind the western mountains. Shortly in a low cloud cornice Gable’s head was buried, and billow after billow of mist possessed the higher ground: at Rosthwaite the glow of day, here the portents of night and foul weather. “Fraternal Three” and the old wad-mine took but a moment’s attention, then away, up the narrow dell.

WASTWATER, FROM STRANDS
Night fast closed round. Our last look back barely showed the curve of Borrowdale. Gillercombe, scored by tremendous ravines, presided over a scene of almost indescribable wildness. The wind roared and boomed above, the steady drift of fine rain was in our faces. Hoarsely down its rugged bed the beck sang in accord. Grey light and dashing water, with gloom intense above and a rain-sodden world below, our path uncertain, picked out by boulders. Bogs of sphagnum, sponged a foot high with water, runnels where in summer are hollows filled with wee splinters, the rills all shouting becks, and the becks flooding torrents. Our boots full of water, wet to the thigh, we still squelched on. In a while we came to a narrow footbridge, and crossed the chief torrent. “Where is the path?” I knew not, nor cared. Swinging bogs were all about; a grisly light crept through the clouds in front: that showed the pass-head, and was my guide. Now, we stood within twenty yards of Stye Head Tarn—what a scene! Half invisible, a patch of wind-spurned waters, dark 84 mountains sweeping upward, cloven by black ghylls, whitish beards of cloud stealthily moving along and hiding the higher ground in ghostly embrace. The sounds—the tongues of many waters, and the night wind weirding among crags and crannies. Ten minutes more, our path in a long curve swept down the rock-shelves toward the dale. What a gulf of gloom, the waterfalls roaring and possessing the night! Take care, take care, the way is full of stumbling-blocks, of pitfalls; to the right is steep rock, to the left a precipice. Over it—crane your neck and see if foothold is visible beneath. Such is Stye Head Pass at night.

WASTWATER AND SCAWFELL
We reach the scree where the route is safer, but at the zig-zags more than once overshoot the path. The clouds apparently are densest near the mountains, for beyond the rock-girt valley some brighter clouds render darkness almost visible. There is a dream of a grey Wastwater, a mirage of something not chaos beyond. A spark of light shows where the hotel lies, but it is far away. Some twenty minutes from the pass-head we find grass beneath our feet. Looking backward, there is a walpurgis of grey shadow and black night. Now the path is easier and we walk more rapidly, though frequently stumbles remind us that the path is far from smooth. The light—from hospitable windows—is nearing perceptibly. Now, in front, is a darker mass—the yew-trees crowding round a tiny House of God, shielding it by their tough green limbs from the storms. We were walking quietly in the narrow lane thinking of the gloom on all things made, when a white shadow beyond that of the dale-church arrested us. What is it? Memory hasted back a week to that most terrible disaster in the annals of Lakeland rock-climbing—the accident on the Scawfell Pillar. Four fine young men were killed, and three are laid here. A heap of white flowers, like a pall of mountain snow, masks the grave. Sadly impressive is the scene; the white wilting flowers represent fitly the brief human span of life—to-day we are, to-morrow we are not, thus is the will of God: the dense green yew-trees symbolise death, the time-long end of man. But look higher, I felt—around. “O death, where is thy sting?” for, though the mists of night bewilder, great rock-ribs are rising upward, higher, ever higher, till earth and heaven meet. And the yew of death will moulder by the kirkgarth, but the mountains must stand fast to prove eternity—immeasurable, infinite.
Wastwater, its shores treeless and forlorn, its waters rippling against their shingly bays, with mountains beyond and around, curtains of rock and ribbons of scree. In the cool days of spring the mountains are delightful, but sometimes there is a sudden revulsion to winter. A shade sweeps from nor’east, and behold a squall plastering all with snow, a gale shrieking around, and the temperature tumbling to zero. Such mischances apart, the bracing air makes a new creature of one after the fogs of winter, and you simply stroll up the ascents. So much has been written of 86 the mountain-climbing around Wastwater that to infuse romance, to say any new thing, is difficult. Steep ghylls there are to ascend, loose bands of scree to pass, bogs varying in depth according to weather. Here a rushing rivulet to ford, there, winding beneath crazy rock fragments, the path hangs on the brink of a deep ravine; collar work up five hundred feet of slippery grass, and splendid poising exercise over beds of boulders. When winter holds sway and a white garb hides the bloom of meadows and hillsides, Wastwater is a very home of loneliness. Its surface is no home for the wildfowl from northward: a wastewater it is to them and not worth a minute of the foody, oozy sands of Irt and Esk, seven miles away. Loneliness and silence. When the babel of the flock in the intakes ceases to the ear, the absence of all sound will depress the liveliest soul. The air, chill and cutting, goes soundlessly by; the lake broods in leaden, stirless gloom. There is no sound of tinkling rivulets; the raven’s croak, the curlew’s wild shriek, are no longer heard; the plover, the heron, and the birds of the hedgerow have flown to less sombre regions. When the stars are mirrored in the steely blue water and the moon throws shafts of glory across the mountain barrier, the silence is more crushing. One side the dale is in shadow; frost spangles give to the other an ethereal, unreal illume. Gable and the Scawfells are snowbound where on ledge and scree snow can lie; the rocks, through which, from the mountain’s heart, hidden springs are driven, are sheathed with ice. Day after day, the deadness of living nature seems to increase; day after day, the unknowable mysteries of the mountains seem to deepen. The loudest voice seems hushed; the most fervid imagination is consciously dwarfed. Then the weather changes; the air turns raw and damp, and day seemingly forgets Wastwater. Silent, implacable, falls the rain. Down almost to the water trail the ragged cloud-beards—they choke day from the low land. Up the mountains—he is a hardy wight who dares to be there. Half-molten snowdrifts, torrents roaring, cascading from unseen above to invisible below, gouts of water cleaving through the mistwreaths. But seldom does such a wanderer brave the elements long. Turgid torrents and close-enwrapping fogs charm no one. Indoors the fires burn bright; save for a brief space about noon, when a sickly lightening proclaims day’s climax and glory, the lamps are hardly out. To the gloom of the clouded sky is added the great shadows of close-hemming mountains; there are houses among the fells on which for three months of the year the sun never shines.
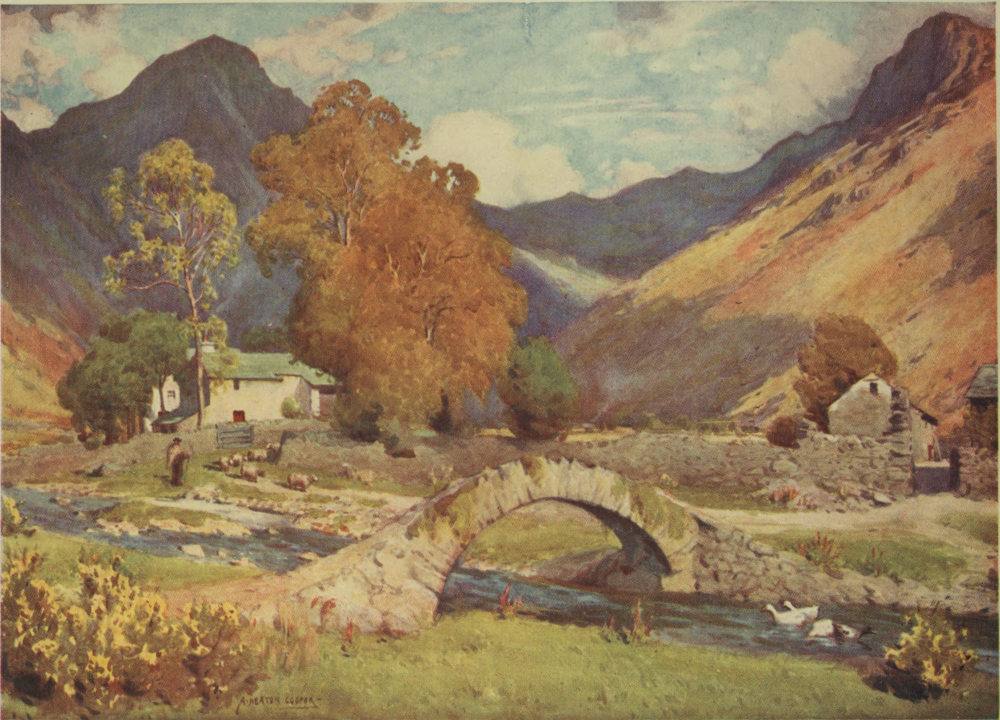

WASTDALEHEAD AND GREAT GABLE
Towards evening in autumn
Wastwater, and the Screes. Three miles of buttresses crumbling down in fan-shaped beds of ruin. It is grand to pace the opposite shore and watch the play of light and shade on the rugged mountainside. Streaked with rich brown are some of the yawning gullies: up there are stores of ruddle or native iron. Soft and soluble as mud, the substance once had a value as providing an indelible mark for 88 sheep. The shepherd lads from distant dales came here to collect it—for a premium of sixpence per pound from their masters. On the brink and halfway down the face of the shivery rocks are the little veins of ruddle found. A steady step and a firm nerve had the lads who dared such labour, for a misstep might split their foothold to pieces and throw them far down the ravines. We are told that many lives were lost in the pursuit of ruddle: compared with it, modern rock-climbing, with the skilfully used safeguards, is safe, though of course far more arduous. The climber of to-day chooses a sound crag for his work: the ruddle-gatherer could only work among the loosest, craziest ground.
The best way to see the Screes is to take a boat and row close to them. High above your head, a great rampart of rock, scored since the world began with the cabalistic record of frost and storm, hides the sky. Somewhere betwixt the crags and lake, following the smoothest route, is a rough path. In and out of parks of huge boulders (many, geologists say, still sliding downwards at speeds varying from slothful inches to a bustling six feet per annum), the track threads, affording a grand though tiring walk. After frost there is danger in approaching some of the crags. Huge breasts of stone are so finely hung that the ice wedging their crannies rends them as surely as gunpowder. There have been some tremendous rockfalls in the Screes. A century ago one of the sights of Wastwater was a lofty fragment to which an uncouth imagination gave the name of Wilson’s Horse. For long the vicinity had been shunned: pieces of rock were for ever disintegrating from the mass. Then, after a winter grim with frost and snow, came the final catastrophe. At dead of night was heard the roar of falling rock, and at daybreak the Horse had disappeared. Judging from the splintery gulf whence the Horse fell, “What a splash it must have made!” interjected one as we scrambled about the place. It is said that a twenty-foot wave passed north and south after the rock struck the water.

WASTWATER SCREES
Wastwater, the home of many shepherds. As you scramble their flocks are ever around you. And from among desolate-looking rocks, between beds of lichened boulders, they obtain sustenance. There is a tuft of grass just by that patch of parsley fern; a little fringe of soft green nestles beneath that boulder; a skin of living verdure finds root where the scree lies fine as dust. For these wisps of grass the hardy Herdwicks assiduously search, and on such meagre fare they thrive. Our sheep are small in size compared with those of the lowlands but more robust, and so intelligent that no dweller in the mountain-land can understand that cant phrase “a silly sheep.” There are other animals with far less resource or real initiative when faced by danger. The life of the mountain shepherd possesses little of Arcadian joy and pastoral romance. The stress of winter when storm sweeps down from the Gable and the air is riotous with snow, the terrible “clash” at lambing-time when the weather turns wet for weeks, 90 militate against such idylls as are fancied in brighter lands. So ruthless is fact in its war with poetic vapourings that even the glories of the shepherd’s summer do not remain. Instead of the shepherd piping and watching the sheep with lambs by their sides streaming over green swelling hills, in the English mountain-land it is the season of the detested maggot. This cruel pest burrows through wool and skin into the living flesh beneath and devours that. It is almost too sickening to recall the piteous scenes of visible spines and ribs from which the flesh has been denuded; of sheep still living in the most awful agony. Nearly the worst characteristic of this terrible visitation is that a sheep when attacked generally turns recluse and wanders as far as possible from its fellows. Thus, when the shepherd should theoretically be at ease, he is really, ointment pot in hand, climbing about the roughest parts of his holding. Once, when wandering near Wastwater, I met a shepherd.
“Been salving?” I queried.
“Nay, been trying to find some to salve. I’ve a mind they’re somewhere in these ghylls, but I can’t come at ’em.”
“How many do you reckon there’ll be?”
“Mappen sebben or eight. I’m going to try this beck course.”
“Yes, do,” I said: “I think there’s a few up above.”

WASTDALEHEAD CHURCH
The smallest in the district—perhaps in England
Then I explained that from across the mere I had noticed a few white dots, and had entered into remarks thereon with one who through field glasses was scanning the great hillside. He could scarce believe that the small grey masses cluthering in the ghyll were sheep. “They’re far too still.” I admitted the mournful fact, also that they were much above the zone of grass, but added that they were “smitten by wicks.” The shepherd assured that this was the very ghyll, up we went. It was not long before we came to the lowest—I dare not say animal. So weak and emaciated was the living organism from ravages of the terrible maggot that the shepherd immediately kicked out its brain. “Can’t save it,” he muttered through set teeth. The next was not so far gone. The shepherd, with deft hands, cut away the clotted wool and speedily the cleansing ointment was at work. The plunging and baa-ing of the sheep showed that the cure was a “smarty” one. One by one the other sheep were found and remedies applied, so that the shepherd went back to the farm at rest.
Wastwater, haunt of the char and the botling, the latter a mysterious fish. Now and again he turned up, and his appearance spread dread through the country-side—what had not happened when last this hermit fish came ashore? Fever and agues were by some said to follow his occurrence, or trouble about heafage rights. But progressive science scared him from existence (the botling was ever a male) with his little hoard of lore. The fish was taken at the fall of the year in the little becks and among spawning 92 trout. He was a powerful fellow, differing chiefly from his associates in greater size and thickness, and in the manner in which his under jaw turned up and was hooked. In weight the botling ranged from four to twelve pounds. One killed by leister, or fish spear, was so thick that its girth was in excess of its length by four inches. In colour and marking the botling resembled the ordinary lake trout, the brown spots on its back being only proportionately larger. Probably it was only a local variation of Salmo ferox (the great lake trout); it might possibly have been a hybrid fish. At any rate, here the argument must be left: for half a century the botling has not been heard of—his train of woe, however, has not been so considerate.

NEARING THE TOP OF STYHEAD PASS, WASTDALE
Like our other lakes, Wastwater is most fishable when a faint breeze ruffles its waters—for the benefit of the visitor-angler, the coch y bondhu and Broughton Point are the best general flies, with red hackle during the summer. There is little sport with the char: the lake-bed does not permit netting, and the fish are not present in sufficient numbers to encourage the use of the plumb-line. One of my old acquaintance was wont to walk from Langdale over the mountains to fish here, in the days of the now proscribed lath. Poor old Tom, it needs a vivid imagination to picture thy age-wrung frame climbing steep Rossett Ghyll, to think of thy dim old eyes as alert enough to seek out the path as in semi-darkness thou wandered among bogs and benks, screes and boulders. Still more difficult is it to see thee bending over the lead-weighted board with its twin lines and their droppers of gut, fly, and barb, keen to get the instrument on its journey. In one of the coves where purls down a rivulet, the lath is launched; the faint current carries it outward till the breeze ruffling the lake catches its upturned edge. Twenty yards out, where the lake sheers down to its great depth, fish are lying, taking what food air and stream drift to them. Slowly the lath sails outward, Tom unwinding further line as required. The board is now, thinks Tom, beyond the shoal, and the droppers should be presenting their temptations to the fish. Its movement is therefore checked, and the linesman waits for the fish to bite. Tom’s right hand after a while draws one end of the lath nearer, the breeze catches it and it floats sidewise. To the right is a few yards of water from which Tom has previously taken good fish. In an hour he rises from the shadows, and draws the board slowly to land. At first the lines come steadily enough, and are coiled neatly; then there is greater resistance. The right line jerks about in all directions: here comes a big trout. A faint ruffle breaks from a back fin just beneath the surface, there is a little wimple as the fish sinks down again. Gently, gently Tom draws in line. Now there is a brisk curl quite close to his feet near the rocks, a few splashes, and Tom is handling a half-pounder. So strong was the tackle used for lath-fishing that no delicate precision, little fine “play,” was requisite. Poor old Tom! 94 Hadst thou then a taste for the picturesque, what lovely memories thou must be revelling in now when in age thine eye to outward things grows dim! Nights by lovely mountain tarns, when the northward light made the water glow like steel, when the great ribs of the mountains seemed in their nakedness to support the dome of night. Star-spangled skies, and the soft mists of summer by the lake-shore when everything droned to rest. The adventure Tom remembers best is of Wastwater. A keeper had suspected lathing on the western shore, and secreted himself to watch. Tom came over from Langdale, and near Yewbarrow made ready his lines. The board floating out attracted the keeper’s attention. He was mounted, and rode as fast as he could to cut off the poacher. Tom heard the thud of hooves on the soft grass, threw his lines into the mere, and made up the hillside as fast as he could run. A few score yards the horseman pursued, but the poacher managed to cross a deep but narrow gully which the keeper’s pony could not leap. Then, as Tom quaintly remarks, “He thought he hed hed enew on’t, and turned back to the lake. But I got my lines and board in spite of all. Aye, and there was about twenty pounds of fish on ’em.”

WASTDALEHEAD, WASTWATER
Wastwater—its memories are quite innumerable. On cycle the western shore is not difficult. The road undulates, but its surface is fair. It was a warm afternoon; rain had fallen during the previous night, but bright sunshine and sweeping breeze had dried up the exposed portions of the road, though under the trees it was still muddy. We started from Santon Bridge, a sweet hamlet in the gorge of the Irt, not usually found by those whose faces are toward Wastwater. For a couple of miles the road was up, up, and the hills were long; then down, down, down, and the descents were merry. And the Screes rose loftier in front, and looked more and more broken. Soon the level blue of Wastwater comes in sight over larch-tops. Then, as we pedal into a beech avenue, the full view is lost, but we see a succession of entrancing vistas: narrow shafts of meadow and woodland, of water and upspringing screes, framed in by dainty sprays of copper foliage. Through the tunnel of overhanging boughs is a glimpse of open moor and of distant fell. The road declines and our speed increases. To northward we see almost the full length of the mere; the faint breeze is urging the water to gayest laughter. The Screes, with their rainbow hues of native coal and iron, of green slate and brown conglomerate, are opposite. The afternoon sun is playing about their gullies: in some we see long, thin cascades, but between the cliffs fringing other ravines is a straight, heavy shadow. In there, unseen by the sun, the water jets and sprays in leaden glories; no rainbow dances in the soft white veils; dank, slimy cave-ferns grow in plenty.
Our road now passes into the wild moorland—terrace after terrace of hillocks we wind through, keeping near the lake’s level. The feature in this approach to Wastwater head is Yewbarrow. Seen 96 from other points this seems rather tame, but from here it is impressive, commanding the whole view. The lake is still waving under the influence of the breeze; green, green and gold are the hillsides with grass and bracken. Among the stones the staghorn moss threads, sending up club-like spikes in profusion; every boulder is fringed with parsley fern. Yewbarrow, always changing shape, now appears as if cloven by a chasm from the great mass of mountains, and the name of the chasm is Bowderdale. There is heather by the roadside now, its tufts perfect masses of bloom, and the broom’s yellow glory is not wanting. In half a mile we leave the desolation of rock and grass—here are trees and even a few pieces of hedges, rowan and hawthorn, with a few scrubby oaks. The level plain of Wastdale head appears in front; we coast round guardian Yewbarrow, pass cottage and farm as far as the road serves, then push our machines to the church of the dale. Now the weather changes. The brilliant sunshine suddenly glooms and dies away. I look up to Great Gable, weather oracle of the glen—and am surprised. Half an hour ago a fluffy cloud seemed resting on it, but now a dark mass of vapour, distended with wind and bearded with unshed rain, has taken its place. And over the pass from Ennerdale on the left, and through the gully from Borrowdale on the right, the hosts of storm cloud are boiling. A contrary gust whispers a shrill warning; we seek shelter at once, but with a seething and a roar the storm is upon us, lashing 97 rain-lines in our faces. Fifty yards away the vicar’s house offers shelter—we are not acquaintances, but—— In three minutes we are in his kitchen, looking out toward the glen of Mosedale. At first nothing more is visible than a grey mass of whirling rain, then, for a summer storm is but brief, again the flanks of the nearer fells come in sight. The pall passes rapidly, and the sunshine is pouring over the spine of Yewbarrow before the last rush of rain has streamed down the hospitable window. Ere long, the glen is again rejoicing in sunshine; the grass sparkles with fairy gems, the streaming crags are touched into shields of silver, the hoary crown of Gable seems to brighten as though the new spirit of life below made even it, the monarch, rejoice.
Lying beyond the pale of great mountains, and only connected by rugged passes with other sights of Lakeland, the lake of Ennerdale does not attract many tourists. The approach to it, otherwise than by mountain road, is circuitous; the traveller, coming by ordinary routes from the outside world, is carried across a great ironworking district, where every stream runs red mud, and where black smeltery smoke hangs low. Yet Ennerdale in its own peculiar fashion is beautiful.
In my early days the lake seemed connected, in my mind, with stories of pirates and privateers—Paul Jones hovered on the coast near by till a gale drove him and his cursing hordes out to sea—and as more intimate knowledge came to me I still found Ennerdale connected with illicit seafaring. Smugglers—and my ancestors are reputed to have been among the most active of these—landed cargoes in the coves about St. Bees Head. From there goods were sent northward by the coast to Carlisle and the Border, and eastward over the fells to Penrith, Kendal, and distant towns and villages of the Pennine. The first route was early closed, but that over the passes baffled the revenue officers for years. The head of Ennerdale was quite out of the world then. The smugglers built rough caches to store their loads in wild weather, and even engineered with skill a path over Great Gable in the direction of Borrowdale. To-day this green band is known as Moses’s Sledgate. Moses, however, was not a smuggler, but an illicit distiller who, after the decline of the finer art, reared his “worm” in the wilderness.

ENNERDALE LAKE AT SUNSET
A long climb over grassy open common brings the cyclist from Egremont to Ennerdale bridge: that irregular knot of houses, with its moss-veiled church, was in the past a mountain metropolis. Wordsworth’s poem, “The Brothers,” centres in this churchyard of the dale. As the poet thought out his theme, through his mind there must have passed memories of that grand, encircling chain of mountains, rugged Revelin, precipiced Pillar, and scree-strewn Iron Crag, with many more. Only in one real particular was the licence poetic indulged, for there were gravestones here, modest indeed, flat among smothering grasses or fringing the boundary walls.
Perhaps not at Ennerdale, but in equally remote districts, the church was used by smugglers. Under the rush-laid floor, cellars were dug to contain kegs of liquor, the miserably paid parsons conniving, often acting as selling agents. Church attendance would doubtless arouse more enthusiasm among grown men in days when the spent bottle could be exchanged 100 after service for a full one, and there were “lashings” to drink beside. In one place where the parson could not be brought to see his “duty,” the kirkgarth was often tenanted by most eerie “corpse lights,” and had to be shunned accordingly by all honest folks and preventive men. Those “in the know,” however—and they were many—knew that brandy and rum would be plentiful next day, for a new supply of liquor had been hid in a raised vault, from which the parish clerk drew it as need arose.
From Ennerdale bridge the road climbs a couple of miles to the lake: in fact it somewhat overclimbs, for when at last the mere is viewed the wanderer is about three hundred feet too high, and has to descend by a very steep route to the Anglers Inn. That first glimpse is splendid: for half a mile back the hedgerows have prevented the eyes from wandering far, then suddenly bursts the glory. The waters deep beneath follow the mood of the day; laugh and sparkle when the sun shines and a warm breeze whispers; well gloomy and leaden when a host of clouds presses the mountains and shadows the lake-basin; swoon tender and soft when evening’s purple vapour drifts through passes and over summits, to collect in a pool in the valley beneath; surge and heave in breakers when a gale sweeps through the air; brood silent and sombre and still as a slab of jet when winter clothes the sky with deepest blue and the steeps with majesty of white.

THE PILLAR ROCK OF ENNERDALE
I prefer a boat for exploring the beauties of Ennerdale Water within and without, for the road to Gillerthwaite is rough, and the path by Anglers Crag not without some difficulty. Ennerdale within is represented by some fine trout and by an occasional char. On this lake the char in early autumn will come to the lure of a red ant. These insects at this season develop feeble wings; they haunt the sandy soil near the lake and are for ever essaying flights. A slight breeze is enough to sweep whole crowds of them over the water; they fly to the end of their strength, fall into the lake and are snapped up by the fish which lie in wait near the surface. In winter the char resort to the main stream entering the lake, for the purpose of spawning. For many years a certain part of the beck was known as the Char Dub, for in it, in numbers sufficient to render the bottom invisible, the shoals of fish lay. At the present day, however, the diminished char elect to spawn on a shingle further up the stream.
For its trout-fishing Ennerdale is justly noted: there can be little finer sport than trolling here, the boat moving slowly on, the waves lap-a-lap against its timbers. When the attention is taken from the water, what a fine panorama of steep and rocky mountains!
Maytime among the mountains—a day of soft creeping shadows and warm sunlight, the firmament white with lofty clouds, though here and there a wide rag of blue shows between. The boat welts away from the pier; clack, clack, fall the oars on to their pins, a moment later, to a rumble and a churn of water, 102 the rower falls to work. Local men do not use the rowlock and the feathering oar; a rigid pin is fitted on the side of the boat upon which a perforation in the oarshaft slots. The contrivance has undoubted advantages to anglers, as the oars do not need to be lifted inboard when not in use; secure on their pins they can trail through the water. But why all lake boats should be so fitted is beyond comprehension, for the superiority of the rowlock and the feathering oar is palpable: a boat can be pulled faster and more easily, and in moments of danger—which on a day of sudden squalls are frequent—are not less reliable.
As our boat slips away, the upper lake, a field of splendid blue, comes in sight. In mid-lake a tuft of rock claims attention—the boat glides to it over the faint ripples. It proves indeed to be a cluster of loose fragments, pushed up from the lake-floor to be a resting-place for the birds of land and water. So piled are the stones that it seems impossible human hands have not been busy in the midst of this waste of waters. Anglers and others have proved by crude methods that the protrusion is the crest of a sheer column of rock, or rocks as the case may be. If the figures confidently given are approximately correct, when, if ever, Ennerdale runs dry, an inaccessible pinnacle will be found to puzzle our rock gymnasts. Herons alight here to meditate and digest their toll of troutlets; and swift warriors of the air, buzzard, peregrine, and more humble sparrow-hawk, hover down 103 to the islet-rock to rest and plan anew their forays. When afloat on Ennerdale the mountains, with infinite variety of shadow and gleam, rock and grass and downpouring water, demand most of my attention. I seldom look to the lake’s outlet: it is a comparatively flat scene if your boat is past the rugged slopes of Revelin. A long larch-wood fringes the shore—its monotonous blob of green in strong contrast to the livelier fellside dabbed with creamy, blooming hawthorns. Next to it, over a knot of buildings, rises an unsightly shaft of brick, belonging to a long-disused thread mill. The effect of rectangular wood and cylindrical chimney is dreary, stupid; it apes a modernity which here, in God’s wilderness, is at least unpicturesque.
Our vigorous friend at the oars has meanwhile brought us close to Anglers Crag. The bottom of the lake remains invisible, though the boat’s nose grates against the sheering rock; looking over the side, through the clear water, the slabs drop lower and lower till gathering gloom hides them from sight. The “crag” above, though steep, is quite climbable; it is worth while going ashore to scramble for ten minutes. The boat accordingly turns into a narrow bay where we may land on a beach of shelving shingle. The bank above is plenteously strewed with slabs of rock, though the “crag” is to our right. Up the hillside we find our view rapidly extending to westward, though the mountains still hem us in on all other sides. Shortly the sea is visible beyond smoky West Cumberland. The forms of shipping can be made 104 out, sailing the channels through the shoals of Solway. And farther away still, if the day be clear, the hills of Scotland rise in an undulating line of blue. St. Bees Head is the only feature in a comparatively regular shore: a mass of sandstone, it sheers up four hundred feet above the strand. Here, on its very crest, once was a monastery, the lands of which were won by a miracle. St. Bega and her zealots landed hereabouts and found the people worshippers of strange Norse gods, unwilling to hear the new gospel and impatient for the visitors to be gone.
“Your God is almighty!” sneered the chief, “I will give you all the land in my domain that to-morrow bears snow. Your God is almighty; and you need nothing from humans—ask Him, then, for snow.”
The morrow was Midsummer Day; at early morn the folks of the country rose to find a mantle of cold, glistering white covering nearly all the land betwixt mountain and sea. The chief’s jest was, so runs the tale, carried out in full, and through war and peace the monks held to their inheritance till smooth King Henry divided their lands to others.
Down we come to the lake edge again, to raid the haunt of coot and heron—both birds not rare on Ennerdale Lake, the quietude of which is just perfect. Our boat floats in as wild and savage a scene as is to be made by mere and fell. The Char Dub is visited, the huge mass of Pillar Crag noted at as near a point as possible. Now, coasting barren fields above which 105 the skylarks are trilling, and by shores decked with star-primroses, we return from the wilderness to the forest lands of oak and ash and alder.
Ennerdale Lake, though less visited than the other waters, is in its way as beauteous as they.
Close enfolded in the lap of mountains, Loweswater is seldom seen by the casual tourist. At Scale Hill, a rugged ravine with a white river dashing down, is pointed as the direction in which it lies. At the sight of that crag-set hillside the cyclist turns regretfully and, down the good Lorton road, speeds away for Cockermouth or Keswick. Yet if the writer were compelled to seek another home among the Lakes, after Rothay’s magic glen he would select Loweswater. And there are others who would do likewise, who year after year come to the little secluded lake for holiday. For tell it not loudly, its trouting is the best in the Lake Country. The angling is not public, but it is possible to obtain permission for a week’s pleasure. The trout rule large for our northern waters, fish of over three pounds being landed every season.

LOWESWATER
As mentioned already, the lake is hidden in the flank of Mellbreak, the front of which sheds scree and occasional boulders into Crummock. For ages the dell was a stronghold of the ’statesmen who lived on their own holdings, but as hard times came the mischievous jointure system caused one small estate after another to come into the market. Lucky the monied in that dark era: the farmers grew despondent as their obligations increased. After centuries of abstemity rum and whisky began to be relished, with dire results. Wool which for long had stood at a good price fell rapidly to almost a nominal figure. Desperate farmers did not market their “clips” for several seasons in the hope that times would mend. But old stock was finally sold at whatever price offered. The vast imports from the new Australian colonies in the middle of last century thus completed the destruction which the Repeal of the Corn Laws began. Some who do not wish to see a return to Protectionism point out patches cumbered with heather where wheat was cultivated in those days of inflated prices. To force up prices that such wastes might become profitable, they say, would not benefit the farmer, the shepherd, or the dalesman now, as it did not in the past. The opponents to this view point with equal confidence to the days when the ’statesman was firm on his own soil, living and working at profit enough to pay out the jointures placed on him in his father’s anxiety to “do fair by his own.” A change, they sigh, might bring back those happy days. I take no side, save to say that the highest tariff imaginable cannot bring back the worthy, faulty ’statesman families. They are gone for ever. Strangers dwell within their gates, and till their fields.
There are no great houses round Loweswater, no castle was ever built in this domain of peace. The 108 ancient farms, with their guardian yews, speak of gone days. I never see the twin trees by a farmstead with the inevitable box edge from gate to door without thinking of the old custom of setting a bowl of box in the porch of the house where a corpse was lying. Every one who visited was expected to take a sprig. Box grows slowly—the hedge planted by a man is hardly seen at maturity by his great-grandson; the Cumbrian peasant custom must have been an effectual reminder to all of man’s narrow span on earth.
To me Loweswater is a great reminder of olden days. No glaring hotel, no road traversed by hooting motor-cars or rattling coaches. A man can sit far up the slope of Mellbreak, look down on placid water and quiet vale, and allow his mind to ramble back fifty or a hundred years. He can re-picture the old glen and its society. First the priest. His church was small, his stipend ditto. As he was the head of society, christening babies, marrying the grown, and burying the dead, so the schoolmaster was generally the opposite. He was ordinarily despised, whereas the parson sometimes was revered. During the week the vicar was a farmer among farmers; he had a tithe of wool, could have sheep free on the heafs above the enclosures, which his parishioners had to look after. He took tithe of the sheaves at harvest, and of every kind of produce. The greater part of the schoolmaster’s remuneration was in the shape of victuals: he went “whittle-gate” by turns to the home of his pupils, living a week here, a week there. He was scrivener and will-maker to the parish where the priest did not take that office. He taught but few subjects: reading, writing, little arithmetic. But sometimes there was Latin and Greek and Hebrew for the really studious, as behind ale-soaked clothes, and in a fuddled brain, a schoolmaster might possess real classical knowledge. On the other hand, men who had had accidents at other callings, or were too worthless for manual labour, drifted into the teaching profession. Knowing only the merest rudiments and careless of learning more, they could not benefit the children, and were often a fearful example for them.

THE OLD POST OFFICE, LOWESWATER
One of the main amusements of old dales-life in winter was dancing, either at merry nights, or at what were called “dancing classes.” To provide the music for these lived a class of wandering minstrels. What lives they led! I well remember poor old Tim, the last of these to come within my sight. He came to our knot of houses just as dusk was falling. He carried his fiddle in a green bag, and as he neared, took out the instrument and tuned a single string. Then his old voice trolled out, “Home, sweet home,” in faltering accents as he walked back and forward. Ages ago minstrels played by the hearths of the great, and sang the legends of golden renown: here Tim, tottering, his fiddle almost in ruins, his voice quavering over the well-known words, trying to get from poor cottagers enough to buy drink, or a night’s lodging. Poor Tim! His story was sad. He had money left him when he was a hard-working shoemaker 110 nearly thirty years of age. To that time his only solace had been in music. The legacy turned his head, and in a short six months he was ruined. The little shop where he had mended boots was in the hands of the bailiffs, his wife and children were on the road with him. For awhile they travelled together, then the children were rescued by relatives—the poor wife dragged along alone in the wake of the drunken fiddler. At last too she faded away, died by a snow-covered roadside, and Tim went down to the bed-rock of despair. “I want no money, give me ale.” Fiddling here, and singing there till his voice gave way, he wandered a score years. Many tried to rescue him; once his little shop was restored him and for a whole summer he stuck to his “last.” But with dark nights, music was required at the inn, and he was tempted again. He trailed himself across from one merrymaking to another. He lived as he might; he slept as he could. And the morning before I saw him a farmer walking on the top of his hay-mow stepped on something that cracked. “Dash thee! thoo’s brokken my fiddle, and I’ll hae to play at t’ Ploo to-neet.” As he felt old age and death creeping on him, he wandered away from the country-side which was his home, and put miles of flat country between him and the mountains before the final call.
Another person who knew much of the dale in the old time would be the dumb fortune-teller. Persons without the power of speech were always credited in Cumbria with divination. The fortune-tellers were the 111 most respectable of vagabonds: they worked satisfactorily and were well paid. No gloomy forecast was ever to my knowledge delivered. I have seen many of their hieroglyphs, some in picture-writing, promising untold good to the person who had consulted them. But the gipsies were, and are, another matter. The pedlar, too, was a well-known figure; with his pack on back he would go from farm to farm, selling all sorts of little tempting things.
To come to the lake at last. It is one of our smaller meres, and the quietest. It lies in a land of meadows, but lofty hillsides rise above its glen. No boats are kept for public use, but a visitor can usually arrange a loan with some farmer. Loweswater is not a lake to exhaust in one afternoon: the cunning ones lodge by the week at the clean, comfortable farms, enjoying the plain fare of rural Cumberland with a delight bred of open air and keen exercise. The rod is hardly ever from the waters, except for a siesta at midday—and not then if the day be overcast, with a warm breeze kissing the water and enticing broods of new insects from the depths. There are no char in Loweswater, though attempts have been made at introduction: probably the water is hardly deep enough to suit it.
To row out on a warm summer night and to fish here from midnight to dawn is a splendid experience. Though along the northern ridges a pale night-glow glimmers and fades, and the stars like diamonds glitter in the light blue above, down on the level waters 112 everything is gloom. The man resting on his oars is a dark shadow: your companion’s “kent” face, though he has turned toward the light, is a patch of featureless grey. To see your fly it must be held high enough to come between your eyes and the narrow swathe of light on the horizon. Your boat drifts through the prattling wavelets slowly, slowly. Then along the line comes the expected tremor: a fish at last. No use trying to play him—get him to the surface: your tackle is strong enough to take some risks. Your rod responds to its struggles, yet you cannot guess where the trout is. Perhaps it may rush to the top and set up a faint wimple that catches the night light. In a few minutes, however, the fish is tired out and you draw it alongside. The largest of trout are nocturnal feeders, and the angler is occasionally delighted by very heavy fish. Persons unaccustomed to night on the water assert that the silence is almost appalling: save for the ripples against the timbers there is no sound. To me, however, there is pleasure in that far-off whistle of an otter; in the churrs and twitters, hoots and shrieks, of night birds. There is a romance in gloom of which garish day knows nothing. The fairy world visits you again, and you witness gay revels in the starlight.
The lake to the angler, the hillside and the meadows to the wanderer, are the charms of the vale. He who is not satisfied with the softly trawling boat, the midge-worried hour of non-success, can ramble in the woods and fields, with their glories of sedge and iris and 113 cloying meadow-sweet, and up the rivulets dancing down shadowy ghylls. Climb the shoulder of Mellbreak, sit down every five minutes and look around. By this method a full enjoyment of the peaceful vale will be obtained. Notice the nearest things—the rose beetles: your friend down below in the green old boat will be sighing for such a one as that just turned over; and that crushing mass of parsley fern which, though the whole hillside is open to it, sticks close by that grey, weathered stone. The lake is now quite small below, a mere dot shows you the lazily floating boat: think scornfully now of the angler and his petty work. Look beyond, the great moors rolling toward St. Bees, the hills fining down to the North Cumberland plain, the Derwent here and there gleaming between banks of living green. Criffel and the Dumfries-shire hills, across the Solway. A patch of smoke shows the cathedral city of Carlisle, and you feel a pity for the workers under that pall. They think they see the sun shine, but you in a purer air rejoice in a more life-giving light than that pale gleam they praise. The bracken too is here, unfolding its last tendrils, and away goes a single red grouse with a mighty whirr and a squauking “Go back!”
A sound of human and canine voices comes now to the ear; and turning an outstanding rock, we come immediately to a busy scene. It is a sheep-washing; to the clamour of dogs, and the whistling and shouting of shepherds, are added the bleatings of two thousand sheep. One drove is on the hillside above marshalled by a pair 114 of collies, another is below, threading an almost unseen track toward some distant holding. A shepherd is in charge of these, his dogs scouting to right and left. No straggler can bolt into the confusion of sheep in the little glen. Here a dam has been built just below a rudely piled fold. The sheep are driven into an outer court, then drafted into a small inner space. From this they are thrown into the water, which has been collecting since yesterday (so meagre is the stream), where men standing waist deep catch them. Holding the sheep’s head above water these quickly pass hands back and forward over the fleece, raising it so that water penetrates to the under-wool. This done to satisfaction the sheep are allowed to swim out. When one flock has been washed, it is sent to the portion of unfenced hillside from which it came. The scene is one of bustle; the work is arduous too, some of the men have been collecting and driving down their flocks since early dawn. Shortly after the washing, comes the day of “clipping,” when the fleece is removed, but the days of great “clippings” are past. Wool becomes ripe at different periods; and instead of treating the flock on a certain day only, the shepherd now shears as fast as fleeces are ready.
Standing above the washing pool we look down on the little animated patch—the struggling ewes, the water turgid with “dip,” the skilful men in water and on land, the ’cute collies watching their master’s flock and allowing no stranger to enter it. Beyond the dry stones of the river-bed, in a vista bounded by the 115 steep sides of the gully, we see the lake in all its beauty. Woods, fields, diminished with distance, yet seem but over the brink of the chasm there.
Now from heather and bracken we return to green pastures and to the little ivied farmhouse, with old-fashioned doorway and chimney, which is our temporary home. All is peace around: the rookery is hardly heard across the intervening fields; the raven, in the blue above, scarce in all its wheels and hovers sends down one menacing croak. The day is spent, and up the western sky spreads a suffuse of crimson, flecked with wisps of cloud; at last night draws on, softly, bluely, creeping into the hollows of the hills and into the deeper shadows; the radiant lake dies from crimson to grey, and then, to the clatter of rowlocks, our boat comes home to the grassy pier.
Two chief routes bring you easily to Crummock Water—the first to Scale Hill at its foot, the other to its head, over Newlands Hause. From northward, as you approach, the hills on either side the vale of Lorton rise to higher flights, to greater ruggedness. At Scale Hill there is a sudden glimpse up the lake, a silvery level stretching far into the mountain land. Your way has wound round a great tumulus of rock and larch and oak which chokes the vale, to bring you so quickly to this lovely view.

CRUMMOCK WATER, FROM SCALE HILL
Wild and stern is Crummock. All is particularly gloomy and forlorn on an afternoon threatening snow. The hillsides start up grey and stark and desolate. The only sounds you hear are the occasional yelp of a sheep dog in the fields near by and the sulky croak of a raven, a black spot up there where a grim cloud is hovering, shutting out the life of day, and sending the weather-wise sheep cluthering to sheltered spots by ghyll and fence. Suddenly the grey firmament above drops on to the hilltops and smothers them. Then snow begins to flutter, first in single flakes, then in a small shower which grimes the nearer fields and paths. Finally the storm giant asserts himself and a continuous shadow of white falls around. That far-off mist-wall which showed the head of the vale is shut off; only a few yards of grey lake trembling and tossing into little waves as the north wind harries it. At such a time it is well to seek shelter, for the gale may be wild and strong as day dies, and the snow fall in winding sheets. Rather, then, turn indoors and listen to stories of stress—the shepherd can tell you of peril faced for the sake of his flock; the postman, of danger in his daily round: men as wild and strong and devoted in their way as pioneer-heroes in a cannibal land, and as deserving to furnish matter for stories of renown. Through rain and shine, when torrents brawl havoc, rending bridges like straws, when drifts hide even the tall tree tops,—
“The service admits not a ‘but’ or an ‘if’”
and the gritty postman, by one device or another, wins through with his mails to solitary farm or wild moorland hamlet. And they live long, despite their hardships, as witness one who, after a day’s wrestle with the unbanded elements, was asked how he fared.
“Why, man, it’s wild on t’ top. I tried to git ower t’ moor, but I couldn’t. I gat to that lile [little] black planting, hooivver, aboot halfway, and I rested a bit. Then I said to mesel, I said, ‘Noo, Wat, thoo’s faced it four and fifty year, thoo sureli isn’t gaen to gie in noo.’ And at that I set tull again, and I gat ower; but it was hard wark, mindst ta.”
By calm hearth the dalesmen tell their stories; the gale rumbles against the house, and the windows tinkle to the driving of snowflakes. By morning the storm has passed, the ground is deep in snow, sky and hilltops are clear, stars still shine down on a scene of quietness and savage peace. Soon dawn-beams fire the east, and the summits are touched with rose. With full day the greyness clinging to the mountain flanks disappears, revealing riven glens and beetling crags. A boat is being launched for an expedition to seek what wild fowl may during the storm have taken refuge on the lake, and on it we go. On the open water the cold is terrible; pulling with might and main would hardly relieve the numbness of hands and feet, but our game is wary and any incautious rattle of oars would send them beyond reach. For half an hour we put up with the discomfort, then find that the boat is leaking badly and that a baler has to be used freely to keep the floors from floating. We ask to be put ashore!
On the road, walking is less difficult than we had imagined. At one place is quite a hundred yards of wind-swept path, but at a gateway the soft snow is piled deep. It is hard work passing even occasional drifts where you wade waist-deep for yards. At places the road between cliff and lake is so blocked that we climb along the open hillside. Now from an outstanding crag above the road we have a view of the lake and its surroundings. The water lies in a huge trough, bounded by immense walls of mountain, hardly 119 ever falling far enough back to allow an alluvial meadow to slip between. Mellbreak! What a mighty mass! White are the wide fans of scree, but black and frowning the tiers of precipice. Above in a grand sweep comes the head of the mighty monarch, from which the sunshine is striking a thousand frost spangles. The sky is deep blue overhead. Hark to the croaking of the ravens; they seem to have found some carrion—perhaps a dead sheep—in yonder ghyll, and down they come, one, two, three, in all six, a crowd for these unsociable birds. Some of the ghylls are choked with snow, but others show black, rocky rents in the snowfields. Particularly I look for the great ravine down which comes Scale Force, the highest of our waterfalls. Once I climbed that gorge on a moonlit night in winter. Never to be forgotten that scene! An opal sky streaming with faint beams of aurora, tall crags closing the chasms, the fern-like alders limned against the starry glow above, the water rolling in pearly waves over the rock-edge toward me, then falling through an unseen zone to trouble the darkling pool at my feet.
Part of our homeward route lies through woodlands, where we watch a busy squirrel visiting its cache of nuts, and where, among the snow-laden branches, scores of little birds flit and twitter. Once we hear a buzzard mewing high above, and a sparrow-hawk’s raucous voice, but neither bird is seen.
Crummock in midsummer is a dream of delight. Once lately, on a warm summer evening, I cycled up its shore from Scale Hill. The road is rather gritty 120 and loose of surface, but quite ridable. The sun was dipping toward the mountain ridges, pouring a flood of glorious light into the valley. From the lake came the chunk-unk of oars; two heavy-laden boats were being pulled toward the foot of the lake, and soon a clear young voice rippled across the water to us the charming strains of “Killarney.” What a sublime scene! Lofty Mellbreak sheering from the water’s edge, Grassmoor and many another craggy giant sweeping up to invisible heights above us, the golden green of new bracken, the purple bloom of heather, here and there an emerald patch of larches. To me there is infinite change in a view over a wide lake. Those huge, irregular phantoms are the shadows of a cloud above: they sweep across the lake, then dull the mountainside; drop away into some deep glen, pass on to dim far-away summits ere they slide over the horizon. The emotions of the heavens are reflected in God’s mirror beneath. Should a thunderstorm gather, then the lake is cast in gloom, sable ripples heave and fall. To the roaring of heaven’s artillery and the blinding flare of lightning, the fury approaches, passes, and the water wimples and rejoices in the falling curtains of rain. After storm, how noble and sweet that restful bosom! With fresh sunlight the land renews life and hope. The down-bent harebell rises again to dance in the gentle airs that play about; the heather casts off its gleaming pearls—down the sinewy fronds of bracken runs a tribute to the thin soil. Birds burst forth in wild chorus: the throstle and the blackbird make the rowaned ghylls resound; wagtails, wrens, linnets, each pipe their tuneful parts. To these from on high joins in the ringing of the skylark—a wild song of defiance to the storm, of thanks for coming calm to the Most High. And the lake, ruffled with passing breezes, seems to rejoice as well. There is a fragrance of earth and air and land after a summer storm on Crummock Water.

CRUMMOCK WATER AND BUTTERMERE
Away across the lake, by the bouldery ness the torrent of Scale has driven into the mere, are two islets, and from one a smudge of smoke is travelling lazily. What more delightful than to have a foretaste of the joy of picnicing there? The road now inclines from the water, and we climb toward the village of Buttermere where a new series of views awaits.
Perhaps fewer people live by Crummock than by any other lake: the fells hem it in too closely for farms to be settled. There is much shepherding on the commons, where flocks wander unchecked over wide areas. It was in a scene similar to this that a touring Devonian ventured to tell his Cumberland host that he did not think much of this sort of country, for, he explained:
“Down in Devonshire we have land, we can grow apples, and we have green meadows.”
“Div ye mean ther’s nae land here?” said the Cumbrian, sweeping his hand toward jagged crag, sleeping lake, and boulder-strewn field. “Why, man, ther’s that mich land here that it hes to be piled togither, one farm on top o’ t’other. Why, man, 122 ther’s eneu’ land to mak’ fifty farms i’ Benkle Crag theer.”
“Aye,” assented the Devonian grimly, “and enough waste water to till the lot there,” pointing to the shimmering lake.
The wild moorland above the lake is one of the few remaining English breeding-places of the dotterel. This is a migrant of the plover type from high latitudes; odd pairs are apt to stay all summer, and to rear broods. The nest is increasingly rare: for collectors will give long prices for a complete clutch of eggs, and the native shoots the bird on sight, for no more successful lure for trout exists than a fly made from the underwing of a dotterel. I have declined £5 offered to disclose the whereabouts of a nest. Once I undertook to show a naturalist a nest, but though I had marked the place ever so carefully I failed to give him “the sight of a lifetime.” There are great difficulties in the way of a non-resident again finding, in a maze of benks and boulders, ghylls and riggings, so small an object as a dotterel’s nest. Other summer birds of the mountains are the ring-ouzel, a white-throated blackbird, the peregrine, the kestrel, and the sparrow-hawk. The bittern no longer booms in the upper glens or by the lake; hen-harriers and their kindred are also gone. But the wailing of the curlew still rings in our ears, the plover is never at rest, and the sinister “dowk” or carrion crow gorges on every dead carcase on the uplands. Of lesser birds, by every rill you see the pretty dipper 123 in his uniform of brown and white, and less often the bright metallic sheen of the kingfisher. Winter brings the fieldfare and redwing to the mountain valleys, with now and then a flock of snow buntings. On the lake too come the pochard and the golden eyed ducks from the frozen North, with rarer species such as the sheldrake, the wigeon, and the shoveller.
Buttermere is Crummock’s sister-lake, divided only by half a mile of level, swampish meadows. Doubtless, in early ages, the twain formed one long water, reaching from the foot of Fleetwith eight miles to the hill at Scale. In size the upper lake is much the smaller: even more than Crummock it is a mountain mere. The fells rising from its shores are among the lofty ones of the Lake Country: Red Pike and High Stile with their back views into Ennerdale, Robinson and Hindscarth facing the vale of Derwent and far-away Skiddaw, and Brandreth hiding behind Fleetwith. Buttermere is a solitary place: the presence of the hamlet, the sheep-farms, the small, dark woodlands, and the one mansion on a head driven out by the activities of a fell beck, almost accentuate its loneliness, for the bare pikes of mountain dwarf them almost away. It is the coach-road which brings the idea of modern life and relationships here. It runs close to the lake, and every day in summer and autumn a procession of vehicles passes along just before the luncheon hour. From Keswick they have started—coach, char-a-banc, wagonette, or more lordly landau, wheeled into lovely Borrowdale to the merry crack of the whip and gleesome blast of horn; with a long pull, they have been hauled up steep Honister Hause, with a brake-wrenching plunge they have safely negotiated the narrow shingle-shelf called a road. Timorous passengers have shrunk in terror as they gazed at awful depths below, but now all nerves compose themselves as the hooves rattle on the hard, undulating road by the lake-side. After a suitable rest the horses will draw the crowd away over Newlands Hause, where out of the green hillsides a road has been delved, to Keswick, and our dale and lake will forget disturbance till to-morrow. The eternal silence of a mountain-land will fall around and render rapturous evening and night and blithesome morning. To drive from Keswick to Buttermere and return is no mean item in a tourist’s day; it is a noble day’s work for horses, and only good ones can endure frequent journeys over these rugged passes. Even the “easier” slope of Honister is sufficient to “break many a horse’s heart.”

HEAD OF BUTTERMERE
The villaget of Buttermere was apparently unknown to Roman, Saxon, and the building tribes of old; its only historic building is the lowly public-house where the Maid of Buttermere dwelt. Mary was the belle of the glen in good King George’s day—a blithesome Cumberland lass, bonny enough to charm a yeoman’s eye, wealthy enough in a modest way to bring his love and hand. But she was not for the dalesmen or the shepherds of the mountains. Her fate was ripe 126 when one day a post-chaise brought to the little inn a grand gentleman from Keswick. His dress was fine, his looks noble, he had plenty of money. He gave himself out to be Colonel Hopetown, son of a peer and otherwise highly connected. Soon the guest condescended to woo the Beauty, and ere a short summer passed they were married. A few weeks later the “colonel” was arrested on a charge of forgery—“franking” letters with his “relative’s” name to pass the Post Office—and was proved to be the son of menial parents. Many other and viler frauds had he practised after leaving the South Country, but these he was never called to book for on this earth. Forgery was a crime involving death under the merciless penal code of those days, and the impostor duly suffered at Carlisle. Mary of Buttermere, so forcibly parted from her husband, did not repine him long, but married a neighbouring farmer and lived to a good old age. The small chapelry of Buttermere was, some time previous to the happenings mentioned, held by one of Wordsworth’s heroes, “Wonderful Walker,” the curate of Duddonside Seathwaite, whose life-story of labour and frugality was once so well known and esteemed. How he lived several years in his office here is almost a “wonder” in itself, for Buttermere allowed its priest no more than “whittle-gate” and twenty shillings yearly. (Some accounts aver that the remuneration was “clog-shoes, harden-sark, whittle-gate, and guse-gate”—that is, a pair of shoes clogged or iron-shod, a coarse shirt once a year, free living at each parishioner’s house for a 127 certain number of days, and the right to pasture a goose or geese on the common.) Either scale would not be too luxurious for even a successor of the Apostles, bound to forswear the lusts of the flesh and the pride of life. The person who held Newlands chapel in the time of George II. was a tailor, a clogger and butterpat maker, and the Mungrisdale priest had £6 0s. 9d. a year. Such cures were often held by unordained persons—hedge-parsons with a vengeance.
The day I first came to Buttermere forms one of my fairest memories. Starting before midnight on the opposite edge of Lakeland, at daybreak I stood on Dunmail raise; by breakfast-time I reached Keswick; then I went up Skiddaw by way of Latrigg, descending by the same route—the only one I then knew of on that shoulder of the mountain; at noon I was on Newlands Hause, plodding on cheerily. Hot and grimed with dust, my eyes bleared with sweat and the glare, I wonder if I looked so disreputable, so much of a tramp, as I felt. A stripling of seventeen, not stoutly built, poor in dress and pocket (I left home with 1s. 9½d. and returned with but 3d. less), carrying on my back a satchel with food for my day, to be eaten in the open air and washed down with water; there would be little jauntiness of face or body or stride, I trow, after that forty-eight miles’ tramp. And this was not the end of the journey. Buttermere was only the Mecca, the turning-point, of my walk; after passing it I turned up rugged Honister for Borrowdale, and then by the Stake pass to Langdale, 128 and so home. Perhaps it were unmannerly to boast, but eighty-five miles of road, mountain, glen, and pass, in twenty-five and a half hours, is not a feat of my every-day. As I entered the valley that day the clouds closed down, shutting off the beating sunrays and throwing a light, refreshing shower. Like the mountain daisies, the wanderer for a full minute raised a rejoicing face to the cooling raindrops. Then, like the sky, he felt a trouble. “Nay, nay, it’s nobbut cestin’ a shooer,” said an aged shepherd, and my heart was comforted. Not long before I had walked thirty miles through pouring rain, and found it no light matter. Like a soft slab of slate the lake stretched from the fringe of treetops before to the stony, scrubby hillside opposite. Save where coots and water-hens played by the sedges and rooty river-mouths, the surface was calm, the light rain merged into the water without splash or circle. The hillsides round Buttermere are furrowed into ravines, dark and gaping they split the festive green swathes of summer-tide. And down these hollows dash lively rivulets playing hide-and-seek, mazily threading through shadow of alder and rowan, by groves of flowering hawthorns, now lost in the depths of a ghyll, now spouting in lively haste over a ledge curtained with fern and bracken.
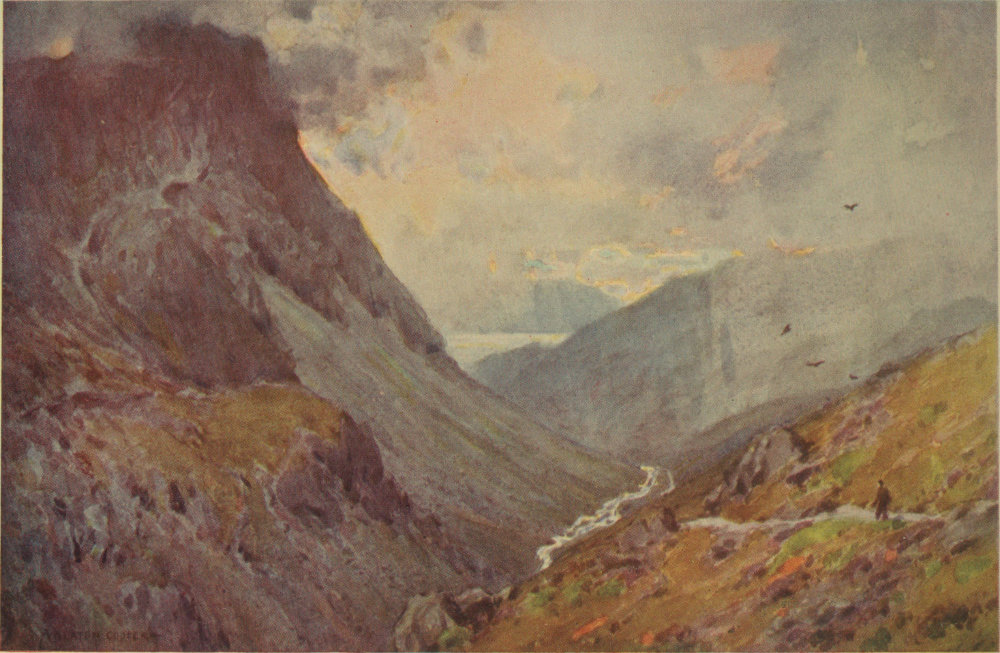

HONISTER PASS AND BUTTERMERE
It is a rare pleasure to be at Buttermere after a series of rain-storms. From the rockrib wherefrom the church commands its little flock, you look into a great amphitheatre of crag-set mountains. Beneath the eye is the water; it seems to be palpitating with movement from the rich riot its tributaries are hurling down the steeps. See how it wimples beneath the farther shore—through a wide rent in the lake-bed untold gallons of water are being forced upward from the heart of the earth; that flat circle in mid-lake against which the creeping catspaw of wind in vain forces its feeble ripples shows another fountain swelling up in quiet power. The steep hillsides are seamed with threads of white; Sour Milk ghyll, in a shimmering veil, sways from skyline to lake-shore. Where often a hermit stream hides and glides behind crest of rock, beneath screen of bracken, now is all tearing, jumping, spreading fosse. Every fold in the hillside casts down its bounding cascade; there is nothing in the air so loud as this turmoil of waters, this joy-song of deeps bursting from dark prisons in bog and crag. Already, we are warned, the paths to Wastdale and Ennerdale are impassable; the floods are out at Gatescarth. Climbing would be a questionable pleasure to-day; “beck-dodging” is far more suitable. At first our road is dry, washed free from dust by the heavy rain; through wide culverts the floods rumble beneath. The wider becks are bridged: look up this tree-hung gullet and see how the waters wilder down. Not in waves do they come, but in great gush after great gush, green and white. How they crash against unseen rocks, throwing feathers of spray at every shock, till the stream shooting beneath the arch seems but a flying mass of airy, tortured foam! There comes the sprite, the winged spirit of the day, robed 130 in brown and white—the dipper, our mountain water-crow. How it chirrups and revels in the tumult! how it flirts its tiny wings and dives through some curling gout of spray! how it scolds the volume roaring through the darkened tunnel beneath the road, causing it, O highly important fairy, to flight up like a mere blackbird, among the dripping plumes of larch!
“Boat ahoy!” we shout anon, and our friend afloat a field’s breadth away waves answer; in a minute the boat is grinding the gravel, and we are almost down the soaking field to reach it.
“What, tired of fishing?” we ask. He is a desperate keen one with the rod as a rule, yet his tackle is packed up.
“No,” he grumbles, “can’t catch anything.”
“Now I did think to-day would suit you. Good spates in the becks, a light breeze, and plenty of cool clouds,” I marvel.
“Now look here,” protested the angler wearily, “it’s no good talking like that. The floor of this lake is leaking upwards as though the steam was escaping by a thousand cracks in the ceiling of the nether regions and being condensed into Buttermere. Why, man, the lake bottom’s that lively that the trout and the char, the big pike down to the tiny minnow, are all having a job to hold the water at all. I bet every minute they’re expecting a geyser that’ll blow the whole lot of ’em over Red Pike to Ennerdale.”
When an angler relapses into this mood he is hopeless to cheer, so we silently respect his sorrows. 131 Perhaps into that vigorous pulling he will throw some of his despondency. Now Fleetwith, flanked by the precipice of Honister, is frowning at us over the low fields. To the right, against a background of watery clouds, is limned rugged Scarf Gap; the path to it is white with rushing waters. The rocks everywhere glimmer with oozing springs: down Honister pass a wide torrent is foaming, attracting to it many a milky force from Robinson and Fleetwith-side. The scraggy stone-pines by the lake-head give a characteristic finish to this scene of sodden brae and spouting rill. Save for the sycamores round the farm of Gatesgarth, there is hardly a tree for shelter; the aspect is bleak and storm-riven. The boat is run on to the shingles beneath the Scotch firs that we may land. Not far away is the main road; we pass up the hillside beyond it. In the recess beneath Fleetwith we are conscious of a flood indeed. Much of the stony level is swamped; with difficulty the sheep have been brought from danger, and are flocked near the farmstead. The torrents rushing in at the head of the mere can be traced, first by white horses, then by dark, level-flowing currents, far down the lake. From this height we again feel that the great water is rocking in its cradle of mountains. The furrows of incoming rills give the peculiar idea of ever-changing level to the water. I have never yet seen the whole level to Scale under water—one lake of eight miles instead of two smaller ones—but viewed from these heights it must be a noble sight indeed. Our boat pushed into the in-dashing 132 beck, rapidly rides to halfway down the lake, thence by carefully avoiding unfavourable currents we easily make our landing-place.
To my mind, the valley is hardly less interesting when a thick winter mist glooms it, when, for all you can see, there is no difference between Honister top, the crest of Robinson, and the stony fields round Gatescarth. Under such circumstances it is well to be afloat an hour, and allow impressions to establish themselves in your mind. Twenty yards out you lose the land: the boat glides along in a grey circle of moving fogbeards and rippling waters. Save for the sounds from bow and rowlock you are in a dead silence. Shortly, however, the ear catches faint echoes: the croak of the raven, the skirl of the curlew, ranging in clear upper air, with now and then the attenuated bleat or low or crow from the farmlands. In mid-lake there are few sounds of water-birds, though at an odd time a coot, traversing the width, may show, a scared patch of brown and white, inside your zone of vision. The lake-birds are cuttering softly close inshore, finding the curtain of cloud an effective cloak for feeding. An hour of boating thus, in gloom and rowk, will form an experience not to be forgotten.

THE BORROWDALE YEWS
Evening
The fishing of Buttermere is now in a few hands: sportsmen have leased the mere and devoted much attention to its re-stocking. The result is that few anglers outside this coterie come here, though on an occasional day the mountain becks are worthy attention. Most visitors here are active enough to relish rambles over the fells, and there are many routes to select from. Away from the narrow band of meadow-land touching the lake, there are few obstacles to free-and-easy wanderings. Sheep walks are divided by wire fences, but these are fairly negotiable, by climbing over at the “posts” or squeezing between the running strands where slackest. Stout folks find the latter the preferable method. To make the circuit of the glen of the lake is a fairly big task, but it can be divided into three moderate courses. You start by crossing the meadows and climbing Scale Force brow, then, left-handed, along Red Pike and High Stile (over bog and bracken, across ghyll and up steep, with a glimpse into Ennerdale here, a peep through Newlands at Derwentdale there, and always the moor in sight, with a clean, sweet breeze and, if the day be clear, a wedge of blue sea on the horizon), finally descending into Scarf Gap, the home of mists, where an easy return path ends course one. From Scarf Gap, into the back-o’-beyont country behind Haystacks, and to Brandreth with its legs into Buttermere, Ennerdale and Borrowdale, always keeping to the right, and ending the course over Fleetwith to Honister Hause. From Brandreth it is easy to pass over Green Gable to Great Gable, and so to gain Wastwater. Honister pass-head is the scene of a legendary battle between Britons and Picts, or between Angles and Scots—history hardly decides which. One party had been a-foraying in Borrowdale and hoped to withdraw over this pass with their spoil; their pursuers, however, cut them 134 off and, after a wild resistance, recovered the cattle. From Honister Hause—it is a wild place of rocks and screes and untamable streams—the final stage carries the wanderer over Dale Head to Hindscarth, whence he descends by Robinson to Buttermere or to Newlands Hause.
Every one walks up Honister as a matter of course. What is it like on a bright July day, when the beating heat is tempered by a smart breeze? Every rambler should live with eyes open to nature; to-day will repay him his interest. Up in the brilliant blue ravens and hawks are hovering, crows and rooks are ever passing over the glen. From one wood to another the wild pigeon wings rapidly, the blackbirds in the hedges are busy at their nestage duties. Take note of the flowers, O man with seeing eyes. In the pastures are great purple spikes of loose-strife, amid the white waves of ox-eyes; round by the lake are belts of blue lobelia. The air is full of the scent of meadow-sweet, the honey-suckle here and there throws trailers, adorned with creamy bloom, along the hedges, and in great clusters blow the wild roses. Up the shady beck-courses you might find the blue forget-me-not and the still bluer birdlime, and in the mossy springs the violet-shaped butterwort. Butterflies and dragon-flies, softer moths and gaudy beetles, are attracted by the multi-flavoured feast spread about.
Now we come to Gatescarth, the largest sheep-farm within many a mile. A noted breeder of mountain sheep lives here, one who has done much to improve 135 our semi-wild Herdwicks—much honour to him. The farmlands, even in the glorious to-day, look harsh and bare, though the soft, short sward is of the greenest. In winter there is often severe stress here; at times the shepherds are called upon to collect, in a day of storm, the flocks from far-off crags and ghylls. Long hours are spent battling the elements, collecting the unwilling sheep, and bringing them down. The wanderer here on a stormy winter night is not unlikely to see a light patrolling far up the hillsides—one of the belated shepherds patiently driving his sheep down from the danger of flood and drift and gale. The white cross which is attracting the eye, O inquirer, is erected to the memory of a young lady accidentally killed at that spot: “In the midst of life we are in death,” is carved on it. The incident is one to make every mountaineer pause and think. It was an everyday risk, alas! The lady descending a steep slope held her alpenstock straight in front of her; the point struck the ground, but the lady slipped, her chin caught on the butt of the stick and, such was the force of the fall, her neck was dislocated, causing immediate death. Such an accident is possible a score times in every day’s walk here. Now the great crag of Honister is frowning by our very side. Around its base the rambler will find broad tracts of alpine ladies’ mantle, while forked spleenwort and many a rare plant besides are among the screes and shelving rocks. Among the grass and boulders near our path are long fantastic growths of stagshorn moss, with more alpine 136 ladies’ mantle, with wild thyme, the precious eyebright and yellow tormentil lifting their lovely heads in the desolate wilderness. Now we reach the passhead: Honister is the wildest of our passes, the place where the great thews of Nature are least hid. But the slate quarries make Honister less desirable to some eyes; great confusions of debris, railroads sweeping up into the bowels of the great crags; for nowadays men do not work here, as they did in Wordsworth’s time, hanging down the cliff in frail basket-chairs tapping and blasting the surface rock, nor do they carry down the slate on handsledges as they did two score years or so ago. The mining is more scientific—more reliance is placed on machinery than on men. The new railroad, carrying slates to Seatollar has improved one thing at any rate—there is far less of that penetrating screaming of brakes than when the loaded carts descended the pass-road. On a calm day the racket could be heard for miles.

LODORE AND DERWENTWATER
A summer’s morn
Proud Cumberland ranks Derwentwater as queen of the English Lakes; but I was born south of Dunmail raise, and feel at liberty to worship at other altars. To see the lake at its best one needs be afoot long before the coaches and motors appear. A road smothered in dust clouds, an atmosphere quivering with clatter, the fumes of petrol and the general unpleasantness of heavy traffic, detract from the most imperious beauty. At daybreak the town is almost silent: sweet mountain air has descended to dissipate the closeness of midnight; the songs of larks and throstles are wafted into the medley of houses and streets from the fields and woods; the murmur of flowing Greta is pleasant indeed. On Friars Crag you may meet an early visitor, and at the landings a boatman is cleaning up. As you stand there, in a pleasant but undeniable way the waters call. “A boat, sir? Certainly. Will you wait till I’ve finished here?” And you watch the man haste on his scrubbing and polishing. In two minutes he scrambles on to the pier, selects oars and cushions, sees you safe in your place, and gives a push off.
As yet no other boat is astir: you have the wide expanse to yourself. From Friars Crag scores of people in the summer watch the sun set. And at the close of a clear day the scene is glorious, even sublime. Around a hundred peaks, ranging from noble Skiddaw to humble Swineside and Catbells, the shafts of light fall and ebb. Here in the rift between two summits is a stretch of purple, there a patch of rosy light fades on a scree-seamed brae. If the sun sets in a flurry of crimson cloud the spectators will hardly take their eyes from the lake: the reflections of the sky are so charming, so magnificent. No painter could match the evanescent changes, the kindlings of the sky, the soft portrayal of each living flame on the shimmering water, the green gloom of overhanging mountains. What boots it if the fiery splendour is a presage of rain when so splendid a pageant is the forecast? To your left is rocky Derwent Isle. Fountains Abbey held it, before the Dissolution of Monasteries, as Vicars Isle; it has had half a dozen names since. Secluded, a fringe of trees hiding its narrow lawn, a house stands here which for sheer romantic situation would be hard to beat in the Lake Country or wide England. I would sit in an upper room there, on a day of April squalls. First in the grey nor’-east I would see the storm clouds gather darkly behind the cone of Skiddaw.

DERWENTWATER, FROM CASTLE HEAD
A bright morning
Derwentwater is lap-lapping merrily against the stony beaches beyond the green sward, every wave wearing a sunlit crown. The great hollows of the mountain range are now filled with battling vapour; from right and left round lower summits they move to desperate attack—dun curls of skirmishers in front, heavy phalanxes of infantry grey behind. Down the air comes a whisper of riot and war, and with soundless impact we see the two hordes meet, shock, and mingle. Jagged as with unseen artillery, the battle sways from end to end; then, like a bolt of Jove, over brawny Skiddaw hurls a deluge of rain-sodden grey, the strife ceases, a sharp, steady line of mists cuts off the seen from the unseen. Now a grey shadow steals over the land, the bubbling life is chilled from the waters, and they rattle black and harsh against the cobble-stones. But on Grange fell the russet bracken is bathed in ephemeral sunshine. The shadow in the air grows darker, the distance is obscured with the grime of rain. The nearer hills, the fields, the town, are blotted out ere the full fury of the squall shakes our window and shrieks among the island trees. Like crest of cruelly spurred horse, the waves toss high, the mad gusts catch the rising gouts, wrench them clear into the air and hustle them along to crash in resounding sheets far up the shore. No boat was, we recollect with pleasure, visible before the squall descended: it would go hard with such a one just now. One experience of a squall on a mountain lake is enough for the most daring. I remember my baptism in such manner vividly. The yacht had but one sail spread to the breeze, but maniac Boreas caught it, pinned us down while water poured into the well, wrenched and screamed and worried 140 at the mast and gear till that went overboard with a crash, then, with a final paroxysm, spun the hulk round and passed away over a waste of churning, creaming waters. More comfortable to face the gale with thin glass in front than to fare like that. The trees bend like switches, but the gloom is now rising from north-east. In a minute a flood of sunlight is pouring down, waking to brilliance the flooded lawn, and making sparkle the drop-decked boughs. Look into the wake of the retiring storm. The lake is still leaping white and racing along; a dim film hides the crags above Grange: now it passes, so quickly as almost to make one start at the rapid change. It would be dowly living at Derwent Isle when fog dark and drear hid lake and town: one might feel lonesome when the blizzards whistled and fumbled against window and door, and the waves crashed without the snug retreat. But how joyous this morning, when the sun is aloft and day has risen refreshed from the bath of night and is newly beginning a pageant of song and life and changing colour!
Further up the lake is Lord’s Isle, where once lived the Earls of Derwentwater. On the attainder and execution of the last of the title the mansion fell into ruins: some of its stone was used in building Keswick market-hall. The last earl was much loved in Cumberland; he was staunch to the Stuarts, as were most Northern gentry, and intrigued widely to bring about their return. When the first Pretender landed, bringing such sorry allies and little promise beyond, 141 the earl foresaw that insurrection would be useless and dangerous to the participants. He argued that, although the Stuart was in Scotland, no rebellion need be attempted in the North of England until the party there were better prepared. In the secret council the earl was held little better than a traitor; at home his wife accused him of cowardice, demanding his sword and horse that a Derwentwater, though a woman, might take the accustomed place in the battle for King James. The earl was no coward: he took the mocked sword from his wife, and cast himself into the turmoil of rebellion. It is history that the rising was crushed with ease, and that as a ringleader the earl was beheaded on Tower Hill. Powerful men at court sued unavailingly for the young noble’s pardon. Money was lavished on the king’s favourites in vain. To raise funds the countess came north to the island-home; the Cumbrians, incensed at her forcing the Earl into the plot to save his honour at her hands, gave her a chilly reception. Legend luridly asserts that her horses were stolen while she was on the island, and that she and her servants were threatened. At dead of night a boat was rowed to near Lodore, where the lady landed and escaped by way of the fells to Penrith and the south. With her she carried a large quantity of jewels, which were offered to save the young husband’s head. The ravine by which the countess climbed to the open moors is pointed out as Lady’s Rake. If it were my province here to examine the story in detail, I would find that it was hardly to 142 escape the Derwentwater tenants that the lady left in such haste. She was, for her share in the late rebellion, marked for arrest, or at least observation, by the Hanoverian authorities.
Seven islands dot Derwentwater: on no other mere are islands the feature we see here. Instead of snags of rock sticking up from deep water, with trees keeping precarious hold in clefts and crannies, these are level, well-wooded places, standing behind ample shallows.
Having passed Lord’s Island, with its sorrowful story of a life risked and lost for a banished prince, Lodore is the next point. Every one knows by repute Southey’s poem-de-force describing the terrific rush of its waters. After heavy rain the old poet’s description can be tested—at the expense of a wetting. Down a wide stair from the moorland, bristling with crags and boulders and outstanding seams, come the waters—their frolic can often be heard at Keswick, though Greta is charging, headlong, noisily down its rugged course. The moment you enter the gully—should you desire to see the heart of its beauty—you are swathed in spray; never in flood-time can you see more than a few yards ahead; your eyes film with moisture; the air to your lungs is choky with mist; the day is gloomed with spindrift. You see a white front of water hurtling down from invisibility: it eddies at your side, then drops away in gathering water-smoke. Nothing can you hear at such a time but continuous liquid thunder. Say the luxurious, there is then but little to see except the watery path you are climbing? Once I climbed this ravine at flood-time. As I passed into the zone of water-smoke, there were blurred visions of tumbling cascades, shadows of huge rocks dimly seen across the ravine, dripping branches of shrubs and plants among the streaming rocks. Then, what a transformation! A flash of sunlight swept into the hollow way. An atmosphere of shifting jewels of rainbow hue above, around; strings and clusters of pearls and diamonds dripping down reddish crags veined and barred with gold and silver; grasses poising delicate racemes of turquoise; mosses adorned with tiaras of ethereal beauty, ruffles of ivory spray caressing the currents of rich emerald. The brief glow faded, and all became grey and black and dull green again. For a glimpse of another such fairyland I would face stress much wilder than greets one in the gap of Lodore.
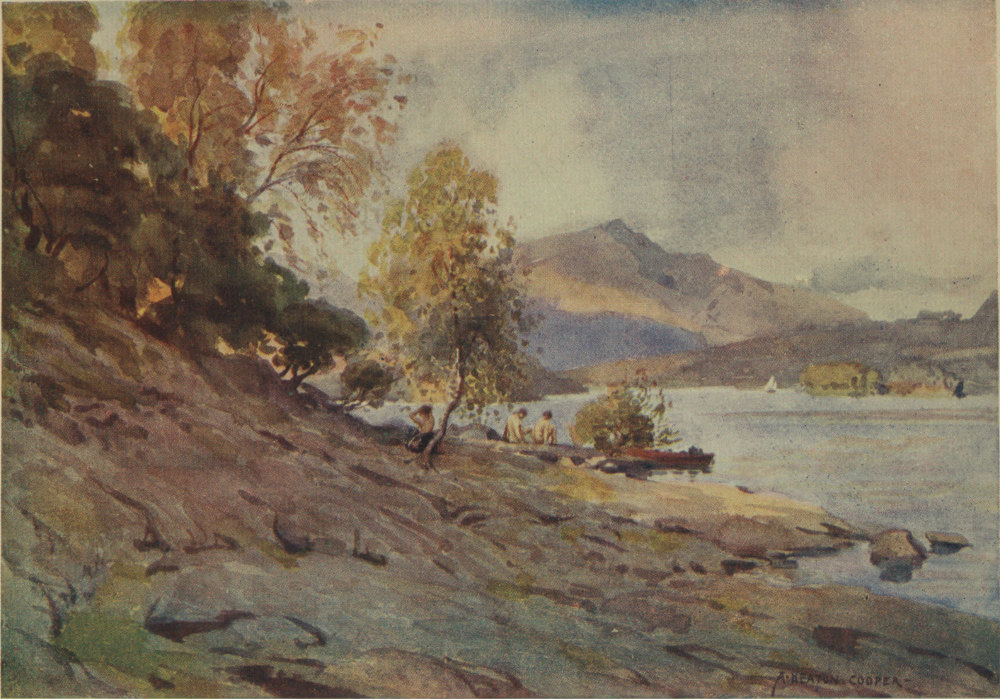
BY THE SHORES OF DERWENTWATER
Another ravine in the cliff near by possesses a beautiful waterfall, but Barrow Cascade is on private ground and the free rambler can hardly be brought to see it. The head of Derwentwater is so grown with weed that a path has to be cut to allow boats to reach Lodore landings. Near here the once wonderful Floating Island anchors. A mat of vegetable fibre lying on the lake-bed at times becomes inflated with natural gas and rises to the surface. In 1864 a second floating isle put in an appearance, and during that dry summer it seemed likely that many acres of adjoining lake-floor would follow suit. Floating Island shares 144 fell to tremendous discount and have never recovered. The Derwent here enters the lake by two channels through ooze and tangled water-grass. Few lakes have so extensive shoals as Derwentwater: for acres hereabout you may look over the boat’s side through some feet of clear, amber water at the growing reeds, white spathes piercing the mud, green stems, and hasty leaves unfolding ere they reach the upper air, or thin waving threads linking a tuft of foliage on the surface with unseen roots beneath; all kinds of pond-life creeping and swimming about. Where the lake-bed lies fallow the eye rests on soft levels of mud, with a passing host of minnows, a red-necked perch, or even a trout or pike. Here and there rock-spines pierce the level floor, or perchance a bank of pebbles, large and small, set in smooth mosaic, blood-red of granite picked out with sea-blue slate, grey pebbles of volcanic ash intermingled with knobs of salmon sandstone, and conglomerate of every colour and shape. Watch the sunlines creeping and chasing and quivering as little ripples undulate the lake’s surface.

GRANGE IN BORROWDALE
Early morning
The narrow glen ahead is Borrowdale: its entrance guarded by heathery Grange fell to left and by Gate Crag to right, with Castle Crag uprising in the centre as though jealous of an opening secret. A century ago the world ended at Grange: hardy he who toured into the sunset land beyond. The dalesmen were simpletons—“men of Gotham,” who hardly knew the use of wheels or saddlery. Castle Crag presents a precipitous front; unknown hands have fashioned earthworks on its crest. As the lake is not low, the boat comes some way upstream towards Grange. Here, when Borrowdale was its possession, Furness Abbey had a barn for its harvests. Nothing remains of it, however—possibly it was a mere skeleton of wood which, when the Dissolution prevented the harvesting of the monks, fell into ruin and was annexed piecemeal by neighbours as required. Casual observers have remarked, anent this penchant of our forefathers in the Fell Country, that they took much trouble to steal, carrying great distances timber they might have felled at hand, stones which in bewildering profusion lay upon their farmlands. Our forefathers knew the toughness of the mountain oak and ash; to fell the trees was simple, but no tools for shaping planks and baulks were obtainable, while worked stone is still worth carting far in the dales. Not every boulder is fit for building stone, my kindly critic, and it is hard northern sense which prevents the products of labour lying fallow in grassy mounds.
Grange stands in one of the sweetest recesses of Cumberland: the wide bed of Derwent furrows the tiny level; in front and behind rise, pile on pile, the rocky fells, dotted above with grey fleeces, below with red and white and scanty black of milch cattle. I take it a fine sight to sit by the bridge here and watch the sun’s last rays spread golden raiment on rugged Eel crags and Maiden moor; down below a shadow of blue is sweeping over intakes and screes, night hastening on ere day has thought farewell. The boat now drifts back to 146 the lake, and passes along the Catbells shore. The bays, with steep woods or brackened slopes rising out of them, are all sweet and pretty, fit places for an afternoon’s quiet thought. This is the tip of an old lead mine; the whole country-side is rich in unworked minerals, from once-precious wad or plumbago (from Borrowdale for years the chief supply of the world was drawn) down to tin and copper. In the days of Elizabeth a colony of German miners was imported to improve the craft; several leading lake families are descended in part from them. The foreigners were not loved by the fell-landers, and for generations scarce mingled with them. The success of a new process has opened the mines at Church Coniston—will the same occur here? In days when theological argument was common, a Lake Country Quaker frequently encountered, and sometimes worsted, a dignitary of the Church.
“You may best me,” said the cleric, “but you do not convince me yet.”
“Friend,” rejoined the other calmly, “if but the man was to convince, I could convince thee at once; but what man’s talk can pierce through that armour of gold thou renewest yearly? Forget thy church money, friend, for an hour, and I’ll convince thee.”
If the mines are opened and our lakes and rivers made pools and streams of mud, the glory of our hillsides wasted with metal-fumes, the pen of the writer will avail little against the chant of profit. The large island now at hand is St. Herbert’s—the most 147 renowned of all. In the early days of Christianity, an acolyte of Holy Isle, off Northumbria, came here to spend his life in divine contemplation and communion.
The story of Herbert’s death forms our prettiest unassailed legend. Once a year the hermit left his island-cell and made a journey to his beloved Cuthbert, who remained on Holy Isle. Age did not prevent their tryst; and when eternal rest was nigh, the venerable Christians each prayed that his departure should not cause his friend to grieve. That petition, says Bede, was granted.
One afternoon Cuthbert, surrounded by students of God’s Word, suddenly ceased the lesson he was expounding; his aged face took on a joyous smile, and in a moment he was dead. A messenger set out to carry the mournful news to Derwentdale, but on the way he met one hurrying to tell Cuthbert that on a certain day his beloved friend had passed away. At the same hour they both had entered the portals of death. Centuries after Herbert’s death his memory drew pilgrims here from distant parts: at Portinscale dwelt a smith who sold the image of the saint in silver-alloy and lead. Some years ago his mould and fragments of his wares were dug up near an old landing convenient to the island.
There is no recognised ruin on St. Herbert’s Isle; the few worked stones scattered about may be remains of the chapel built during the pilgrimages. It was for long the custom of the good folks of Keswick to celebrate St. Herbert’s day by a procession 148 of boats up to the island and a service in the open air to his memory. Opposite St. Herbert’s Isle is a belt of land touching the lake beneath and the open commons of Catbells above, now secured as a public pleasure-ground for ever. In this is Keswick blessed above all Lakeland towns. The striking of eight o’clock from some campanile in the town brings back the mind to prosaic human necessity. My back bends to the oars and quickly the boat comes to rest in the reflections of Friar’s Crag. For a modest fee indeed I have had three hours of Derwentwater at its best.
Another good way to see the beauties of the valley is to walk or cycle round. The road takes you to Crosthwaite church and over the meadows to Portinscale, then winds into the glen of Newlands. But just within, the way turns sharply, climbing up a corner of Catbells, running in a long slope down to Grange, Lodore, and so to the town again. Skiddaw, rather than Derwentwater, is the most prominent object as we leave Keswick northward. Just at present that mountain is empurpled with heather, its great flanks vivid with bloom and with the lighter green of bracken fronds. Latrigg, the fell nearest at hand, has been planted with larches; not so many years ago it was treeless as Skiddaw and as beautiful. Not far from the road is the home of Southey, poet and gentleman.

CROSTHWAITE CHURCH, KESWICK
Crosthwaite church has been subject of many pens. The history of the present building goes back beyond the great Reformation. Somewhere near this point St. Kentigern of Strathclyde raised the cross when banished from his native court. The present building is doubtless the last of several which have successively weathered the storms of fourteen hundred years. Probably the first were built of willow wands and clay, like the daub huts still to be found in remoter Cumbria. With the Saxon still stronger in the land a house of timber would be raised. Foundations under the present building show an earlier stone edifice probably built just before the Norman Conquest, which in this stubborn region was not accomplished till almost two centuries after the fight at Senlac. The church stands out among the meadows, and in times of flood is sometimes cut off from its congregation. More than once within the recent past service has had to be suspended on account of rising waters. Present-day congregations may possibly be easily daunted, but I wonder how the friars of old used to manage when Derwent swelled across the meadows! The monks’ road was some feet below dale-level, and probably ran like a millrace. Did the old monks hold service in the belfry? Did they in a body shirk attendance at church, or was a boat hired to take down the votary whose turn it was to conduct worship, and the rest remain at home? We cannot tell now; but had the ancient records mentioned these things instead of others much less interesting to us, their study would attract more attention. Inside the church at Crosthwaite, apart from points of architecture valuable to those who understand, most striking is the effigy of Southey, done in white marble by Lough, the 150 self-taught sculptor from Northumbria. The lines on it are by William Wordsworth. After the monument was in its place, the poet felt this tribute not sufficient for his dead friend’s merits: accordingly he rewrote some of the lines in loftier terms and had part of the tablet newly engraved. This too, remember, by that poet whom his contemporaries asserted to be without sympathy for the feelings of others!
Outside the church in the graveyard looking towards Skiddaw’s triple crown, is the grave of Southey: a plain stone tomb, with no highsounding phrases—fit memorial of him who found the name of poet linked with that of drunkard and libertine, and who exalted it in himself and his school of thought to glorious equality with that of gentleman. There is a font of great age in the church, and effigies and memorials of the Ratcliffe family, extinct with the last Earl of Derwentwater. Beyond the church the road passes between flowery meadows, across slow-flowing Derwent, and on through Portinscale the magnificent, with a glimpse of Derwentwater across its levels, and of course a succession of views of Skiddaw’s everchanging breast. Once there is a vision of Bassenthwaite, but greenery hides it almost as soon as seen. A turning here might carry one miles from sight and sound of twentieth-century life.

DRUID CIRCLE, NEAR KESWICK
Moonlight
For a mile Swineside is fringed—a common whereon not long ago half-wild pigs were pastured; then we hover by the vale of Newlands with its splendid background of mountains. The road sways undecidedly on the watershed: through a tangle of treetops we see farms below; along a far-off hillside are the ruins of a long flume down which water was conducted to drive that tall waterwheel. The skeleton remains, a blur on the pastoral beauty, though watercourse and mine buildings are in indistinguishable ruin. At last, the road throws a branch between banks of meadow-sweet down to rattling Newlands beck; our way sweeps toward cone-fronted Catbells. Shortly we descend into a narrow glen, then zigzag up the flank of the fell. After a hard pull (the day is hot; the distant hills are swinging in vapour) we come to easier angles. The road is delved out of the hillside, the home of bracken and creeping stagshorn, with, by rills almost silent with drought, trees of hawthorn, alder and rowan. Below us—over spears of larch, over chevaux-de-frise of oak and ash and birch, over green and bronze cupolas of sycamore and beech, is the vale of Derwent, from Lodore to the furthest Man of Skiddaw. How sweet and dreamy the blue stretch of water, dappled with shades of high-floating clouds, with emerald islets scattered in bay and reach, with the swift launches and the slow march of oared craft glinting back the sunlight at the dip of every blade! To northward lush fields and verdant woodlands border the mere, with hillsides, soft green and swelling among the levels, but, opposite, sheer and bristling with crags they rise from the water, crowded in by the heathy moors. Then the town on a tousled plain between Derwent and Greta, and beyond, the hills giving place 152 to mountains, Blencathra and Helvellyn, shadows wavering in August’s blue sky. From this corner of Catbells you curve slowly down to Grange; the road is ever fair, but he is an ardent cyclist who prefers to ride all along this incline of beauty.
From Grange it is easy to pass up to the jaws of Borrowdale, in autumn one of the best pictures of Lakeland, when the birches’ silvern bark is half seen, half hid in the thinning leafage; the river is flooding down too, not hiding in pools and filtering under long stretches of white pebbles. Of course you see the Bowder Stone if it is your first visit. It is by a quarry quite close to the foot of Castle Crag.
One can reach Watendlath by a mountain track from Rosthwaite. This is a shallow dip in the moorland, containing a pretty tarn and one or two small farms. Not many years ago a Cumbrian visitor put the following note in his diary: “I came to a village called Watendlath, the most primitive place I ever saw in Cumberland. I entered one of the houses. There was no fireplace, but only logs of wood and turf burning on the floor.” Not here, but still within the Lake Country, I stumbled upon a similar thing. My queries aroused the ancient dame’s curiosity. “You divvent mean to tell me you’ve nivver seen a hearth fire afore? Well, well.” I was eager to know how, minus an oven, she baked bread. The old eyes sparkled with amusement. “Why, I make it in t’ pan ower t’ fire.” I didn’t see the process, but I tested the quality of the product, which was excellent. A century ago ovens were rare in the dales; on baking day the dough was placed in a covered pan, which was laid on the hearth. Fuel was then heaped around and on top of the pan. When sufficient time had elapsed the housewife raked aside the burning embers, opened the pan and took out the baked batch. Had it been possible for any wandering reader to witness the bakery, I would have told the place; but five years after my discovery, wishing to see again the old-time oven, I visited the dale. Alas! the cottage was empty, falling into ruins, and a green mound in the church garth covered my aged dame. The tarn of Watendlath is fed mainly by a stream which comes down the desolate back of Armboth fells, passing through Blea tarn on its way. This beck it is that goes down the thunder-chasm of Lodore. It is an interesting ramble, giving some splendid views of Derwentwater and Bassenthwaite, down to the Keswick road, by Ashness bridge.

FALCON CRAG, DERWENTWATER
But we are for Keswick, to recall briefly three scenes in its market-place beneath the old tower. Imagine, if you can, crowds of soberly dressed people passing in and out of this space—Convention week! How the dark clothes appal you as day after day passes! The streets have the air of devotion, but behind the houses the lanes teem with business. Another scene: the same streets are crowded, but the throng is of a wild gaiety—motley are the hues that press in and out. Not the steady, respectable murmur of conversation, but a wild medley of sounds, snatches of 154 song, bursts of sound from uncouth unmusical instruments, shouts and laughter and much merrymaking. It is a bank holiday crowd, come to be entertained at all hazards. Five hours ago the town was peaceful as that morning when I rowed out on Derwentwater; shortly the crowd will have diminished, till by curfew-time many of the weary folks of Keswick will cast down their tasks to breathe something of evening’s calm.

THE VALE OF ST. JOHN, NEAR KESWICK
My last scene is the dalesman’s Keswick, as I first saw it many a year ago. The square is filled with moving sheep: it is the great October fair day and a long flock is now passing toward the narrow Borrowdale road. How the air quivers to their plaints! and the grey walls echo the tumult—the sharp barkings of busy dogs, and the loud shoutings of the shepherds. We descend to where the farm-wives sit with eggs and butter, and one offers us barley-bread, that luxury now so seldom seen and appreciated outside rural Cumbria. Or is it home-made cheese we would buy? Tough as leather and white as milk, ’tis true Willimer. Strong jaws and patience enough has the man who can enjoy this. Outside the narrow market are cartloads of potatoes and turnips; further down a couple of loads of wheat are for public auction. The congregation of buyers and sellers is interesting: hard-featured dalesmen, their ruddy wives and daughters, neater-dressed town-dwellers bargaining with them. Here comes another drove of sheep—judged by Southron standards they are small, but their mutton is the sweetest to be had. There is little “silly sheep” about them. Intelligent faces, alert limbs, they have already learnt to sup on heather-tops when the grass is buried in snow, silently to endure the wild blizzards and the rainstorms, to avoid swamp and torrent and crumbling edge of cliff. In their train comes friend Jacob, from the Bassenthwaite side of Skiddaw. All through this series of descriptions I have wished to introduce one lake as seen by those who dwell close to it. Bassenthwaite, being out of the tourist route, offers excellently for the experiment. Jacob’s rich dialect would, however, be difficult for those who know not the North Country, and to give the literal English would be to destroy the extreme raciness of the speech. Therefore, a middle way is attempted, retaining where possible the Cumbrian construction of phrase, and idiom.
Jacob is wary and needs some management. First we chat about the exceeding fine autumn passing. “Aye, it’s fine, hooivver.” Jacob is slow of idea and of speech: no duty in his varied life ever needs lightning thought or action; he is decisive enough, but never precipitate. A typical dalesman—tall and broad-shouldered, stooping somewhat. Until you have walked a few miles by his side, you think he is a slow plodder, but experience teaches much. Without the slightest exertion he makes his four miles in the hour, over smooth road, soft meadow, or rocky hillside alike. As you see him face an ascent, you marvel how a man so accustomed to the work should have such an awkward style. But, defiant of all rules of the climbing and walking cults, he works his way up, down, or across the slopes with ease. Three hours of his work on the mountain is enough to tire most casual ramblers who know him. Once I worked a long day collecting sheep with him, but the sense of exhaustion was too severe to make me wish to proffer help again.
“If ye’d a summer on t’ fell ye’d do varra weel,” was his comment as I wearied through supper afterwards.

DERWENTWATER AND BASSENTHWAITE LAKE, FROM HIGH LODORE
“Ye want me to tell ye’r frend aboot Bassenthet?” he queries. “Nay, nay, ther’s nowt to tell. In summer it’s aw wark on t’ land, and in winter aw’s ter’bl’ dree. Nay, ther’s nowt at aw, man, as I can tell ye on. I’m net yan as talks mich. I’s leev’d aw me life aboot Bassenthet, as did me father an’ gran’-father afoor me. It’s nobbut a lile farm, but ther’s a fair bit o’ heaf-gang on Skiddaw. It gives us a lock o’ wark in summer, like at clippin’ an’ weshin’. What’s that, lad? Du I ivver gang tu laik? [My friend has asked if Jacob ever goes to the lake, but has been misheard.] Well, I’s no bairn, I’s leev’d in t’ reigns o’ three kings an’ a queen, but I deu like a bit o’ spooart. You should come and hev a hunt wi’ us. We hev grand runs noo an’ then. Mr. Crozier’s hoonds are rare uns. They’ll chase a fox five er sex times roond Skiddaw rayther ’n it sud git away. John Crozier’s dead noo; he was a grand un for t’ daels [dales]—a good gentleman. Then ther’s a few hares [the Cumbrian pronunciation of this word evades the science of print] in t’ boddems. But they’re nobbut babby-wark at best, fit for a day wi’ t’ sna on t’ tops. We used to hev a bit o’ cockfeightin’ yance ower, but t’ police er doon on it noo. But, hooivver, we mannish [manage] a main noo an’ then in spite on ’em a’, eh?”
“Ever do any fishing, Jacob?” I asked—my friend cannot get the old man from the fells to the lake.
“Nay, nut mich. T’ lads gropple us a fry when t’ beck’s lah [low], and on a wet day ther’s a few to gitten wi’ t’ worm. But I nivver caerd [cared] for booats, and hevn’t been across t’ lake in yan mair en a duzzen times i’ me life.”
“What do you think of the lake in spring?” asks my companion. Jacob is not deaf, but the tongue of a Southerner is as difficult to him as the accent of a Frenchman might be. Again he mistakes.
“Ther’s a gradely many, ower many springs,” he grumbles. “I think ef they’d nobbut get to wark an’ drain it ther’d be some fairish land underneath it. Mappen we woddent need to send oor sheep away t’ winterin’. It wod mak some bonny nice pastur’, eh? Mair like sensible than throwing [Cumbrian, thrahin’] brass away to mek gomerals o’ t’ bairns an’ fine gentlemen o’ t’ skulemaisters.”
“It’s gay bonny under Skiddaw in lambing-time, isn’t it, Jacob?” I interpose. The ancient is puzzling himself as to what my friend has meant; he is aware that he has again misunderstood, and is, I am afraid, becoming irritable.
“I don’t see mich to blaw aboot; there’s wark enow on t’ fell, an’ precious lile leet [light] for owt else. Then yan hardly knas [knows] when it is spring. Some days it’s like midsummer, an’ then next day it’s cald enough to flay yan alive. Auld Michael Fletcher, as leev’d up at t’ Yeds, ewst [used] to say, I mind him varra weel, when yan happened to eks [ask] him aboot t’ wedder: ‘Nay, bairn, I don’t 159 kna. Yance ower we used to hae it mak’ o’ decent, rain an’ droot just as t’ land needed ’em. That was when God A’mighty hed t’ job o’ mannishin’ [managing], but noo that them dashed Americans hae gitten hod on’t yan hardly knas what mak o’ wedder we’re gaen to hae t’ next.’ But t’ years er better an’ warse wi’ us; this year t’ wedder was middlin’ nicish, but I mind lots o’ times when it’s been aboot as bad as it weel could be. Ther was yan year i’ particular. We hed aboon six hundred yows [ewes] to leuk after, and when it com a girt sna-storm ther was some dewins. We hed put a vast on ’em on t’ heaf, an’ we hed to gang roond wi’ hay to ’em, for t’ sna wur varra nar a yerd deep; t’ sheep hed gitten into varra nar ivvery okard spot on t’ yall fell. T’ sna was that thick as we hed to sled t’ hay, an’ t’ drifts wer that deep as we couldn’t hae t’ horses at aw ower many a yakker [acre]. Ther was yan ginnel where we hed some wark to git at t’ sheep at aw. T’ top was blockt wi’ a fair wall o’ sna, an’ t’ top o’ that hung ower like t’ thack on a stack. You couldn’t git doon at aw, an’ baeth sides wer as bad, what wi’ girt steep crags an’ mair sna. We tried to git intull ’t fra bela’, but that was war then baeth o’ t’ othern. Yan girt drift piled on t’ top on anudder. I began to think it wur gaen to be a bad job till lile Tommy Moffat, as hed leev’d amang t’ fells, com up.
“‘Why Jacob,’ he says, ‘tou mun git a raep tull ’em.’
“‘And what gud will a raep be tull ’em, tou Daft 160 Watty? They’re nut likely to want any skippin’. Mappen a streaw raep wod dew, but it ud tak a bit ta wind enough for t’ lot on ’em’—ther was forty if ther was yan doon in t’ ghyll—’an’ then I woddent be reet weel sewer they wod kna as it was for ’em to it [eat].’
“‘Noo, Jacob, it’s thee as is Daft Watty. Send for as menny cart raeps as tou hes, an’ I’ll show thee hoo to git doon. We hae warse sna drifts an’ rougher ghylls ner these i’ Ennerdale.’
“Well, when we gat aw t’ raeps he set three on t’ farm lads to hod t’ end, efter he hed tied ’em aw togidder, an then he stuck a gavelock in t’ drift as far as it would gang.
“‘Noo, Jacob, I’s gaen ower t’ edge o’ t’ drift.’
“An sewer enough ower he went, an’ I clam along t’ crags as far as I could to watch. I tell ye it wor queer, he wor far enough frae me, to see him hingin’ away by that bit o’ threead-like. But efter a bit he gat on tull a foothod, and began to walk aboot t’ ghyll. What he was efter I didn’t see, but in a bit he come up again.
“‘It’s aw reet, Jacob, aw tou hes ta dew wi’ them yows is to thra plenty o’ hay doon t’ ghyll tull em. But tou mun thra it fra here’—an’ he marked a spot—‘else it ull catch on t’ crags, an’ the yows ’ll nivver git up tull it.’
“Well, that ud niwer dew, an’ for a week we fed them yows ivvery day be thrahin’ t’ hay doon t’ drift tull em. When things hed thowed a bit nowt wod suit Tommy but gangen doon wi’ his dog. ‘I’s gaen to drive ’em oot afoor this drift starts faa’ing to bits. Some on ’em mout git laemt.’
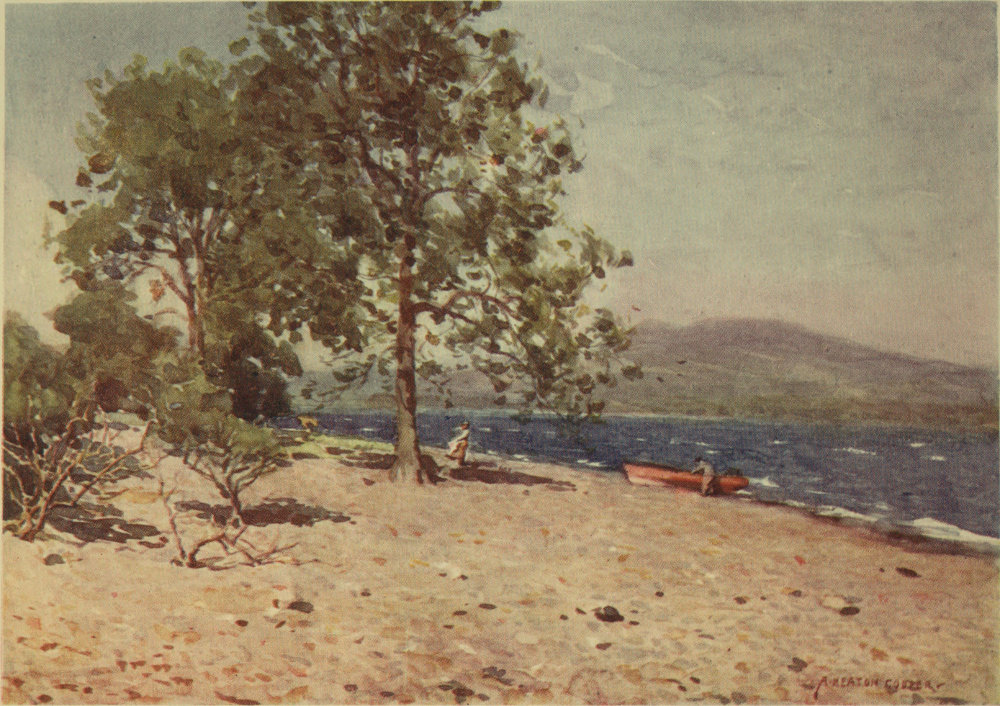
BASSENTHWAITE LAKE
A breezy morn
“Noo, I didn’t caw him Daft Watty, but hooivver cud he git them sheep up that brant o’ sna’ whar he couldn’t climm hissel? Hooivver ower he went as I said, an’ I went ower t’ crags to watch. He hed his dog in his arms as they lowered him doon, an’ he let it off that minute he gat doon to t’ bottom—it was like lukkin intull a well frae whar I was at. Tommy hed gone reet doon to t’ end o’ t’ hooal, an’ began hoonden t’ sheep up intull yan corner. Ther was a bit on a slack theyer, an’ what wi’ him shooten an’ t’ dog hoonden it wasn’t lang afoor he hed ’em climmin’ up t’ sna like as if they wur sae manny flees. It maed me feel white dizzy to see t’ lile dog drivin’ away at ’em; an’ as fur Tommy, why he was climmin’ away up t’ drift whar it wor like a hoose end, shooten an’ whistlen as if he wur as saef as on t’ main rooad. It wasn’t many minutes afoor I sah as t’ sheep hed getten up t’ warst part o’ t’ ginnel side, an’ I went roond to meet ’em. They com up like fleein’ things, wi’ that yella-an’-tan dog worryin’ ahint. An’ aboot t’ saem time Tommy com up t’ raep, an’ shooted ‘Noo, Jacob, wha’s t’ Daft Watty?’ It wornt Tommy at enny raet.
“Tommy went back to Ennerdale t’ followen summer, an’ I’s nivver seen him sen. Hae you? I mind you said yance that you hed seen him in Ennerdale last back-end.”
Yes, I had seen him, and found him overjoyed to hear of his one-time chum on Bassenthwaite side. These old-timers of the fell-heads are essentially men of their own localities. A journey of ten miles would bring them often into a terra incognita. The two old men mentioned above had a sincere regard for one another, yet it never occurred to them to traverse the fifteen miles of mountain which lay between their homes, nor to expend the three or four shillings which by rail would have carried them almost to the doorstep of each other. Perhaps such an incident as the following deters them. One old man of my acquaintance held a strong regard for another who for half a century he had not seen—and the while their domiciles were hardly ten miles apart. One day after much consideration old John decided that the time was ripe for a visit to old Billy, and off he set by the low moor road, with a pocket full of provisions to eat on the way. Two hours after he had got away, a hale old chap entered the hamlet inquiring for him. “Old John?” said I to the stranger. “Why, he’s just gone over the fell to see a friend in ——”
“Was it to see Billy Longmire?”
“Yes.”
“Then Jack’s just as daft as ivver. Here I’ve com be railyway to see him, an’ what mun he dew but set off be rooad to see me.”
The two veterans did not meet, for Billy would not sacrifice the return half of his “railyway” ticket, and Jack was so disgusted at the occurrence that he would not await his friend’s return. Though the pair lived at least ten years longer, they never made another attempt to meet.

BASSENTHWAITE LAKE AND SKIDDAW
But it is of Jacob that I should be speaking, and of the day when in Keswick market-place I tried to lure him on to description.
“I think a man like you will have met a few great men in your time,” suggested my friend in a halfhearted manner. “I mean did you ever see Southey, or Wordsworth?”
“No, I can’t say I ivver did. I hae often heard of Mr. Southey, but he was often away in t’ Sooth. But ther was yan chap I mind varra weel—t’ Skidda Hermit we used to caw him. Whar he com fra we nivver knew, but yan summer we began to find ther was some body leeven in t’ huts on t’ fell as hed nowt to do wi’ shipherds. But for many a day we nivver cam across him. We fand him at last in a ghyll penten’ a picter of a waterfa’—an’ a fine picter it was hooivver. But he woddent speak tull us. We thowt he was dumb and wanted him to tell our fortens, but he was as sulky as could be. He went off aw at yance leaven his painten and things just as they wor, and for a week or two we didn’t see him again. He was a tall chap, nut varra dirty seein’ how he leeved on t’ fell, and allus was fairly put on. But though he gat as he wod talk tull sum on us, he wod nivver say nowt about his name nor whar he com frae—you hed just to mention that and he was off like a deer and ye didn’t see seet on him agaen 164 for many a day. He didn’t stop on Skidda always, but he was oftenest there—it is aboot t’ whietest [quietest] place in England on t’ moor there. Then yan back-end he went off; he gev me a bit of blue cobble pented wi’ a grey sheep just afoor, but I lost it on t’ fell—it was weel done——”
“Coming, Jacob?” through the bleats and barks and whistles and shouts a voice interrupts; it is one of our friend’s neighbours prepared to go home.
“Aye. Good-day,” this last to us, and he steps into the trap.
Such is a Cumbrian’s description of Bassenthwaite. We went to hear about the lake, but alas! Jacob hardly had a word to say about it. Next time I will ask him about shepherd-life on Skiddaw and he will probably reel off stories innumerable of the water in summer and winter, and of the men who give to the lake the attention due. Jacob is typical of his class, and his reticence was not due to any wish to keep information from us.
The fact that Thirlmere is the reservoir for the drinking water of Manchester renders it somewhat unapproachable. Main roads encircle the lake at no great distance, but the whole watershed—Dunmail, Helvellyn-side, and Armboth—has been purchased on behalf of the city, and at hardly any point can one reach the lake-shore without breaking some bylaw. There is, I believe, only one boat allowed on its surface, strictly for the surveyors responsible for the embankment, etc. Though the lake was restocked after its conversion and large trout are now fairly plentiful, angling is hardly permitted.
The city of course has a perfect right to seclude the lake if by so doing they prevent impurity in its waters, and after all it is somewhat of a satisfaction to feel that a few square miles of Lakeland are tolerably certain of escaping the builder and the miner. The mines of Helvellyn are now likely to remain closed for our generation.
Old Thirlmere, like a winding river, connected a series of wider pools; at its narrowest point, near Armboth, it was spanned by stone bridges. Now, 166 by judicious embankment, its area has been doubled, yet there still remains a very definite river-lake. I think Thirlmere a place of beauty, though I do not forget viewing, from mid-lake (this pleasure was illicit, of course), those harsh lines through the trees and along the hillsides behind which the new roads are cunningly contrived. However, when you are on Armboth road the disagreeable “line” does not trouble; instead you admire a beautifully engineered way through the mountains, giving entrancing glimpses up narrow ghylls, vertical peeps into pretty bays, with the grand contours of Helvellyn ever present either through a film of leafage or more clearly between the groups of trees.
Most of us see Thirlmere from the coach or from our cycles. Though the scenery is so fair, there is no escape from the wheeled procession. The quiet retirement of the old bridle-road is vanished. From Grasmere the head of the lake is about half a dozen miles distant, to Keswick it is not much more than four from its foot. From the former the approach is up the pass of Dunmail.
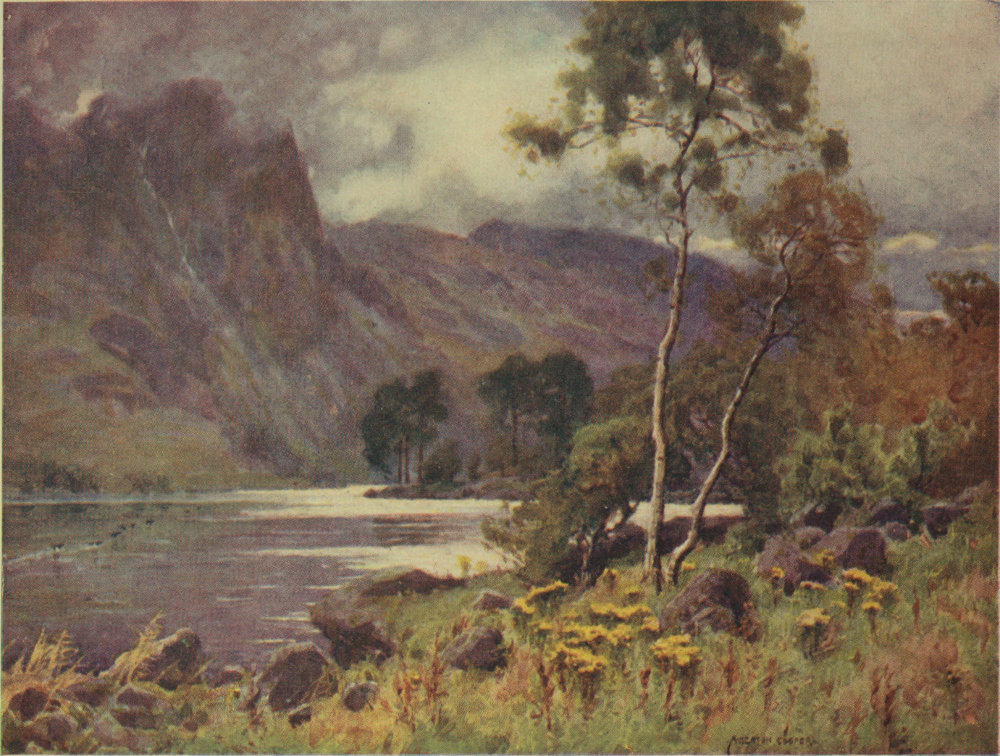

RAVEN CRAG, THIRLMERE
And this is the scene which meets the eye after you have toiled up the long slope. Behind is the bold and curious-shaped summit of Helm Crag, sage Asphodel, the Witch crooning over her hell-kail. Far off is Loughrigg fell with larch woods clustering up its sides, and the lake of Grasmere so dull with green reflections that a quick eye is necessary to distinguish it from its surroundings. Rising from your side is Seat Sandal, a host of carrion crows wheeling round its rugged knots; Steel Fell rises opposite, flecked with wandering sheep. The sky is bright blue, with soft white clouds lazily drawing their way across the narrow gulf. In wide patches the sunshine seems to drift about the landscape, picking out a green benk here, throwing a shadow over the crags there into some deep ravine. The scene at the head of the pass is of extreme wildness. The hillsides are scattered with scree, the uneven bottoms with boulders of every shape and size. The cairn of Dunmail, last king of Pictish Cumbria slain in battle with Edgar the Saxon, is here, a formless pile of stones. There is a legend concerning this spot.
The crown of Dunmail was charmed, giving to its wearer a succession in his kingdom. Therefore King Edgar of the Saxons coveted it above all things. When Dunmail came to the throne of the mountain-lands a wizard in Gilsland Forest held a master-charm to defeat the purpose of his crown. He Dunmail slew. The magician was able to make himself invisible save at cock crow, and to destroy him the hero braved a cordon of wild wolves at night. At the first peep o’ dawn he entered the cave where the wizard was lying. Leaping to his feet the magician called out, “Where river runs north or south with the storm” ere Dunmail’s sword silenced him for ever. The story came to the ear of the Saxon, who after much inquiry of his priests found that an incomplete curse, though powerful against Dunmail, could scarcely harm 168 another holder of the crown. Spies were accordingly sent into Cumbria to find where a battle could be fought on land favourable to the magician’s words. On Dunmail raise, in times of storm even in unromantic to-day, the torrent sets north or south in capricious fashion. The spies found the place, found also fell-land chiefs who were persuaded to become secret allies of the Saxon. The campaign began. Dunmail moved his army south to meet the invader, and they joined battle on this pass. For long hours the fight was with the Cumbrians; the Saxons were driven down the hill again and again. As his foremost tribes became exhausted, Dunmail retired and called on his reserves—they were mainly the ones favouring the Southern king. On they came, spreading in well-armed lines from side to side of the hollow way, but instead of opening to let the weary warriors through they delivered an attack on them. Surprised, the army reeled back, and their rear was attacked with redoubled violence by the Saxons. The loyal ranks were forced to stand back-to-back round their king; assailed by superior masses they fell rapidly, and ere long the brave chief was shot down by a traitor of his own bodyguard.
“My crown,” cried he, “bear it away; never let the Saxon flaunt it.”

THIRLMERE AND HELVELLYN
A few stalwarts took the charmed treasure from his hands, and with a furious onslaught made the attackers give way. Step by step they fought their way up the ghyll of Dunmail’s beck—broke through all resistance on the open fell, and aided by a dense cloud evaded their pursuers. Two hours later the faithful few met by Grisedale tarn, and consigned the crown to its depths—“till Dunmail come again to lead us.” And every year the warriors come back, draw up the charmed circlet from the depths of the wild mountain tarn, and carry it with them over Seat Sandal to where their king is sleeping his age-long sleep. They knock with his spear on the topmost stone of the cairn, and from its heart comes a voice, “Not yet; not yet; wait awhile, my warriors.”
The road now turns down the pass, a long, swinging slope where the steadying brake is necessary. To northward show the storm-washed sides of Helvellyn, with new rents staring like fresh-turned loam in the sunshine. A blue peak of Skiddaw is holding, as though unwilling to part with, a fleecy cloud, and here sweep into sight Raven Crag with its precipitous front, and the laughing summits of Armboth, one by one. Our cycles are gaining speed; we reach a corner, the top of a steep pitch,—there before us is a sudden view of Thirlmere, with Saddleback rising in rugged majesty behind. The open water is ruffled with breezelets, but every sheltered cove shines level blue. The pace becomes faster; the long curves are turned at ever-increasing speed. On either side are wide grass slopes, cut up by stony gullies. We are still above the zone of trees, if we except the fringes of rowan, the solitary hawthorns. Now across a bridge, spanning a wilderness of rubble where after heavy rain 170 a flood roars and even throws veils of spray on to the road. A straight descent, and below we view the gardens and trees, white-walled inn, and grey church at Wythburn. Now, instead of allowing the machines full way to race in fifty seconds down the half-mile incline, we approach more leisurely, for halfway down the steep the road we are to take turns off at a tangent. Out of a clump of tall sycamores an old farm emerges; this is the Post Office, far removed from neighbouring houses! To the right Helvellyn is now in fuller sight, furrowed with watercourses, jagged with scaurs, with the sunshine dancing on the brackens and warming up the sober green stretches of grass. The dale is desolate and barren, yet a portion is known as the City, in memory possibly of a settlement of Britons in its stony waste.
The great gap of Wythburn Head will afford a pleasant ramble to any one who has the time. There is no towering crag, no huge cataract, no narrow, yawning ravine, but an infinite variety of the sweetest brook scenery. Only a few hundred yards from the road is a small basin of water, entirely hedged by slabs of stone, ten feet deep, and so clear that the least pebble on the floor can be seen—a place scoured by floods as clean of sand and soil as though Nature were the most expert of housemaids. On the bottom, in their season, the chrysalides of the Mayfly crawl—how wonderfully protected they are by their stick-like shape and their coats of sand! most realistically they 171 imitate a piece of rotting twig as they lie in a chink of the pool-bed.
Another sweet corner I remember well. It is a dream of beauties in miniature. The down-pouring rivulet divides round a boulder, throwing two pearly cascades into the gloomy pool a fathom below. Round this pool the rocks rise sharply, crowned with foxgloves, heath and bog-violet, with a single stem of fly-orchis, with ivy and a cluster of the grass of Parnassus; more ivy wreathes around the roots of the trees, and long beards of moss drip with the outpourings of secret springs. Overhead, the alder, the rowan, and a few spindly self-grown ashes flourish, with a bush of glorious wild roses wilting loose petals into the slow-moving, bubbling circle. Ferns cluster among the tree-stems and on haphazard ledges, parsley and oak, the broad buckler and others, together with hardy bracken and other ubiquitous plants of the uplands. In a hole there a wren has built her nest, a thrush homes in the thickest holly, while the hawthorns are inhabited by a colony of hedge-sparrows and titmice. It is an active corner in bird-life if you have time to see it and your patience exceeds that of the busy midges.
The road has a slight incline which carries the cycle along with small exertion. The fences, as is customary in tourist Lake Country, are partly wall, topped with wire rail—a plan which allows the journeyer by road fully to enjoy the scenery. Tall, moss-grown walls and dense hedges are a feature of unfashionable 172 Lakeland, but, pretty as they undoubtedly are, they sadly narrow the wanderer’s vision. The lake is now close by, stretching into the reedy level meadows. One curious feature is a now useless bridge, raising its hog-back in the mere. Wee looks the white-walled inn across the glen, with the great mountain range almost overhanging it. The fellside above us is bristling with crags, some splintered and hanging as though a breath of wind would hurl a shower of stone down upon us; others rise in flawless tiers, grandly immovable, impervious to the forces of Nature. And beneath them is the dainty, dancing harebell, the jocund foxglove, the sweet blooming heather, and many a starry mountain flower. Few trees are in sight; round an abandoned farm is a lonely cluster of sycamores; gulls are screaming and paddling in what was once pasture-land. Bare and stern is the last back-glance ere our way curves into a passage cut through the rocks. Then, suddenly—is this a new land, a new Thirlmere? The transformation is sudden and complete. To northward, many a mile, stretches a narrow lake, basking in the afternoon sun. Dense coppice and green larches clothe the slopes rising from the water; there is no indication of farms, of humanity.
The lake is quite close, we gaze down a terrace of rock at its shining mass. A knoll crowned with tough, short oaks is almost cut out from the land; a faint swell breaks entirely round a rock on which heather is in bloom. In the bay some wild ducks are feeding; Thirlmere in the quiet of winter is a 173 grand haunt of migrants from ice-covered Northern seas. The lake is at its widest here; right opposite is the sham castle which Manchester erected over the pipe which draws, through ninety miles of mountain and meadow, the waters of Thirlmere. It is a pretentious battlemented horror of red sandstone at present, an insult to the shade of dour and grey Helvellyn. But perhaps time, and ivy, will soften the harshness, dull the too vivid colours, and the ugliness of to-day may be the beauty of a not-far-off to-morrow. On the road swings, ever softly on the incline, making the cycle run easier, and we pass through aisles of tall larch, beneath the shadow of sheering crags.
For a mile or so we pass through avenues of larch woods with broken crags ever shouldering against the roadside; then we come to Launchy Ghyll, the most extensive break in the mountain wall this side the lake. Not far from the ghyll, yet some little climb above the road, is the flat-topped boulder called the Justice Stone. It has been a famous landmark. It is suggested that its first use was in the plague years when the folks of Keswick laid money here to exchange with pedlars for goods from the outside world. Up to a century ago the shepherds of the neighbouring valleys used to meet at this place and exchange straying sheep. The climb up to the Stone gives splendid views of the lake and its surroundings, of Helvellyn range from Seat Sandal to Clough Head, of three-piked Saddleback, and of Skiddaw.
Armboth House is the next feature: the haunt of 174 the grisliest set of phantoms the Lake Country holds. For once a year, on All Hallowe’en, it is said, the ghosts of the Lake Country, the fugitive spirits whose bodies were destroyed in unavenged crime, come here. I would not like to be present at their banquet, for they are, according to Harriet Martineau, an unpleasant lot. Bodies without heads, the skulls of Calgarth with no bodies, a phantom arm which possesses no other member, and many a weird shape beside. But they are a moral lot—victims and not sinners. Does the wild shriek in which ere dawning ends their banquet mean that to the spirit eyes has come a revelation of their wrongers in torment? But I forget: no man can hear that cry and live. Yet people will not believe the straight-forward story of the Armboth ghosts, of windows lit up with corpse-lights, of clankings of chains in corridors, of eternal shriekings which cannot be traced, as though murder was being done in some secret chamber. But why has this house been compelled to be a ghosts’ haunt? I have never heard a word against its reputation, ancient or modern. Perhaps it is most central for the guests to the ghost supper.
From Armboth a road turns over the moors for Watendlath and Borrowdale. It is a breezy moorland walk ending in a beautiful glen.
The road leaves the woodlands, and we cycle for some distance in full view of the water. The land is fertile meadow; a welcome change from the sterile wastes. A wood clothes the further shore; the hillside 175 in front is known as the Benn, its summit stands well out from the fellside to which, if you trouble to climb so high, you find it is attached by a narrow spine of rock. Up here the Britons of old had a fort impregnable to assault. Now we reach the embankment, which has enlarged the bounds of the mere. It rises to a great height above the waters at present, but the engineers say that by a trifling amount of work the lake would rise sufficiently for a man, leaning over the parapet, to wash his hands in it. A road runs the width of the bank, giving a view up the sheening waters to far-off Dunmail. It is a pretty picture this—a succession of bluffs, some bare and stern, others clothed in clinging scrub of oak and ash, clustering with larch.
The return road winds round the hill into Legburthwaite, faces Helvellyn as though seeking a passage to its stone-strewn head, then turns sharply over a rise, and we are by Thirlmere again. The first view is exceedingly pretty. Neither sham castle nor embankment is visible, and you need not remember that the mere is semi-artificial. The fells of Armboth face one like a wall, broken here and there by a narrow ravine. On the fell you find the dip where Harrop tarn, beloved of wild fowl, is lying; you trace its rivulet threading down toward its long home in the lake. For a long mile we cycle along a terrace road high above the water, with Helvellyn rising to invisible heights to the left.
The next point of interest is Wythburn, its little 176 church and inn across the way known over the wide world. Wordsworth describes his “Waggoner” making a journey past here at midnight, and halting at the Cherry-tree (now a farm), a public-house on the disused lower road where a merrynight was in progress. Coleridge has given his tribute to the little house of God, and other equally famous names occur to one, who have not disdained to ponder on the simplicity here. Wythburn was once among the smallest of English churches, but an addition has been made to the chancel since those days. In a batch of notes collected from aged dalesmen many years ago I have the following story concerning Wythburn.
The rector, after forty-six years’ constant and punctual work, caught a chill which, as the week wore on, prostrated him. On Sunday morning his wife persuaded him to send word to the clerk to take service as far as possible and then dismiss the congregation. Ten o’clock came and a quarter past, when the single bell should have tolled to assemble the congregation. But to the concern of the invalid its welcoming clatter did not ring out. To appease him his wife hurried to the church, half a mile away, to ascertain the cause. She found the clerk scrambling up the moss-grown roof with a newly twisted straw rope which had to be fixed ere the bell could be rung. A wild goat (there were wild goats on Helvellyn then as on the Coniston fells now) had during the week descended from the fell where keep was scant, had leapt on to the low roof, and, nimbly stepping along 177 the ridge tiles, had found something eatable in the bell rope.
In another fellside the thatch of the church was once eaten by sheep. Services were not held in the building during winter; that was a particularly hard season, and a snowstorm had scattered the flocks ere they could be brought down. At still another fellside church a sudden jerk of the rope was apt to cause the bell to vacate the steeple, and with a rumble and a thud it would land in the adjacent field. Something was wrong with the swivel, but the yeoman who acted as bell-ringer did not know how to repair it. When the bell had finished its journey he would carry it back to its old position, and trust to luck for its remaining there awhile. But the parish clerk was a character, a class of himself in the dales, and on theological topics his voice carried little less weight than that of the parson. He was an independent fellow as a rule, and even the visit, once in a lifetime, of a bishop could not induce him to vary the methods which had descended to him through half a dozen generations.
In touring, extremes in conveyances and men meet—or perhaps, in these days of petrol, avoid one another. As the motor begins to monopolise the main roads, the true pedestrian is driven to the byways and field-paths. Gone for us seems the pleasure of swinging steadily, easily, over the hard turnpike; instead, we trudge in narrow, rutted lanes. Where, ten years ago, we watched the great events of the dale—the funerals, the weddings, the infants carried to church—now we must acquire a love for the everyday repose of Nature, else the Cult of the Hobnail knows us no more. Green hedges, grass-pitted roadways, ferns and flowers, birds and beasts of the wilder sort, must afford us food for observation and contemplation. Deeper and still deeper into the unknown countrysides have we to pierce, to taste again the keen delights of old.

HAWESWATER
It is a summer evening; the sky is packed with loose clouds; the sun’s rays, pouring through an archway left between two grey masses, merely touch the mountain-tops and are reflected down into the hollow glen about us. Not a sigh rustles the dense foliage; everything is dead calm save for the tinkle of water in yonder dingle—and the birds! The lark, the thrush, the whitethroat from its tuft of bosky grass; the sweet trills of the hedge-sparrow and linnet in the hedges, the yellow-hammer and the wagtail among the weatherbeaten outcrops. The stonechat too is here in his sober livery—but the harsh “natching” calls we hear are not all from its throat. There are three migrants hereabouts with almost identical characteristics—the whinchat, the wheatear, and the stonechat; but the last-named alone gives the call to perfection. There he stands on a notch of mossy rock on the roadside, his body seesawing as he gives forth the crisp, clear notes. That tuft of crimson feathers on his alert head distinguishes him from the others. Extending from the eye backward, they give the appearance of wearing a closely fitting skull-cap.
The hillsides around are steep, small crags jut out of their sides. Naddle Forest’s northern flank is clothed with a garth of small oak, through which in rides and patches the lovelier, livelier sward is seen. As we top a short rise, our view opens further, and into the distance stretches another narrow glen, its utmost limits invisible in a sea of filmy blue mist. In front, against a patch of bright blue sky, Walla Crag seems to mount to a tremendous height, its bare rocky facets catching the wandering gleams. The chorus of evening rises to rhapsody; then, as the light fades, the feathered choirs droop to silence and repose. Like a sheet of dull steel, between banks of darkening green Haweswater 180 now appears. Its outlet is through the plain of rushes, tall grass, and tangled underwood to the left. What an ideal spot for a heron! and seldom will you visit Haweswater without seeing one, more often a pair, here. The true wanderer will not deem half an hour ill spent in watching this interesting bird. As we ramble on, the glassy surface of the lake is ruffled by the rising evening breeze. The green and black-grey shadow of Walla Crag—the clear water had carried it so faithfully that I thought of Tennyson’s undersea isle—
“Where the water is clearer than air:
Down we looked: what a garden! O bliss, what a Paradise there!
Bowers of a happier time, low down in a rainbow deep
Silent palaces, quiet fields of eternal sleep.”
But now “the Paradise trembles away,” the vivid detail is blurred, its beauty marred.
To Measand we walk in silence. Ever darker, yet lovely in its gloom, is the lake beside us. Against the grey skyline the Force, coming in irregular foamy streaks down the crags, stands out finely. Where tall hedgerows overhung the roadway, we met a lad carrying a rod. His fresh, honest face, as fine in its lines as that of many a woman, attracted my companion, and, as a fellow in Walton’s craft, he asked what sport the youngster had had. His pannier showed nine trout, two of fair size. The lad had climbed over the fellsides to Cordale glen: after rain the upland streams become torrents and the trout feed voraciously. With these small brown fish life must indeed consist of a 181 few feasts and long, weary fasts. When asked what lure he had been using, the lad replied that, though he had carried a bundle of worms, the sleugh was more valuable. This, also called by the dalesmen the docking-grub, is a small white maggot chiefly to be found under flat stones in wet places. From angling, the chat turned to the native red deer. Yes, they were often seen, two or three generally haunting the ridges just above. Last winter one died there of starvation, and to-day, in Cordale glen, the boy had found the skeleton of another.
The beck we have just crossed comes from Fordendale, a gully prized by geologists as showing perfectly the course and action of a past British glacier. A wood-owl now begins its long-drawn “hoot-hoo,” from some glen across the water. A ring-ouzel, the mountain blackbird of the natives, though it wears a white crescent on its breast, next flies past. This is one of the later migrants to arrive, and does not leave us so long as berries remain on the rowan-trees by the ghylls. Now we are on the lakeside again: a trout leaps and returns to the water with a heavy “plunk.” A swallow flits along the dark expanse, hawking the last of the dayflies, and at the same time, with soft cuttering song, winging home. The last light is almost dead over the western ridges, and the detail of things by the roadside is uncertain. See, on that patch of dripping moss, five flat yellowish leaves from the centre of which, on a slender bending stem, rises a flower not unlike the woodland violet in shape. It 182 is the butterwort, most inaptly named, one of the three British insectivorous plants. Unroll that curling leaf and you will find a store of partly-digested flies. With us in Lakeland the butterwort is usually found far from cultivation. A plant of the wilds it is, trusting to the free air rather than to the thin, poor soil for sustenance. The owl in Naddle Forest has now roused up a mate: their combined voices come across distinctly. A faint whistle sounds up the mere: an otter is out for its nightly raid. As I have observed him this creature is not an arch-enemy of trout. In wanton sport he may mutilate numbers of fish, but his chief diet is the freshwater crayfish. A casual examination of an otter’s hole will prove so much from the appearance of the excreta; and, while you are at such close quarters, note the plenty of fish-life in the pools near by. No further evidence is needed to correct much misjudgment. In the water the otter is graceful; in the meadows he lopes along at great speed when such is necessary. Overland he occasionally crosses even mountain ranges: lying on Kentmere High Street one midnight I heard the unmistakable calls of a pair close by, but the night was too dark for me to see the creatures.

SHAP ABBEY
Now the road leaves the waterside, and we soon come to the fell where, in a recess of the rocks, Hugh Holme hid from his enemies in the days of King John. Hugh was the first “King” of Mardale, and through a long line his name held that peaceful post. The last direct male descendant died less than twenty years ago—he held the ancestral home to the end, while the Mounseys, “Kings” of warlike Patterdale, parted with their birthright long ago. A curious faint whistling has been gradually drawing my attention. With a wild cry, like “whisp” long drawn out, a woodcock “flights” in the jerky manner peculiar to its kind at eventide. The dale is now enveloped in midsummer darkness; the meadows, but for their wreaths of white flowerets, would be invisible; the lake is hardly to be seen for shadows.
The inn is now little over a mile away. Tramp, tramp,—there is a cheery something to be felt rather than expressed in such an excursion. Moths in quaker grey and white flicker close past; beneath the sycamores night-beetles hum in busy flight. Now, on our right, a darker clump: the famous yews of Mardale almost burying the tiny church in their green sweep. Tramp, tramp. The yew-tree was favourite with our fighting fathers: from it they tore staves for the longbow. The yeomen of Lord Dacre, recruited from these dales, stood stern and immovable at Flodden, and by their well-aimed shafts turned back the Scots in dire defeat. Tradition says that Rudolphus Holme founded an oratory here in the fourteenth century. The present little church dates back some two hundred years; its graveyard was not consecrated till many years afterward. Even yet old dalesfolk will point out where the corpse-road crossed the fells to Bampton. According to such, there were two roads into Mardale: the assize road, 184 by which, almost as the crow flies, juries went to the county town; and the road we have mentioned, used almost exclusively for funerals. There were no bridges in the dale then, and during winter, and even summer, the torrents were at times quite impassable.
Just as we pass into the short lane to the inn, there is a chorus of loud “cronks” above, and against the grey night pack we see six dots: a family of carrion crows hastening home, belated, from some dingle where perchance a dead sheep is lying. The carrion crow is larger and more powerful than the rook (which in the dales is misnamed the crow); its note is harsher and more jarring. It lacks the majesty of the raven’s croak, and stands apart from the not unmusical garrulity of the rook. Now, within doors, lights are gleaming. The hotel looks a home in a land which, in darkness, to jaded limbs would soon become weary. Our hostess, with a quiet laugh, says:
“‘Birds o’ passage’ ye call yerselves; ‘here to-day and gone to-morrow.’ The hedges and woods are comfortable to the wee things that come with the hawthorn—we’ll try to make our inn as welcome for ye.”
To see Ullswater is to love it, and to love a scene is to often travel that way. I often travelled there even when so to do meant an eighteen miles’ tramp there and an eighteen miles’ tramp back again. I have walked there to go fox-hunting, and some rare chases I have enjoyed—crags of Fairfield and Helvellyn, yes! (I have tramped back, too, with shins bumped and skinned through scrambling among the rocks, and oh, so weary and footsore.) But we are not fox-hunters always in the land of the fells, whatever our detractors say. We do not see beauty in the same places as they. The “splendidly rugged” hillside of the rambler is only “bad ground” to the shepherd kind; and the waterfall thundering in the gloomy dell, so admired by the emotional, arouses little interest with those who in wild winter have to wrestle with torrents as foamy and rock-tortured as the finest peep of Aira or Lodore. We see beauty in the small things of our everyday life—in our wee birds and springing flowers (when the flock does not make us too busy to notice them). I have seen—I almost said I know, but that is too big a boast for even those who 186 dwell there—Ullswater under almost all conditions. My first view was from far-off Kentmere High Street. Only a small portion was visible, still that much was Ullswater. The next time I saw its long stream from Helvellyn, but the time was not ripe for going down. My feet were toward Thirlmere, and the other lake had to wait awhile.
Shortly, however, I had opportunity—I started ere sunrise, and met the light on the top of High Street. I was still a novice at fellscraft, and knew but little of the lay of the land. Still, with face set so sure toward Ullswater, neither map nor guide-book was required to keep direction. It is wonderfully deceptive, that descent of Fusedale. From the ridge it seems that ten easy minutes down the slope would bring one there, but an hour passed and I had not reached Howtown bay. On the way I had a distant glimpse of some deer. On the fells hereabouts a herd of native red deer roam in a wild state. Sometimes outlyers go far south, and more than once they have been chased miles by hounds. A forester looks after the herd—no light matter when there is no keep on the uplands and the half-starved animals break into the turnip fields, or drive the sheep away from the hay thrown out for their benefit. The forester also regulates the constitution of the herd: occasionally there is a day of thinning out redundant stags or hinds. The red deer was till comparatively recent times known on several of our wilder fells. At Ennerdale a piece of rugged fell known as the Side was a rallying point for them, and from this they ranged the mountains to Buttermere and Wastdale, where some few homed about craggy Scawfell. There was a wild herd on the Rydal fells for long, and within the memory of persons not long dead deer used to wander occasionally on the moorland between Duddon and Esk. Stories of how their fathers fought the deer in winter from the stackyards are often told by the dwellers on Ullswater farms. Hereabouts, too, nested the golden eagle long after it was extinct in less stern parts. The last was recorded as shot on the Martindale fells by a local named Sisson, about seventy years ago. The bird had been unknown since 1790, when a mature specimen was shot or trapped in the wilds near Buttermere. The birds and beasts of Ullswater at that period would make an interesting list indeed: kites, eagles, bittern; martens, badgers, wild cats, and the like. I don’t believe there are any wild cats now, but the sweetmart is not yet extinct, and latterly there has been a recrudescence of the badger. The foumart is a noisome beast, and capable of doing great damage in a poultry roost. Dogs will hunt it with glee, but are content to corner it, not to bowl it over.

ULLSWATER, FROM GOWBARROW PARK
A sultry June morn
I was disappointed this first time I reached Howtown to find that the road did not follow the lake shore. Instead it curves backward over the ridge between Hallin fell and wall-like High Street. This is a bit of bleak road when the Helm wind is tearing up the lake, but the meadows around the wyke are so snug that tents are not seldom there until November. Hardy 188 campers these! Martindale is a really odd corner—I think it got its distinctive atmosphere under the forest laws of Rufus; for except a new bridge and maybe half a dozen red-painted carts, everything has the indefiniteness of hoary age. Perhaps it is a knowledge of its old-world fauna which makes me place Martindale so far remote in the ages. The road passes the church; the growing greyness of this makes its exact year of erection difficult to fix. The clergyman in charge for long had the smallest direct revenue in the diocese of Carlisle, and the benefice was often awaiting acceptance. Nowadays, however, the three pounds yearly is greatly improved upon.
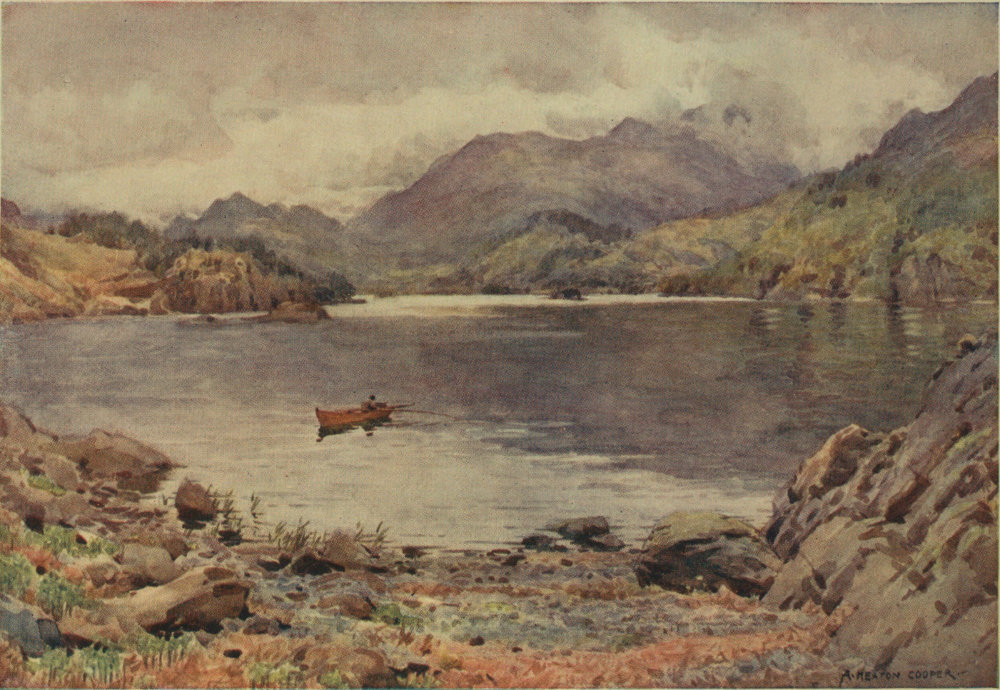

ULLSWATER: SILVER BAY
Past Sandwick there is a return to the mountain track winding in bracken and cevin. Then for miles, now a hundred feet up the hillside, now at its level, the lake is skirted. There is a succession of fine views, near and distant: of the steamer slipping through the deep blue water within stone’s throw of the crags, for the lake-bed falls in a precipice here; of sheep climbing and grazing on the shelving hillside, and timorously rushing off at our approach; of the swell when a breeze lifts it along, bursting green on the boulders and throwing shimmering spray into the air; of birches in their summer radiance; of thin green shadows of ghylls where rivulets are slipping down to the lake through piles of moss; of the bramble, and the fox-glove and the heather; of the juniper, the rowan, and the bilberry; of green Glencoin, and mine-torn Glenridding; of thorny Gowbarrow; of the hilltops embosoming Matterdale and its quaint old church, where the sacramental wine was long kept in a wooden keg, and where many a dalesman was baptized “of riper years,” opportunity not serving to traverse the weary miles from home when he was an infant. One dweller at least in remote Martindale (whose chapel was then unused for want of a cleric), can tell of his “kursennin’” here. He was a big lad when the family party were rowed across Ullswater and clomb the brow by Aira Force. The little church he remembers well, especially he noted a big bass fiddle hung on the wall near the font. Fifty years or so later he revisited the place and pointed out where the fiddle had hung on that memorable day. One of the fiddlers left his instrument here between services, out of the way of the lads. The village orchestra was a feature in old dales churches—we were far behind other parts in adopting the harmonium or the organ. At one place the parson’s wife used to lead the singing on a concertina—not very many years ago.
Rounding the fell corner, there is a glorious view of Helvellyn and Fairfield, empurpled with scree, rifted with ravines, solid, smooth crags sheering skyward, often aloof from the bulk of the mountain. A ragged line etched against the sunny green fell shows the Striding Edge’s top, that other ruggedness ending with a sharp peak is Swirrel Edge with Catchedecam. Between these two, and beneath the wide breast of Helvellyn is that romantic rock-basin 190 where lies Red Tarn, the most notable and highly elevated of our mountain waters. Trout caught here are remarkably thick in the shoulder. Our ancient writers make the char also occupant, but no one living has, so far as I know, ever seen one there. As the water is deep, attempts were made half a century ago to introduce that fish; but whether ova, fry, or fullgrown fish were turned in, their enemies accounted for them so well that not one was observed again. An ancient friend of mine—an angler and poacher of wide repute in the old lath-fishing days—once told me a wonderful story—“aye, an’ I’ve caught ’em mesel’, up to a poond weight”—of a unique race of fish dwelling in the fringe of the mist at Red tarn. He called them the silver trout. Their scales were silvery, their fins small, their flesh dainty. Only in the deepest pools beyond the reach of a shore rod were they found; to the lath with its trailing baits alone they fell. I have from other sources heard a similar story, but no one lights upon the silver trout in these days. Old Tom was quite unlettered; it is unlikely that he ever heard that old books asserted that the skelly or gwyniad, as well as the char, was to be found here.
In peak and frowning crag, in shadowy slack and deep cove, Helvellyn extends far to westward, finally breaking away at the sun-filled hollow of Grisedale. Westward again, the debacle, an amazing tangle of mountains, some throwing a mossy green shoulder into view, others jagged precipices or walls of scree—Fairfield and Cofa Pike, St. Sunday’s Crag and Hartsop Dodd, Red Screes, Kirkstone, and many another. But to describe yard by yard the opening view were tedious indeed; when one has climbed almost every moor and mountain within sight, and walked in many of the coves and valleys, one is apt to have much to say which must be familiar to all who know the Lake Country by repute.
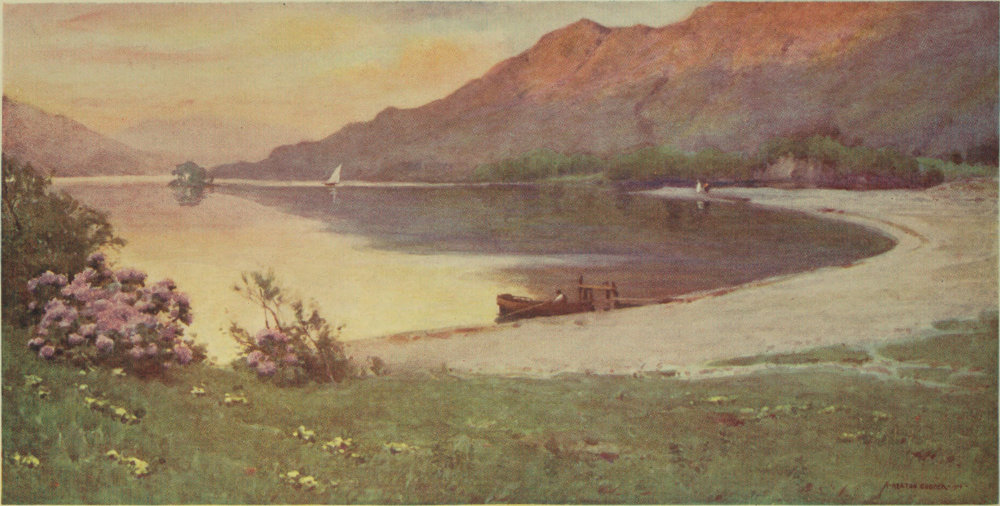

ULLSWATER: THE SILVER STRAND
Afterglow
There is little of history in the Patterdale of to-day; the inrush of tourists has caused the old-style cottages and farms to be renovated almost out of existence. Bay windows and upper floors take the place of bottle-glass casements and the old camp bedsteads which stood in recesses of the one long room, and, by their great size, formed really chambers within a chamber. To see Ullswater fully we must be upon it. A boat is secured and we float down the Goldrill, river of pretty name and raging furies of floods, under the bridge. Hereabouts another rivulet joins us, to-day in quiescent a mood as ours; but it has trilled down steep Seat Sandal, eddied in dark Grisedale tarn over the crown of Dunmail, burst in mad career down the dale of the Wild Swine (Grisedale), losing pace in the level meadows, and now in a murmur it glides through the laced alder shade to fall in here. The united currents send us out on to the lake itself, carrying us clear of the wide tangle of grasses growing in the silt the floods carried from Kirkstone and Helvellyn. This upper basin of Ullswater is where the great lake trout was last to be found. Though it is several years since 192 an undeniable example, with hooked underjaw, was caught, the existence of the fish was no myth. Legend makes too much of its size, asserting that fish sixty pounds in weight were landed. At flood time the great trout, states Clarke, writing about a century and a half ago, ascend the Goldrill, as also in autumn at the time for spawning. This in his day gave rise to the sport of spearing, to join in which, he observes that gentlemen came from great distances. The redds, a series of sand-bottomed pools, were visited at night; a torch showed where the fish lay, and the sportsman, armed with a three-pronged spear, kept striking as long as a big trout was within his reach. The ordinary lake trout to-day hasten into the river when a flood is due, after there has been heavy rain on the fells. As our boat is pulled from the shore, the grand panorama of mountains begins to show; the bluffs behind the village dotted with white hawthorn, and the flat lands by the river are not yet dwarfed by more mighty forms. Place fell is the most commanding sight, two thousand feet of rock rising in unbroken slope from the water’s edge. A level tongue of land is now quite close by. The whitened current pouring through acres of silt is silent testimony of mining activity. This stream has its little tragedy. Once the char inhabited Ullswater, and spawned in Glenridding beck. When the mines began to be worked many breeding char were poisoned by pollution. Others to save themselves did not shed their spawn, but returned to the lake. A few afterwards left their ova on the shallows and among the water grasses, but the following seasons the females held back their spawn altogether. The stock of char became rapidly depleted, and for years there has been no trace of the kind in the lake.
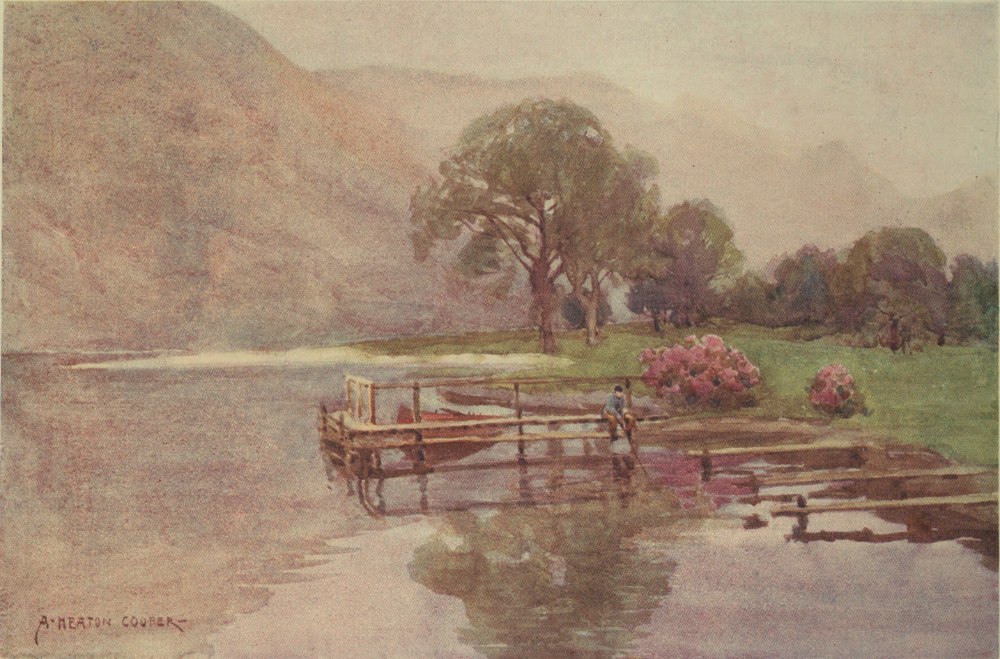
HAZY TWILIGHT, HEAD OF ULLSWATER
My taste is not for big hotels, but I will admit that the Ullswater, with its back to wooded Glenridding, has a splendid site. It faces across the lake the bloomy sweep of Place fell, and Helvellyn, with a tumult of hills around it, is also visible from its grounds. At the foot of its garden is the steamer pier. To me there seems little of anachronism about the Ullswater boats—I wonder why? At Windermere the yachts always seem out of sympathy; at Coniston this is glaringly so (such opinion does not prevent my using them when convenient); Derwentwater’s toy fleet plies between Portinscale and Lodore, from one palatial hotel to its neighbour. The boats here are more business-like. The sharp, near fells, the deep blue of the water, make one think of beauteous Norwegian fiords, of arms of the sea where the rise and fall of tide is scarcely marked on the upspringing rocks, rather than a lake of quiet England.
Our boat is turned inshore, and we feel the coolness of nearing woodlands. Above our heads oaks are clinging in thin profusion to every ledge of a lofty crag—this is Stybarrow, the rocky hill dividing Glenridding from its eastern neighbour. Nowadays a main road has been cut through the foot of the fell, just above the level of the water, but a disused zigzag 194 track shows the way dalesmen of the past travelled to market. Difficult was the track for friends, with many a rut and spongy mire, sharp curves and slippery ascents; but for foes from northward it was for centuries impassable. Little has history to tell of the head of Ullswater; the customs of the country-side, the lack of fortified places, of even a Border tower or of a cattle keep, tell plainly of uninvaded peace. But though their lands were free from harrying, the yeomen of Patterdale were ever willing to fight under the banners of Greystoke and Yanwath. And for thus leading the foray the wild Scots of Liddelsdale once almost dealt them retribution. A strong band stole across the Esk, and during the night rode hard up the Eden valley and across the grassy fells towards the lake. Marching unsignalled, from an unusual direction, their presence was first noted by the shepherds as they rose from sleeping in the folds on Helvellyn. One ran to rouse the glen, the others made a rush down the mountain wall between Glencoin and their home, hoping to hold the road, the key of the situation, long enough for their friends to rally and beat back the invasion. Mounsey was a stout yeoman, had seen service long and hard in Border campaigns, and he it was who took command. He placed his few where the road narrowed between two crags and was steepest, where the rocky ground prevented the dreaded charge of the enemy’s horse. The Scots came riding on, unaware that their presence had been discovered till a flight of arrows whizzed from rock and bush. Thrown into disorder by these, a second volley sent the raiders hot-trod to the foot of the hill. Here they formed an attack, leaving their ponies, taking what cover they could find. They reached the belt of timber, and carefully crept through it without finding an enemy, for the men of the dale had after their ambush retired, so that the shock with the full weight of the Scottish force could not be brought to bear on them at a disadvantage.

A MOUNTAIN PATH, SANDWICK, ULLSWATER
The leader halted at the upper edge of the forest to survey the situation. To his eye, there was no way of winning up that lofty hill while the bows were plied from shelter secure. Accordingly he halted, sending scouts to right and left. The chief had certain knowledge of the number of men-at-arms in Patterdale; he had brought a party strong enough to crush their utmost resistance, and had cut off their chance of alarming their allies of the low country. One scout told that away to the left the fell became a terrific precipice, along the wooded ledges of which a party might move to attack the dalesmen’s rear. Fifty were accordingly detached to force the way of the cliff. Safely they passed through the wood of Glencoin, then swarmed cautiously from ledge to ledge of the dizzy crag; the blue lake beneath received the stones they dislodged. Of a sudden the leader of the forlorn hope reeled, threw up his arms, fell back and down—down—down. Undaunted by his wild cry and the splash which after a pause showed that his body had fallen from ledge to ledge into the lake, from their path in mid-air the Scots sought the archer 196 in vain. Another man, with a strange gurgle, swung round, grasping at the cloth-yard that had transfixed him. He too fell into the abyss. When the tenth had been struck, one of the Scots espied the enemy. So far away, and deep below, that he looked merely a doll, an archer stood on a rock by the shimmering water. Mounsey had divined their plan, and with his strong arm and sure aim saved Patterdale from invasion.
The Scottish leader waited hour after hour for the wild slogan which should proclaim that his men had attacked the ridge, then a few stragglers returned from the face of the cliff and told him of the disaster which had befallen. The word was given at once “to horse,” and the raiders sped back to the Border. For his service the men of Patterdale claimed the Mounsey as their king. He was given the best house and land, on condition that he, and his heirs for ever, should be able and willing to lead the dalesmen to victory. For centuries the family held their post with distinction. The first Scottish rabble to break into the glen were the men of the Forty-Five. And they did not get far beyond, for the men of Troutbeck manned the narrow head of their dale and, unaided by the Royal army, beat back the invasion. For which the courage of Patterdale is still slighted across the fell. The last King of Patterdale flourished a century ago; his estates were afterwards sold to the Marshall family. The name and lineage of Mounsey still exists in the dale.
I find legend a too-fascinating topic; get the boat pushed forward if we have to see Aira Force this golden afternoon. The wavelets rattle gay under the bow as we sweep past soft Glencoin, with a solitary house glimmering through the trees—Seldom Seen, once, it is said, the jewel-house of the Howards in time of serious war. But the greatest beauty is on Place fell. In bands of green and brown and golden yellow, in purple streak and white, it rises rock on rock, slope on slope, more the presiding genius of Ullswater than vaunted but distant Helvellyn. The rugged Gowbarrow we are approaching is tame and smooth compared with the giant across the water. Tree-fringed, with brake of bramble and low bushes, the road runs along the northern shore; beyond bay after bay we find it keeping pace with us apparently. It is a level run for the cyclist, and happy is he who first at sunset approaches by it. On a curve of white shingle we land; the field is glorious with water buttercups, and the last wild roses star the brakes around. The gorge of Aira is quite half a mile from the lake. Leaving the road Lyulph’s tower cannot be evaded by the observing eye. Who Lyulph was is a disputed point among the Doctors; his name was given to this place after he was long dead: he wasn’t foolish enough to design or build this erection. Relief comes to the soul when, rising up the hill, you see the meadows where the daffodils blow, the place where Dorothy Wordsworth pointed out to her gifted brother the flowers dancing in the breeze and struck the chord which gave us 198 the fine poem known as “The Daffodils.” Aira Force too has its story of love and romance, which is briefly stated thus: A lady dwelling beneath knotty Gowbarrow loved a knight of Cumbria, and they were wont to tryst by the waterfall. The lover, to prove his love and gain honour, joined a crusade. No news of him came from Syria for years—he was a prisoner there—and the lady, lonely and much troubled, began to fear that he had fallen. At length the knight broke prison and hastened home. At night he approached the trysting place of old, and through the trees saw a lady in white moving. He sprang forward to meet her—it was his own true love for whom he had jeopardised his life—just as she came to the crag which overhangs the torrent’s leap. In his arms he held her a moment, then she started back, back, and out of sight—down that terrible rock, into the gloom of the spout. After her leapt the brave knight—he found her in the whirlpool, caught her, and reached the shore. And there, as he bent over her, she opened her eyes a moment and recognised him; with his name on her lips she died. The sudden shock, the fall, the deep waters, had beaten out the frail life of the somnambulist. By the waterfall the knight built him a cell, and, a hermit, dwelt in the solitude.
The hollow of Aira is a gloomy place: moist-loving ferns spread over the rocks, there is wet moss everywhere, spray ever hangs dank in the air. In height Aira is great among our waterfalls. In flood-time it is a glorious medley: flying waters, shiny fangs of rock, dripping trees and grass and weed and fern.

BROUGHAM CASTLE, PENRITH
Although the lower portions of the lake, toward Pooley, do not come into this brief survey, they are far from unlovely, though to most the beauties do not begin till Hallin fell is abreast and wild Gowbarrow. The eastern reaches are more domesticate—green swelling hills and wide woodlands, with many-acred spaces of smooth pasture. To the south of the lake’s outlet is Swarth fell, a haunt of straight-necked foxes (I have been at their chase from far-off Kentmere), and to the north is Dunmallet, another of those curious “teeth” found among our lake mountains.
My finest experience of Ullswater was on a summer evening. Our boat, to quiet pulling, stole out into the upper lake. The sun was nearly down to Fairfield. When about opposite Silver Bay oars were taken in—their solemn steady chunking sound seemed to mar the harmony of even. A few men and women were wandering the paths by the mouth of Glenridding, but no one was afloat. Away over the horizon, behind the fells, thunder is still echoing. An hour ago raindrops dimpled the lake’s surface; the air was dark and brooding, every few seconds a vivid flash of lightning rent the gloom, and blast after blast of heaven’s trumpet seemed to shake the mountains to their deep-set foundations. After storm, calm—and refreshment and peace at eventide. From westward pour the generous, kindly beams of light, pouring out new life to rain-dashed fields and woodlands, giving 200 new songs and glorious to the birds. What a glory of colouring mantles field and fell and forest. Though a wide gate is cleared for the sun in its latest hour, dense clouds are still overhead, and the north-east is ink-black. The sun touches the topmost ridge of Fairfield with living fire, and just beneath is a deep fold of violet vapour. Place fell is glorious with purple light, its riven ghylls mysterious with a deeper tinge. Along the craggy face of Helvellyn a soft veil of mist is rolling: from hollow Grisedale come cloudy wreaths and streams which bathe the mountain-top ere they dissolve in the amber even. Around us Ullswater spreads, blue as the bluest of our summer skies; its ripples, like frolicking children, rejoice in careless mirth. Now the sun hides behind the turmoil of mountain-tops, and we are in a vale of glorious shadow. The faint lake-current and the soft-moving breeze drift us ever down the mere: we are past Glenridding, the climbing shadow has risen far up Place fell. Above, all is clear and golden; a sharp line passing along the hillside marks off the zone of light. The sheep are wandering upward as the day retires; from the summits they will greet the first gleams of to-morrow. The dusk gathers in every hollow; night is softly, reluctantly, drawing in. Still the drama of sunset ebbs tardily on the rocky heights; a wee wafer of cloud, the last of its tribe it seems, is drawing away from the flaming west. As it curls and rolls its course up the sky, its brilliance fades to crimson, to thin purple, and, as a grey lock, it fades 201 out of sight at the zenith. Boats are now astir on our Ullswater: hardly can there live a man, or woman, so dead to the beauties of Nature as to willingly stay indoors on such an eventide. So time passes: we drift beneath the bulk of Place fell, then the oars are put out and in the shade we steal along. Grey-blue are the heights behind Glencoin, all the glory has gone from the western sky. The clouds have crept out of the north, and streaks of pulsing night-glow come up in their stead. Brown the woods on the hillside above us, and a silence of sleep reigns supreme. A rill falling into the lake rattles pleasantly; the soft whistle of an otter, the wing-beat of a bird hawking the night moths, the sudden splash as a trout falls from its leap into mid-air, break pleasantly on the ear.
Look above: the mountains shoulder to great frowning heights, but the marvel of all is the sky. There seems no firmament, no bound to the ranging eye. Only the gate of heaven itself seems withdrawn from vision. Star-drift, in soft luminous puffs, besprinkles the great violet dome: planet and fixed star, great and small, dust over the immeasurable width with ten million sparkling lights. On most nights it is the stars that seem so far away, but to-night, by quiet Ullswater, they discover themselves as milestones near us on the way to that distant blue curtain which is the nearer boundary of heaven itself. More comprehensible is the element beneath us, where over plunging depths are mirrored the twinkling stars. 202 There again the light is a veil to a mystery, but not a boundless one. For we know what manner of things lie beneath the waters: their pits have been plumbed and their secrets discovered. There is a flush of pale primrose in the east: the moonrise. How the the frail light glows! We turn the corner of Hallin fell toward Howtown ere the full orb at last rolls into sight. In a few minutes the fells are radiant with the peaceful beams, and a broad track of silver leaps down the bay.
Perhaps it were more correct to say “minor waters,” for some are hardly within the pale of the mountains. There are, on fell and in dale, above thirty of these tarns, and, as the lakes vary in type of charm, so do these. Their variety, moreover, is even more bewildering than that of the lakes. In the latter’s wide landscapes, no matter what the circumstances of weather or season, one cannot mistake Windermere for Ullswater, Derwentwater for Wastwater. The tarns are, however, entirely different. I think particularly of three views of Angle tarn, under Bowfell, so distinct in what a poet would call their emotions, that memory will hardly recognise the three as having but one geographical position. Scarcely daybreak, we had passed the summit of Bowfell into Ewer Gap. We could see hardly five yards in front, and ere long our leader, though well accustomed to the fell under most circumstances, confessed that he was astray. But on we plodded: “We’ll get somewhere,” though that might be over the crags into Eskdale or headlong down the precipices into Langstrath. At last, when 204 the others began to descend a dangerous slope, the bottom of which could not be seen for boiling mist, I commanded a halt. In a minute or two the mist was torn aside by the morning breeze,—chill, raw, and damp it was even after the fold of night-cloud,—and there “blae as wad,” as we of the dales say, was Angle tarn sheer beneath. Solitary, within a weirdly uptossed land, its shoals seen through a veil of blue water, its depths showing in greater quality of cobalt. We were perched on the front of a lofty rock: a dozen yards forward might have ended in an accident. I am not likely to forget that scene: grey dawn, the brisk breeze, the mist scurrying out of the riven crags around, the eerie feeling of desolation—we were in touch with the soul of Nature at her moment of uprising. Again I saw the tarn at daybreak. We had climbed in the velvety July darkness up the rough penance of Rossett ghyll. The small expanse of water looked violet cool in the growing light; it was calm, and austere with the austerity of a virgin Alpine pool it seemed to me. A soft greyness which the most marvellous steel engraving cannot picture draped all things made, till the great sun leapt over Helvellyn and hurled day on to a land of dreamy repose. Again I came that way when the August sun beat down, and the great barrier of mountains seemed to tremble and to swim in heat-haze. The waters laving the harsh crags were a deep pitiless blue. One felt that the hard blaze had driven all sense of coolness from them. The grass drooped on the fellsides, parsley fern and mountain moss suspended life and made patches of dusty brown, the crags were grey with drought. Not a tree in sight, not a line of shadow save right up there, almost at the mountain-top, a refreshing triangle of darkness, “the shadow of a great rock in a weary land.” One’s inmost soul felt the harshness of that day, and that by it the land was robbed of much fairness.

ANGLE TARN, ESK HAUSE
And what romantic situations are occupied by some of our tarns. There is Red tarn, above which towers the upper rampart of Helvellyn. To right is Striding Edge, to left the narrow ridge of Catchedecam. How fine a gloom does the old mountain throw at sunset over this beauteous spot! There is Stye Head tarn, abode of horror, the gloom and beauty of which so impressed Ruskin. The romance of this tarn is heightened when one is privileged to visit it by moonlight. How the great rock-billows, greyly seen, overtower the tiny gully! How man with all his petty conceits falters in the presence of the greatness of Nature’s majesty! One side the pass is impenetrable darkness; across, the light accentuates every ruggedness; streaks from the skyline show where the rivers fall from parent heights. “I felt that I could take out a half-penny and crawl out of sight under it,” said a very unimpressionable person to me after such an experience. “The loneliness crushed my voice, my mind, and, as it seemed to me, my stature. I would have hidden from the scorn of all things made.”
Our minor waters cannot claim much history: most 206 of them are too far into the wilds to be mentioned in ancient story, except in a hazy and collective fashion. Several of our lakes have been served likewise. But that humanity knew of them in far-off ages is sure. By Whinfell tarn Britons of old lived; a canoe was some years ago dug out of the oozy peat there. And on the opposite side of the Country there are extensive ruins of a city within a mile of Devoke Water. Who built Barn Scar cannot be told with surety; for long legend put it down to Danes who peopled it with lads of Drigg and lasses of Beckermet.
But if legitimate history has failed, there is amplitude of legend. Most will have heard of the deathless fish who are said to live in the depths of Bowscale tarn; of the fairy chasm in the sunless deeps of Scales tarn under the frowning Edges of Saddleback. On the fells about them have been seen mysterious armies, coming, coming. Brothers Water has its story of gloom and death: how two pairs of brothers were drowned in it. Of Grisedale tarn, storehouse of King Dunmail’s crown, I have told the story. Gates Water, by Coniston Old Man, has a few weird stories, but they are entwined hopelessly almost. There are stories of pigmies and giants who lived in the wildernesses, of fairies and evil spirits who wail over shapeless mounds of rock, ruins of cities of uncouth days for aught we know.

DALEGARTH FORCE, ESKDALE
To see the heart of Lakeland, one should make the pilgrimage of the Mountain Tarns. It will not be an easy task: the highest fells will have to be crossed—it will need perseverance and strong boots. And even in these days of motor and cycle some humans can and will walk. Many a mile of breezy moorland will be found on such a pilgrimage; not weary when the heather’s purple bells are at their widest, when green grass clothes the ghylls, when the rowan flowers, and the white foam of hawthorn dapples the fellsides,—many a mile of rock and crag, rain-washed, frost-scored, scree-strewn, lichen-covered, many a mile of smooth upland where curlew and plover whistle and wail, where raven and hawk flight for carrion and live prey, where fox and otter, and even red deer, are to be discovered by the alert, nooks where grow our rarest ferns and mosses, waterfalls and rattling cascading becks.
Such a pilgrimage would commence outside the range of the fells. The pedestrian would strike north from the town of Kendal—a grey “burgh of ancient charter proud”—for Whinfell tarn. This is a tarn of the renascence, think the fell-wanderers; Nature having shed her grandest pearls in the gorges and on the rock-shelves to westward, came to bestow her final blessing in the low country. She sat beneath whin-patched Beacon and wept over the sweet scene she could not really decorate. But of all her plenishings she still had a trace, and well she bestowed them: the roach, forgotten when char were placed in Winander; a knot of curious weeds which soft currents sway in the peat-bottomed pools, and—a boat. This old punt so often went to the bottom that it was as muddy 208 as a street on a wet day. Nature, those countless æons ago, endowed Whinfell tarn with it—it was long before emulous Britons fashioned that moss-buried canoe—and what better craft was there, said the contented folk who lived thereabout. But Nature has been superseded in these days, and a boat made by man floats near the reed beds where the angler seeks the pike.
Thence up “Robert Elsmere’s” dale to Greycrag tarn—a lonesome sheet of water under a towering fell-end. It has, say some, a store of amphibious fish; nine months of the year they rejoice in water, the remainder they spend in the depths of the moss. During hot weather the tarn is often quite invisible. I have never seen trace of a fish in Greycrag’s mere, but Old Bob, a veteran rodman of the glens, assures me that they exist.
“But,” I once protested, “they can’t.”
“Noo, luk sta here: when t’ watter’s lah, thoo can hear ’em as weel as see ’em. Yan warm day ah was walkin’ on t’ bog be t’ tarn edge, an’ aw on a sudden ah hard ’em. Yan said, ‘Say, Billy, it’s rare an’ warm to-day?’ ‘Aye, an’ ther’s less watter an’ aw. T’ lile crag’s a yerd oot.’ ‘Thoo nivver says sae! Well, well, hooivver. We’ll hae to git to wark an’ dig doon.’ T’ watter just afoor me turnt aw mucky, an’ ah couldn’t see t’ fish.” That’s corroboration with a vengeance.
Old Bob it was also who first gave me the story of the overland pike and eels which reside in Skeggles 209 Water, a peaty pool on the waste between Longsleddale and Kentmere, visible as you climb up the steeps to Greycrag. These marvellous fish have the power o’ wet nights of leaving the tarn, and slithering their way across the grass patches to where the water runs down into Longsleddale. I have found a dozen men willing to swear they have seen the fish on their journey, but not one who has actually captured a specimen.
From the realms of fancy to the domain of beauty and to Kentmere tarn. This laves the lower screes of Hillbell and Froswick, but Nature’s Kentmere was four miles down the glen. Thirty years or so ago the landlords organised draining operations, and found that they had exchanged two hundred acres of beautiful water for as much useless marsh. Nature, interfered with, had retaliated. The upper reservoir is more strikingly situated. Great mountains leap upward from its shores, scores of brawling streamlets force their way down the sides into it. There are two favourite times for fishing this mere—when a gentle sou’wester ruffles the surface and you get out your fine river tackle, and when after rain the fish scent a feast. It is a case of knowing where the shoals lie thickest for making a pannier.
As we stroll by the water, we have in front the tallest buttress of High Street, about the flanks of which are studded four beautiful waters—Small Water, Blea Water, Hayes Water, and Angle tarn. The nearest of these is reached over Nan Bield pass by 210 which a fair amount of inter-dale traffic passes. One day a flock of sheep will make the grey rocks ring with their plaints, another they may resound to the mellower lowings of driven cattle. My first glimpse of Small Water was at sunset. Afternoon was far spent when we faced the mountain ways. Along the hilltops the sun flashed golden fire, the fells to eastward were haloed in bright mist, cool shadows fell and spread around. Then after an (it seemed an interminable) hour, we came here. Not a spark of direct light fell into the hollow of the hills, but the waters shook off responsive glows to day’s aftermath reigning in the skies. The air was hushed, the wagtails flittering about the grey stones were soothed to cuttering monotones. Oh, to stay were glorious indeed, to watch the now radiant vault fade through most subtle hues to grey and then to clear blue of night and starry rest. But on we had to go—often the most ravishing scene has to be inexorably hurried through, for man has many interests, and the most peaceful, the most soul-filling, are not in the way of the world the most important. Would that more of us could, like the poets whose dreamings inspired the mighty deeds of old, and of to-day as well, sit by the hour in these realms of beauty and delight, and calmly let their spirit sink into us. We would write better, live better; but what we call duty intervenes and the inner pulsations of living nature remain unknowable. Nature as seen indoors with the microscope is unfolded to us every day by our great leaders of thought; but few of these great minds care for or have the leisure to instil into themselves, and thence transmit to us, the broader splendours of field and fell and mere.

BLEA TARN AND LANGDALE PIKES
Small Water fills a tiny depression in the mountain; it is well stocked with trout, many of which have a curiously large number of vermilion spots on them. The angler who comes here on an evening in late July may find recompense for his trouble, but a rodman’s panoply is no light weight to bring those three miles from Mardale, or six from Kentmere.
From the upper crags of High Street one looks into a deep well, bounded by rock and scree, to see lonely Blea Water. Its shores are fringed with great fragments rent from the rugged heights which almost overhang. The raven nests in inaccessible gullies above the rippling waters, and one associates their solemn croakings with the shadow-filled basin of crag. A few stunted perch exist in the sterile mere: what hope of rich life can there be from rain-flooded ghylls and mist-moistened crags? Only at sunrise does the scene become joyous. From beyond the Pennines the day’s first warming beams kiss life into seams and rents, signs of wild winter nights and gloomed, frosty days. One great rock-sentinel has a story of the dalesman sport of fox-hunting to tell. Its front is split up by a score ravines, where the stone is rotten and weather-worn. Ledges where a fox can lie at peace from the baying pack are there in scores: Reynard can climb up and down where the agilest hound dare not approach. During one long chase the fox, sorely 212 pushed, attempted to “benk” in this crag. The pack, to prevent accidents, were “whipped off.” The followers essayed to examine the rock-face to discover the redskin and, if possible, to oust him from his refuge. In his eagerness one Dixon, scrambling in a rotten ghyll-head, slipped and fell headlong to a great depth. His body rebounded thrice from the rocks—hence the shattered watercourse is known as “Dixon’s Three Loups.” With both legs broken, the fallen sportsman came to rest, jammed behind a pinnacle of rock. Espying the fox making cautiously over the vertical rock he called to his friends, who were with the hounds, “It’s cummen oot be t’ hee end; lig t’ dogs on.” Reynard’s ruse was frustrated, and a kill made in due course. Dixon’s injuries, beyond the fractured legs, must have been confined to contusions, for, years afterwards, he joined in the hunt with unabated keenness.
Hayes Water has no story to tell the wanderer: it is out of the way of history and legend. Many a hunt passes along its glen, but no commanding crags claim adventure and peril. It is among the most beautiful of our tarns, and the ghyll by which its outflow passes to the Goldrill is a paradise. Cataract and dimpling pool, lush moss and clinging ivy, alder, rowan, ash, and birch; here the beck gurgling in a deep channel, there, in the realm of bracken, sliding down the hardened stone it cannot pierce. The stream is a playground of the dipper, the wagtail, the kingfisher. Suddenly the rivulet charges down a rocky ravine, and emerges, as a clear, calm brook, in the level glen of Goldrill. But one hardly yet follows it, for across the heather and towsled grass there is an Angle tarn to see. This small pool on the level moor is a haunt of the wild red deer from Martindale. Skeletons of several of them were found here after the terrible winter of 1895, when for weeks the ground was frost-bound, and the heather buried in snow. But Angle tarn, as well as Hayes Water, is famous to the angler; permission to enjoy this sport must, however, be sought from the lord at Lowther Castle, in whose manor both lie.

A SUDDEN SHOWER, BLEA TARN
Brothers Water, up a branch of the Goldrill, affords fair sport to the rod. Its shores the wandering kind would think, but erroneously, tame. No huge crag leaps up from it, but its surroundings are of singular ruggedness. The lofty, bristling front of Red Screes, and the purpled fields of broken crag on Kirkstone fell, face the nobbly Hartsop Dodd. The ridges are cut up by narrow chasms down which in flood-time, like hordes of wild horses, unbridled torrents fling. The glen above the tarn is given over to one of the largest sheep-farms in the district. Its acreage is counted, as its fleeces, by the thousand.
It is a far cry and a rugged way to Grisedale tarn, but the climb is worth doing. Up the ghylls you climb on your route to Fairfield; and when you reach the topmost ridge in sight, you find the deep narrow gulf of Deepdale lies between. You detour round the head of this glen. It is glorious wild country, this 214 home of shepherd craft. There is no good path; you follow the wandering sheep-tracks where they serve, and leave them the moment you find their trend unfavourable. It is eerie when the mist suddenly wraps around. Then you may have to trust to dead reckoning for your safety. But, on a clear day, the vertical views from the narrow approach to Fairfield, into Rydal and Deepdale are charming: on either horizon is the flash of water—Windermere, Coniston, Ullswater. The ridge of Fairfield crossed, suddenly breaks a new glen into the mountain wall, and at the same time there is revealed to you a whirlpool of distant summits. Right below is the tarn of Grisedale. Seen on a dull day it is an abode of mystery: deep, so deep blue that one feels that it were a lower firmament; pure, so pure and fresh that it seems impossible that through it one might not journey to a fairy paradise.
This grand cleft in the mountain wall was haunt of the wild boar and of great eagles for long after less wild regions were cleared. To-day you see nothing sterner than the peregrine whizzing after towering larks. I well remember assisting to drive a flock across this upland basin. Of all scenes in dales life, few are prettier than well-driven sheep passing over open land. The collies, watchful, obedient to call or whistle of their master, follow the wings of the mob; the shepherd is behind the centre, and the broad front of grey fleeces and black faces, a thousand or more strong, steadily, readily, moves to pastures new, and the delicate green grass, with grey crags and darker stripes of moss, combines all into an idyllic picture.

KIRKSTONE PASS AND BROTHERS’ WATER
From Grisedale, there is Helvellyn to climb on the way to Red tarn, and to a tiny pool beneath the northern screes known as Keppel Cove tarn. A tour further afield would be across the knife-like Edges of Saddleback to the lonesome tarns immured beneath their cliffs. We, however, journey over the ridge between Fairfield and Seat Sandal for Grasmere’s sweet vale. There are many views across the pass to Helm Crag, with its uncouth rocks on top, figures of monsters frozen speechless from the dim twilight of time.
From Grasmere there is a particularly fine mountain walk, with a ring of tarns as its objective. Starting from the tourist village one passes up Easedale, then begins to ascend the side of Sour Milk ghyll. Come when there has been rain and a tortured chain of water flies down four hundred feet of rocks, in a succession of gleaming spouts. But in the days of drought the rocky pathway is bare and almost dry, the rivulet drips noiselessly down the inclined rocks. At the head of the force you enter the realm of the fell properly. The true mountain moth flutters by; the moss beneath your feet is racemed with fox’s tail, least civilised of plants. The ring-ouzel, the blackbird of the fells, is often here—in the waterworn rocks are its nesting-places. The bracken throws off its sweetest scent. The tarn side is a peaceful scene under most conditions, but when a gale rages you see the water fly off in 216 sheets. The scene is glorious, but the buffetings are tremendous. Easedale tarn is among the larger in size, its trout are more easily caught at hours and seasons when the tourist is unknown. At evening get out the boat and float toward the outlet. The weeds here are the nightly haunt of the best fish.
Our next tarn is Codale, perched on a shelf six hundred feet higher than Easedale tarn—a mere rock pool, but in situation most romantic. Fishing here—well, there are a few trout to be got by the lucky. “Codale tarn? Ah, we used to come at it after we had done Stickle tarn. Old Jonty knew it well. Once when I was with him—it was a blazing June day—he said he could get the fish in Codale. ‘How?’ I asked. ‘By minding my own business.’ He produced two lengths of line, and along them fixed the hooks and baits common to the lath. ‘Noo, thee gang that side o’ t’ tarn, ah’ll gang this.’ The line was between, and we soon dragged the narrow water from one to the other. There wasn’t a fish missed. One after another they swum up; what the baits were Old Jonty wouldn’t say—salmon roe most like, for he was a terrible poacher. We got four pounds of fish with the single drag, more than I had seen in a week of tarn fishing in that blazing weather.”

STEPPING-STONES, FAR EASEDALE, GRASMERE
A few weird things are told of the wild upland where lies Codale tarn, stories as wild as the demon hunts of Dartmoor. Through the mists the wanderer often fancies a face distraught with pain and toil. It is the weird of a lost soul. The first time I was a-wandering in this region I was caught in a dense cloud, and, the stories still fresh in my mind, I felt rather nervous that some horror would come to light. It is wonderful what vivid imaginings come when one is astray in the mist. I have a great many times seen visions in the grey beards—so clear, so true, that once I hailed a comrade whose face I saw, though he himself was forty miles away. Codale tarn, to my mind, is the prettiest mere of all: stand back from its outlet and drink in the picture—the narrow dark band of water, the great pile of rock dabbed with spits of grass, seamed with moss-laces and with parsley fern. Above the crags, where a spot of snow oft lingers till June, is the azure sky, and the dots of winged things.
Over the hills and away to the tarn of Stickle. At clear midnight the hollow is at its finest—when the sky is gemmed with stars and over the jagged Pavey Ark the northern light pulses and flows, and the mountains swim in delicate folds of vapour. It is fairy time—the wee folk must survive in this abode of eternal peace. The crags overhanging the tarn are full of problems for the rock-climbing cult—one or two of the gullies are almost first-rate. The “shepherd’s path,” which few dalesmen ever use, is dangerous to any one not trained to this severe work—I mention this as a warning. The tarn holds trout of large size and exceptional quality. In winter this basin is an awesome place for a ramble. The great plinth which ends Pavey Ark rises almost without a patch of white—a pillar of darkness. Other parts 218 of the fell are plentifully smeared with drifts. When the snow has lain for a week or two there is snow craft to be practised here, but things are better further afield on the Scawfell group.
From Stickle our wanderings should carry us down past the racing fosse, and away into Little Langdale where we pause at Blea tarn. This was the haunt of Wordsworth’s “Solitary,” chief figure in his poem, “The Excursion.” Little Langdale tarn, which lies somewhat further down the glen is a small weedy pool in a meadow-land. Its waters for long have provided little sport, for they are overstocked with tiny useless trout. A net used with judgment might improve the fishing here. But Little Langdale tarn has its own peculiar charm of quietness. It is a haunt of the heron and otter. And over it stands the grand barrier of Tilberthwaite fell, from the base of which, in solemn echoing blasts, “the quarried thunders ring.” The hillsides around are pitted with ugly little scars of abortive quarries. Still down the glen, we pass Colwith, where the stream makes a sudden leap into a lower country. It is a pretty enough spout, but on enclosed ground, and therefore few wanderers of the fells confess its beauty. The white farm at the cross road, as you turn into Great Langdale, of course has been an inn. One of its old-time landladies was wont only to brew when there was a prospect of sale. The water from the spring was good enough for her household, with milk if they felt dainty. Her customers chiefly came eastward over Wrynose pass. It was a long stretch, and a thirsty, from the last tavern in that direction. The landlady was not accustomed to waste material, so every morning when she judged that packmen from Whitehaven were due she walked up the hill above the farm to watch for their coming. If but few ponies appeared crawling down the steep, then the malt was stinted, but if the pass-head was, in her opinion, “black wi’ folk,” more ale was prepared. One morning a traveller, tired of the slow pack-train, pushed on ahead, and duly came to the inn. Ale he called for, and was informed: “Oh aye, ye can hae ale, but it’s rayther warm just yet.” The traveller had beaten the new brew down to Colwith.

LITTLE LANGDALE TARN
To Elter Water the lane winds through dense coppice, and emerges into the open just before the village is reached. Here the chief industry is the making of gunpowder, with also slate quarrying and the production of the famous Langdale linen. John Ruskin it was whose teaching brought this craft back into being, and in a quiet way it is doing good to the valley. I wonder if the dales farmer will ever turn his attention to the cultivation of flax. At one time a plot of this staple was more necessary to a farmstead than a vegetable or even a herbal garden.
Elter Water is a larger picture of the elements comprised in Little Langdale tarn. Except that it is at the foot of the Langdales there is little to be said about it. The pike are so numerous that few perch even stay with them. Loughrigg tarn, which we visit before getting over the ridge to Grasmere, is of a 220 different class to any we have yet met with. Christopher North described it as “a diamond set in emeralds,” and he was not wrong. Where are waters more sparkling, or meadows greener than these? In a secluded corner of the world, Loughrigg does nothing but look pretty: there is no message to the mind from its beauty save that of surpassing beauty in repose.
Coniston is a splendid place to start from for another journey. The nearest point is Gates Water, under Dow crags. The way is not particularly difficult, but the scenery is impressive. The great crag rising sheer almost from the water’s edge is a haunt of the raven, a bird yearly growing scarcer as the wildernesses become less wild, and as the shepherd gets more reliable fire-arms. But, says legend, there is one raven quite impossible to reach. It has dwelt on Kurnal Crag since the dawn of Britain’s history. Yet it failed its post. It was the Druid’s familiar, and when invasion rolled nor’ward it became a sentry over the settlement of Torver. “False bird,” cried the old Druid, when from the mystic holly circle he saw the Britons’ camp burning and the Roman legion pursuing the defeated remnant of his people, “and this is how thy promise of sleepless day and night is fulfilled. Thou wast to croak when danger threatened, and instead I wake to see thee join the invader’s rank.” “Nay, father Druid, I went to fight the yellow bird they carry in their van. It is but a bit of burnished bronze they hold up, and no bird, and I stayed too long surveying it.” “Venerable bird, venerable as myself and as old, I had it in my mind to condemn thee to die, but instead thou shalt live, live, live on the topmost crag of Dow, till another army sweep away the Roman, and the yellow bird is carried southward over sands.” The time came when the Roman legions hurried south, and the raven, well stricken in years, hoped for release; but it did not come, for the last legion, on a misty morning, became involved in a swamp on Torver moor, and standard-bearer and burnished bird were swallowed in deep mud. There they lie and moulder, and the old story is that unless they are found and the eagle carried south the raven of Kurnal Crag may not die. You can hear its aged, rumbling croak afar off, at times when thunder is in the air, and you linger in the gulf of Gates Water to hear the first echoing bellow of the storm.

ELTERWATER AND LANGDALE PIKES
From Gates Water the wanderer goes over the Old Man to Low Water, really one of the most elevated mountain waters. It is splendidly situated, screes and boulders from forbidding cliffs falling right to its shores. It is pleasant to be here at sunset and watch the gloom collect on the summits around. The tarn is credited with almost diabolically large trout, but no one catches them now, and anglers are sceptic. The hillside you traverse to reach Levers Water is almost honeycombed with the shafts of old copper mines. “Mines Valley” indeed was once the busiest haunt of men in the Lake Country. Its copper is now being exploited afresh, and the prosperity of sixty years 222 ago may be repeated. Some of us would rather hear the skirl of the curlew than the roar of ore-mills, but if dividends are possible the lover of the untamed land will once again have to move on. There is no guarantee, save at Thirlmere, that an unspeakable hideousness of industry will not suddenly blot out our remotest haunt. From Levers Water the rambler climbs the ridge toward Seathwaite tarn, now a reservoir for the use of warrior Barrow. This tarn the lord of the manor had the exclusive right to net, and the annual occasion was always made a picnic. Nets were shot, and the finny spoil, char, trout and perch, drawn ashore. Then, as quickly as possible, a tithe of them was prepared and cooked at fires on the shingly strand. The merry-making was a splendid break in the silence of the year here. The tarn also has a small gullery, though miles from the nearest arm of the sea.
The charms of Tarn Hows I have mentioned in my chapter on Coniston Water; it is well worthy an afternoon’s ramble, though if the visitor can put off the hour till the last charabanc has rattled down the glen, he will be the more repaid.

SEATHWAITE TARN, DUDDON VALLEY
My space limit has long run out, so I must only indicate the positions of a last knot of tarns. Devoke Water, within a few miles of Eskdale Green, holds pink-fleshed trout, the progenitors of which are said to have been brought by the monks of Furness Abbey from sunny Italy. Burnmoor tarn lies between lofty Scawfell and Wastwater Screes. The moor around is studded with Druid circles and other memorials of a vanished race. Then in Stye Head pass is a dark brooding tarn; on the fell towards Great End is Sprinkling tarn, near which is the famous rain gauge, where annually the highest English rainfall is recorded. In twenty minutes an inch of rain once fell here; I have had several quick-time drenchings in this neighbourhood. On the fells between Wastwater and Ennerdale are Scoat and Lowfell tarns, the former of which is reputed to contain a golden fish, and the latter a silvery one. Floutern tarn is the furthest away of the mountain waters, lying on the desolate fell between Buttermere and Ennerdale.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
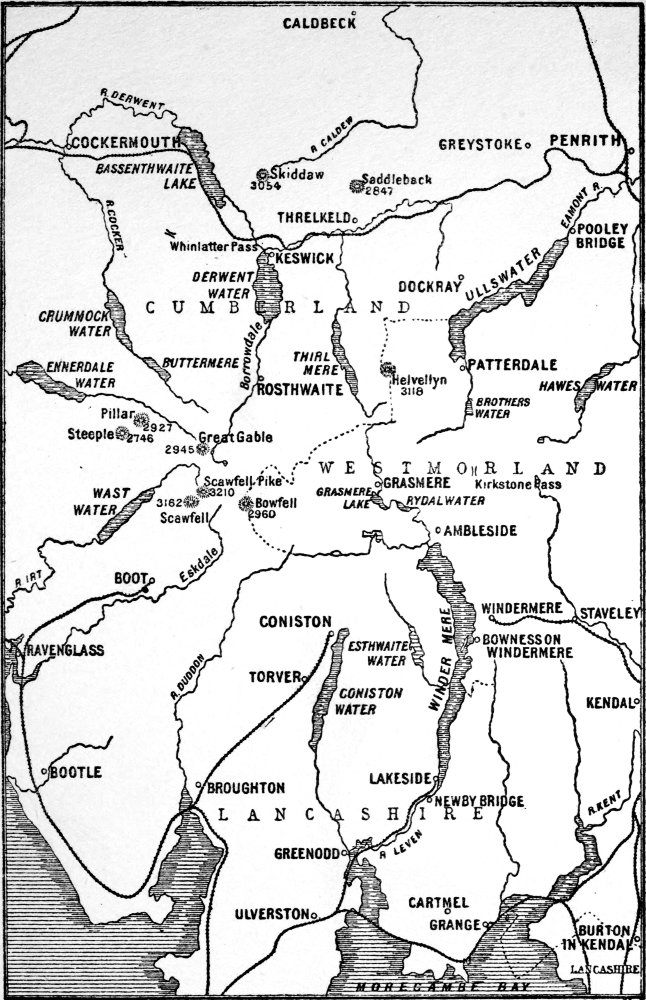
SKETCH MAP OF THE ENGLISH LAKE DISTRICT.
A. AND C. BLACK . SOHO SQUARE . LONDON . W
PRINTED BY
HAZELL, WATSON AND VINEY, LD.,
LONDON AND AYLESBURY.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The English Lakes, by W. T. Palmer
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE ENGLISH LAKES ***
***** This file should be named 57664-h.htm or 57664-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/7/6/6/57664/
Produced by Donald Cummings, Adrian Mastronardi, Stephen
Hutcheson, and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team
at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images
generously made available by The Internet Archive/Canadian
Libraries)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will
be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright
law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works,
so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United
States without permission and without paying copyright
royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part
of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm
concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark,
and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive
specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this
eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook
for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports,
performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given
away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks
not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the
trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
START: FULL LICENSE
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full
Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or
destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your
possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a
Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound
by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the
person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph
1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this
agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the
Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection
of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual
works in the collection are in the public domain in the United
States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the
United States and you are located in the United States, we do not
claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing,
displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as
all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope
that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting
free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm
works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the
Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily
comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the
same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when
you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are
in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States,
check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this
agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing,
distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any
other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no
representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any
country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other
immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear
prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work
on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed,
performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no
restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it
under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this
eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the
United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you
are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is
derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not
contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the
copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in
the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are
redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply
either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or
obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any
additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms
will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works
posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the
beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including
any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access
to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format
other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official
version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site
(www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense
to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means
of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain
Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the
full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
provided that
* You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is owed
to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he has
agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments must be paid
within 60 days following each date on which you prepare (or are
legally required to prepare) your periodic tax returns. Royalty
payments should be clearly marked as such and sent to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the address specified in
Section 4, "Information about donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation."
* You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or destroy all
copies of the works possessed in a physical medium and discontinue
all use of and all access to other copies of Project Gutenberg-tm
works.
* You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of
any money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days of
receipt of the work.
* You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than
are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing
from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The
Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project
Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may
contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate
or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other
intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or
other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or
cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium
with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you
with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in
lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person
or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second
opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If
the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing
without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO
OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of
damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement
violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the
agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or
limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or
unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the
remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in
accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the
production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses,
including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of
the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this
or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or
additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any
Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of
computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It
exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations
from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future
generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see
Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at
www.gutenberg.org
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by
U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the
mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its
volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous
locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt
Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to
date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and
official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND
DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular
state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To
donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project
Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be
freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and
distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of
volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in
the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not
necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper
edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search
facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.