

| FIRST EDITION | 1892 |
| SECOND EDITION | 1892 |
| THIRD EDITION | 1893 |
| FOURTH EDITION | 1899 |
| FIFTH EDITION | 1903 |
TRUSLOVE AND BRAY
PRINTERS
WEST NORWOOD S E

ENGLISH SATIN-WOOD
DRESSING-TABLE.
WITH PAINTED DECORATION.
END OF XVIII CENTURY.
FROM THE EARLIEST TO
THE PRESENT TIME BY
FREDERICK LITCHFIELD
AUTHOR OF "POTTERY AND PORCELAIN"
WITH NUMEROUS ILLUSTRATIONS
LONDON: TRUSLOVE & HANSON LIMITED
NEW YORK: JOHN LANE MDCCCCIII

 N the following pages the Author has placed before
the reader an account of the changes in the
design of Decorative Furniture and Woodwork,
from the earliest period of which we have any reliable
or certain record until the present time.
N the following pages the Author has placed before
the reader an account of the changes in the
design of Decorative Furniture and Woodwork,
from the earliest period of which we have any reliable
or certain record until the present time.
A careful selection of illustrations has been made from examples of established authenticity, the majority of which are to be seen, either in the Museums to which reference is made, or by permission of the owners; and the representations of the different "interiors" will convey an idea of the character and disposition of the Furniture of the periods to which they refer. These illustrations are arranged, so far as possible, in chronological order, and the descriptions which accompany them are explanatory of the historical and social changes which have influenced the manners and customs, and directly or indirectly affected the Furniture of different nations. An endeavour is made to produce a "panorama," which may prove acceptable to many, who, without wishing to study the subject deeply, may desire to gain some information with reference to it generally, or with regard to some part of it, in which they may feel a particular interest.
It will be obvious that within the limits of a single volume of moderate dimensions it is impossible to give more than an outline sketch of many periods of design and taste which deserve far more consideration than is here bestowed upon them; the reader is, therefore, asked to accept the first chapter, which refers to "Ancient Furniture" and covers a period of several centuries, as introductory to that which follows, rather than as a serious attempt to examine the history of the Furniture during that space of time. The fourth chapter, which deals with a period of some hundred and fifty years, from the time of King James the First until that of Chippendale and his contemporaries, and the last three chapters, are more fully descriptive than some others, partly because trustworthy information as to these times is more accessible, and partly because it is probable that English readers will feel greater interest in the Furniture of which they are the subject. The French meubles de luxe, from the latter half of the seventeenth century until the Revolution, are also treated more fully than the Furniture of other periods and countries, on account of the interest which has been manifested in this description of the cabinet maker's and metal mounter's work during the past fifteen or twenty years. There is evidence of this appreciation in the enormous prices realised at notable auction sales, when such Furniture has been offered for competition to wealthy connoisseurs.
In order to gain a more correct idea of the design of Furniture of different periods, it has been necessary[vii] to notice the alterations in architectural styles which influenced, and were accompanied by, corresponding changes in the fashion of interior woodwork. Such comments are made with some diffidence, as it is felt that this branch of the subject would have received more fitting treatment by an architect, who was also an antiquary, than by an antiquary with only a limited knowledge of architecture.
Some works on "Furniture" have taken the word in its French interpretation, to include everything that is "movable" in a house; other writers have combined with historical notes, critical remarks and suggestions as to the selection of Furniture. The Author has not presumed to offer any such advice, and has confined his attention to a description of that which, in its more restricted sense, is understood as "Decorative Furniture and Woodwork." For his own information, and in the pursuit of his business, he has been led to investigate the causes and the approximate dates of the several changes in taste which have taken place, and has recorded them in as simple and readable a story as the difficulties of the subject permit.
Numerous acts of kindness and co-operation, received while preparing the work for the Press, have rendered the task very pleasant; and while the Author has endeavoured to acknowledge, in a great many instances, the courtesies received, when noticing the particular occasion on which such assistance was rendered, he would desire generally to record his thanks to the owners of historic[viii] mansions, the officials of our Museums, the Clerks of City Companies, Librarians, and others, to whom he is indebted. The views of many able writers who have trodden the same field of enquiry have been adopted where they have been confirmed by the writer's experience or research, and in these cases he hopes he has not omitted to express his acknowledgments for the use he has made of them.
The large number of copies subscribed for, accompanied, as many of the applications have been, by expressions of goodwill, and confidence beforehand, have been very gratifying, and have afforded great encouragement during the preparation of the work.
If the present venture is received in such a way as to encourage a larger effort, the writer hopes both to multiply examples and extend the area of his observations.
F. L.
32, ST. JAMES'S STREET, S.W.

PAGE
BIBLICAL REFERENCES: Solomon's House and Temple—Palace of Ahasuerus. ASSYRIAN FURNITURE: Nimrod's Palace—Mr. George Smith quoted. EGYPTIAN FURNITURE: Specimens in the British Museum—The Workman's Stool—Various Articles of Domestic Furniture—Dr. Birch quoted. GREEK FURNITURE: The Bas-reliefs in the British Museum—The Chest of Cypselus—Laws and Customs of the Greeks—House of Alcibiades—Plutarch quoted. ROMAN FURNITURE: Position of Rome—The Roman House—Cicero's Table—Thyine Wood—Customs of wealthy Romans—Downfall of the Empire 1
Period of 1,000 years from Fall of Rome, A. D. 476, to Capture of Constantinople, 1453—The Crusades—Influence of Christianity—Chairs of St. Peter and Maximian at Rome, Ravenna, and Venice—Edict of Leo III. prohibiting Image worship—The Rise of Venice—Charlemagne and his successors—The Chair of Dagobert—Byzantine character of Furniture—Norwegian carving—Russian and Scandinavian—The Anglo-Saxons—Sir Walter Scott quoted—Descriptions of Anglo-Saxon Houses and Customs—Art in Flemish Cities—Gothic Architecture—The Coronation Chair at Westminster Abbey—Penshurst—French Furniture in the 14th Century—Description of rooms—The South Kensington Museum—Transition from Gothic to Renaissance—German carved work; the Credence, the Buffet, and Dressoir 17
CHAPTER III.
THE RENAISSANCE IN ITALY: Leonardo da Vinci and Raffaelle—Church of St. Peter, contemporary great artists—The Italian Palazzo—Methods of gilding, inlaying and mounting Furniture—Pietra-durá and other enrichments—Ruskin's criticism. THE RENAISSANCE IN FRANCE: François I. and the Chateau of Fontainebleau—Influence on Courtiers—Chairs of the time—Design of Cabinets—M. E. Bonnaffé on The Renaissance—Bedstead of Jeanne d'Albret—Deterioration of taste in time of Henry IV.—Louis XIII. Furniture—Brittany woodwork. THE RENAISSANCE IN THE NETHERLANDS: Influence of the House of Burgundy on Art—The Chimney-piece at Bruges, and other casts of[x] specimens at South Kensington Museum. THE RENAISSANCE IN SPAIN: The resources of Spain in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries—Influence of Saracenic Art—High-backed Leather Chairs, the Carthusian Convent at Granada. THE RENAISSANCE IN GERMANY: Albrecht Dürer Famous Steel Chair of Augsburg—German seventeenth century carving in St. Saviour's Hospital. THE RENAISSANCE IN ENGLAND: Influence of Foreign Artists in the time of Henry VIII.—End of Feudalism—Hampton Court Palace—Linen Pattern Panels—Woodwork in the Henry VII Chapel at Westminster Abbey—Livery Cupboards at Hengrave—Harrison quoted—The "parler," alteration in English customs—Chairs of the sixteenth century—Coverings and Cushions of the time, extract from old inventory—South Kensington Cabinet—Elizabethan Mirror at Goodrich Court—Shaw's "Ancient Furniture"—The Glastonbury Chair—Introduction of Frames into England—Characteristics of Native Woodwork—Famous Country Mansions—Alteration in design of Woodwork and Furniture—Panelled Rooms at South Kensington—The Charterhouse—Gray's Inn Hall and Middle Temple—The Hall of the Carpenters' Company—The Great Bed of Ware—Shakespeare's Chair—Penshurst Place 47
CHAPTER IV.
English Home Life in the Reign of James I.—Sir Henry Wotton quoted—Inigo Jones and his work—Ford Castle—Chimney Pieces in South Kensington Museum—Table in the Carpenters' Hall—Hall of the Barbers' Company—The Charterhouse—Time of Charles I.—Furniture at Knole—Eagle House, Wimbledon—Mr. Charles Eastlake—Monuments at Canterbury and Westminster—Settles, Couches, and Chairs of the Stuart period—Sir Paul Pindar's House—Cromwellian Furniture—The Restoration—Indo-Portuguese Furniture—Hampton Court Palace—Evelyn's description—The Great Fire of London—Hall of the Brewers' Company—Oak Panelling of the time—Grinling Gibbons and his work—The Edict of Nantes—Silver Furniture at Knole—William III. and Dutch influence—Queen Anne—Sideboards, Bureaus, and Grandfather's Clocks—Furniture at Hampton Court 91
CHAPTER V.
CHINESE FURNITURE: Probable source of artistic taste—Sir William Chambers quoted—Racinet's "Le Costume Historique"—Dutch Influence—The South Kensington and the late Duke of Edinburgh Collections—Processes of making Lacquer—Screens in the Kensington Museum. JAPANESE FURNITURE: Early History—Sir Rutherford Alcock and Lord Elgin—The Collection of the Shôgun—Famous Collections—Action of the present Government of Japan—Special characteristics. INDIAN FURNITURE: Early European influence—Furniture of the Moguls—Racinet's Work—Bombay Furniture—Ivory Chairs and Tables—Specimens in the India Museum. PERSIAN WOODWORK: Collection of Objets d'Art formed by General Murdoch Smith, R.E.—Industrial Arts of the Persians—Arab influence—South Kensington Specimens. SARACENIC WOODWORK: Oriental customs—Specimens in the South Kensington Museum of Arab Work—M. d'Aveune's Work 125
CHAPTER VI.
PALACE OF VERSAILLES: "Grand" and "Petit Trianon"—The three Styles of Louis XIV., XV., and XVI.—Colbert and Lebrun—André Charles Boule and his Work—Carved and Gilt Furniture—The Regency and its Influence—Alteration in Condition of French Society—Watteau, Lancret, and Boucher. LOUIS XV. FURNITURE: Famous Ébenistes—Vernis Martin Furniture—Caffieri and Gouthière Mountings—Sêvres Porcelain introduced into Cabinets—Gobelins Tapestry—The "Bureau du Roi." LOUIS XVI. AND MARIE ANTOINETTE: The Queen's Influence—The Painters Chardin and Greuze—More simple Designs—Characteristic Ornaments of Louis XVI. Furniture—Riesener's Work—Gouthière's Mountings—Specimens in the Louvre—The Hamilton Palace Sale—French influence upon the design of furniture in other countries—The Jones Collection—Extract from the "Times" 145
CHAPTER VII.
Chinese Styles—Sir William Chambers—The Brothers Adams' work—Pergolesi, Cipriani, and Angelica Kauffmann—Architects of the time—Wedgwood and Flaxman—Chippendale's Work and his Contemporaries—Chair in the Barbers' Hall—Lock, Shearer, Hepplewhite, Ince, Mayhew, Sheraton—Introduction of Satinwood and Mahogany—Gillows, of Lancaster and London—History of the Sideboard—The Dining Room—Furniture of the time 173
CHAPTER VIII.
The French Revolution and the First Empire—Influence on design of Napoleon's Campaigns—The Cabinet presented to Marie Louise—Dutch Furniture of the time—English Furniture—Sheraton's later work—Thomas Hope, architect—George Smith's designs—Fashion during the Regency—Gothic revival—Seddon's furniture—Other makers—Influence on design of the Restoration in France—Furniture of William IV. and early part of Queen Victoria's reign—Baroque and Rococo styles—The Panelling of Rooms, Dado, and Skirting—The Art Union—The Society of Arts—Sir Charles Barry and the new Palace of Westminster—Pugin's designs—Auction Prices of Furniture—Christie's—The London Club Houses—Steam—Different Trade Customs—Exhibitions in France and England—Harry Rogers' work—The late Queen's cradle—State of Art in England during the first part of Queen Victoria's reign—Continental designs—Italian carving—Cabinet work—General remarks 203
CHAPTER IX.
THE GREAT EXHIBITION:—Exhibitors and contemporary Cabinet Makers—Exhibition of 1862, London; 1867, Paris; and subsequently—Description of Illustrations—Fourdinois, Wright and Mansfield—The South Kensington Museum—Talbert's Work—Revival of Marquetry—Comparison of Present Day with that of a Hundred Years ago—Æstheticism—Traditions—Trades-Unionism—The Arts and Crafts Exhibition Society—Kensington School of Woodcarving—Independence of Furniture—Present Fashions—Writers on Design—The New Renaissance—"Trade" Journals—Modern Furniture in other Countries—Concluding Remarks 229
APPENDIX.
Lists of Artists and Manufacturers of Furniture—Woods—Tapestry used for French Furniture—The processes of Gilding and Polishing—The Pianoforte 251
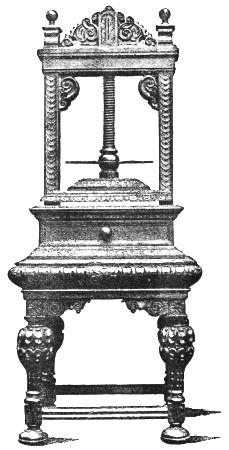
CARVED OAK NAPKIN PRESS.
Lent to the South Kensington Museum by II. Farrer, Esq.
EARLY XVII. CENTURY.
| CHAPTER I. | ||
|---|---|---|
| COLORED FRONTISPIECE facing | Title | |
| PAGE | ||
| "GRANDFATHER" CLOCK | iv. | |
| A SEVENTEENTH CENTURY NAPKIN PRESS | xii. | |
| VIGNETTE OF BAS-RELIEF—EGYPTIAN SEATED, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 1 | |
| ASSYRIAN BRONZE THRONE AND FOOTSTOOL | 3 | |
| CHAIRS FROM KHORSABAD AND XANTHUS AND ASSYRIAN THRONE | 4 | |
| REPOSE OF KING ASSHURBANIPAL | 5 | |
| EXAMPLES OF EGYPTIAN FURNITURE IN THE BRITISH MUSEUM: Stool; Stand for a Vase; Head Rest or Pillow; Workman's Stool; Vase on a Stand; Folding Stool; Ebony Seat inlaid with ivory |
6 | |
| AN EGYPTIAN OF HIGH RANK SEATED facing | 6 | |
| AN EGYPTIAN BANQUET | 7 | |
| CHAIR WITH CAPTIVES AS SUPPORTS | 8 | |
| BACCHUS AND ATTENDANTS VISITING ICARUS facing | 8 | |
| GREEK BEDSTEAD WITH A TABLE | 9 | |
| GREEK FURNITURE | 10 | |
| INTERIOR OF AN ANCIENT ROMAN HOUSE facing | 12 | |
| A ROMAN STUDY | 13 | |
| ROMAN SCAMNUM OR BENCH | } | 14 |
| ROMAN BISELLIUM, OR SEAT FOR TWO PERSONS | ||
| ROMAN COUCH, GENERALLY OF BRONZE | 15 | |
| BRONZE LAMP AND STAND | 16 | |
| ROMAN TRICLINIUM, OR DINING ROOM facing | 16 | |
| CHAPTER II. | ||
| VIGNETTE OF GOTHIC OAK ARMOIRE, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 17 | |
| CHAIR OF ST. PETER, ROME | 19 | |
| DAGOBERT CHAIR | 21 | |
| A CARVED NORWEGIAN DOORWAY facing | 22 | |
| SCANDINAVIAN CHAIR | 23 | |
| COVER OF A CASKET CARVED IN WHALEBONE | 24 | |
| SAXON HOUSE (IX. CENTURY) | 25 | |
| ANGLO-SAXON FURNITURE OF ABOUT THE X. CENTURY | 27 | |
| THE SEAT ON THE DAIS | } | 28 |
| SAXON STATE BED | ||
| ENGLISH FOLDING CHAIR (XIV. CENTURY) | } | 29 |
| CRADLE OF HENRY V. | ||
| CORONATION CHAIR, WESTMINSTER ABBEY | 31 | |
| CHAIR IN YORK MINSTER | 32 | |
| TWO CHAIRS OF THE XV. CENTURY facing | 32 | |
| TABLE AT PENSHURST | 33[xiv] | |
| BEDROOM (XIV. CENTURY) | 34 | |
| CARVED OAK BEDSTEAD AND CHAIR | 35 | |
| INTERIOR OF A BEDROOM—"THE NEW BORN INFANT" | 37 | |
| PORTRAIT OF CHRISTINE DE PISAN | 38 | |
| STATE BANQUET, WITH ATTENDANT MUSICIANS (two woodcuts) | 39 | |
| A HIGH BACKED CHAIR (XV. CENTURY) | 40 | |
| MEDIÆVAL BED AND BEDROOM facing | 40 | |
| A SCRIBE OR COPYIST | 41 | |
| TWO GERMAN CHAIRS | 42 | |
| CARVED OAK BUFFET (French Gothic) | 43 | |
| OLD ENGLISH OAK BUFFET | 44 | |
| FLEMISH BUFFET facing | 44 | |
| A TAPESTRIED ROOM | } | 45 |
| A CARVED OAK SEAT | ||
| INTERIOR OF APOTHECARY'S SHOP | 46 | |
| DWELLING ROOM OF A FRENCH CHATEAU following | 46 | |
| COURT OF THE LADIES OF QUEEN ANNE OF BRITTANY | 46 | |
| CHAPTER III. | ||
| VIGNETTE OF THE CARYATIDES CABINETS, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 47 | |
| REPRODUCTION OF DECORATION BY RAFFAELLE following | 48 | |
| SALON OF M. BONAFFÉ " | 48 | |
| A SIXTEENTH CENTURY ROOM " | 48 | |
| CHAIR IN CARVED WALNUT | 49 | |
| VENETIAN CENTRE TABLE | 50 | |
| MARRIAGE COFFER IN CARVED WALNUT following | 50 | |
| MARRIAGE COFFER " | 50 | |
| PAIR OF ITALIAN CARVED BELLOWS | 51 | |
| CARVED ITALIAN MIRROR FRAME, XVI. CENTURY | 52 | |
| A SIXTEENTH CENTURY COFFRE-FORT | 53 | |
| ITALIAN COFFER | 55 | |
| ITALIAN CHAIRS | 56 | |
| EBONY CABINET facing | 56 | |
| VENETIAN STATE CHAIR | 57 | |
| ORNAMENTAL PANELLING IN ST. VINCENT'S CHURCH, ROUEN following | 58 | |
| CHIMNEY PIECE (FONTAINEBLEAU) " | 58 | |
| CARVED OAK PANEL (1577) | 59 | |
| FAC SIMILES OF ENGRAVINGS ON WOOD | 60 | |
| CARVED OAK BEDSTEAD OF JEANNE D'ALBRET following | 60 | |
| CARVED OAK CABINET, XVI. CENTURY " | 60 | |
| CARVED OAK CABINET (LYONS) " | 60 | |
| LOUIS XIII. AND HIS COURT | 62 | |
| DECORATION OF A SALON IN LOUIS XIII. STYLE facing | 62 | |
| AN EBONY ARMOIRE (FLEMISH RENAISSANCE) | 64 | |
| A BARBER'S SHOP AND A FLEMISH WORKSHOP (XVI. CENTURY) | 65 | |
| A FLEMISH CITIZEN AT MEALS | 66 | |
| SEDAN CHAIR OF CHARLES V. | 67 | |
| SILVER TABLE (WINDSOR CASTLE) | 63 | |
| CHAIR OF WALNUT OR CHESTNUT WOOD, SPANISH, WITH EMBOSSED LEATHER following | } | 68[xv] |
| WOODEN COFFER (XVI. CENTURY) following | ||
| THE STEEL CHAIR (LONGFORD CASTLE) facing | 70 | |
| GERMAN CARVED OAK BUFFET | 71 | |
| CARVED OAK CHEST | 72 | |
| CHAIR OF ANNA BOLEYN | 74 | |
| TUDOR CABINET | 75 | |
| THE GLASTONBURY CHAIR | 78 | |
| CARVED OAK ELIZABETHAN BEDSTEAD | 80 | |
| OAK WAINSCOTING facing | 80 | |
| DINING HALL IN THE CHARTERHOUSE | 82 | |
| SCREEN IN THE HALL OF GRAY'S INN facing | 82 | |
| HALL OF GRAY'S INN | 83 | |
| CARVED OAK PANELS (CARPENTERS' HALL) | 85 | |
| PART OF AN ELIZABETHAN STAIRCASE | 86 | |
| THE ENTRANCE HALL, HARDWICK HALL facing | 86 | |
| SHAKESPEARE'S CHAIR | 88 | |
| THE "GREAT BED OF WARE" facing | 88 | |
| THE "QUEEN'S ROOM," PENSHURST PLACE | 89 | |
| CARVED OAK CHIMNEY PIECE IN SPEKE HALL | 90 | |
| CHAPTER IV. | ||
| A CHAIR OF XVII. CENTURY, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 91 | |
| OAK CHIMNEY PIECE IN SIR W. RALEIGH'S HOUSE | 92 | |
| CHIMNEY PIECE IN BYFLEET HOUSE | 93 | |
| "THE KING'S CHAMBER," FORD CASTLE | 94 | |
| CENTRE TABLE (CARPENTERS' HALL) | 95 | |
| CARVED OAK CHAIRS | 96 | |
| OAK CHIMNEY PIECE FROM LIME STREET, CITY facing | 96 | |
| OAK SIDEBOARD | 97 | |
| SEATS AT KNOLE | 99 | |
| ARM CHAIR, KNOLE | 100 | |
| THE "SPANGLE" BEDROOM, KNOLE | 101 | |
| COUCH, CHAIR, AND SINGLE CHAIR (PENSHURST PLACE) facing | 104 | |
| "FOLDING" AND "DRAWINGE" TABLE | 106 | |
| CHAIRS, STUART PERIOD | 107 | |
| CHAIR USED BY CHARLES I. DURING HIS TRIAL | 108 | |
| SETTLE OF CARVED OAK facing | 108 | |
| TWO CARVED OAK CHAIRS | 109 | |
| STAIRCASE IN GENERAL IRETON'S HOUSE | 110 | |
| SETTEE AND CHAIR (PENSHURST PLACE) facing | 110 | |
| SEDES BUSBIANA | 112 | |
| THE MASTER'S CHAIR IN THE BREWERS' HALL | 115 | |
| CARVED OAK "LIVERY" CUPBOARD | 116 | |
| THREE CHAIRS FROM HAMPTON COURT, HARDWICKE, AND KNOLE facing | 116 | |
| CARVED OAK SCREEN IN STATIONERS' HALL | 117 | |
| SILVER FURNITURE AT KNOLE | 119 | |
| THREE CHIMNEY PIECES BY JAMES GIBBS facing | 122 | |
| CHAIR IN HOLLAND HOUSE, DESIGNED BY CLEYN | 123[xvi] | |
| CHAPTER V. | ||
| PATTERN OF A CHINESE LAC SCREEN | 124 | |
| AN EASTERN (SARACENIC) TABLE, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 125 | |
| JAPANESE CABINET OF RED CHASED LACQUER-WORK | 130 | |
| CASKET OF INDIAN LACQUER WORK | 134 | |
| DOOR OF CARVED SANDAL WOOD FROM TRAVANCORE facing | 136 | |
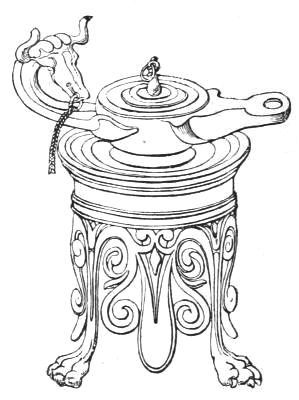
| PERSIAN INCENSE BURNER OF ENGRAVED BRASS | 137 | |
| GOVERNOR'S PALACE, MANFALÛT | 140 | |
| SPECIMEN OF SARACENIC PANELLING | 141 | |
| CARVED DOOR OF SYRIAN WORK | 142 | |
| SHAPED PANEL OF SARACENIC WORK | 143 | |
| CHAPTER VI. | ||
| BOULE ARMOIRE (HAMILTON PALACE) | 144 | |
| VIGNETTE OF A LOUIS QUATORZE COMMODE, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 145 | |
| BOULE ARMOIRE (Jones Collection) facing | 146 | |
| PEDESTAL CABINET BY BOULE (Jones Collection) | 148 | |
| A CONCERT IN THE REIGN OF LOUIS XIV. | 149 | |
| A BOUDOIR (LOUIS XIV. PERIOD) | 150 | |
| DECORATION OF A SALON IN THE LOUIS XIV. STYLE facing | 150 | |
| A BOULE COMMODE | 152 | |
| FRENCH SEDAN CHAIR facing | 152 | |
| A SCREEN PANEL BY WATTEAU | 153 | |
| CARVED AND GILT CONSOLE TABLE | 154 | |
| LOUIS XV. "FAUTEUIL" (CARVED AND GILT) | 155 | |
| LOUIS XV. COMMODE (Jones Collection) | 156 | |
| A PARQUETERIE COMMODE | 157 | |
| PART OF A SALON (LOUIS XV.) | 158 | |
| "BUREAU DU ROI" facing | 158 | |
| PART OF A SALON IN LOUIS XVI. STYLE | 160 | |
| A MARQUETERIE CABINET (Jones Collection) | 162 | |
| WRITING TABLE (RIESENER) facing | 162 | |
| THE "MARIE ANTOINETTE" WRITING TABLE | 164 | |
| BEDSTEAD OF MARIE ANTOINETTE facing | 164 | |
| A CYLINDER SECRETAIRE (Rothschild Collection) | 165 | |
| AN ARM CHAIR (LOUIS XVI.) | 166 | |
| CARVED AND GILT SETTEE AND ARM CHAIR following | 166 | |
| A SOFA EN SUITE | 166 | |
| A MARQUETERIE ESCRITOIRE (Jones Collection) | 167 | |
| A NORSE INTERIOR, SHEWING FRENCH INFLUENCE | 169 | |
| A SECRETAIRE WITH SEVRES PLAQUES | 170 | |
| A CLOCK BY ROBIN (Jones Collection) | 171 | |
| HARPSICHORD, ABOUT 1750 | 172 | |
| CHAPTER VII. | ||
| VIGNETTE OF A CHIPPENDALE GIRANDOLE, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 173 | |
| FAC-SIMILE OF DRAWINGS BY ROBERT ADAM | 175 | |
| ENGLISH SATIN WOOD DRESSING TABLE following | 176 | |
| CHIMNEY-PIECE AND OVERMANTEL, DESIGNED BY W. THOMAS following | 176[xvii] | |
| TWO CHIPPENDALE CHAIRS IN THE "CHINESE" STYLE | 177 | |
| FAC-SIMILE OF TITLE PAGE OF CHIPPENDALE'S "GENTLEMAN AND CABINET MAKER'S DIRECTOR" | 178 | |
| TWO BOOK CASES FROM CHIPPENDALE'S "DIRECTOR" facing | 178 | |
| TEA CADDY CARVED IN THE FRENCH STYLE (CHIPPENDALE) | 179 | |
| A BUREAU FROM CHIPPENDALE'S "DIRECTOR" | 180 | |
| A DESIGN FOR A STATE BED FROM CHIPPENDALE'S "DIRECTOR" following | 180 | |
| "FRENCH" COMMODE AND LAMP STANDS | 180 | |
| BED PILLARS | 180 | |
| CHIMNEY-PIECE AND MIRROR | 180 | |
| PARLOUR CHAIRS BY CHIPPENDALE | 181 | |
| CLOCK CASE BY CHIPPENDALE | 182 | |
| CHINA SHELVES, DESIGNED BY W. INCE | 184 | |
| GIRANDOLES AND PIER TABLE, DESIGNED BY W. THOMAS | 185 | |
| PARLOUR CHAIRS, DESIGNED BY W. INCE | 187 | |
| LADIES' SECRETAIRES, DESIGNED BY W. INCE | 188 | |
| DESK AND BOOKCASE, DESIGNED BY W. INCE | 189 | |
| CHINA CABINET, DESIGNED BY J. MAYHEW | 190 | |
| "DRESSING CHAIRS," DESIGNED BY J. MAYHEW | 191 | |
| DESIGNS OF FURNITURE FROM HEPPLEWHITE'S "GUIDE" facing | 192 | |
| PLAN OF A ROOM (HEPPLEWHITE) | 193 | |
| INLAID TEA CADDY AND TOPS OF PIER TABLES, FROM HEPPLEWHITE'S "GUIDE" | 194 | |
| KNEEHOLE TABLE BY SHERATON | 195 | |
| CHAIRS BY SHERATON | 196 | |
| CABINET AND BOOKCASE WITH SECRETAIRE, BY SHERATON | 197 | |
| CHAIR BACKS, FROM SHERATON'S "CABINET MAKER" | 198 | |
| A SIDEBOARD IN THE STYLE OF ROBERT ADAM facing | 200 | |
| TOILET GLASS AND URN STANDS | 201 | |
| CARVED JARDINIERE BY CHIPPENDALE | 202 | |
| CHAPTER VIII. | ||
| VIGNETTE OF AN EMPIRE TRIPOD, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 203 | |
| CABINET PRESENTED TO MARIE LOUISE facing | 204 | |
| STOOL AND ARM CHAIR (NAPOLEON I. PERIOD) | 205 | |
| NELSON'S CHAIRS BY SHERATON facing | 206 | |
| DRAWING ROOM CHAIR, DESIGNED BY SHERATON | 207 | |
| DRAWING ROOM CHAIR | 208 | |
| "CANOPY BED" BY SHERATON following | 208 | |
| "SISTERS' CYLINDER BOOKCASE" BY SHERATON | 208 | |
| SIDEBOARD AND SOFA TABLE (SHERATON) | 209 | |
| DESIGN OF A ROOM BY T. HOPE | 211 | |
| LIBRARY FAUTEUIL, FROM SMITH'S "BOOK OF DESIGNS" | 213 | |
| PARLOR CHAIRS | 214 | |
| BOOKCASE BY SHERATON facing | 214 | |
| DRAWING ROOM CHAIRS, FROM SMITH'S BOOK | 215 | |
| PRIE-DIEU IN CARVED OAK, DESIGNED BY MR. PUGIN | 218 | |
| SECRETAIRE AND BOOKCASE (German Gothic Style) | 219[xviii] | |
| CRADLE FOR H.M. QUEEN VICTORIA, BY H. ROGERS | 222 | |
| DESIGN FOR A TEA CADDY BY J. STRUDWICK | 223 | |
| DESIGN FOR ONE OF THE WINGS OF A SIDEBOARD BY W. HOLMES | 224 | |
| DESIGN FOR A WORK TABLE BY H. FITZCOOK | 225 | |
| VENETIAN STOOL OF CARVED WALNUT | 228 | |
| CHAPTER IX. | ||
| EXAMPLES OF DESIGN IN FURNITURE IN THE 1851 EXHIBITION:— | ||
| SIDEBOARD, IN CARVED OAK, BY GILLOW following | 228 | |
| CHIMNEY-PIECE AND BOOKCASE BY HOLLAND AND SONS | 228 | |
| CABINET BY CRACE | 228 | |
| BOOKCASE BY JACKSON AND GRAHAM | 228 | |
| GRAND PIANOFORTE BY BROADWOOD | 228 | |
| VIGNETTE OF A CABINET, MODERN JACOBEAN STYLE, as Ornament to Initial Letter | 229 | |
| LADY'S ESCRITOIRE BY WETTLI, BERNE | 230 | |
| LADY'S WORK TABLE AND SCREEN IN PAPIER MACHÉ | 232 | |
| SIDEBOARD (SIR WALTER SCOTT) BY COOKES, WARWICK following | 232 | |
| A STATE CHAIR BY JANCOWSKI, YORK | 232 | |
| SIDEBOARD, IN CARVED OAK, BY DURANT, PARIS | 232 | |
| BEDSTEAD, IN CARVED EBONY, BY ROULÉ, ANTWERP | 232 | |
| PIANOFORTE, BY LEISTLER, VIENNA | 232 | |
| BOOKCASE IN LIME TREE, BY LEISTLER, VIENNA | 232 | |
| CABINET, WITH BRONZE AND PORCELAIN, BY GAMBS, ST. PETERSBURG | 232 | |
| CASKET OF IVORY, WITH ORMULU MOUNTINGS, BY MATIFAT, PARIS | 233 | |
| TABLE AND CHAIR, IN THE CLASSIC STYLE, BY CAPELLO, TURIN | 234 | |
| CABINET OF EBONY, WITH CARNELIONS, BY LITCHFIELD AND RADCLYFFE | ||
| (1862 Exhibition, Paris) | 235 | |
| CABINET OF EBONY WITH BOXWOOD CARVINGS, BY FOURDINOIS, PARIS | ||
| (1867 Exhibition, London) following | 236 | |
| CABINET OF SATINWOOD, WITH WEDGWOOD PLAQUES, BY WRIGHT AND MANSFIELD | ||
| (1867 Exhibition, Paris) following | 236 | |
| CABINET OF EBONY AND IVORY BY ANDREA PICCHI, FLORENCE | ||
| (1867 Exhibition, Paris) following | 236 | |
| DINING ROOM BY BRUCE J. TALBERT facing | 238 | |
| THE ELLESMERE CABINET | 243 | |
| THE SALOON AT SANDRINGHAM HOUSE following | 244 | |
| THE DRAWING ROOM AT SANDRINGHAM HOUSE | 244 | |
| CARVED FRAME BY RADSPIELER, MUNICH | 248 |

BIBLICAL REFERENCES: Solomon's House and Temple—Palace of Ahasuerus. ASSYRIAN FURNITURE: Nimrod's Palace—Mr. George Smith quoted. EGYPTIAN FURNITURE: Specimens in the British Museum—The Workman's Stool—Various Articles of Domestic Furniture—Dr. Birch quoted. GREEK FURNITURE: The Bas-reliefs in the British Museum—The Chest of Cypselus—Laws and Customs of the Greeks—House of Alcibiades—Plutarch quoted. ROMAN FURNITURE: Position of Rome—The Roman House—Cicero's Table—Thyine Wood—Customs of wealthy Romans—Downfall of the Empire.
 HE first well-known reference to woodwork is
to be found in the Book of Genesis, in
the instructions given to Noah to make
an Ark of gopher[1] wood, "to make a
window," to "pitch it within and without
with pitch," and to observe definite
measurements. From the specific directions
thus handed down to us, we may
gather that mankind had acquired at a
very early period of the world's history
a knowledge of the different kinds of
wood, and of the use of tools.
HE first well-known reference to woodwork is
to be found in the Book of Genesis, in
the instructions given to Noah to make
an Ark of gopher[1] wood, "to make a
window," to "pitch it within and without
with pitch," and to observe definite
measurements. From the specific directions
thus handed down to us, we may
gather that mankind had acquired at a
very early period of the world's history
a knowledge of the different kinds of
wood, and of the use of tools.
We know, too, from the bas-reliefs and papyri in the British Museum, how advanced were the Ancient Egyptians in the arts of civilization, and that the manufacture of comfortable and even luxurious furniture was not neglected. In them, the Hebrews must have had excellent workmen for teachers and taskmasters, to have enabled them to acquire sufficient skill and experience to carry out such precise instructions as were given for the erection of the Tabernacle, some 1,500 years before Christ—as to the kinds of wood, measurements, ornaments, fastenings ("loops and[2] taches"), curtains of linen, and coverings of dried skins. We have only to turn for a moment to the 25th chapter of Exodus to be convinced that all the directions there mentioned were given to a people who had considerable experience in the methods of carrying out work, which must have resulted from some generations of carpenters, joiners, weavers, dyers, goldsmiths, and other craftsmen.
A thousand years before Christ, we have those descriptions of the building and fitting by Solomon of the glorious work of his reign, the great Temple, and of his own, "the King's house," which gathered from different countries the most skilful artificers of the time, an event which marks an era of advance in the knowledge and skill of those who were thus brought together to do their best work towards carrying out the grand scheme. It is worth while, too, when we are referring to Old Testament information bearing upon the subject, to notice some details of furniture which are given, with their approximate dates as generally accepted, not because there is any particular importance attached to the precise chronology of the events concerned, but because, speaking generally, they form landmarks in the history of furniture. One of these is the verse (2 Kings chap. iv.) which tells us the contents of the "little chamber in the wall," when Elisha visited the Shunammite, about B.C. 895; and we are told of the preparations for the reception of the prophet: "And let us set for him there a bed and a table and a stool and a candlestick." Another incident is some 420 years later, when, in the allusion to the grandeur of the Palace of Ahasuerus, we catch a glimpse of Eastern magnificence in the description of the drapery which furnished the apartment: "Where were white, green, and blue hangings, fastened with cords of fine linen and purple, to silver rings and pillars of marble; the beds were of gold and silver, upon a pavement of red and blue and white and black marble." (Esther i. 6.)
There are, unfortunately, no trustworthy descriptions of ancient Hebrew furniture. The illustrations in Kitto's Bible, Mr. Henry Soltau's "The Tabernacle, the Priesthood, and the Offerings," and other similar books, are apparently drawn from imagination, founded on descriptions in the Old Testament. In these, the "table for shew-bread" is generally represented as having legs partly turned, with the upper portions square, to which rings were attached for the poles by which it was carried. As a nomadic people, their furniture would be but primitive, and we may take it that as the Jews and Assyrians came from the same stock, and spoke the same language, such ornamental furniture as there was would, with the exception of the representations of figures of men or of animals, be of a similar character.

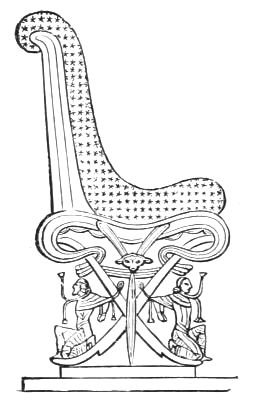
PART OF ASSYRIAN BRONZE THRONE AND FOOTSTOOL, ABOUT B. C. 888, REIGN OF ASSHURNAZIRPAL.
(From a Photo by Mansell & Co. of the Original in the British Museum.)
The discoveries which have been made in the oldest seat of monarchical government in the world, by such enterprising travellers as Sir Austin Layard, Mr. George Smith, and others who have thrown so much light upon domestic life in Nineveh, are full of interest in connection with this branch of the subject. We learn from these authorities that the furniture was ornamented with the heads of lions, bulls, and rams; tables thrones, and couches were made of metal and wood, and probably inlaid with ivory; the earliest chair, according to Sir Austin Layard, having been made without a back, and the legs terminating in lion's feet or bull's hoofs. Some were of gold, others of silver and bronze. On the monuments of Khorsabad, representations have been discovered of chairs supported by animals, and by human figures, probably those of prisoners.[4] In the British Museum is a bronze throne, found by Sir A. Layard amidst the ruins of Nimrod's Palace, which shews ability of high order for skilled metal work.
Mr. Smith, the famous Assyrian excavator and translator of cuniform inscriptions, has told us in his "Assyrian Antiquities" of his finding close to the site of Nineveh, portions of a crystal throne somewhat similar in design to the bronze one mentioned above, and in another part of this interesting book we have a description of an interior that is useful in assisting us to form an idea of the condition of houses of a date which can be correctly assigned to B.C. 860:—"Altogether in this place I opened six chambers, all of the same character, the entrances ornamented by clusters of square pilasters, and recesses in the rooms in the same style; the walls were colored in horizontal bands of red, green, and yellow, and where the lower parts of the chambers were panelled with small stone slabs, the plaster and colours were continued over these." Then follows a description of the drainage arrangements, and finally we have Mr. Smith's conclusion that this was a private dwelling for the wives and families of kings, together with the fact that on the other side of the bricks he found the legend of Shalmeneser II. (B.C. 860), who probably built this palace.
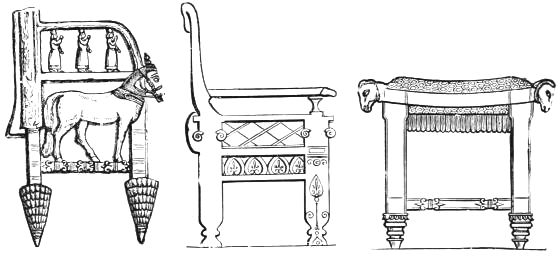
ASSYRIAN CHAIR FROM KHORSABAD. ASSYRIAN CHAIR FROM XANTHUS. ASSYRIAN THRONE.
(In the British Museum.) (In the British Museum.) (In the British Museum.)
In the British Museum is an elaborate piece of carved ivory, with depressions to hold colored glass, etc., from Nineveh, which once formed part of the inlaid ornament of a throne, shewing how richly such objects were ornamented. This carving is said by the authorities to be of[5] Egyptian origin. The treatment of figures by the Assyrians was more clumsy and more rigid, and their furniture generally was more massive than that of the Egyptians.
An ornament often introduced into the designs of thrones and chairs is a conventional treatment of the tree sacred to Asshur, the Assyrian Jupiter; the pine cone, another sacred emblem, is also found, sometimes as in the illustration of the Khorsabad chair on page 4, forming an ornamental foot, and sometimes being part of the merely decorative design.
The bronze throne, illustrated on page 3, appears to have been of sufficient height to require a footstool, and in "Nineveh and its Remains" these footstools are specially alluded to. "The feet were ornamented, like those of the chair, with the feet of lions or the hoofs of bulls."
The furniture represented in the following illustration, from a bas-relief in the British Museum, is said to be of a period some two hundred years later than the bronze throne and footstool.
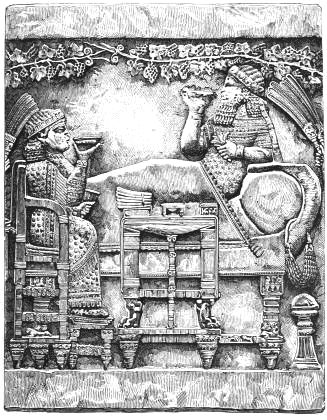
REPOSE OF KING ASSHURBANIPAL.
(From a Bas-relief in the British Museum.)
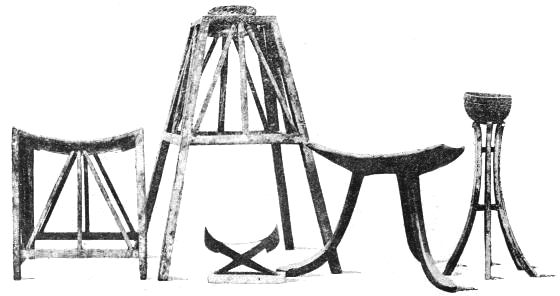
Stool. Stand for a Vase. Head Rest or Pillow. Workman's Stool. Vase on a Stand.
FOLDING STOOL. EBONY SEAT INLAID WITH IVORY.
(From Photos by Mansell & Co. of the Originals in the British Museum.)
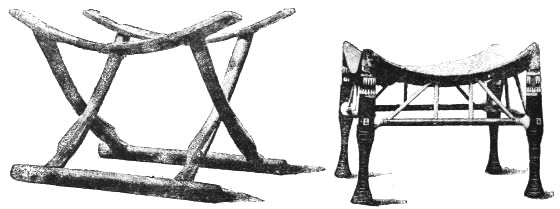
In the consideration of ancient Egyptian furniture we find valuable assistance in the examples carefully preserved to us, and accessible to every one in the British Museum, and one or two of these deserve passing notice. Nothing can be more suitable for its purpose than the "Workman's Stool:" the seat is precisely like that of a modern kitchen chair (all wood), slightly concaved to promote the sitter's comfort, and supported by three legs curving outwards. This is simple, convenient, and admirably adapted for long service. For a specimen of more ornamental work, the folding stool in the same glass case should be examined; the supports are crossed in a similar way to those of a modern camp-stool and the lower parts of the legs carved as heads of geese, with inlayings of ivory to assist the design and give richness to its execution.

AN EGYPTIAN OF HIGH RANK SEATED.
(From a Photo by Mansell & Co. of the Original Wall Painting in the British Museum.)
PERIOD: B.C. 1500-1400.
Portions of legs and rails, turned as if by a modern lathe, mortice holes and tenons, fill us with wonder as we look upon work which, at the most modern computation, must be 3,000 years old, and may be of a date still more remote.
In the same room, arranged in cases round the wall, is a collection of several objects which, if scarcely to be classed under the head of furniture, are articles of luxury and comfort, and demonstrate the extraordinary state of civilisation enjoyed by the old Egyptians, and help us to form a picture of their domestic habits.

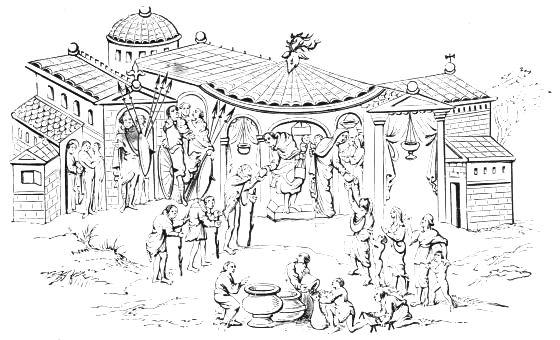
AN EGYPTIAN BANQUET.
(From a Wall Painting at Thebes.)
Amongst these are boxes, some inlaid with various woods, and also with little squares of bright turquoise blue pottery let in as a relief; others veneered with ivory; wooden spoons carved in most intricate designs, of which one, representing a girl amongst lotus flowers, is a work of great artistic skill; boats of wood, head rests, and models of parts of houses and granaries, together with writing materials, different kinds of tools and implements, and a quantity of personal ornaments and requisites.
"For furniture, various woods were employed, ebony, acacia, or sont, cedar, sycamore, and others of species not determined. Ivory, both of the hippopotamus and elephant, were used for inlaying, as also were glass pastes; and specimens of marquetry are not uncommon. In the paintings in the tombs, gorgeous pictures and gilded furniture are depicted. For cushions and mattresses, linen cloth and colored stuffs, filled with feathers of the waterfowl, appear to have been used, while seats have plaited bottoms of linen cord or tanned and dyed leather thrown over them, and sometimes the skins of panthers served this purpose. For carpets they used mats of palm fibre, on which they often sat. On the whole an Egyptian house was lightly furnished, and not encumbered with so many articles as are in use at the present day."
The above paragraph forms part of the notice with which the late Dr. Birch, the eminent antiquarian, formerly at the head of this department of the British Museum, has prefaced a catalogue of the antiquities alluded to. The visitor to the Museum should be careful to procure one of these useful and inexpensive guides to this portion of its contents.
Some illustrations taken from ancient statues and bas-reliefs in the British Museum, from copies of wall paintings at Thebes and other sources, give us a good idea of the furniture of this ancient people. Amongst the group of illustrations on p. 6 will be seen a representation of a wooden head-rest, which prevented the disarrangement of the coiffure of an Egyptian lady of rank. A very similar head-rest, with a cushion attached for comfort to the neck, is still in common use by the Japanese of the present day.
CHAIR WITH CAPTIVES AS SUPPORTS.
(From Papyrus in British Museum.)
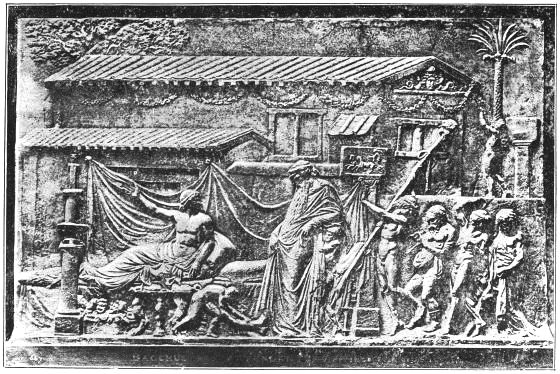
BACCHUS AND ATTENDANTS VISITING ICARUS.
(Reproduced from a Bas-relief in the British Museum.)
PERIOD: ABOUT A.D. 100.
An early reference to Greek furniture is made by Homer, who describes coverlids of dyed wool, tapestries, carpets, and other accessories, which must therefore have formed part of the contents of a great man's residence centuries before the period which we recognise as the "meridian" of Greek Art.
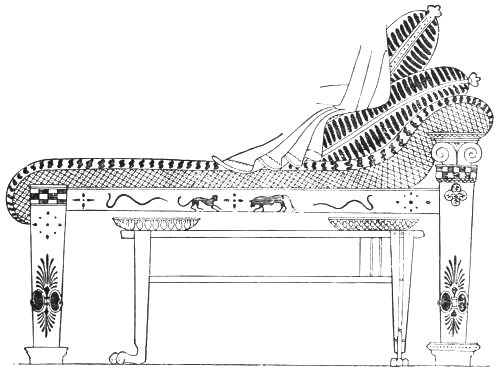
GREEK BEDSTEAD WITH A TABLE.
(From an old Wall Painting.)
In the second Vase-room of the British Museum the painting on one of these vases represents two persons sitting on a couch, upon which is a cushion of rich material, while for the comfort of the sitters there is a footstool, probably of ivory. Facing page 8 there is an illustration of a bas-relief in stone, "Bacchus received as a guest by Icarus," in which the couch has turned legs and the feet are ornamented with carved leaf work. Illustrations of tripods used for sacred or other purposes, and as supports for braziers, lead us to the conclusion that tables were made of wood, of marble, and of metal; also folding chairs, and couches for sleeping and resting, but not for reclining at meals, as was the fashion at a later period. In most of the designs for these various articles of furniture there is a similarity of treatment of the head, legs, and feet of lions, leopards, and sphinxes to that which we have noticed in the Assyrian patterns.

GREEK FURNITURE.
(From Antique Bas-reliefs.)
The description of an interesting piece of furniture may be noticed here, because its date is verified by its historical associations, and it was seen and described by Pausanias about 800 years afterwards. This is the famous chest of Cypselus of Corinth, the story of which runs that when his mother's relations, having been warned by the Oracle of Delphi, that her son would prove formidable to the ruling party, sought to murder him, his life was saved by his concealment in this chest, and he became ruler of Corinth for some 30 years (B.C. 655-625). It is said to have been made of cedar, carved and decorated with figures and bas-reliefs, some in ivory, some in gold or ivory part gilt, and inlaid on all four sides and on the top.
The peculiar laws and customs of the Greeks at the time of their greatest prosperity were not calculated to encourage display or luxury in private life, or the collection of sumptuous furniture. Their manners were simple and their discipline was very severe. Statuary, sculpture of the best kind, painting of the highest merit—in a word, the best that Art could produce—were all dedicated to the national service in the enrichment of Temples and other public buildings, the State having indefinite and almost unlimited power over the property of all wealthy citizens. The public surroundings of an influential Athenian were therefore in direct contrast to the simplicity of his home, which contained the most meagre supply of chairs and tables, while the chefs d'œuvre of Phidias, Apelles and Praxiteles adorned the Senate House, the Theatre, and the Temple.
There were some exceptions to this rule, and we have records that during the later years of Greek prosperity such simplicity was not observed. Alcibiades is said to have been the first to have his house painted and decorated, and Plutarch tells us that he kept the painter Agatharcus a prisoner until his task was done, and then dismissed him with an appropriate reward. Another ancient writer relates that "The guest of a private house was enjoined to praise the decorations of the ceilings and the beauty of the curtains suspended from between the columns." This occurs, according to Mr. Perkins, the American translator of Dr. Falke's German book "Kunst im Hause," in the "Wasps of Aristophanes," written B.C. 422.
The illustrations, taken from the best authorities in the British Museum, the National Library of Paris, and other sources, shew the severe style adopted by the Greeks in their furniture.
As we are accustomed to look to Greece in the time of Pericles for purity of style and perfection of taste in Art, so do we naturally expect its gradual demoralisation in its transfer to the great Roman Empire. From that little village on the Palatine Hill, founded some 750 years B.C., Rome had spread and conquered in every direction, until in the time of Augustus she was mistress of the whole civilized world, herself the centre of wealth, civilisation, luxury, and power. Antioch in the East, and Alexandria in the South, ranked next to her as great cities of the world.
From the excavations of Herculaneum and Pompeii we have learned enough to conceive some general idea of the social life of a wealthy Roman in the time of Rome's highest prosperity. The houses had no upper story, but enclosed two or more quadrangles, or courts, with arcades into which the rooms opened, receiving air and ventilation from the centre open court. The illustration opposite p. 12 will give an idea of this arrangement.
In Mr. Hungerford Pollen's useful handbook there is a description of each room in a Roman house, with its proper Latin title and purpose; and we know from other descriptions of Ancient Rome that the residences in the Imperial City were divided into two distinct classes—that of the domus and insula, the former being the dwellings of the Roman nobles, and corresponding to the modern Palazzi, while the latter were the habitations of the middle and lower classes. Each insula consisted of several sets of apartments, generally let out to different families, and was frequently surrounded by shops. The houses described by Mr. Pollen appear to have had no upper story, but as ground became more valuable in Rome, houses were built to such a height as to be a source of danger, and in the time of Augustus there were not only strict regulations as to building, but the height was limited to 70 feet. The Roman furniture of the time was of the most costly kind. Tables were made of marble, gold, silver, and bronze, and were engraved, damascened, plated, and enriched with precious stones. The chief woods used were cedar, pine, elm, olive, ash, ilex, beech, and maple. Ivory was much used, and not only were the arms and legs of couches and chairs carved to represent the limbs of animals, as has been noted in the Assyrian, Egyptian, and Greek designs, but other parts of furniture were ornamented by carvings in bas-relief of subjects taken from Greek mythology and legend. Veneers were cut and applied, not as some have supposed for the purpose of economy, but because by this means the[13] most beautifully marked or figured specimens of the woods could be chosen, and a much richer and more decorative effect produced than would be possible when only solid timber was used. As a prominent instance of the extent to which the Romans carried the costliness of some special pieces of furniture, we have it recorded on good authority (Mr. Pollen) that the table made for Cicero cost a million sesterces, a sum equal to about £9,000, and that one belonging to King Juba was sold by auction for the equivalent of £10,000.
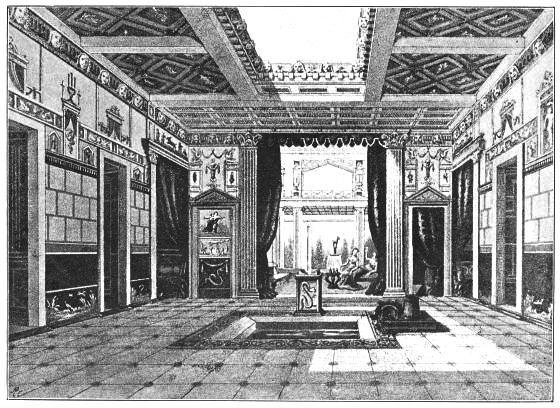
INTERIOR OF AN ANCIENT ROMAN HOUSE.
Said to have been that of Sallust.
PERIOD: B.C. 20 TO A.D. 20.
A ROMAN STUDY.
Shewing Scrolls or Books in a "Scrinium;" also Lamp, Writing Tables, etc.
Cicero's table was made of a wood called Thyine—wood which was brought from Africa and held in the highest esteem. It was valued not only on account of its beauty but also from superstitious or religious reasons. The possession of thyine wood was supposed to bring good luck, and its sacredness arose from the fact that from it was produced the incense used by the priests. Dr. Edward Clapton, of St. Thomas' Hospital, who made a collection of woods named in the Scriptures, managed to secure a specimen of thyine, which a friend of his obtained on the Atlas Mountains. It resembles the woods which we know as tuyere and amboyna.[2]
Roman, like Greek houses, were divided into two portions—the front for the reception of guests and the duties of society, with the back for household purposes, and the occupation of the wife and family; for although the position of the Roman wife was superior to that of her Greek contemporary, which was little better than that of a slave, still it was very different to its later development.
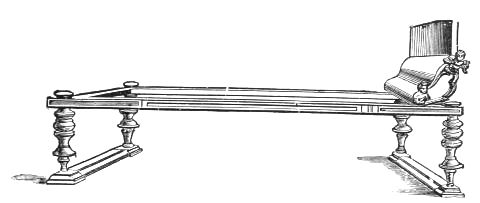
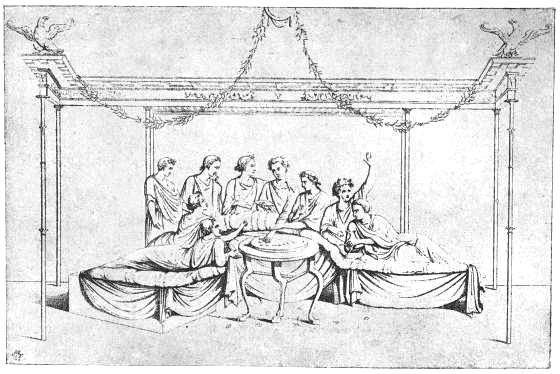
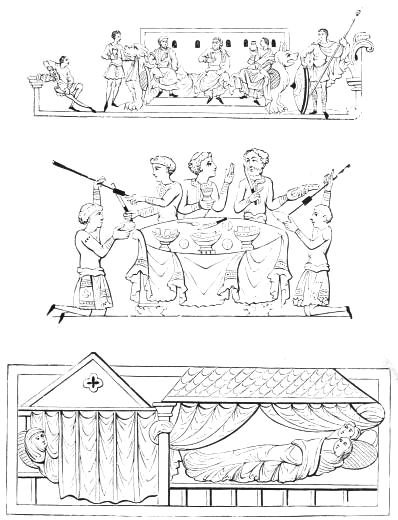
The illustration following p. 16, of a repast in the house of Sallust, represents the host and his eight male guests reclining on the seats of the period, each of which held three persons, and was called a triclinium, making up the favourite number of a Roman dinner party, and possibly giving us the proverbial saying—"Not less than the Graces nor more than the Muses"—which is still held to be a popular regulation for a dinner party.
ROMAN SCAMNUM OR BENCH.
ROMAN BISELLIUM, OR SEAT FOR TWO PERSONS.
But generally occupied by one, on occasions of festivals, etc.
From discoveries at Herculaneum and Pompeii a great deal of information has been gained of the domestic life of the wealthier Roman citizens, and there is a useful illustration on the preceding page of the furniture of a library or study in which the designs are very similar to the Greek ones we have noticed; it is not improbable they were made and executed by Greek workmen.
It will be seen that the books such as were then used, instead of being placed on shelves or in a bookcase, were kept in round boxes called Scrinia, which were generally of beech wood, and could be locked or sealed when required. The books in rolls or sewn together were thus easily carried about by the owner on his journeys.
Mr. Hungerford Pollen mentions that wearing apparel was kept in vestiaria, or wardrobe rooms, and he quotes Plutarch's anecdote of the purple cloaks of Lucullus, which were so numerous that they must have been stored in capacious hanging closets rather than in chests.
In the atrium, or public reception room, was probably the best furniture in the house. According to Moule's "Essay on Roman Villas," "it was here that numbers assembled daily to pay their respects to their[15] patron, to consult the legislator, to attract the notice of the statesman, or to derive importance in the eyes of the public from the apparent intimacy with a man in power."
The growth of the Roman Empire eastward, the colonisation of Oriental countries, and subsequently the establishment of an Eastern Empire, produced gradually an alteration in Greek design, and though, if we were discussing the merits of design and the canons of taste, this might be considered a decline, still its influence on furniture was doubtless to produce more ease and luxury, more warmth and comfort, than would be possible if the outline of every article of useful furniture were decided by a rigid adherence to classical principles. We have seen that this was more consonant with the public life of an Athenian; but the Romans, in the later period of the Empire, with their wealth, their extravagance, their slaves, their immorality and gross sensuality, lived in a splendour and with a prodigality that well accorded with the gorgeous coloring of Eastern hangings and embroideries, of rich carpets and comfortable cushions, of the lavish use of gold and silver, and meretricious and redundant ornament.
ROMAN COUCH, GENERALLY OF BRONZE.
(From an Antique Bas-relief.)
This slight sketch, brief and inadequate as it is, of a history of furniture from the earliest time of which we have any record, until from the extraordinary growth of the vast Roman Empire, the arts and manufactures of every country became as it were centralised and focussed in the palaces of the wealthy Romans, brings us down to the commencement of what has been deservedly called "the greatest event in history"—the decline and fall of this enormous empire. For fifteen generations, for some five hundred years, did this decay, this vast revolution, proceed to its conclusion. Barbarian hosts settled down in provinces they had overrun and conquered, the old Pagan world died as it were, and the new Christian era dawned. From the latter end of the second century[16] until the last of the Western Cæsars, in A.D. 476, it is, with the exception of a short interval when the strong hand of the great Theodosius stayed the avalanche of Rome's invaders, one long story of the defeat and humiliation of the citizens of the greatest power the world has ever known. It is a vast drama that the genius and patience of a Gibbon has alone been able to deal with, defying almost by its gigantic catastrophes and ever raging turbulence the pen of history to chronicle and arrange. When the curtain rises on a new order of things, the age of Paganism has passed away, and the period of the Middle Ages will have commenced.
ROMAN BRONZE LAMP AND STAND.
(Found in Pompeii.)
THE ROMAN TRICLINIUM, OR DINING ROOM.
The plan in the margin shews the position of guests; the place of honor was that which is indicated by "No. 1," and that of the host by "No. 9."
(The Illustration is taken from Dr. Jacob von Falke's "Kunst im Hause.")
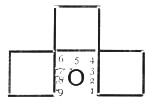
Plan of Triclinium.
Period of 1,000 years from Fall of Rome, A.D. 476, to Capture of Constantinople, 1453—The Crusades—Influence of Christianity—Chairs of St. Peter and Maximian at Rome, Ravenna, and Venice—Edict of Leo III. prohibiting Image worship—The Rise of Venice—Charlemagne and his successors—The Chair of Dagobert—Byzantine character of Furniture—Norwegian carving—Russian and Scandinavian—The Anglo-Saxons—Sir Walter Scott quoted—Descriptions of Anglo-Saxon Houses and Customs—Art in Flemish Cities—Gothic Architecture—The Coronation Chair at Westminster Abbey—Penshurst—French Furniture in the 14th Century—Description of rooms—The South Kensington Museum—Transition from Gothic to Renaissance—German carved work; the Credence, the Buffet, and Dressoir.
 HE history of furniture is so thoroughly a
part of the history of the manners and
customs of different peoples, that one can
only understand and appreciate the several
changes in style, sometimes gradual and
sometimes rapid, by reference to certain
historical events and influences by which
such changes were effected.
HE history of furniture is so thoroughly a
part of the history of the manners and
customs of different peoples, that one can
only understand and appreciate the several
changes in style, sometimes gradual and
sometimes rapid, by reference to certain
historical events and influences by which
such changes were effected.
Thus, we have during the space of time known as the Middle Ages, a stretch of some 1,000 years, dating from the fall of Rome itself, in A.D. 476 to the capture of Constantinople by the Turks under Mahomet II. in 1453, an historical panorama of striking incidents and great social changes bearing upon our subject. It was a turbulent and violent period, which saw the completion of Rome's downfall, the rise of the Carlovingian family, the subjection of Britain by the Saxons, the Danes, and the Normans; the extraordinary career and fortunes of Mahomet; the conquest of Spain and a great part of Africa by the Moors; and the Crusades, which united in a common cause the swords and spears of friend and foe.
It was the age of monasteries and convents, of religious persecutions and of heroic struggles of the Christian Church. It was the age of feudalism, chivalry, and war, but towards its close a time of comparative civilisation and progress, of darkness giving way to the light which followed; the night of the Middle Ages preceding the dawn of the Renaissance.
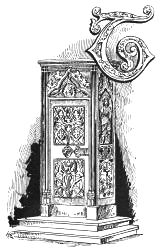
With the growing importance of Constantinople, the capital of the Eastern Empire, families of well-to-do citizens flocked thither from other parts, bringing with them all their most valuable possessions: and the houses of the great became rich in ornamental furniture, the style of which was a mixture of Eastern and Roman,—that is, a corruption of the early Classic Greek developing into the style known as Byzantine. The influence of Christianity upon the position of women materially affected the customs and habits of the people. Ladies were allowed to be seen in chariots and open carriages, the designs of which, therefore, improved and became more varied; the old custom of reclining at meals ceased, and guests sat on benches; and though we have, with certain exceptions, such as the chair of St. Peter at Rome, and that of Maximian in the Cathedral at Ravenna, no specimens of furniture of this time, we have in the old Byzantine ivory bas-reliefs such representations of circular throne chairs and of ecclesiastical furniture, as suffice to show the class of woodwork then in vogue.
The chair of St. Peter is one of the most interesting relics of the Middle Ages. The woodcut will shew the design, which is, like other work of the period, Byzantine, and the following description is taken from Mr. Hungerford Pollen's introduction to the South Kensington catalogue:—"The chair is constructed of wood, overlaid with carved ivory work and gold. The back is bound together with iron. It is a square with solid front and arms. The width in front is 39 inches; the height in front 30 inches, shewing that a scabellum or footstool must have belonged to it.... In the front are 18 groups or compositions from the Gospels, carved in ivory with exquisite fineness, and worked with inlay of the purest gold. On the outer sides are several little figures carved in ivory. It formed, according to tradition, part of the furniture of the house of the Senator Pudens, an early convert to the Christian faith. It is he who gave to the Church his house in Rome, of which much that remains is covered by the Church of St. Pudenziana. Pudens gave this chair to St. Peter, and it became the throne of the See. It was kept in the old Basilica of St. Peter's." Since then it has been transferred from place to place, until now it remains in the present Church of St. Peter's, but is completely hidden from view by the seat or covering made in 1667, by Bernini, out of bronze taken from the Pantheon.
Much has been written about this famous chair. Cardinal Wiseman and the Cavaliere de Rossi have defended its reputation and its history, and Mr. Nesbitt, some years ago, read a paper on the subject before the Society of Antiquaries.
CHAIR OF ST. PETER, ROME.
Formerly there was in Venice another "chair of St. Peter," of which there is a sketch from a photograph in Mrs. Oliphant's "Makers of Venice." It is said to have been a present from the Emperor Michael, son of Theophilus (824-864), to the Venetian Republic in recognition of services rendered, by either the Doge Gradonico, who died in 864, or his predecessor, against the Mahommedan incursions. Fragments only now remain, and these are preserved in the Church of St. Pietro, at Castello.
There is also a chair of historic fame preserved in Venice, and now kept in the treasury of St. Mark's. Originally in Alexandria, it was sent to Constantinople and formed part of the spoils taken by the Venetians in 1204. Like both the other chairs, this was also ornamented with ivory plaques, but these have been replaced by ornamental marble.
The earliest of the before-mentioned chairs, namely, the one at Ravenna, was made for the Archbishop about 546 to 556, and is thus described in Mr. Maskell's "Handbook on Ivories," in the Science and Art series:—"The chair has a high back, round in shape, and is entirely covered with plaques of ivory arranged in panels carved in high relief with scenes from the Gospels and with figures of saints. The plaques have borders with foliated ornaments, birds and animals; flowers and fruits filling the intermediate spaces. Du Sommerard names amongst the most remarkable subjects, the Annunciation, the Adoration of the Wise Men, the Flight into Egypt, and the Baptism of Our Lord." The chair has also been described by Passeri, the famous Italian antiquary, and a paper upon it was read by Sir Digby Wyatt, before the Arundel Society, in which he remarked that as it had been fortunately preserved as a holy relic, it wore almost the same appearance as when used by the prelate for whom it was made, save for the beautiful tint with which time had invested it.
Long before the general break up of the vast Roman Empire, influences had been at work to decentralise Art, and cause the migration of trained and skilful artisans to countries where their work would build up fresh industries, and give an impetus to progress, where hitherto there had been stagnation. One of these influences was the decree issued in A.D. 726 by Leo III., Emperor of the Eastern Empire, prohibiting all image worship. The consequences to Art of such a decree were doubtless similar to the fanatical proceedings of the English Puritans of the seventeenth century; and artists, driven from their homes, were scattered to the different European capitals, where they were gladly received and found employment and patronage.
It should be borne in mind that at this time Venice was gradually rising to that marvellous position of wealth and power which she afterwards held.
Her wealthy merchants were well acquainted with the arts and manufactures of other countries, and Venice would be just one of those cities to attract the artist refugee. It is indeed here that wood carving as an Art may be said to have specially developed itself, and though, from its destructible nature, there are very few specimens extant dating from this early time, yet we shall see that two or three hundred years[21] later, ornamental woodwork flourished in a state of perfection which must have required a long probationary period.
DAGOBERT CHAIR.
Chair of Dagobert, of gilt bronze, now in the Museé de Souverains, Paris. Originally as a folding chair said to be the work of St. Eloi, 7th century; back and arms added by the Abbe Suger in 12th century. There is an electrotype reproduction in the South Kensington Museum.
Turning from Venice. During the latter end of the eighth century the star of Charlemagne was in the ascendant, and though we have no authentic specimen, and scarcely a picture of any wooden furniture of this reign, we know that, in appropriating the property of the Gallo-Romans, the Frank Emperor-King and his chiefs were in some degree educating themselves to higher notions of luxury and civilisation. Paul Lacroix, in "Manners, Customs, and Dress of the Middle Ages," tells us that the trichorum, or dining room, was generally the largest hall in the palace: two rows of columns divided it into three parts, one for the royal family, one for the officers of the household, and the third for the guests, who were generally numerous. No person of rank who visited the King could leave without sitting at his table or at least draining a cup to his[22] health. The King's hospitality was magnificent, especially on great religious festivals, such as Christmas and Easter.
In other portions of this work of reference we read of "boxes" to hold articles of value, and of rich hangings, but beyond such allusions little can be gleaned of any furniture besides. The celebrated chair of Dagobert (illustrated on p. 21), now in the Louvre, and of which there is a cast in the South Kensington Museum, dates from some 150 years before Charlemagne, and is probably the only specimen of furniture belonging to this period which has been handed down to us. It is made of gilt bronze, and is said to be the work of a monk.
For the designs of furniture of the tenth to the fourteenth centuries we are in a great measure dependent upon old illuminated manuscripts and missals of these remote times. There are some illustrations of the seats of State used by sovereigns on the occasions of grand banquets, or of some ecclesiastical function, to be found in the valuable collections of old documents in the British Museum and the National Libraries of Paris and Brussels. It is evident from these authorities that the designs of State furniture in France and other countries dominated by the Carlovingian monarchs were of Byzantine character, that pseudo-classic style which was the prototype of furniture of about a thousand years later, when the Cæsarism of Napoleon I., during the early years of the nineteenth century, produced so many designs which we now recognise as "Empire."
No history of mediæval woodwork would be complete without noticing the Scandinavian furniture and ornamental wood carving of the tenth to the fifteenth centuries. There are in the South Kensington Museum plaster casts of some three or four carved doorways of Norwegian workmanship, of the tenth, eleventh, and twelfth centuries, in which scrolls are entwined with contorted monsters, or, to quote Mr. Lovett's description, "dragons of hideous aspect and serpents of more than usually tortuous proclivities." The woodcut of a carved lintel conveys a fair idea of this work, and also of the old juniper wood tankards of a much later time.
There are also at Kensington other casts of curious Scandinavian woodwork of more Byzantine treatment, the originals of which are in the Museums of Stockholm and Copenhagen, where the collection of antique woodwork of native production is very large and interesting, and proves how wood carving, as an industrial Art, has flourished in Scandinavia from the early Viking times. One can still see in the old churches of Borgund and Hitterdal much of the carved woodwork of the seventh and eighth centuries; and lintels and porches full of national character are to be found in Thelemarken.

A CARVED NORWEGIAN DOORWAY.
PERIOD: X. TO XI. CENTURY.
Under the heading of "Scandinavian" may be included the very early Russian school of ornamental woodwork. Before the accession of the Romanoff dynasty in the sixteenth century, the Ruric race of kings came originally from Finland, then a province of Sweden; and so far as one can see from old illuminated manuscripts, there was a similarity of design to those of the early Norwegian and Swedish carved lintels which have been noticed above.
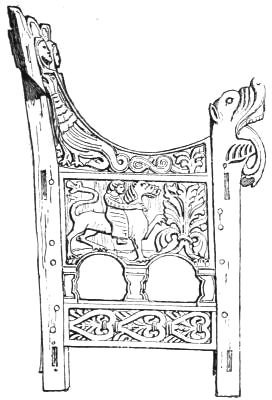
CARVED WOOD CHAIR, SCANDINAVIAN WORK.
PERIOD: 12th and 13th Century.
The coffers and caskets of early mediæval times were no inconsiderable items in the valuable furniture of a period when the list of articles coming under that definition was so limited. These were made in oak for general use, and some were of good workmanship; but of the very earliest none remain. There were, however, others, smaller and of a special character, made in ivory of the walrus and elephant, of horn and whalebone, besides those of metal. In the British Museum is one of these, of which the cover is illustrated on the following page, representing a man defending his house against an attack by enemies armed with spears and shields. Other parts of the casket are carved with subjects and runic inscriptions which have enabled Mr. Stephens, an authority on[24] this period of archæology, to assign its date to the eighth century, and its manufacture to that of Northumbria. It most probably represents a local incident, and part of the inscription refers to a word signifying "treachery." It was purchased by the late Sir A. W. Franks, F.S.A., and is one of the many valuable specimens given to the British Museum by its generous curator.

COVER OF A CASKET CARVED IN WHALEBONE.
(Northumbrian, 8th Century. British Museum.)
Of the furniture of our own country previous to the eleventh or twelfth centuries we know but little. The habits of the Anglo-Saxons were rude and simple, and they advanced but slowly in civilisation until after the Norman invasion. To convey, however, to our minds some idea of the interior of a Saxon thane's castle, we may avail ourselves of Sir Walter Scott's antiquarian research, and borrow his description of the chief apartment in Rotherwood, the hospitable hall of Cedric the Saxon. Though the time treated of in "Ivanhoe" is quite at the end of the twelfth century, yet we have in Cedric a type of man who would have gloried in retaining the customs of his ancestors, who detested and despised the new-fashioned manners of his conquerors, and who came of a race that had probably done very little in the way of "refurnishing" for some generations. If, therefore, we have the reader's pardon for relying upon the mise en scéne of a novel for an authority, we shall imagine the more easily what kind of furniture our Anglo-Saxon forefathers indulged in.
"In a hall, the height of which was greatly disproportioned to its extreme length and width, a long oaken table—formed of planks rough hewn from the forest, and which had scarcely received any polish—stood ready prepared for the evening meal.... On the sides of the apartment hung implements of war and of the chase, and there were at each corner folding doors which gave access to the other parts of the extensive building.
SAXON HOUSE OF 9TH OR 10TH CENTURY.
(From the Harleian MSS. in the British Museum.)
"The other appointments of the mansion partook of the rude simplicity of the Saxon period, which Cedric piqued himself upon maintaining. The floor was composed of earth mixed with lime, trodden into a hard substance, such as is often employed in flooring our modern barns. For about one quarter of the length of the apartment, the floor was raised by a step, and this space, which was called the daïs, was occupied only by the principal members of the family and visitors of distinction. For this purpose a table richly covered with scarlet cloth was placed. transversely across the platform, from the middle of which ran the longer and lower board, at which the domestic and inferior persons fed, down towards the bottom of the hall. The whole resembled the form of the letter T, or some of those ancient dinner tables which, arranged on the same principles, may still be seen in the ancient colleges of Oxford and Cambridge. Massive chairs and settles of carved oak were placed upon the daïs, and over these seats and the elevated tables was fastened a canopy of cloth, which served in some degree to protect the dignitaries who occupied that distinguished station from the weather, and especially from the rain, which in some places found its way through the ill-constructed roof. The walls of this upper end of the hall, as far as the daïs extended, were covered with hangings[26] or curtains, and upon the floor there was a carpet, both of which were adorned with some attempts at tapestry or embroidery, executed with brilliant or rather gaudy colouring. Over the lower range of table the roof had no covering, the rough plastered walls were left bare, the rude earthen floor was uncarpeted, the board was uncovered by a cloth, and rude massive benches supplied the place of chairs. In the centre of the upper table were placed two chairs more elevated than the rest, for the master and mistress of the family. To each of these was added a footstool curiously carved and inlaid with ivory, which mark of distinction was peculiar to them."
A drawing in the Harleian MSS. in the British Museum is shewn on page 25, illustrating a Saxon mansion in the ninth or tenth century. There is the hall in the centre, with "chamber" and "bower" on either side; there being only a ground floor, as in the earlier Roman houses. According to Mr. Wright, F.S.A., who has written on the subject of Anglo-Saxon manners and customs, there was only one instance recorded of an upper floor at this period, and that was in an account of an accident which happened to the house in which the Witan or Council of St. Dunstan met, when, according to the ancient chronicle which he quotes, the Council fell from an upper floor, and St. Dunstan saved himself from a similar fate by supporting his weight on a beam.
The illustration here given shews the Anglo-Saxon chieftain standing at the door of his hall, with his lady, distributing food to the needy poor. Other woodcuts represent Anglo-Saxon bedsteads, which were little better than raised wooden boxes, with sacks of straw placed therein, and these were generally in recesses. There are old inventories and wills in existence which shew that some value and importance was attached to these primitive contrivances, which at this early period in our history were the luxuries of only a few persons of high rank. A certain will recites that the "bedclothes (bed-reafs) with a curtain (hyrfte) and sheet (hepp-scrytan), and all that thereto belongs," should be given to his son.
In the account of the murder of King Athelbert by the Queen of King Offa, as told by Roger of Wendover, we read of the Queen ordering a chamber to be made ready for the Royal guest, which was adorned for the occasion with what was then considered sumptuous furniture. "Near the King's bed she caused a seat to be prepared, magnificently decked and surrounded with curtains, and underneath it the wicked woman caused a deep pit to be dug." The author from whom the above translation is quoted adds with grim humour, "It is clear that this room was on the ground floor."
ANGLO-SAXON FURNITURE OF ABOUT THE 10TH CENTURY.
(From old MSS. in the British Museum.)
1. A Drinking Party.
2. A Dinner Party, in which the attendants are serving the meal on the spits on which it has been cooked.
3. Anglo-Saxon Beds.
There are in the British Museum other old manuscripts whose illustrations have been laid under contribution, representing more innocent occupations of our Anglo-Saxon forefathers. "The seat on the daïs," "an Anglo-Saxon drinking party," and other illustrations which are in existence, prove generally that, when the meal had finished, the table was removed and drinking vessels were handed round from guest to guest; the story-tellers, the minstrels, and the gleemen (conjurers) or jesters, beguiling the festive hour with their different performances.

THE SEAT ON THE DAÏS. SAXON STATE BED.
Some of these Anglo-Saxon houses had formerly been the villas of the Romans during their occupation, which were altered and modified to suit the habits and tastes of their later possessors. Lord Lytton has given us, in the first chapter of his novel "Harold," the description of one of such Saxonized Roman houses, in his reference to Hilda's abode.
The gradual influence of Norman civilisation, however, had its effect, though the unsettled state of the country prevented any rapid development of industrial arts. The feudal system, by which every powerful baron became a petty sovereign, often at war with his neighbour, rendered it necessary that household treasures should be few and easily[29] transported or hidden, and the earliest oak chests which are still preserved date from about this time. Bedsteads were not usual, except for kings, queens, and great ladies; tapestry covered the walls, and the floors were generally sanded. As the country became more calm, and security for property more assured, this comfortless state of living disappeared; the dress of the ladies was richer, and the general habits of the upper classes were more refined. Stairs were introduced into houses, the "parloir" or "talking room" was added, and fire places of brick or stonework were made in some of the rooms, where previously the smoke was allowed to escape through an aperture in the roof. Bedsteads were carved and draped with rich hangings. Armoires made of oak and enriched with carvings, and "Presses" date from about the end of the eleventh century.

ENGLISH FOLDING CHAIR, 14TH CENTURY. CRADLE OF HENRY V.
It was during the reign of Henry III., 1216-1272, that wood-panelling was first used for rooms, and considerable progress generally appears to have been made about this period. Eleanor of Provence, whom the King married in 1236, encouraged more luxury in the homes of the barons and courtiers. Mr. Hungerford Pollen has quoted a royal precept which was promulgated in this year, and it plainly shews that our ancestors were becoming more refined in their tastes. The terms of this precept were as follows, viz., "The King's great chamber at Westminster to be painted a green colour like a curtain, that in the great gable or frontispiece of the said chamber, a French inscription should be painted, and that the King's little wardrobe should be painted of a green colour to imitate a curtain."
In another 100 or 150 years we find mediæval Art approaching its best period, not only in England, but in the great Flemish cities, such as Bruges and Ghent, which in the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries[30] played so important a part in the history of that time. The taste for Gothic architecture had now well set in, and we find that in this, as in every change of style, the fashion in woodwork naturally followed that of ornament in stone; indeed, in many cases it is more than probable that the same hands which planned the cathedral or monastery also drew the designs for furniture, especially as the finest specimens of wood carving were devoted to the service of the church.
The examples, therefore, of the woodwork of this period to which we have access are found to be mostly of Gothic pattern, with quaint distorted conceptions of animals and reptiles, adapted to ornament the structural part of the furniture, or for the enrichment of the panels.
To the end of the thirteenth century belongs the Coronation Chair made for King Edward I., 1296-1300, and now in Westminster Abbey. This historic relic is of oak, and the woodcut on the opposite page gives an idea of the design and decorative carving. It is said that the pinnacles on each side of the gabled back were formerly surmounted by two leopards, of which only small portions remain. The famous Coronation Stone, which, according to ancient legend, is the identical one on which the patriarch Jacob rested his head at Bethel, when "he tarried there all night because the sun was set, and he took of the stones of that place and put them up for his pillows" (Gen. xxviii.), can be seen through the quatrefoil openings under the seat.[3]
The carved lions which support the chair are not original, but modern work; and were re-gilt in honour of the Jubilee of Her Majesty in 1887, when the chair was last used. The rest of the chair now shews the natural colour of the oak, except the arms, which have a slight padding on them. The wood was, however, formerly covered with a coating of plaster, gilded over, and it is probably due to this protection that it is now in such excellent preservation.
Standing by its side in Henry III.'s Chapel in Westminster Abbey is another chair, similar, but lacking the trefoil Gothic arches, which are carved on the sides of the original chair; this was made for and used by Mary, daughter of James II. and wife of William III., on the occasion of their double coronation. Mr. Hungerford Pollen has given us a long description of this chair, with quotations from the different historical notices which have appeared concerning it. The following is an extract which he has taken from an old writer:—
"It appears that the King intended, in the first instance, to make the chair in bronze, and that Eldam, the King's workman, had actually[31] begun it. Indeed, some parts were even finished, and tools bought for the clearing up of the casting. However, the King changed his mind, and we have accordingly 100s. paid for a chair in wood, made after the same pattern as the one which was to be cast in copper; also 13s. 4d. for carving, painting, and gilding two small leopards in wood, which were delivered to Master Walter, the King's painter, to be placed upon and on either side of the chair made by him. The wardrobe account of 29th Ed. I. shows that Master Walter was paid £1 19s. 7d. 'for making a step at the foot of the new chair in which the Scottish stone is placed; and for the wages of the carpenters and of the painters, and for colours and gold employed, and for the making a covering to cover the said chair.'"
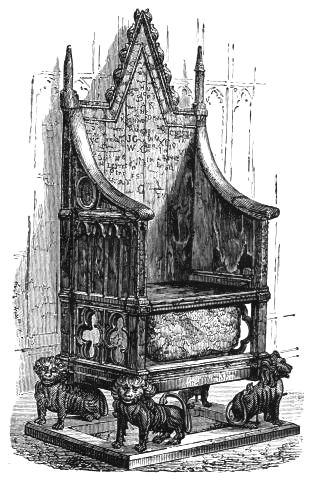
CORONATION CHAIR, WESTMINSTER ABBEY.
In 1328, June 1, there was a royal writ ordering the abbot to deliver up the stone to the Sheriff of London, to be carried to the Queen-Mother; however, it was not sent. The chair has been used upon the occasion of every coronation since that time, except in the case of Mary, who is said to have used a chair specially sent by the Pope for the occasion.
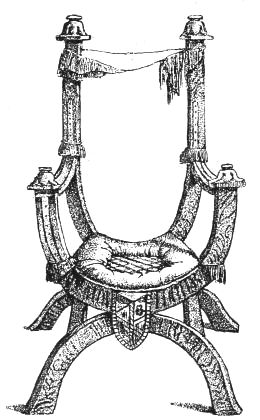
CHAIR IN THE VESTRY OF YORK MINSTER.
Late 14th Century.
The above drawing of a chair in York Minster, and the two more throne-like seats on a full-page illustration, will serve to shew the best kind of ornamental Ecclesiastical furniture of the fourteenth century. In the choir of Canterbury Cathedral there is a chair which has played its part in history, and, although earlier than the above, it may be conveniently mentioned here. This is the Archbishop's throne, and it is also called the chair of St. Augustine. According to legend, the Saxon kings were crowned thereon, but it is probably not earlier than the thirteenth century. It is an excellent piece of stonework, with a shaped back and arms, relieved from being quite plain by the back and sides being panelled with a carved moulding.
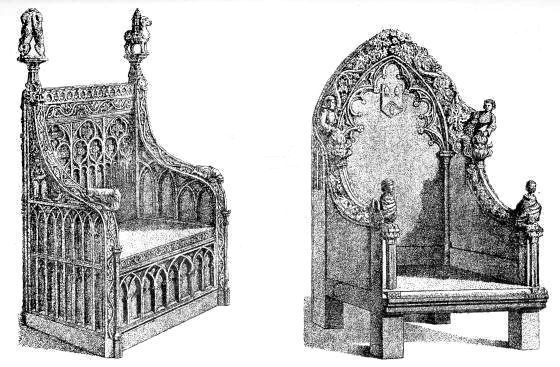
CHAIR. CHAIR.
In St. Mary's Hall, Coventry. From an Old English Monastery.
PERIOD XV. CENTURY.
"STANDING" TABLE AT PENSHURST, STILL ON THE DAÏS IN THE HALL.
Penshurst Place, near Tonbridge, the residence of the late Lord de l'Isle and Dudley, the historic home of the Sydneys, is almost an unique example of what a wealthy English gentleman's country house was about the time of which we are writing, say the middle of the fourteenth century, or during the reign of Edward III. By the courtesy of the late Lord de l'Isle, the writer was allowed to examine many objects of great interest there, and from the careful preservation of many original fittings and[34] articles of furniture, one may still gain some idea of the "hall" as it appeared when that part of the house was the scene of the chief events in the daily life of the family—the raised daïs for host and honoured guests, the better table which was placed there (illustrated on the preceding page), and the commoner ones for the body of the hall; and though the ancient buffet which displayed the gold and silver cups is gone, one can see where it would have stood. Penshurst is said to possess the only hearth of that period now remaining in England, an octagonal space edged with stone in the centre of the hall, over which was once the simple opening for the outlet of smoke through the roof; and the old andirons or firedogs are still there.
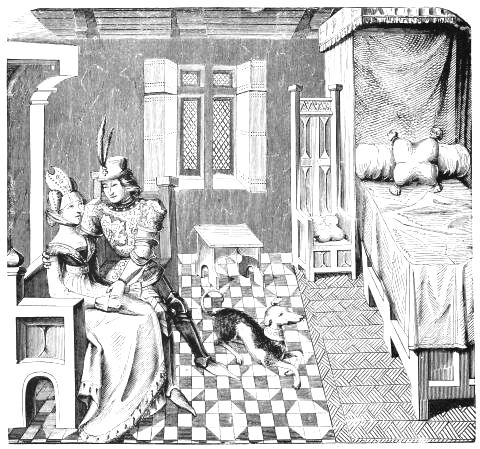

BEDROOM IN WHICH A KNIGHT AND HIS LADY ARE SEATED.
(From a Miniature in "Othea," a Poem by Christine de Pisan. XIV. Century, French.)

BEDSTEAD AND CHAIR IN CARVED OAK.
(From Miniatures in the Royal Library, Brussels.)
PERIOD: XIV. CENTURY.
An idea of the furniture of an apartment in France during the fourteenth century is conveyed by the illustration on this page, and it is very useful, because, although we have on record many descriptions of[35] the appearance of the furniture of state apartments, we have very few authenticated accounts of the way in which such domestic chambers as the one occupied by "a knight and his lady" were arranged. The prie-dieu chair was generally at the bedside, and had a seat which lifted up, the lower part forming a boxlike receptacle for devotional books, then so regularly used by a lady of the time.[36] Towards the end of the fourteenth century there was in high quarters a taste for bright and rich coloring; we have the testimony of an old writer who describes the interior of the Hotel de Bohême, which, after having been the residence of several great personages, was given by Charles VI. of France in 1388 to his brother the Duke of Orleans. "In this palace was a room used by the duke, hung with cloth of gold, bordered with vermilion velvet embroidered with roses; the Duchess had a room hung with vermilion satin embroidered with crossbows, which were on her coat of arms; that of the Duke of Burgundy was hung with cloth of gold embroidered with windmills. There were besides eight carpets of glossy texture with gold flowers, one representing 'the seven virtues and seven vices,' another the history of Charlemagne, another that of Saint Louis. There were also cushions of cloth of gold, twenty-four pieces of vermilion leather of Aragon, and four carpets of Aragon leather, 'to be placed on the floor of rooms in summer.' The favourite arm-chair of the Princess is thus described in an inventory—'a chamber chair with four supports, painted in fine vermilion, the seat and arms of which are covered in vermilion morocco, or cordovan, worked and stamped with designs representing the sun, birds, and other devices bordered with fringes of silk and studded with nails.'"
The thirteenth and fourteenth centuries had been remarkable for a general development of commerce; merchants of Venice, Genoa, Florence, Milan, Ghent, Bruges, Antwerp, and many other famous cities had traded extensively with the East and had grown opulent, and their homes naturally shewed signs of wealth and comfort that in former times had been impossible to any but princes and rich nobles. Laws had been made in compliance with the complaints of the aristocracy, to place some curb on the growing ambition of the "bourgeoisie"; thus we find an old edict in the reign of Philippe the Fair (1285-1314)—"No bourgeois shall have a chariot, nor wear gold, precious stones, nor crowns of gold and silver. Bourgeois not being prelates or dignitaries of state shall not have tapers of wax. A bourgeois possessing 2,000 pounds (tournois) or more, may order for himself a dress of 12 sous[4] 6 deniers, and for his wife one worth 16 sous at the most," etc., etc., etc.
This and many other similar regulations were made in vain: the trading classes became more and more powerful, and we quote the[37] description of a furnished apartment from P. Lacroix's "Manners and Customs of the Middle Ages."
"The walls were hung with precious tapestry of Cyprus, on which the initials and motto of the lady were embroidered, the sheets were of fine linen of Rheims, and had cost more than 300 pounds, the quilt was a new invention of silk and silver tissue, the carpet was like gold. The lady wore an elegant dress of crimson silk, and rested her head and arms on pillows ornamented with buttons of oriental pearls. It should be remarked that this lady was not the wife of a great merchant, such as those of Venice and Genoa, but of a simple retail dealer who was not above selling articles for 4 sous; such being the case, we cannot wonder that Christine de Pisan should have considered the anecdote 'worthy of being immortalized in a book.'"

"THE NEW BORN INFANT."
Shewing the interior of an Apartment at the end of the 14th or commencement of the 15th century.
(From a Miniature in "Histoire de la Belle Hélaine," National Library of Paris.)
As we approach the end of the fourteenth century, we find canopies added to the "chaires" or "chayers á dorseret," which were carved in oak or chestnut, and sometimes elaborately gilded and picked out in color. The canopied seats were very bulky and throne-like constructions,[38] and were abandoned towards the end of the fifteenth century; and it is worthy of notice that though we have retained our word "chair," adopted from the Norman French, the French people discarded their synonym in favour of its diminutive "chaise" to describe the somewhat smaller and less massive seat which came into use in the sixteenth century.

PORTRAIT OF CHRISTINE DE PISAN.
Seated on a Canopied Chair of carved wood the back lined with tapestry.
(From Miniature on MS., in the Burgundy Library, Brussels.)
PERIOD: XV. CENTURY.
The skilled artisans of Paris had arrived at a very high degree of excellence in the fourteenth century, and in old documents describing valuable articles of furniture, care is taken to note that they are of Parisian workmanship. According to Lacroix, there is an account of the court silversmith, Etienne La Fontaine, which gives us an idea of the[39] amount of extravagance sometimes committed in the manufacture and decorations of a chair, into which it was then the fashion to introduce the incrustations of precious stones; thus for making a silver arm chair and ornamenting it with pearls, crystals, and other stones, he charged the King of France, in 1352, no less a sum than 774 louis.
The use of rich embroideries at state banquets and on grand occasions appears to have commenced during the reign of Louis IX.—Saint Louis, as he is called—and these were richly emblazoned with arms and devices. Indeed, it was probably due to the fashion for rich stuffs and coverings of tables, and of velvet embroidered cushions for the chairs, that the practice of making furniture of the precious metals died out, and carved wood came into favour.

STATE BANQUET, WITH ATTENDANT MUSICIANS.
(From Miniatures in the National Library, Paris.)
PERIOD: XV. CENTURY.
Chairs of this period appear only to have been used on very special occasions; indeed, they were too cumbersome to be easily moved from place to place, and in a miniature from some MSS. of the early part of the fifteenth century, which represents a state banquet, the guests are seated on a long bench with the back carved in Gothic ornament of the time. In Skeat's Dictionary, our modern word "banquet" is said to be derived from the "bancs" or benches used on these occasions.
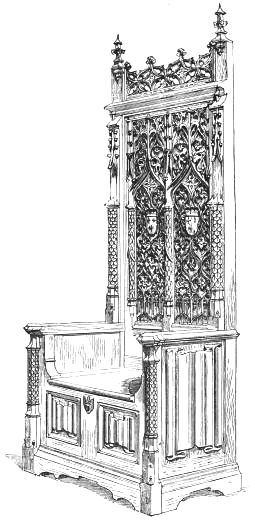
A HIGH BACKED CHAIR IN CARVED OAK (GOTHIC STYLE).
PERIOD: XV. CENTURY. FRENCH.
The great hall of the King's Palace, where such an entertainment as that given by Charles V. to the Emperor Charles of Luxemburg would have taken place, was also furnished with three "dressoirs" for the display of the gold and silver drinking cups, and vases of the time; the repast[41] itself was served upon a marble table, and above the seat of each of the Princes present was a separate canopy of gold cloth embroidered with fleur de lis.

MEDIÆVAL BED AND BEDROOM.
(From Viollet-le-Duc.)
PERIOD: XIV. TO XV. CENTURY. FRENCH.
The furniture of ordinary houses of this period was very simple. Chests, more or less carved, and ornamented with iron work, settles of oak or of chestnut, stools or benches with carved supports, a bedstead and a prie-dieu chair, a table with plain slab supported on shaped standards, would nearly complete the inventory of the furniture of the chief room in a house of a well-to-do merchant in France until the fourteenth century had turned. The table was narrow, apparently not more than some 30 inches wide, and guests sat on one side only, the service taking place from the unoccupied side of the table. In palaces and baronial halls, the servants with dishes were followed by musicians, as shewn in an old miniature of the time, reproduced on page 39.
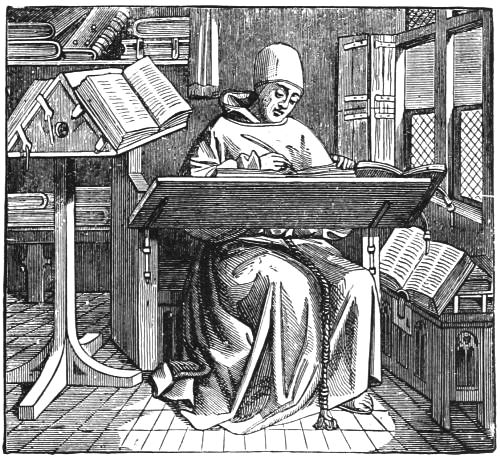

SCRIBE OR COPYIST
Working at his desk in a room in which are a reading desk and a chest with manuscript.
(From an Old Miniature.)
PERIOD: XV. CENTURY.
Turning to German work of the fifteenth century, there is, in the South Kensington Museum, a cast of the famous choir stalls in the Cathedral of Ulm, which are considered to be the finest work of the Swabian school of German wood carving. The magnificent panel of foliage on the front, the Gothic triple canopy with the busts of Isaiah. David, and Daniel, are thoroughly characteristic specimens of design; the signature of the artist, Jörg Syrlin, with date 1468, are carved on the work. There were originally 89 choir stalls, and the work occupied the master from the date mentioned, 1468, until 1474.
The illustrations of the two chairs of German Gothic furniture, formerly in some of the old castles, are good examples of their time, and are from drawings made on the spot by Prof. Heideloff.

TWO GERMAN CHAIRS, LATE 15TH CENTURY.
(From Drawings made in Old German Castles by Prof. Heideloff.)
There are in our South Kensington Museum some full sized plaster casts of important specimens of woodwork of the fifteenth and two previous centuries, and being of authenticated dates, we can compare them with the work of the same countries after the Renaissance had been adopted and had completely altered the design. Thus in Italy there was, until the latter part of the fifteenth century, a mixture of Byzantine and Gothic, of which we can see a capital example in the casts of the celebrated Pulpit in the Baptistry of Pisa, the date of which is 1260. The pillars are supported by lions, which, instead of being introduced heraldically into the design, as would be the case some two hundred years later, are bearing the whole weight of the pillars and an enormous superstructure on the hollow of their backs in a most impossible manner. The spandril of each arch is filled with a saint in a grotesque position amongst Gothic foliage, and there is in many respects a marked contrast to the casts of examples of the Renaissance period which are in the Museum.[43]
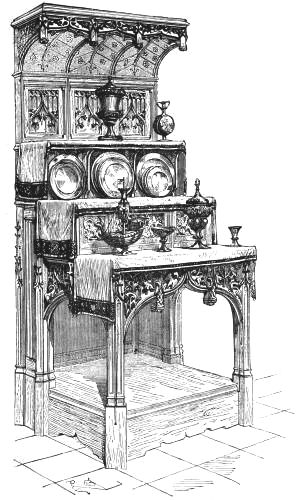
CARVED OAK BUFFET IN GOTHIC STYLE (VIOLLET LE DUC).
PERIOD: XV. CENTURY. FRENCH.
This transition from Mediæval and Gothic, to Renaissance, is clearly noticeable in the woodwork of many cathedrals and churches in England and in continental cities. It is evident that the chairs, stalls, and pulpits in many of these buildings have been executed at different times, and the change from one style to another is more or less marked. The Flemish buffet illustrated (opposite page 44) is an example of this transition, and may be contrasted with the French Gothic buffet illustrated on page 43, and referred to on page 44. There is also in the central hall of the South[44] Kensington Museum a plaster cast of a carved wood altar stall in the Abbey of Saint Denis, France: the pilasters at the sides have the familiar Gothic pinnacles, while the panels are ornamented with arabesques, scrolls, and an interior in the Renaissance style; the date of this is late in the fifteenth century.

OLD ENGLISH OAK BUFFET, 15TH CENTURY.
(Drawn from the original in the possession of Seymour Lucas, Esq., R.A.)
English examples of this period are very scarce, and the buffet illustrated here is a favourable specimen of our national work late in the fifteenth century. While the crocketted enrichment in the brackets shews the Gothic taste, there are mouldings and some flutings in the upper part which mark the tendency to adopt classic ornament, which came in at the end of the fifteenth century. It was probably made for one of our old abbeys, but Mr. Seymour Lucas, R.A., to whom it belongs, and from whose drawing the illustration is made, says it was for a long time at Freenes Court, Sutton, the ancient seat of Sir Henry Linger.
The buffet on page 43 is an excellent example of the best fifteenth century French Gothic oak work, and the woodcut shews the arrangement of gold and silver plate on the white linen cloth with embroidered ends, in use at this time.

FLEMISH BUFFET
Of Carved Oak; open below, with panelled cupboards above. The back evidently of later work, after the Renaissance had set in.
(From a Photo by Messrs. R. Sutton & Co. from the Original in the S. Kensington Museum.)
PERIOD: GOTHIC TO RENAISSANCE, XV. CENTURY.

A TAPESTRIED ROOM IN A FRENCH CHATEAU. CARVED OAK SEAT.
With Oak Chests as Seats. With movable Backrest, in front of Fireplace.
PERIOD: LATE XV. CENTURY. FRENCH.
We have now arrived at a period in the history of furniture which is confused, and difficult to arrange and classify. From the end of the fourteenth century to the Renaissance is a time of transition, and specimens may be easily mistaken as being of an earlier or later date than they really are. M. Jacquemart notices this "gap," though he fixes its duration from the thirteenth to the fifteenth century, and he quotes as an instance of the indecision which characterised this interval, that workers in furniture were described in different terms; the words coffer maker, carpenter, and huchier (trunk-maker) frequently occurring to describe the same class of artisan.
It is only later that the word "menuisier," or joiner, appears, and we must enter upon the period of the Renaissance before we find the term "cabinet maker," and later still, after the end of the seventeenth century, we have such masters of their craft as Riesener described as "ébenistes," the word being derived from ebony, which, with other eastern woods, came into use after the Dutch settlement in Ceylon. Jacquemart also notices the fact that as early as 1360 we have record of a specialist, "Jehan Petrot," as a "chessboard maker."

INTERIOR OF AN APOTHECARY'S SHOP.
Late XIV. or Early XV. Century. Flemish.
(From an Old Painting.)

INTERIOR OF A FRENCH CHATEAU SHEWING FURNITURE OF THE TIME.
PERIOD: LATE XIV. OR EARLY XV. CENTURY.

COURT OF THE LADIES OF QUEEN ANNE OF BRITTANY.
(From a Miniature in the Library of St. Petersburg.)
Representing the Queen weeping on account of her Husband's absence during the Italian War.
PERIOD: XV. CENTURY.
THE RENAISSANCE IN ITALY: Leonardo da Vinci and Raffaelle—Church of St. Peter, contemporary great artists—The Italian Palazzo—Methods of gilding, inlaying and mounting Furniture—Pietra-dura and other enrichments—Ruskin's criticism. THE RENAISSANCE IN FRANCE: François I. and the Chateau of Fontainebleau—Influence on Courtiers—Chairs of the time—Design of Cabinets—M. E. Bonnaffé on The Renaissance—Bedstead of Jeanne d'Albret—Deterioration of taste in time of Henry IV.—Louis XIII. Furniture—Brittany woodwork. THE RENAISSANCE IN THE NETHERLANDS: Influence of the House of Burgundy on Art—The Chimney-piece at Bruges, and other casts of specimens at South Kensington Museum. THE RENAISSANCE IN SPAIN: The resources of Spain in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries—Influence of Saracenic Art, high-backed leather chairs, the Carthusian Convent at Granada. THE RENAISSANCE IN GERMANY: Albrecht Dürer—Famous Steel Chair of Augsburg—German seventeenth century carving in St. Saviour's Hospital. THE RENAISSANCE IN ENGLAND: Influence of Foreign Artists in the time of Henry VIII.—End of Feudalism—Hampton Court Palace—Linen Pattern Panels—Woodwork in the Henry VII. Chapel at Westminster Abbey—Livery Cupboards at Hengrave—Harrison quoted—The "parler," alteration in English customs—Chairs of the sixteenth century—Coverings and Cushions of the time, extract from old inventory—South Kensington cabinet—Elizabethan Mirror at Goodrich Court—Shaw's "Ancient Furniture"—The Glastonbury Chair—Introductions of Frames into England—Characteristics of Native Woodwork—Famous Country Mansions, alteration in design of Woodwork and Furniture—Panelled Rooms at South Kensington—The Charterhouse—Gray's Inn Hall and Middle Temple—The Hall of the Carpenters' Company—The Great Bed of Ware—Shakespeare's Chair—Penhurst Place.
 T IS impossible to write about the period of the
Renaissance without grave misgivings as to the
ability to render justice to a period which has
employed the pens of many cultivated writers, and
to which whole volumes, innumerable, have been
devoted. Within the limited space of a single
chapter all that can be attempted is a brief glance
at the influence on design by which furniture and
woodwork were affected. Perhaps the simplest way
of understanding the changes which occurred, first
in Italy, and subsequently in other countries, is to
divide the chapter on this period into a series of
short notes arranged in the order in which Italian
influence would seem to have affected the designers
and craftsmen of several European nations.
T IS impossible to write about the period of the
Renaissance without grave misgivings as to the
ability to render justice to a period which has
employed the pens of many cultivated writers, and
to which whole volumes, innumerable, have been
devoted. Within the limited space of a single
chapter all that can be attempted is a brief glance
at the influence on design by which furniture and
woodwork were affected. Perhaps the simplest way
of understanding the changes which occurred, first
in Italy, and subsequently in other countries, is to
divide the chapter on this period into a series of
short notes arranged in the order in which Italian
influence would seem to have affected the designers
and craftsmen of several European nations.
Towards the end of the fifteenth century there appears to have been an almost universal rage for classical literature, and we believe some attempt was made to introduce Latin as a universal language; it is certain that Italian Art was adopted[48] by nation after nation, and a well-known writer on architecture (Mr. Parker) has observed: "It was not until the middle of the nineteenth century that the national styles of the different countries of Modern Europe were revived."
As we look back upon the history of Art, assisted by the numerous examples in our Museums, one is struck by the want of novelty in the imagination of mankind. The glorious antique has always been our classic standard, and it seems only to have been a question of time as to when and how a return was made to the old designs of the Greek artists, then to wander from them awhile, and again to return when the world, weary of over-abundance of ornament, longed for the repose of simpler lines on the principles which governed the Athenian artists of old.
Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance. Leonardo da Vinci and Raffaelle may be said to have guided, or led, the natural artistic instincts of their countrymen to discard the Byzantine-Gothic which, as M. Bonnaffé has said, was adopted by the Italians not as a permanent institution, but "faute de mieux" as a passing fashion.
It is difficult to say with any certainty when the first commencement of a new era actually takes place, but there is an incident related in Michael Bryan's biographical notice of Leonardo da Vinci which gives us an approximate date. Ludovico Sforza, Duke of Milan, had appointed this great master Director of Painting and Architecture in his academy in 1494, and, says Bryan, who obtained his information from contemporary writers, "Leonardo no sooner entered on his office, than he banished all the Gothic principles established by his predecessor, Michaelino, and introduced the beautiful simplicity and purity of the Grecian and Roman styles."
A few years after this date, Pope Julius II. commenced to build the present magnificent Church of St. Peter's, designed by Bramante d'Urbino, kinsman and friend of Raffaelle, to whose superintendence Pope Leo X. confided the work on the death of the architect in 1514. Michael Angelo had the charge committed to him some years after Raffaelle's death.
These dates give us a very fair idea of the time at which this important revolution in taste was taking place in Italy, at the end of the fifteenth and the commencement of the following century, and carved woodwork followed the new direction.
REPRODUCTION OF DECORATION BY RAFFAELLE.
In the Loggie of the Vatican.
PERIOD: ITALIAN RENAISSANCE.

SALON OF M. EDMOND BONNAFFE.
DECORATED AND FURNISHED IN THE RENAISSANCE STYLE.
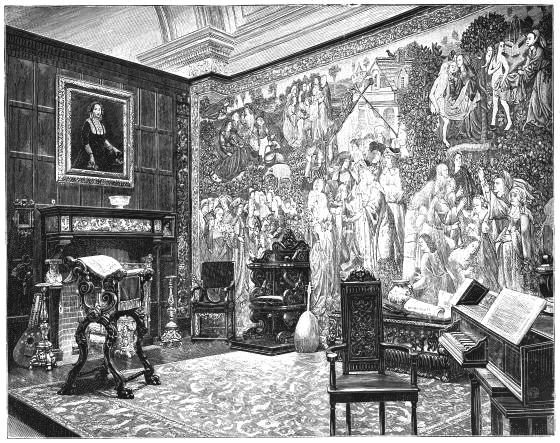

A SIXTEENTH CENTURY ROOM.
Reproduced from the "Magazine of Art." (By Permission.)
Leo X. was Pope in 1513. The period of peace which then ensued after war, which for so many decades had disturbed Italy, as France or[49] Germany had in turn striven to acquire her fertile soil, gave the princes and nobles leisure to rebuild and adorn their palaces; and the excavations which were then made, brought to light many of the Works of Art which had remained buried since the time when Rome was mistress of the world. Leo X. was a member of that remarkable and powerful family the Medicis, the very mention of which is to suggest the Renaissance, and under his patronage, and with the co-operation of the reigning dukes and princes of the different Italian states, artists were given encouragement and scope for the employment of their talents. Michael Angelo, Titian, Raffaelle Sanzio, Andrea del Sarto, Correggio, and many other great artists were raising up monuments of everlasting fame; Palladio was re-building the palaces of Italy, which were then the wonder of the world; Benvenuto Cellini and Lorenzo Ghiberti were designing those marvellous chefs d'œuvre in gold, silver, and bronze which are now so rare; and a host of illustrious artists were producing work which has made the sixteenth century famous for all time.
CHAIR IN CARVED WALNUT.
Found in the house of Michael Angelo.
The circumstances of the Italian noble caused him to be very amenable to Art influence. Living chiefly out of doors, his climate rendered him less dependent on the comforts of small rooms, to which more northern people were attached, and his ideas would naturally incline towards pomp and elegance, rather than to home life and utility. Instead of the warm chimney corner and the comfortable seat, he preferred furniture[50] of a more palatial character for the adornment of the lofty and spacious saloons of his palace, and therefore we find the buffet elaborately carved with a free treatment of the classic antique which marks the time; it was frequently "garnished" with the beautiful majolica of Urbino, of Pesaro, and of Gubbio. The sarcophagus, or cassone, of oak, or more commonly of chestnut or walnut, sometimes painted and gilded, sometimes carved with scrolls and figures; the cabinet designed with architectural outline, and fitted up inside with steps and pillars like a temple; chairs which are wonderful to look upon as guardians of a stately doorway, but uninviting as seats; tables inlaid, gilded, and carved, with slabs of marble or of Florentine mosaic work, but which from their height are as a rule impossible to use for any domestic purpose; mirrors with richly carved and gilded frames: these are all so many evidences of a style which is palatial rather than domestic, in design as in proportion.

VENETIAN CENTRE TABLE, CARVED AND GILT.
(In the South Kensington Museum.)
The walls of these handsome saloons or galleries were hung with rich velvet of Genoese manufacture, with stamped and gilt leather, and a composition ornament was also applied to woodwork, and then gilded and painted, a kind of decoration termed "gesso work."
MARRIAGE COFFER IN CARVED WALNUT.
(Collection of Comte de Briges).
PERIOD: RENAISSANCE (XVI. CENTURY) VENETIAN.
A rich effect was produced on the carved console tables, chairs, stools and frames intended for gilding, by the method employed by the Venetian and Florentine craftsmen, the gold leaf being laid on a red preparation, and then the chief portions highly burnished. There are in the South Kensington Museum several specimens of such work, and now that time and wear have caused this red groundwork to shew through the faded gold, the harmony of color is very satisfactory. Other examples of fifteenth century Italian carving, such as the old Cassone fronts, are picked out with gold, the remainder of the work displaying the rich warm color of the walnut or chestnut wood, either of which was most invariably used.

MARRIAGE COFFER.
Carved and Gilt, with Painted Subject.
ITALIAN. XVI. CENTURY.
PAIR OF ITALIAN CARVED BELLOWS, IN WALNUT WOOD.
(South Kensington Museum.) on other drawings
Of the smaller articles of furniture, the "bellows" and wall brackets of this period deserve mention; the carving of these is very carefully finished, and is frequently very elaborate. The illustration on page 51 is that of a pair bellows in the South Kensington Collection. In the famous Magniac Collection, which was sold in July, 1892, a pair of very finely carved Venetian bellows of this description realised the high price of 455 guineas.

CARVED ITALIAN MIRROR FRAME, 16TH CENTURY.
(In the South Kensington Museum.)
The enrichment of woodwork, by means of inlaying, deserves mention. In the chapter on Ancient Furniture we have seen that ivory was used as an inlaid ornament as early as six centuries before Christ, but its revival and development in Europe probably commenced in Venice about the end of the thirteenth century, in copies of geometrical designs, let into ebony and brown walnut, and into a wood something like rosewood; parts of boxes and chests of these materials are still in[53] existence. Mr. Maskell tells us in his Handbook on "Ivories," that probably owing to the difficulty of procuring ivory in Italy, bone of fine quality was frequently used in its place. All this class of work was known as "Tarsia," "Intarsia," or "Certosina," a word supposed to be derived from the name of the well-known religious community—the Carthusians—on account of the dexterity of those monks at this work.[5]

A SIXTEENTH CENTURY "COFFRE-FORT."
Towards the end of the fourteenth century, makers of ornamental furniture began to copy marble mosaic work, by making similar patterns of different woods, and subsequently this branch of industrial Art developed from such modest beginnings as the simple pattern of a star, or bandings of different kinds of wood in the panel of a door, to elaborate picture making, in which landscapes, views of churches, houses, and picturesque ruins were copied, figures and animals being also introduced. This work was naturally facilitated and encouraged by increasing commerce between different nations, which rendered available a greater variety of woods. In some of the early Italian "intarsia" the decoration was cut into the surface of the panel, piece by piece. As artists became more skilful, veneers were applied, and the effect was heightened by burning with hot sand the parts requiring shading; and the lines caused by the thickness of the sawcuts were filled in with black wood or stained glue, to define the design more clearly.
The "mounting" of articles of furniture with metal enrichments doubtless originated in the iron corner pieces and hinge plates which were used to strengthen the old chests, of which mention has been already made, and as the artificers began to render their productions decorative as well as useful, what more natural progress than that the iron corners, bandings, or fastenings, should be of ornamental forged or engraved iron. In the sixteenth century, metal workers reached a point of excellence which has never been surpassed, and those marvels of mountings in steel, iron and brass were produced in Italy and Germany, which are far more important as works of Art than the plain and unpretending productions of the coffer maker, which are their raison d'etre. The woodcut on p. 53 represents a very good example of a "Coffre-fort" in the South Kensington Collection. The decoration is bitten in with acids so as to present the appearance of its being damascened, and the complicated lock, shewn on the inside of the lid, is characteristic of those safeguards for valuable documents at a time when the modern burglar-proof safe had not been invented.
The illustration on the following page is from an example in the same Museum, shewing a different decoration, the oval plaques of figures and coats of arms being of carved ivory let into the surface of the coffer. This is an early specimen, and belongs as much to the period treated in the previous chapter as to that now under consideration.
"Pietra-durá," as an ornament, was first introduced into Italy during the sixteenth century and became a fashion. This was an inlay of highly-polished rare marbles, agates, hard pebbles, lapis lazuli, and other stones; ivory was also carved and applied as a bas-relief, as well[55] as inlaid in arabesques of the most elaborate designs; tortoise-shell, brass, mother-of-pearl, and other costly materials, were introduced, as enrichments in the decoration of cabinets and of caskets. Silver plaques embossed and engraved were pressed into the service as the native princes of Florence, Urbino, Ferrara, and other independent cities vied with Rome, Venice, and Naples in sumptuousness of ornament, and lavishness of expense, until the inevitable period of decline supervened in which exaggeration of ornament and prodigality of decoration gave the eye no repose.
ITALIAN COFFER WITH MEDALLIONS OF IVORY. 15TH CENTURY.
(South Kensington Museum.)
Edmond Bonnaffé, contrasting the latter period of Italian Renaissance with that of sixteenth century French woodwork, has pithily remarked: "Chez eux, l'art du bois consiste à le dissimuler chez nous à le fair valoir."
Mr. Ruskin, in his "Stones of Venice," alludes to this over-ornamentation of the later Renaissance in severe terms. After describing the progress of Art in Venice from Byzantine to Gothic, and from Gothic to Renaissance, he sub-divides the latter period into three classes:—1. Renaissance grafted on Byzantine. 2. Renaissance grafted on Gothic. 3. Renaissance grafted on Renaissance; and this last the veteran Art critic calls "double darkness," one of his characteristic terms[56] of condemnation which many of us cannot follow, but the spirit of which we can appreciate.
Speaking generally of the character of ornament, we find that whereas in the furniture of the Middle Ages, the subjects for carving were taken from the lives of the saints or from metrical romance, the Renaissance carvers illustrated scenes from classical mythology and allegories, such as representations of the elements, seasons, months, the cardinal virtues, or the battle scenes and triumphal processions of earlier times.

CARVED WALNUT WOOD ITALIAN CHAIRS. 16TH CENTURY.
(From Drawings of the Originals in the South Kensington Museum.)

EBONY CABINET.
With marble mosaics, and bronze gilt ornaments, Florentine work.
PERIOD: XVII. CENTURY.
The outlines and general designs of the earlier Renaissance cabinets were apparently suggested by the old Roman triumphal arches and sarcophagi; afterwards these were modified and became varied, elegant[57] and graceful, but latterly as the period of decline was marked, the outlines, as shewn in the two chairs on the preceding page, became confused and dissipated by over-decoration.
VENETIAN STATE CHAIR.
Carved and Gilt Frame, upholstered with Embroidered Velvet. Date about 1670.
(In the possession of H.M. the King at Windsor Castle.)
The illustrations given of specimens of furniture of Italian Renaissance render lengthy descriptions unnecessary. So far as it has been possible to do so, a selection has been made to represent the different classes of work, and as there are in the South Kensington Museum numerous examples of cassone fronts, panels, chairs, and cabinets which can be examined, it is easy to form an idea of the decorative woodwork made in Italy during the period we have been considering.
From Italy the great revival of industrial Art travelled to France. Charles VIII., who for two years had held Naples (1494-96), brought[58] among other artists from Italy, Bernadino de Brescia and Domenico de Cortona; and Art, which at this time was in a feeble, languishing state in France, began to revive. Francis I. employed an Italian architect to build the chateau of Fontainebleau, which had hitherto been but an old-fashioned hunting-box in the middle of the forest, and Leonardo da Vinci and Andrea del Sarto came from Florence to decorate the interior. Guilio Romano, who had assisted Raffaelle to paint the loggie of the Vatican, exercised an influence in France, which was transmitted by his pupils for generations. The marriage of Henry II. with Catherine de Medici increased the influence of Italian Art, and the subsequent union of Marie de Medici with Henri Quatre continued that influence. Diane de Poictiers, mistress of Henry II., was the patroness of artists; and Fontainebleau has been well said to "reflect the glories of gay and splendour loving kings, from François Premier to Henri Quatre."
Besides Fontainebleau, Francis I. built the Chateau of Chambord,[6] that of Chenonceaux on the Loire, the Chateau de Madrid, and others, and commenced the Louvre.
Following their King's example, the more wealthy of his subjects rebuilt or altered their chateaux and hotels, decorated them in the Italian style, and furnished them with cabinets, chairs, coffers, armoires, tables, and various other articles, designed after the Italian models.
The character of the woodwork naturally accompanied the design of the building. Fireplaces, which until the end of the fifteenth century had been of stone, were now made of oak, richly carved and ornamented with the armorial bearings of the "seigneur." The Prie dieu chair, which Viollet le Duc tells us came into use in the fifteenth century, was now made larger and more ornate, in some cases becoming what might almost be termed a small oratory, the back being carved in the form of an altar, and the utmost care lavished on the work. It must be remembered that in France, until the end of the fifteenth century, there were no benches or seats in the churches, and therefore, prayers were said by the aristocracy in the private chapel of the chateau, and by the middle classes in the chief room of the house.
The large high-backed chair of the sixteenth century "chaire à haut dossier," the arm chair "chaire à bras," "chaire tournante," for domestic use, are all of this time, and some illustrations will shew the highly finished carved work of Renaissance style which prevailed.

ORNAMENTAL PANELLING IN ST. VINCENT'S CHURCH, ROUEN.
PERIOD: EARLY FRENCH RENAISSANCE. TEMP. FRANÇOIS I.

CHIMNEY PIECE.
In the Gallery of Henri II., Chateau of Fontainebleau.
PERIOD: FRENCH RENAISSANCE, EARLY XVI. CENTURY.
Besides the "chaire," which was reserved for the "seigneur," there
were smaller and more convenient stools, the ![]() form supports of which
were also carved.
form supports of which
were also carved.

CARVED OAK PANEL, DATED 1577.
Cabinets were made with an upper and lower part; sometimes the latter was in the form of a stand with caryatides figures like the famous cabinet in the Chateau Fontainebleau, a vignette of which forms the initial letter of this chapter; or were enclosed by doors generally decorated with carving, the upper part having richly carved panels, which when opened disclosed drawers with fronts minutely carved.
M. Edmond Bonnaffé, in his work on the sixteenth century furniture of France, gives no less than 120 illustrations of "tables, coffres, armoires, dressoirs, sieges, et bancs", manufactured at Orleans, Anjou, Maine, Touraine, Le Berri, Lorraine, Burgundy, Lyons, Provence, Auvergne, Languedoc, and other towns and districts, besides the Capital, which excelled in the reputation of her "menuisiers," certain articles of furniture being particularised in old documents as "fait a Paris."
He also mentions that Francis I. preferred to employ native workmen, and that the Italians were retained only to furnish the[60] designs and lead the new style; and in giving the names of the most noted French cabinet makers and carvers of this time, he adds that Jacques Lardant and Michel Bourdin received no less than 15,700 livres for a number of "buffets de salles," "tables garnies de leur tréteaux," "chandeliers de bois," and other articles.

FAC SIMILES OF ENGRAVINGS ON WOOD.
By J. Amman, in the 16th century, shewing interiors of Workshops of the period.
The bedstead, of which there is an illustration on the opposite page, is a good representation of French Renaissance. It formed part of the contents of the Chateau of Pau, and belonged to Jeanne d'Albret, mother of Henri Quatre, who was born at Pau in 1553. The bedstead is of oak, and by time has acquired a rich warm tint, the details of the carving remaining sharp and clear. On the lower cornice moulding, the date 1562 is carved.
This, like other furniture and contents of Palaces in France, forms part of the State or National Collection, of which there are excellent illustrations and descriptions in M. Williamson's "Mobilier National" a valuable contribution to the literature of this subject which should be consulted.
Another example of four-post bedsteads of French sixteenth century work is that of the one in the Cluny Museum, which is probably some years later than the one at Pau, and in the carved members of the two lower posts more resembles our English Elizabethan work.
CARVED OAK BEDSTEAD OF JEANNE D'ALBRET.
From the Chateau of Pau. (Collection "Mobilier National.")
PERIOD: FRENCH RENAISSANCE (Date 1562).

FRENCH CARVED OAK CABINET.
In the Musée du Louvre. (Collection Sauvageot.)
PERIOD: EARLY XVI. CENTURY.
(Reproduced by permission of Messrs. Boussod Valadon et Cie.)

CARVED OAK CABINET.
Made at Lyons.
PERIOD: LATTER PART OF XVI. CENTURY.
An important collection of carved furniture of French Renaissance was exhibited in l'exposition rétrospective de Lyon, held in that city in 1877, and M. J. B. Giraud, conservateur of the Archæological Museums of Lyons, has reproduced some fifty of the more important specimens in his valuable work,[7] published in 1880, giving the name of the lender of each example and other details. The "Lyons" cabinet, of which there is an illustration, following p. 60, is one of these, and is in the Collection of Mr. E. Aynard. The "Spitzer" Collection, sold in Paris in 1893, contained several fine examples of French Renaissance oak furniture, which realised large prices.
Towards the latter part of the reign of Henri IV. the style of decorative Art in France became debased and inconsistent. Construction and ornamentation were guided by no principle, but followed the caprice of the individual. Meaningless pilasters, entablatures, and contorted cornices replaced the simpler outline and subordinate enrichment of the time of Henri II., and until the great revival of taste under the "grand monarque," there was in France a period of richly ornamented but ill-designed decorative furniture. An example of this can be seen at South Kensington in a plaster cast of a large chimney piece from the Chateau of the Seigneur de Villeroy, near Menecy, by German Pillon, who died in 1590. In this the failings mentioned above will be readily recognized, and also in another example, namely, that of a carved oak door from the Church of St. Maclou, Rouen, by Jean Goujon, in which the work is very fine, but somewhat overdone with enrichment.
During the "Louis Trieze" period, chairs became more comfortable than those of an earlier time. The word "chaise" as a diminutive of "chaire" found its way into the French vocabulary to denote the less throne-like seat which was in more ordinary use, and, instead of being at this period entirely carved, it was upholstered in velvet, tapestry, or needlework; the frame was covered, and only the legs and arms were visible and slightly carved. In the illustration on p. 62, the King and his courtiers are seated on chairs such as have been described. Marqueterie was more common; large armoires, chests of drawers and knee-hole writing tables were covered with an inlay of vases of flowers and birds, of a brownish wood, with enrichments of bone and ivory, inserted in a black ground of stained wood, very much like the Dutch inlaid furniture of some years later, but with less color in the various veneers than is found in the Dutch work. Mirrors became larger, the decoration of rooms had ornamental friezes with lower portions of the walls panelled, and the bedrooms of ladies of position began to be more luxuriously furnished.
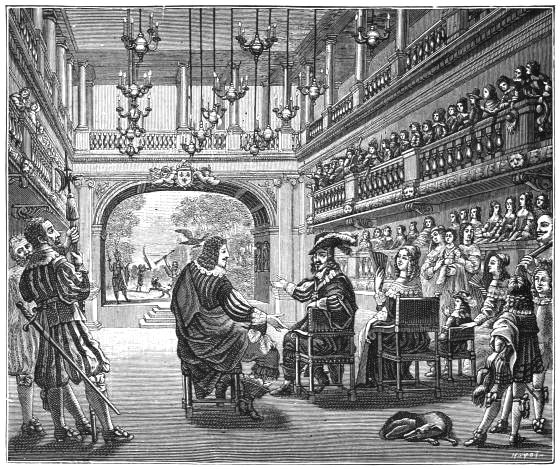
LOUIS XIII. AND HIS COURT IN A HALL WITNESSING A PLAY.
(From a Miniature dated 1643.)
It is somewhat singular that while Normandy very quickly adopted the new designs in her buildings and her furniture, and Rouen carvers and joiners became famous for their work, the neighbouring province, Brittany, was conservative of her earlier designs. The sturdy Breton has through all changes of style preserved much of the rustic quaintness of his furniture, and when some years ago the writer was stranded in a sailing trip up the Rance, owing to the shallow state of the river, and had an opportunity of visiting some of the farm houses in the country district a few miles from Dinan, there were still to be seen many examples of this quaint rustic furniture. Curious beds, consisting of shelves for parents and children, form a cupboard in the wall and are shut in, during the day, by a pair of lattice doors of Moorish design, with the wheel pattern and spindle perforations. These, with the armoire of similar design, and the "huche" or chest with relief carving, of a design part Moorish, part Byzantine, used as a step to mount to the bed and also as a table, are still the garniture of a good farm house in Brittany.
DECORATION FOR A SALON IN LOUIS XIII. STYLE.
The earliest date of this quaint furniture is about the middle of the fifteenth century, and has been handed down from father to son by the more well-to-do farmers. The manufacture of armoires, cupboards, tables, and doors, is still carried on near St. Malo, where also some of the old specimens may be found.
In the Netherlands, the reigning princes of the great House of Burgundy had prepared the soil for the Renaissance, and, by the marriage of Mary of Burgundy with the Archduke Maximilian, the countries which then were called Flanders and Holland passed under the Austrian rule. This influence was continued by the taste and liberality of Margaret of Austria, who, being appointed "Governor" of the Low Countries in 1507, seems to have introduced Italian artists and to have encouraged native craftsmen. We are told that Corneille Floris introduced Italian ornamentation and grotesque borders; that Pierre Coech, architect and painter, adopted and popularised the designs of Vitruvius and Serlio. Wood carvers multiplied and embellished churches and palaces, houses of Burgomasters, Town Halls, and residences of wealthy citizens.
Oak, at first almost the only wood used, became monotonous, and as a relief, ebony and other rare woods, introduced by the then commencing commerce with the Indies, were made available for the embellishments of furniture and woodwork of this time.
One of the most famous examples of rich wood carving is the well known hall and chimney piece at Bruges with its group of cupidons and armorial bearings, amongst an abundance of floral detail. This over ornate chef d'œuvre was designed by Lancelot Blondel and Guyot de Beauregrant, and its carving was the combined work of three craftsmen celebrated in their day, Herman Glosencamp, André Rash and Roger de Smet. There is in the South Kensington Museum a full-sized plaster cast of this gigantic chimney piece, the lower part being colored black to indicate the marble of which it was composed, with panels of alabaster carved in relief, while the whole of the upper portion of the richly carved ceiling of the room is of oak. This chimney piece is noteworthy, not only artistically but historically, as being a monument in its way, in celebration of the victory gained by Charles V. over Francis I. of France, in 1529, at Pavia, the victorious sovereign being at this time not only Emperor of Germany, but also enjoying amongst other titles those of Duke of Burgundy, Count of Flanders, King of Spain and the Indies, etc., etc. The large statues of the Emperor, of Ferdinand and Isabella, with some thirty-seven heraldic shields of the different royal families with which[64] the conqueror claimed connection, are prominent features in the intricate and elaborate design.
There is in the same part of the Museum a cast of the oak door of the Council Chamber of the Hotel de Ville at Oudenarde, of a much less elaborate character. Plain mullions divide sixteen panels carved in the orthodox Renaissance style, with cupids bearing tablets, from which are depending floral scrolls, and at the sides the supports are columns, with the lower parts carved and standing on square pedestals. The date of this work is 1534, somewhat later than the Bruges carving, and is a representative specimen of the Flemish work of this period.
AN EBONY ARMOIRE, RICHLY CARVED. FLEMISH RENAISSANCE.
(In South Kensington Museum.)
The clever Flemish artist so thoroughly copied the models of his different masters, that it has become exceedingly difficult to speak positively as to the identity of much of the woodwork, and to distinguish it from German, English, or Italian, although as regards the latter we have seen that walnut wood was employed very generally, whereas in Flanders, oak was nearly always used for figure work.
After the period of the purer forms of the first Renaissance, the best time for carved woodwork and decorative furniture in the Netherlands was probably the seventeenth century, when the Flemish designers and craftsmen had ceased to copy the Italian patterns, and had established the style which we recognise as "Flemish Renaissance."
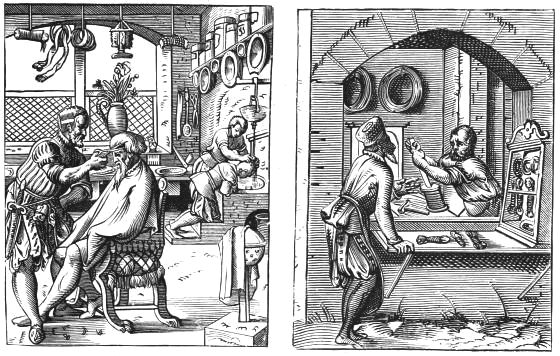
A BARBER'S SHOP. A FLEMISH WORKSHOP.
Showing Furniture of the time.
(From Wood Engravings by J Amman. 16th CENTURY.)
Lucas Faydherde, architect and sculptor (1617-1694)—whose boxwood group of the death of John the Baptist is in the South Kensington Museum—both the Verbruggens, and Albert Bruhl, who carved the choir work of St. Giorgio Maggiore in Venice, are amongst the most celebrated Flemish wood carvers of this time. Vriedman de Vriesse and Crispin de Passe, although they worked in France, belong to Flanders and to the century. Some of the most famous painters—Francis Hals, Jordaens, Rembrandt, Metsu, Van Mieris—all belong to this time, and in some of the fine interiors represented by these Old Masters, in which embroidered curtains and rich coverings relieve the sombre colors of the dark carved oak furniture, there is a richness of effect which the artist could scarcely have imagined, but which he must have observed in the houses of the rich burghers of prosperous Flanders.
In the chapter on Jacobean furniture, we shall see the influence and assistance which England gained from Flemish woodworkers; and the similarity of the treatment in both countries will be noticed in some of the South Kensington Museum specimens of English marqueterie, made at the end of the seventeenth century. The figure work in Holland has always been of high order, and, although as the seventeenth century advanced, this perhaps became less refined, the proportions have always been well preserved, and the attitudes are free and unconstrained.
A very characteristic article of seventeenth century Dutch furniture is the large and massive wardrobe, with the doors handsomely carved, not infrequently having three columns, one in the centre and one at each side, generally forming part of the doors, which are also enriched with square panels, carved in the centre and finished with mouldings. There are specimens in the South Kensington Museum of these, and also of some of earlier Flemish work when the Renaissance was purer in style and, as has been observed, of less national character.
The marqueterie of this period is extremely rich, the designs are less severe, but the coloring of the woods is varied, and the effect is heightened by the addition of small pieces of mother of pearl and ivory. Later, this marqueterie became florid, badly finished, and the coloring of the veneers crude and gaudy. Old pieces of plain mahogany furniture were decorated with a thin layer of highly colored veneering, a meretricious ornamentation altogether lacking refinement.
There is, however, a peculiarity and character about some of the furniture of North Holland, in the town of Alkmaar, Hoorn, and others in this district, which is worth noticing. The treatment has always been more primitive and quaint than in the Flemish cities to which allusion has been made—and it was here that the old farmhouses of the Nord-Hollander were furnished with the rush-bottomed chairs, painted green; with three-legged tables, and dower chests painted in flowers and figures of a rude description; the coloring of which is chiefly green and bright red, and is extremely effective.

A FLEMISH CITIZEN AT MEALS.
(From a XVI. Century MS.)
We have seen that Spain, as well as Germany and the Low Countries, was under the rule of the Emperor Charles V., and therefore it is unnecessary to look further for the sources of influence which carried the wave of Renaissance to the Spanish carvers and cabinet makers.
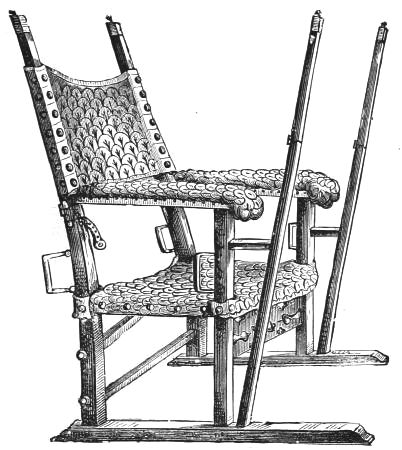
SEDAN CHAIR OF CHARLES V.
Probably made in the Netherlands. Arranged with movable back and uprights to form a canopy when desired.
(In the Royal Academy, Madrid.)
After Van Eyck was sent for to paint the portrait of King John's daughter, the Low Countries continued to export to the Peninsula painters, sculptors, tapestry weavers, and books on Art. French artists also found employment in Spain, and the older Gothic became superseded as in other countries. Berruguete, a Spaniard, who had studied in the atelier of Michael Angelo, returned to his own country with the new influence strong upon him, and the vast wealth and resources of Spain at this period of her history enabled her nobles to indulge their taste in cabinets, richly ornamented with repoussé plaques of silver, and later of tortoise-shell, of ebony, and of scarce woods from her Indian possessions; though in a more general way chestnut was still a favorite medium.

SILVER TABLE, LATE 16TH OR EARLY 17TH CENTURY.
(In the King's Collection, Windsor Castle.)
Contemporaneously with decorative woodwork of Moorish design there was also a great deal of carving, and of furniture made, after designs brought from Italy and the North of Europe; and Mr. J. H. Pollen, quoting a trustworthy Spanish writer, Señor J. F. Riaño, says:—"The brilliant epoch of sculpture (in wood) belongs to the sixteenth century, and was due to the great impulse it received from the works of Berruguete and Felipe de Borgoñu. He was the chief promoter of the Italian style, and the choir of the Cathedral of Toledo, where he worked so much, is the finest specimen of the kind in Spain. Toledo, Seville, and Valladolid were at the time great productive and artistic centres."
The same writer, after discussing the characteristic Spanish cabinets, decorated outside with fine ironwork and inside with columns of bone painted and gilt, which were called "Vargueños," says:—"The other cabinets or escritoires belonging to that period (sixteenth century) were to a large extent imported from Germany and Italy, while others were made in Spain in imitation of these, and as the copies were very similar it is difficult to classify them." * * *

CHAIR OF WALNUT OR CHESTNUT WOOD.
Covered in Leather, with embossed pattern. Spanish. (Collection of Baron de Vallière.)
PERIOD: EARLY XVII. CENTURY.
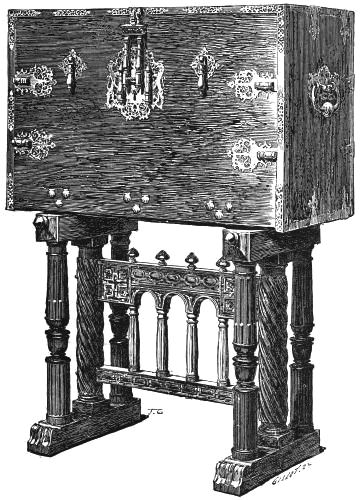
WOODEN COFFER.
With wrought iron mounts and falling flap, on carved stand. Spanish.
(Collection of M. Monbrison.)
PERIOD: XVII. CENTURY.
"Besides these inlaid cabinets, others must have been made in the sixteenth century inlaid with silver. An Edict was issued in 1594, prohibiting, with the utmost rigour, the making and selling of this kind of merchandise, in order not to increase the scarcity of silver." The Edict says that "no cabinets, desks, coffers, braziers, shoes, tables, or other articles decorated with stamped, raised, carved, or plain silver should be manufactured."
The beautiful silver table in His Majesty's collection at Windsor Castle, illustrated on page 68, is probably one of Spanish make of late sixteenth or early seventeenth century.
Although not strictly within the period treated of in this chapter, it is convenient to observe that much later, in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, one finds the Spanish cabinet maker ornamenting his productions with an inlay of ivory let into tortoise-shell, representing episodes in the history of Don Quichotte, and scenes from the National pastime of bull-fighting. These cabinets generally have simple rectangular outlines with numerous drawers, the fronts of which are decorated in the manner described, and when the stands are original they are formed of turned legs of ebony or stained wood. In many Spanish cabinets the influence of Saracenic Art is very dominant; these have generally a plain exterior, the front is hinged as a fall-down flap, and discloses a decorative effect which reminds one of some of the Alhambra work—quaint arches inlaid with ivory, of a somewhat bizarre coloring of blue and vermilion—altogether a rather barbarous but rich and effective treatment.
To the seventeenth century also belonged the high-backed Spanish and Portuguese chairs, of dark brown leather, stamped with numerous figures, birds and floral scrolls, studded with brass nails and ornaments, while the legs and arms are alone visible as woodwork. They are made of chestnut, with some leafwork or scroll carving. There is a good representative woodcut of one of these chairs.
Until Baron Davillier wrote his work on Spanish Art, very little was known of the various peculiarities by which we can now distinguish examples of woodwork and furniture of that country from many Italian or Flemish contemporary productions. Some of the Museum specimens will assist the reader to mark some of these characteristics, and it may be observed generally that in the treatment of figure subjects in the carved work, the attitudes are somewhat strained and, as has been stated, the outlines of the cabinets are without any special feature. Besides the Spanish chestnut (noyer), which is singularly lustrous and was much used, one also finds cedar, cypress wood and pine.
In the Chapel of Saint Bruno, attached to the Carthusian Convent at Granada, the doors and interior fittings are excellent examples of inlaid Spanish work of the seventeenth century; the monks of this order at a somewhat earlier date are said to have produced the "tarsia," or inlaid work, to which some allusion has already been made.
German Renaissance may be said to have made its debût under Albrecht Dürer. There was already in many of the German cities a disposition to copy Flemish artists, but under Dürer's influence this new departure became developed in a high degree, and, as the sixteenth century advanced, the Gothic designs of an earlier period were abandoned in favour of the more free treatment of figure ornament, scrolls, enriched panels and mouldings, which mark the new era in all Art work.
Many remarkable specimens of German carving are to be met with in Augsburg, Aschaffenburg, Berlin, Cologne, Dresden, Gotha, Munich, Manheim, Nuremberg, Ulm, Regensburg, and other old German towns.
Although made of steel, the celebrated chair at Longford Castle in Wiltshire is worthy of some notice as a remarkable specimen of German Renaissance. It is fully described in Richardson's "Studies from Old English Mansions." It was the work of Thomas Rukers, and was presented by the city of Augsburg to the Emperor of Germany in 1577. The city arms are at the back, and also the bust of the Emperor. The other minute and carefully finished decorative subjects represent various events in history; a triumphal procession of Cæsar, the Prophet Daniel explaining his dream, the landing of Æneas, and other events. The Emperor Rudolphus placed the chair in the City of Prague, Gustavus Adolphus plundered the city and removed it to Sweden, whence it was brought by Mr. Gustavus Brander about 100 years ago, and sold by him to Lord Radnor.
As is the case with Flemish wood-carving, it is often difficult to identify German work, but its chief characteristics may be described as an exuberant realism and a fondness for minute detail. M. Bonnaffé has described this work in a telling phrase: "l'ensemble est tourmenté, laborieux, touffu tumultueux."
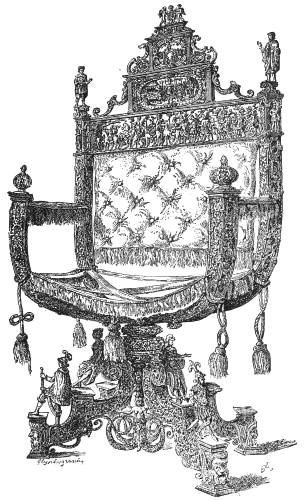
THE STEEL CHAIR.
At Longford Castle, Wiltshire.
There is a remarkable example of rather late German Renaissance oak carving in the private chapel of S. Saviour's Hospital, in Osnaburg Street, Regent's Park, London. The choir stalls, some 31 in number, and the massive doorway, formed part of a Carthusian monastery at Buxheim,[71] Bavaria, which was sold and brought to London after the monastery had been secularised and had passed into the possession of the territorial landlords, the Bassenheim family. At first intended to ornament one of the Colleges at Oxford, it was afterwards resold and purchased by the author, and fitted to the interior of S. Saviour's, and, so far as the proportions of the chapel would admit of such an arrangement, the relative positions of the different parts are maintained. The figures of the twelve apostles—of David, Eleazer, Moses, Aaron, and of the eighteen saints at the back of the choir stalls, are marvellous work, and the whole must have been a harmonious and well-considered arrangement of ornament. The work, executed by the monks themselves, is said to have been commenced in 1600, and to have been completed in 1651, and though a little later than, according to some authorities, the best time of the Renaissance, is so good a representation of German work of this period that it will well repay an examination. As the author was responsible for its arrangement in its present position, he has the permission of the authorities of S. Saviour's to say that anyone who is interested in Art will be allowed to see the chapel.

GERMAN CARVED OAK BUFFET, 17TH CENTURY.
(From a Drawing by Prof. Heideloff.)
England under Henry the Eighth was peaceful and prosperous, and the king was ambitious to outvie his French contemporary, François I., in the sumptuousness of his palaces. John of Padua, Holbein, Havernius of Cleves, and other artists, were induced to come to England and to introduce the new style. It, however, was of slow growth, and we have in the mixture of Gothic, Italian, and Flemish ornament, the style which is known as "Tudor."
It has been well said that "Feudalism was ruined by gunpowder." The old-fashioned feudal castle was certainly no longer proof against cannon, and with the new order of things, threatening walls and serried battlements gave way as if by magic to the pomp and grace of the Italian mansion. High roofed gables, rows of windows and glittering oriels looking down on terraced gardens, with vases and fountains, mark the new epoch.
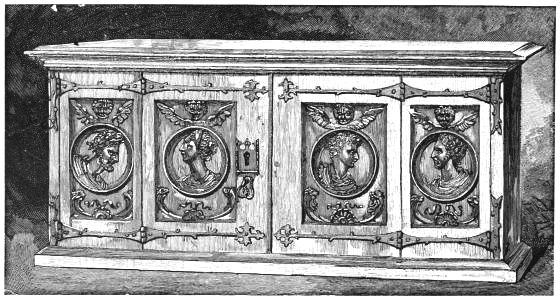
CARVED OAK CHEST IN THE STYLE OF HOLBEIN.
The joiner's work plays very important part in the interior decoration of the castles and country seats of this time, and the roofs were magnificently timbered with native oak, which was available in longer lengths than that of foreign growth. The great Hall in Hampton Court Palace, which was built by Cardinal Wolsey and presented to his master, the halls of Oxford, and many other public buildings which remain to us, are examples of fine woodwork in the roofs. Oak panelling was largely used to line the walls of the great halls, the[73] "linen scroll pattern" being a favorite form of ornament. This term describes a panel carved to represent a napkin folded in close convolutions, and appears to have been adopted from German work; specimens of this can be seen at Hampton Court, and in old churches decorated in the early part of the sixteenth century. There is also some fine panelling of this date in King's College, Cambridge.
In this class of work, which accompanied the style known in architecture as the "Perpendicular," some of the finest specimens of ornamented interiors are to be found, that of the roof and choir stalls in the beautiful Chapel of Henry VII. in Westminster Abbey being world famous. The carved enrichments of the under parts of the seats, or "misericords," are remarkably minute, the subjects apparently being taken from old German engravings. This work was done in England before architecture and wood carving had altogether flung aside their Gothic trammels, and shews an admixture of the new Italian style which was afterwards so generally adopted.
There are in the British Museum some interesting records of contracts made in the ninth year of Henry VIII.'s reign for joyner's work at Hengrave, in which the making of "livery" or service cupboards is specified.
"Ye cobards they be made ye facyon of livery y is wᵀᴴout doors."
These were fitted up by the ordinary house carpenters, and consisted of three stages or shelves standing on four turned legs, with a drawer for table linen. They were at this period not enclosed, but the mugs or drinking vessels were hung on hooks, and were taken down and replaced after use: a ewer and basin was also part of the complement of a livery cupboard, for cleansing these cups. In Harrison's description of England in the latter part of the sixteenth century the custom is thus described:
"Each one as necessitie urgeth, calleth for a cup of such drinke as him liketh, so when he hath tasted it, he delivereth the cup again to some one of the standers by, who maketh it clean by pouring out the drinke that remaineth, restoreth it to the cupboard from whence he fetched the same."
It must be borne in mind, in considering the furniture of the earlier part of the sixteenth century, that the religious persecutions of the time, together with the general break up of the feudal system, had gradually brought about the disuse of the old custom of the master of the house taking his meals in the large hall or "houseplace," together with his retainers and dependants; and a smaller room leading from[74] the great hall was fitted up with a "dressoir" or "service cupboard," for the drinking vessels in the manner just described, with a bedstead, and a chair, some benches, and the board on trestles, which formed the table of the period. This room, called a "parler" or "privee parloir," was the part of the house where the family enjoyed domestic life, and it is a singular fact that the Clerics of the time, and also the Court party, saw in this tendency towards private life so grave an objection that, in 1526, this change in fashion was the subject of a Court ordinance, and also of a special Pastoral from Bishop Grosbeste. The text runs thus: "Sundrie noblemen and gentlemen and others doe much delighte to dyne in corners and secret places," and the reason given, was that it was a bad influence, dividing class from class; the real reason was probably that by more private and domestic life, the power of the Church over her members was weakened.

CHAIR SAID TO HAVE BELONGED TO ANNA BOLEYN, HEVER CASTLE.
(From the Collection of Mr. Godwin, F.S.A.)
In spite, however, of opposition in high places, the custom of using the smaller rooms became more common, and we shall find the furniture, as time goes on, designed accordingly.
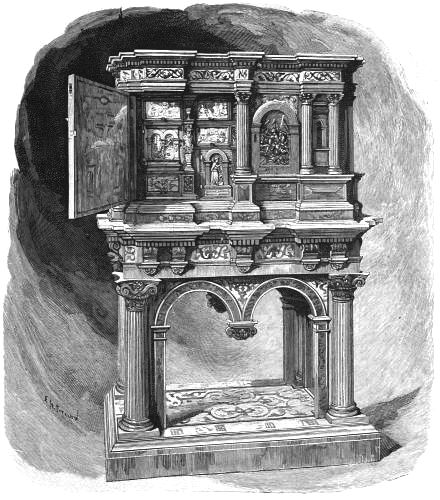

TUDOR CABINET IN THE SOUTH KENSINGTON MUSEUM.
(Described below.)
In the South Kensington Museum there is a very remarkable cabinet, the decoration of which points to its being made in England at this time—that is, about the middle, or during the latter half of the sixteenth century; but the highly finished and intricate marqueterie and[76] carving would seem to prove that Italian or German craftsmen had executed the work. It should be carefully examined as a very interesting specimen. The Tudor arms, the rose and portcullis, are inlaid on the stand. The arched panels in the folding doors and at the ends of the cabinet are in high relief, representing battle scenes, and bear some resemblance to Holbein's style. The general arrangement of the design reminds one of a Roman triumphal arch. The woods employed are chiefly pear tree, inlaid with coromandel and other woods. Its height is 4ft. 7in. and width 3ft. 1in., but there is in it an immense amount of careful detail which could only be the work of the most skilful craftsmen of the day, and it was evidently intended for a room of moderate dimensions where the intricacies of design could be observed. Mr. Hungerford Pollen has described this cabinet fully, giving the subjects of the ornament, the Latin mottoes and inscriptions, and other details, which occupy over four closely-printed pages of his Museum catalogue. It cost the nation £500, and was a very judicious purchase.
Chairs were during the first half of the sixteenth century very scarce articles, and, as we have seen with other countries, only used for the master or mistress of the house. The chair which is said to have belonged to Anna Boleyn, of which an illustration is given on page 74, is from the collection of the late Mr. Geo. Godwin, F.S.A., formerly editor of "The Builder," and was part of the contents of Hever Castle, in Kent. It is of carved oak, inlaid with ebony and boxwood, and was probably made by an Italian workman. "Settles" were largely used, and both these and such chairs as then existed, were dependent, for richness of effect, upon the loose cushions with which they were furnished.
If we attempt to gain a knowledge of the designs of the tables of the sixteenth, and the early part of the seventeenth centuries, from interiors represented in paintings of this period, the visit to the picture gallery will be almost in vain, for in nearly every case the table is covered by a cloth. As these cloths or "carpets," as they were then termed, to distinguish them from the "tapet" or floor covering, often cost far more than the articles they covered, a word about them may be allowed.
Most of the old inventories from 1590, after mentioning the "framed" or "joyned" table, name the "carpett of Turky werke" which covered it, and in many cases there was still another covering to protect the best one, and when Frederick, Duke of Wurtemburg, visited England in 1592, he noted a very extravagant "carpett" at Hampton Court, which was embroidered with pearls and cost 50,000 crowns.
The cushions or "quysshens" for the chairs, of embroidered velvet, were also very important appendages to the otherwise hard oaken and ebony seats, and as the actual date of the will of Alderman Glasseor quoted below is 1589, we may gather from the extract given, something of the character and value of these ornamental accessories which would probably have been in use for some five and twenty or thirty years previously.
"Inventory of the contents of the parler of St. Jones, within the cittie of Chester," of which place Alderman Glasseor was vice-chamberlain:—
This Alderman Glasseor was apparently a man of taste and culture for those days; he had "casting bottles" of silver for sprinkling perfumes after dinner, and he also had a country house "at the sea," where his parlour was furnished with a "canapy bedd."
As the century advances, and we get well into Elizabeth's reign, wood carving becomes more ambitious, and although it is impossible to distinguish the work of Flemish carvers who had settled in England from that of our native craftsmen, these doubtless had acquired from the former much of their skill. In the costumes and in the faces of figures or busts, produced in the highly ornamental oak chimney pieces of the time, or in the carved portions of the fourpost bedsteads, the national characteristics are preserved, and, with a certain grotesqueness introduced into the treatment of accessories, combine to distinguish the English school of Elizabethan ornament from other contemporary work.
Knole, Longleat, Burleigh, Hatfield, Hardwick, and Audley End are familiar instances of the change in interior decoration which accompanied that in architecture; terminal figures, that is, pedestals diminishing[78] towards their bases, surmounted by busts of men or women, elaborate interlaced strap work carved in low relief, trophies of fruit and flowers, take the places of the more Gothic treatment formerly in vogue. The change in the design of furniture naturally followed, for when Flemish or Italian carvers were not employed, the actual execution was often by the hand of the house carpenter, who was influenced by what he saw around him.
The great chimney-piece in Speke Hall, near Liverpool, portions of the staircase of Hatfield, and of other English mansions before mentioned, are good examples of the wood carving of this period, and the illustrations from authenticated examples which are given will assist the reader to follow these remarks.
THE GLASTONBURY CHAIR.
(In the Palace of the Bishop of Bath and Wells.)
There is a mirror frame at Goodrich Court of early Elizabethan work, carved in oak and partly gilt; the design is in the best style of Renaissance, and more like Italian or French, than English work. Architectural mouldings, wreaths of flowers, cupids, and an allegorical figure of Faith are harmoniously combined in the design, the size of the whole frame being 4ft. 5ins. by 3ft. 6ins. It bears the initials R.M., and is dated 1359, the year in which Roland Meyrick became Bishop of Bangor; it is still in the possession of the Meyrick family. A careful drawing of this frame was made by Henry Shaw, F.S.A., and published in "Specimens of Ancient Furniture drawn from existing Authorities," in 1836. This valuable work of reference also contains finished drawings of other noteworthy examples of the sixteenth century furniture and woodwork. Amongst these is one of the Abbot's chair at Glastonbury, temp. Henry VIII., the original of the chair familiar to us now in the chancel of most churches; also a chair in the State-room of Hardwick Hall,[79] Derbyshire, covered with crimson velvet embroidered with silver tissue, and others, very interesting to refer to because the illustrations are all drawn from the articles themselves, and their descriptions are written by an excellent antiquarian and collector, Sir Samuel Rush Meyrick.
The mirror frame just described was probably one of the first of its size and kind in England. It was the custom, as has been already stated, to paint the walls with subjects from history or Scripture, and there are many precepts in existence from early times until about the beginning of Henry VIII.'s reign, directing how certain walls were to be decorated. The discontinuance of this fashion brought about the framing of pictures, and some of the paintings by Holbein, who came to this country about 1511, and received the patronage of Henry VIII. some fourteen or fifteen years later, are probably the first pictures that were framed in England. There are some two or three of these at Hampton Court Palace, the ornament being a scroll in gold on a black background, the width of the frame very small in comparison with its canvas. Some of the old wall paintings were on a small scale, and, where long stories were represented, the subjects, instead of occupying the whole flank of the wall, had been divided into rows some three feet or less in height, these being separated by battens, and therefore the first frames would appear to be really little more than the addition of vertical sides to the horizontal top and bottom which such battens had formed. Subsequently, frames became more ornate and elaborate. After their application to pictures, their use for mirrors was but a step in advance, and the mirror in a carved and gilt or decorated frame, probably at first imported and afterwards copied, came to replace the older mirror of very small dimensions which had been used for toilet purposes.
Until early in the fifteenth century, mirrors of polished steel in the antique style, framed in silver and ivory, had been used; in the wardrobe account of Edward I. the item occurs: "A comb and a mirror of silver gilt," and we have an extract from the privy purse of expenses of Henry VIII. which mentions the payment "to a Frenchman for certayne loking glasses," which would probably be a novelty then brought to his Majesty's notice.
Indeed, there was no glass used for windows[8] previous to the fifteenth century, the substitute being shaved horn, parchment, and sometimes mica, let into the shutters which enclosed the window opening.
The oak panelling of rooms during the reign of Elizabeth was very handsome, and in the example at South Kensington, of which there is[80] here an illustration, the country possesses a very excellent representative specimen. This was removed from an old house at Exeter, and its date is given by Mr. Hungerford Pollen as from 1550-75. The pilasters and carved panels under the cornice are very rich, and in the best style of Elizabethan Renaissance, while the panels themselves, being plain, afford repose, and bring the ornament into relief. The entire length is 52ft., and average height 8ft. 3in. If this panelling could be arranged as it was fitted originally in the house of one of Elizabeth's subjects, with models of fireplace, moulded ceiling, and accessories added, we should then have an object lesson of value, and be able to picture a Drake or a Raleigh in his West of England home.
CARVED OAK ELIZABETHAN BEDSTEAD.
A later purchase by the Science and Art Department, which was added to the Museum in 1891 for the extremely moderate price of £1,000, is the panelling of a room some 23ft. square and 12ft. 6in. high, from Sizergh Castle, Westmoreland. The chimney piece was unfortunately not purchased, but the Department has arranged the panelling as a room with a plaster model of the extremely handsome ceiling. The panelling[81] is of richly figured oak, entirely devoid of polish, and is inlaid with black bog oak and holly, in geometrical designs, being divided at intervals by tall pilasters with flutings of bog oak and having Ionic capitals. The work was probably done locally, and from wood grown on the estate, and is one of the most remarkable examples in existence. The date is about 1560 to 1570, and it has been described in local literature as of nearly 200 years' age.

OAK WAINSCOTING.
From an old house in Exeter. S Kensington Museum.
PERIOD: ENGLISH RENAISSANCE (ABOUT 1550-75.)
While we are on the subject of panelling, it may be worth while to point out that with regard to old English work of this date, one may safely take it for granted that where, as in the South Kensington (Exeter) example, the pilasters, frieze, and frame-work are enriched, and the panels plain, the work was designed and made for the house, but when the panels are carved and the rest plain, they were bought, and then fitted up by the local carpenter.
Another Museum specimen of Elizabethan carved oak is a fourpost bedstead, with the arms of the Countess of Devon, which bears date 1593, and has all the characteristics of the time.
There is also a good example of Elizabethan woodwork in part of the interior of the Charterhouse, immortalised by Thackeray, when, as "Greyfriars," in the "Newcomes," he described it as the old school "where the colonel, and Clive, and I were brought up", and it was here that, as a "poor brother," the old colonel had returned to spend the evening of his gentle life, and, to quote Thackeray's pathetic lines, "when the chapel bell began to toll, he lifted up his head a little, and said 'Adsum!' It was the word we used at school when names were called."
This famous relic of old London, which fortunately escaped the Great Fire in 1666, was formerly an old monastery, which Henry VIII. dissolved in 1537, and the house was given some few years later to Sir Edward, afterwards Lord North, from whom the Duke of Norfolk purchased it in 1565, and the handsome staircase, carved with terminal figures and Renaissance ornament, was probably built either by Lord North or his successor. The woodwork of the Great Hall, where the pensioners still dine every day, is very rich, the fluted columns with Corinthian capitals, the interlaced strap work, and other details of carved oak, are characteristic of the best sixteenth century woodwork in England; the shield bears the date of 1571. This was the year when the Duke of Norfolk, who was afterwards beheaded, was released from the Tower on a kind of furlough, and probably amused himself with the enrichment of his mansion, then called Howard House. In the old Governors' room, formerly the drawing room of the Howards, there is a specimen of the large wooden chimney-piece of the end of the[82] sixteenth century, painted instead of carved. After the Duke of Norfolk's death, the house was granted by the Crown to his son, the Earl of Suffolk, who sold it in 1611 to the founder of the present hospital, Sir Thomas Sutton, a citizen who is reputed to be one of the wealthiest of his time. Some of the furniture given by him will be found noticed in the chapter on the Jacobean period.
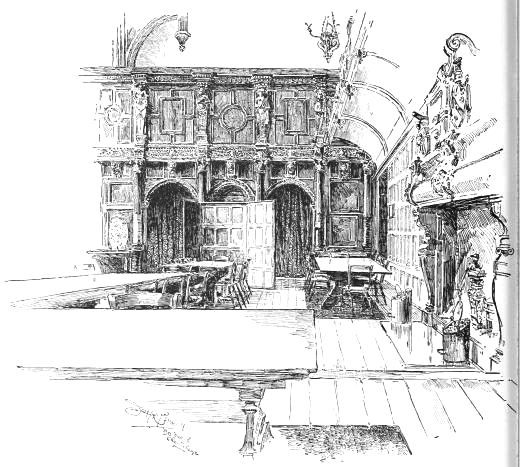

DINING HALL IN THE CHARTERHOUSE.
Shewing Oak Screen and front of Minstrels' Gallery, dated 1571.
PERIOD: ELIZABETHAN.
OAK SCREEN.
IN THE HALL OF GRAY'S INN. SHEWING FURNITURE AT THAT END OF THE HALL.

HALL OF GRAY'S INN.
Shewing Tables and Benches.
There are in London other excellent examples of Elizabethan oak carving. Amongst those easily accessible and valuable for reference, are the Hall of Gray's Inn, built in 1560, the second year of the Queen's reign, and Middle Temple Hall, built in 1570-2. By permission of Mr. William R. Douthwaite, librarian of "Gray's Inn," and author of "Gray's Inn, its History and Associations," we are enabled to give illustrations of the interior of the Hall, and also of the carved screen supporting the Minstrels' Gallery. The interlaced strap work, generally found in Elizabethan carving, encircles the shafts of the columns as a decoration. The table in the centre has also some low relief carving on the drawer front which forms its frieze, but the straight and severe style of leg leads us to place its date at some fifty years later than the Hall. The desk on the left, and the table on the right, are probably of a still later period. It may be mentioned here, too, that the long table which stands at the opposite end of the Hall, on the daïs, said to have been presented by Queen Elizabeth, is not of the design with which the furniture of her reign is associated by experts; the heavy cabriole legs, with bent knees, corresponding with the legs of the chairs (also on[84] the daïs) are of unmistakable Dutch origin, and so far as the writer's observations and investigations have gone, were probably introduced into England about the time of William III.
The same remarks apply to a table in Middle Temple Hall, also said to have been there during Elizabeth's time. Mr. Douthwaite alludes to the rumour of the Queen's gift in his book, and endeavoured to substantiate it from records at his command, but in vain. The authorities at Middle Temple are also, so far as we have been able to ascertain, without any documentary evidence to prove the claim of their table to any greater age than the end of the seventeenth century.
The carved oak screen of Middle Temple Hall is magnificent, and no one should miss seeing it. Terminal figures, fluted columns, panels broken up into smaller divisions, and carved enrichments of various devices, are all combined in a harmonious design, rich without being overcrowded, and its effect is enhanced by the rich color given to it by age, by the excellent proportions of the Hall, by the plain panelling of the three other sides, and above all by the grand oak roof, which is certainly one of the finest of its kind in England. Some of the tables and forms are of a much later date, but an interest attaches even to this furniture from the fact of its having been made from oak grown close to the Hall; and as one of the tables has a slab composed of an oak plank nearly thirty inches wide, we can imagine what fine old trees once grew and flourished close to the now busy Fleet Street, and the bustling Strand. There are frames, too, in Middle Temple made from the oaken timbers which once formed the piles in the Thames on which rested "the Temple Stairs."
In Mr. Herbert's "Antiquities of the Inns of Court and Chancery," there are several facts of interest in connection with the woodwork of Middle Temple. He mentions that the screen was paid for by contributions from each bencher of twenty shillings, each barrister of ten shillings, and every other member of six shillings and eightpence; that the Hall was founded in 1562, and furnished ten years later, the screen being put up in 1574; and that the memorials of some two hundred and fifty "Readers" which decorate the otherwise plain oak panelling, date from 1597 to 1804, the year in which Mr. Herbert's book was published. Referring to the furniture, he says:—"The massy oak tables and benches with which this apartment was anciently furnished, still remain, and so may do for centuries, unless violently destroyed, being of wonderful strength." Mr. Herbert also mentions the masks and revels held in this famous Hall in the time of Elizabeth: he also gives a list of quantities and prices of materials used in the decoration of Gray's Inn Hall.
THREE CARVED OAK PANELS.
Now in the Court Room of the Hall of the Carpenters' Company. Removed from the former Hall.
PERIOD: ELIZABETHAN.
In the Hall of the Carpenters' Company, in Throgmorton Avenue, are three curious carved oak panels, worth noticing here, as they are of a date bringing them well into this period. They were formerly in the old Hall, which escaped the Great Fire, and in the account books of the Corporation is the following record of the cost of one of these panels:—
The price of material (3s.) and workmanship (23s. 4d.) was certainly not excessive. All three panels are in excellent preservation, and the design of a harp, being a rebus of the Master's name, is a quaint relic of old customs. Some other oak furniture, in the Hall of this ancient Company, will be noticed in the following chapter. Mr. Jupp, a former Clerk of the Company, has written an historical account of the "Carpenters," which contains many facts of interest. The office of King's Carpenter or Surveyor, the powers of the Carpenters to search, examine, and impose fines for inefficient work, and the trade disputes with the "Joyners," the "Sawyers," and the "Woodmongers," are all entertaining reading, and throw many side-lights on the woodwork of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.

PART OF AN ELIZABETHAN STAIRCASE.
The illustration of Hardwick Hall shews oak panelling and decoration of a somewhat earlier, and also somewhat later, time than Elizabeth, while the carved oak chairs are of Jacobean style. At Hardwick is still kept the historic chair in which it is said that William, fourth Earl of Devonshire, sat when he and his friends compassed the downfall of[87] James II. In the curious little chapel, hung with ancient tapestry, and containing the original Bible and Prayer Book of Charles I., are other quaint chairs covered with cushions of sixteenth or early seventeenth century needlework.

THE ENTRANCE HALL, HARDWICK HALL.
PERIOD OF FURNITURE, JACOBEAN, XVII. CENTURY.
Before concluding the remarks on this period of English woodwork and furniture, further mention should be made of Penshurst Place, to which there has been already some reference in the chapter on the period of the Middle Ages. It was here that Sir Philip Sydney spent much of his time, and produced his best literary work, during the period of his retirement when he had lost the favour of Elizabeth: and in the room known as the "Queen's Room," illustrated on page 89, some of the furniture is of this period. The crystal chandeliers are said to have been given by Leicester to his Royal Mistress, and some of the chairs and tables were sent down by the Queen, and presented to Sir Henry Sydney (Philip's father) when she stayed at Penshurst during one of her Royal progresses. The room, with its vases and bowls of old Oriental china and the contemporary portraits on the walls, gives us a good idea of the very best effect that was attainable with the material then available.
Richardson's "Studies" contains, amongst other examples of furniture, and carved oak decorations of English Renaissance, interiors of Little Charlton, East Sutton Place, Stockton House, Wilts, Audley End, Essex, and the Great Hall, Crewe, with its beautiful hall screens and famous carved "parloir," all notable mansions of the sixteenth century.
To this period of English furniture belongs the celebrated "Great Bed of Ware," of which there is an illustration. This was formerly at the "Saracen's Head" at Ware, but has been removed to Rye House, about two miles away. Shakespeare's allusion to it in the "Twelfth Night" has identified the approximate date and gives the bed a character. The following are the lines:—
SIR TOBY BELCH.—And as many lies as shall lie in thy sheet of paper altho' the sheet were big enough for the Bed of Ware in England, set em down, go about it.
Another illustration shews the chair which is said to have belonged to William Shakespeare: it may or may not be the actual one used by the poet, but it is most probably a genuine specimen of about his time, though perhaps not made in England. There is a manuscript on its back which states that it was known in 1769 as the Shakespeare Chair, when Garrick borrowed it from its owner, Mr. James Bacon, of Barnet, and since that time its history is well known. The carved ornament is in low relief, and represents a rough idea of the dome of S. Marc and the Campanile Tower.
SHAKESPEARE'S CHAIR.
We have now briefly and roughly traced the advance of what may be termed the flood-tide of Art from its birthplace in Italy to France, the Netherlands, Spain, Germany, and England; and by explanation and description, assisted by illustrations, have endeavoured to show how the Gothic of the latter part of the Middle Ages gave way before the revival of classic forms and arabesque ornament, with the many details and peculiarities characteristic of each different nationality which had adopted the general change. During this period the "bahut" or chest has become a cabinet with all its varieties; the simple prie dieu chair, as a devotional piece of furniture, has been elaborated into almost an oratory, and, as a domestic seat, into a dignified throne; tables have, towards the end of the period, become more ornate, and made as solid pieces of furniture, instead of the planks and tressels which we found when the Renaissance commenced. Chimney pieces, which in the fourteenth century were merely stone smoke shafts or hoods supported by corbels, have been replaced by handsome carved oak erections, ornamenting the hall or room[89] from floor to ceiling, and the English livery cupboard, with its foreign contemporary the buffet, is the forerunner of the sideboard of the future.
THE GREAT BED OF WARE.
Formerly at the Saracen's Head, Ware, but now at Rye House, Broxbourne, Herts.
PERIOD: XVI. CENTURY.
Carved oak panelling has replaced the old arras and ruder wood lining of an earlier time, and with the departure of the old feudal customs and the indulgence in greater luxuries of the more wealthy nobles and merchants in Italy, Flanders, France, Germany, Spain, and England, we have the elegances and grace with which Art, and increased means of gratifying taste, enabled the sixteenth century virtuoso to adorn his home.

THE "QUEEN'S ROOM," PENSHURST PLACE.
(Reproduced from "Historic Houses of the United Kingdom," by permission of Messrs. Cassell & Co., Limited.)
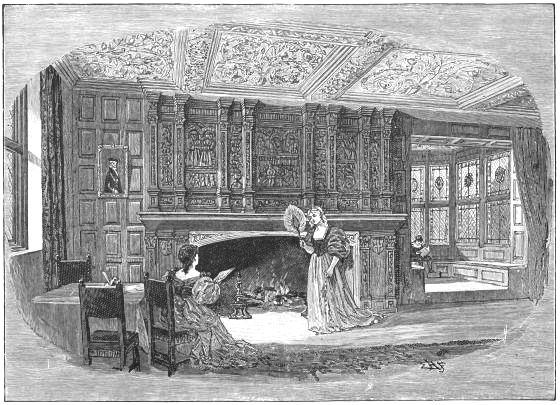

CARVED OAK CHIMNEY PIECE IN SPEKE HALL, NEAR LIVERPOOL.
PERIOD: ELIZABETHAN.
English Home Life in the Reign of James I.—Sir Henry Wotton quoted—Inigo Jones and his work—Ford Castle—Chimney Pieces in South Kensington Museum—Table in the Carpenters' Hall—Hall of the Barbers' Company—The Charterhouse—Time of Charles I.—Furniture at Knole—Eagle House, Wimbledon—Mr. Charles Eastlake—Monuments at Canterbury and Westminster—Settles, Couches, and Chairs of the Stuart period—Sir Paul Pindar's House—Cromwellian Furniture—The Restoration—Indo-Portuguese Furniture—Hampton Court Palace—Evelyn's description—The Great Fire of London—Hall of the Brewers' Company—Oak Panelling of the time—Grinling Gibbons and his work—The Edict of Nantes—Silver Furniture at Knole—William III. and Dutch influence—Queen Anne—Sideboards, Bureaus, and Grandfathers' Clocks—Furniture at Hampton Court.
 N the chapter on "Renaissance" the great Art
revival in England has been noticed; in the
Elizabethan oak work of chimney pieces, panelling,
and furniture, are to be found varying forms of
the free classic style which the Renaissance had
brought about. These fluctuating changes in
fashion continued in England from the time of
Elizabeth until the middle of the eighteenth
century, when, as will be shewn presently, a
distinct alteration in the design of furniture took
place.
N the chapter on "Renaissance" the great Art
revival in England has been noticed; in the
Elizabethan oak work of chimney pieces, panelling,
and furniture, are to be found varying forms of
the free classic style which the Renaissance had
brought about. These fluctuating changes in
fashion continued in England from the time of
Elizabeth until the middle of the eighteenth
century, when, as will be shewn presently, a
distinct alteration in the design of furniture took
place.
The domestic habits of Englishmen were getting more established. We have seen how religious persecution during preceding reigns, at the time of the Reformation, had encouraged private domestic life of families in the smaller rooms and apart from the gossiping retainer, who might at any time bring destruction upon the household by giving information about items of conversation he had overheard. There is a quaint passage in one of Sir Henry Wotton's letters, written in 1600, which shews that this home life was now becoming a settled characteristic of his countrymen.
"Every man's proper mansion house and home, being the theatre of his hospitality, the seate of his selfe fruition, the comfortable part of his own life, the noblest of his son's inheritance, a kind of private princedom, nay the possession thereof an epitome of the whole world[92] well deserve by these attributes, according to the degree of the master, to be delightfully adorned."
OAK CHIMNEY PLACE IN SIR WALTER RALEIGH'S HOUSE, YOUGHAL, IRELAND.
Said to be the work of a Flemish Artist, who was brought over for the purpose of executing this and other carved work at Youghal.
Sir Henry Wotton was Ambassador in Venice in 1604, and is said to have been the author of the well-known definition of an ambassador's calling, namely, "an honest man sent to lie abroad for his country's good." This offended the piety of James I., and caused him for some time to be in disgrace. He also published, some 20 years later, "Elements of Architecture," and being an antiquarian and man of taste, sent home many specimens of the famous Italian wood carving.
It was during the reign of James I. and that of his successor that Inigo Jones, our English Vitruvius, was making his great reputation; he had returned from Italy full of enthusiasm for the Renaissance of Palladio and his school, and of knowledge and taste gained by a diligent study[93] of the ancient classic buildings of Rome. His influence would be speedily felt in the design of woodwork fittings, for the interiors of his edifices. There is a note in his own copy of Palladio, which is now in the library of Worcester College, Oxford, which is worth quoting:—
"In the name of God: Amen. The 2 of January, 1614, I being in Rome compared these desines following, with the Ruines themselves.—INIGO JONES."

CHIMNEY PIECE IN BYFLEET HOUSE.
EARLY JACOBEAN.
In the following year he returned from Italy on his appointment as King's Surveyor of Works, and until his death in 1652 was full of work, although unfortunately for us, much that he designed was never carried out, and much that he carried out has been destroyed by fire. The Banqueting Hall of Whitehall, now Whitehall Chapel; St. Paul's, Covent Garden; the old water gate originally intended as the entrance to the first Duke of Buckingham's Palace, close to Charing Cross; Nos. 55 and 56, on the south side of Great Queen Street, Lincoln's Inn; and one or two monuments and porches, are amongst the examples that remain to us of this great master's work; and of interiors, that of Ashburnham House is left to remind us, with its quiet dignity of style, of this great master. It has been said in speaking of the staircase, plaster ornament, and woodwork of this interior, "upon the whole is set the seal of the time of Charles I." As the work was probably finished during the King's reign, the impression intended to be conveyed was that after wood carving had rather run riot towards the end of the[94] sixteenth century, we had now in the interior designed by Inigo Jones, or influenced by his school, a more quiet and sober style.

THE KING'S CHAMBER, FORD CASTLE.
The above woodcut shews a portion of the King's room, in Ford Castle, which still contains souvenirs of Flodden Field—according to an article in the Magazine of Art. The room is in the northernmost tower, which still preserves externally the stern, grim character of the border fortress; and the room looks towards the famous battle-field. The chair shews a date 1638, and there is another of Dutch design of about fifty[95] or sixty years later; but the carved oak bedstead, with tapestry hangings, and the oak press, which the writer of the article mentions as forming part of the old furniture of the room, scarcely appear in the illustration.
Mr. Hungerford Pollen tells us that the majority of so-called Tudor houses were actually built during the reign of James I., and this may probably be accepted as an explanation of the otherwise curious fact of there being much in the architecture and woodwork of this time which would seem to belong to the earlier period.
The illustrations of wooden chimney pieces will shew this change. There are in the South Kensington Museum some three or four chimney pieces of stone, having the upper portions of carved oak, the dates of which have been ascertained to be about 1620; these were removed from an old house in Lime Street, City, and give us an idea of the interior decoration of a residence of a London merchant. The one illustrated is somewhat richer than the others, the columns supporting the cornice of the others being almost plain pillars with Ionic or Doric capitals, and the carving of the panels of all of them is in less relief, and simpler in character, than those which occur in the latter part of Elizabeth's time.
CARVED OAK CENTRE TABLE.
In the Hall of the Carpenters' Company.
The earliest dated piece of Jacobean furniture which has come under the writer's observation is the octagonal table belonging to the Carpenters' Company. The illustration, taken from Mr. Jupp's book referred to in the last chapter, hardly does the table justice; it is really a very handsome piece of furniture, and measures about 3 feet 3 inches in diameter. In the spandrils of the arches between the legs are the letters R.W., G.I., J.R., and W.W., being the initials of Richard Wyatt, George Isack, John Reeve, and William Willson, who were Master and Wardens of the Company in 1606, which date is carved in two of the spandrils. While the ornamental legs shew some of the characteristics of Elizabethan work, the treatment is less bold, the large acorn-shaped member has become more refined and attenuated, and the ornament is[96] altogether more subdued. This is a remarkable specimen of early Jacobean furniture, and is the only one of the shape and kind known to the writer; it is in excellent preservation, save that the top is split. It shews signs of having been made with considerable skill and care.
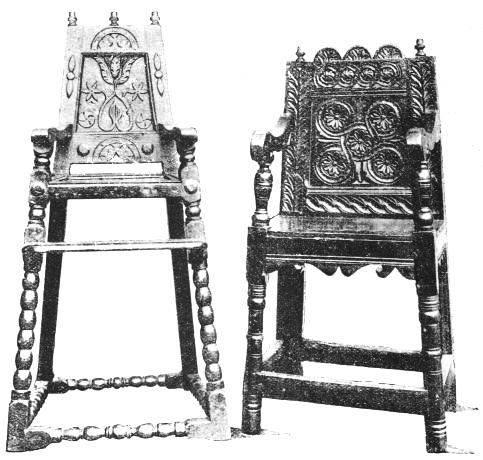
CARVED OAK CHAIR. CARVED OAK CHAIR.
From Abingdon Park. In the Carpenters' Hall.
(From Photos in the S. Kensington Museum Album.)
EARLY XVII. CENTURY. ENGLISH.
The Science and Art Department keep for reference an album containing photographs, not only of many of the specimens in the different museums under its control, but also of some of those which have been lent for a temporary exhibition. The illustration of the above two chairs is taken from this source, the album having been placed at the writer's disposal by the courtesy of Mr. Jones, of the Photographic Department. The left-hand chair, from Abingdon Park, is said to have belonged to Lady Barnard, Shakespeare's grand-daughter, and the other may still be seen in the Hall of the Carpenters' Company.

OAK CHIMNEY PIECE.
Removed from an old house in Lime Street, City.
(South Kensington Museum.)
PERIOD: JAMES I.
In the Hall of the Barbers' Company in Monkswell Street, the Court room, which is lighted with an octagonal cupola, was designed by Inigo Jones as a Theatre of Anatomy, when the Barbers and Surgeons were one[97] corporation. There are some three or four tables of this period in the Hall, having four legs connected by stretchers, quite plain; the moulded edges of the table tops are also without enrichment. These plain oak slabs, and also the stretchers, have been renewed, but in exactly the same style as the original work; the legs, however, are the old ones, and are simple columns with plain turned capitals and bases. Other tables of this period are to be found in a few old country mansions; there is one in Longleat, which, the writer has been told, has a small drawer at the end, to hold the copper coins with which the retainers of the Marquis of Bath's ancestors used to play a game of shovel penny. In the Chapter House in Westminster Abbey, there is also one of these plain substantial James I. tables, which is singular in being nearly double the width of those which were usually made at this time. As the Chapter House was, until comparatively recent years, used as a room for the storage of records, this table was probably made, not as a dining table, but for some other purpose requiring greater width.

OAK SIDEBOARD IN THE S. KENSINGTON MUSEUM.
PERIOD: WILLIAM III.
In the chapter on Renaissance there was an allusion to Charterhouse, which was purchased for its present purpose by Thomas Sutton in 1611, and in the chapel may be seen to-day the original communion table placed there by the founder. It is of carved oak, with a row of legs running lengthways underneath the middle, and four others at the corners; these, while being cast in the simple lines already noticed in describing the tables in the Barbers' Hall, and the Chapter House, Westminster Abbey, are enriched by carving from the base, to the third of the height of the leg, and the frieze of the table is also carved in low relief. The rich carved wood screen which supports the organ loft is also of Jacobean work.
There is in the South Kensington Museum a carved oak chest, with a centre panel representing the Adoration of the Magi, of about this date, 1615-20; it is mounted on a stand which has three feet in front and two behind, which are much more primitive and quaint than the ornate supports of Elizabethan carving; while the only ornaments on the drawer fronts which form the frieze of the stand are moulded panels, in the centre of each of which there is a turned knob by which to open the drawer. This chest and the table which forms its stand were probably not intended for each other. The illustration on the previous page shews the stand, which is a good representation of the carving of this time, i.e., early seventeenth century. The round-backed arm chair which the Museum purchased in 1891 from the Hailstone Collection, though dated 1614, is really more Elizabethan in design than one would expect.
There is no greater storehouse for specimens of furniture in use during the Jacobean period than Knole, that stately mansion of the Sackville family, then the property of the Earls of Dorset. In the King's Bedroom, which is said to have been specially prepared and furnished for the visit of King James I., the public, owing to the courtesy and generous spirit of the present Lord Sackville, can still see the bed, originally of crimson silk, but now much faded, elaborately embroidered with gold. It is said to have cost £8,000, and the chairs and seats, which are believed to have formed part of the original equipment of the room, are in much the same position as they then occupied.
In the carved work of this furniture we cannot help thinking that the
hand of the Venetian craftsman is to be traced, and it is probable that they
were either imported or copied from a pattern brought over for that
purpose. A suite of furniture of that time appears to have consisted of
six stools and two arm chairs, almost entirely covered with velvet, having
the "![]() " form supports, which, so far as the writer's investigations have
gone, appear to have come from Venice. In the "Leicester" gallery[99]
at Knole there is a portrait of the King, painted by Mytens, seated on
such a chair, and just below the picture is placed the chair which is
said to be identical with the one portrayed. It is similar to the one
reproduced on page 100 from a drawing of Mr. Charles Eastlake's.
" form supports, which, so far as the writer's investigations have
gone, appear to have come from Venice. In the "Leicester" gallery[99]
at Knole there is a portrait of the King, painted by Mytens, seated on
such a chair, and just below the picture is placed the chair which is
said to be identical with the one portrayed. It is similar to the one
reproduced on page 100 from a drawing of Mr. Charles Eastlake's.
SEATS AT KNOLE.
Covered with Crimson Silk Velvet.
PERIOD: JAMES I.
In the same gallery also are three sofas or settees upholstered with crimson velvet, and one of these has an accommodating rack, by which either end can be lowered at will, to make a more convenient lounge.
ARM CHAIR.
Covered with Velvet, trimmed with Fringe, and studded with Copper Nails.
EARLY XVII. CENTURY.
(From a Drawing of the Original at Knole, by Mr. Charles Eastlake.)
This excellent example of Jacobean furniture has been described and sketched by Mr. Charles Eastlake in "Hints on Household Taste." He says: "The joints are properly 'tenoned' and pinned together in such a manner as to ensure its constant stability. The back is formed like that of a chair, with a horizontal rail only at its upper edge, but it receives additional strength from the second rail, which is introduced at the back of the seat." In Marcus Stone's well-known picture of "The Stolen Keys," this is the sofa portrayed. The arm chair illustrated above is part of the same suite of furniture. The furniture of another room at Knole is said to have been presented by King James to the first Earl of Middlesex, who had married into the Dorset family. The author has been furnished with a photograph of this room; and the illustration prepared from this will give the reader a better idea than a lengthy description.

THE "SPANGLE" BEDROOM AT KNOLE.
The Furniture of this room was presented by James I. to the Earl of Middlesex.
(From a Photo by Mr. Corke, of Sevenoaks.)
It seems from a comparison of the Knole furniture with the designs of some of the tables and other woodwork produced during the same reign, bearing the impress of the more severe style of Inigo Jones, that there were then in England two styles of decorative furniture. One of these, simple and severe, shewing a reaction from the grotesque freedom of Elizabethan carving, and the other, copied from Venetian ornamental woodwork, with cupids on scrolls forming the supports of stools, having these ornamental legs connected by stretchers, the design of which is, in the case of those in the King's Bedchamber at Knole, a couple of cupids in a flying attitude holding up a crown. This kind of furniture was generally gilt, and under the black paint of those at Knole, traces of the gold are still to be seen.
Mr. Eastlake visited Knole, and made a careful examination and sketches of the Jacobean furniture there, and has well described and illustrated it in his book just referred to; he mentions that he found there a slip of paper tucked beneath the webbing of a settle, with an inscription in Old English characters which fixed the date of some of the furniture at 1620. Mr. Lionel Sackville West has confirmed this date in a letter to the author, by a reference to the heirloom book, which also bears out the author's opinion that some of the more richly-carved furniture of this time was imported from Italy.
In the Lady Chapel of Canterbury Cathedral there is a monument of Dean Boys, who died in 1625. This represents the Dean seated in his library, at a table with turned legs, over which there is a tapestry cover. Books line the walls of the section of the room shewn in the stone carving; it differs little from the sanctum of a literary man of the present day. There are many other monuments which represent furniture of this period, and amongst the more curious is that of a child of King James I., in Westminster Abbey, close to the monument of Mary Queen of Scots. The child is sculptured about life size, in a carved cradle of the time.
Holland House, Kensington, is a good example of a Jacobean mansion. The chief interest, inseparable from this house, is, of course, associated with the memory of the third Lord Holland, "nephew of Fox and friend of Grey," who gathered around him within its walls the most brilliant and distinguished society of the day, presiding over it with that genial courtesy which was the rich inheritance of his family.
Macaulay, at the conclusion of his essay on Lord Holland, has, with his unrivalled power of description, told us of the charm and fascination of "that circle in which every talent and accomplishment, every art and science, had its place"—enumerating also the names of many of those[103] who formed it, and expatiating on "the grace and the kindness, far more admirable than grace, with which the princely hospitality of that ancient mansion was dispensed." Princess Liechtenstein has also preserved for us, in "Holland House," a charming record of many of the historical associations of this famous old place.
There are in the house also many objects of great interest, of various periods, which, by the courtesy of Lady Ilchester, the writer has been allowed to examine. Our business, however, is with the 17th century, and we must now return to a consideration of the furniture and woodwork of that time.
The Holland House of the time of James I. was commenced in the year 1607, as "Cope Castle," by Sir Walter Cope, who then owned the extensive "Manor" of Kensington. Cope's daughter married Sir Henry Rich, who became Earl of Holland in 1624, and was executed by the Parliamentarians in 1649. He it was who added to the house the wings and arcades. Princess Liechtenstein tells us the story of "the solitary ghost of its first lord, who, according to tradition, issues forth at midnight from behind a secret door, and walks slowly through the scenes of his former triumph with his head in his hand."
There is some good old woodwork of the early part of the seventeenth century, and the panelling and chimney piece of the famous "white parlour" are of the times of James I., the work, still in good preservation, being in the best Jacobean taste. The panels are formed by bold uncarved mouldings, separated at intervals by flat pilasters with fluted shafts and carved capitals; the panels in the frieze, between the trusses, which support a "dentilled" cornice, are enriched with fretwork ornaments in relief, and the whole has a simple but decorative architectural effect of the best English rendering of the Renaissance. The "gilt room," where the ghost is said to commence its nocturnal promenade, was decorated by Francesco Cleyn, an Italian, who also worked for the King.[9] The room was prepared for a ball which was purposed to be given in honor of the marriage of Prince Charles to Henrietta Maria. There are now on the chief staircase of Holland House, two chairs with their backs carved as shells, and with legs shaped and ornamented with scrollwork, and masks with swags of foliage, which are also attributed to Cleyn. Horace Walpole, in a reference to Holland House, has mentioned these chairs in[104] "Anecdotes of Painters." "Two chairs, carved and gilt, with large shells for backs ... were undoubtedly from his designs, and are evidences of his taste." Walpole also mentions a garden seat of similar design by Cleyn. A drawing of one of these chairs forms the tail piece of this chapter.
There is another Jacobean house of considerable interest, the property of Mr. T. G. Jackson, A.R.A. An account of it has been written by him, and was read to some members of the Surrey Archæological Society, who visited Eagle House, Wimbledon, in 1890. It appears to have been the country seat of a London merchant, who lived early in the seventeenth century. Mr. Jackson bears witness to the excellence of the workmanship, and expresses his opinion that the carved and decorated enrichments were executed by native and not by foreign craftsmen. He gives an illustration in his pamphlet of the sunk "Strap Work," which, though Jacobean in its date, is also found in the carved ornament of Elizabeth's time.
It is very probable that had the reign of Charles I. been less troublous, this would have been a time of much progress in the domestic arts in England. The Queen was of the Medici family, Italian literature was in vogue, and Italian artists therefore would probably have been encouraged to come over and instruct our workmen. The King himself was an excellent mechanic, and boasted that he could earn his living at almost any trade save the making of hangings. His father had established the tapestry works at Mortlake; he himself had bought the Raffaelle Cartoons to encourage the work—and much was to be hoped from a monarch who had the taste and judgment to induce a Vandyke to settle in England. The Civil war, whatever it has achieved for our liberty as subjects, certainly hindered by many years our progress as an artistic people.
COUCH, ARM CHAIR, AND SINGLE CHAIR.
Carved and Gilt.
Upholstered in Rich Silk Velvet. Part of Suite at Penshurst Place.
Also an Italian Cabinet.
PERIOD: CHARLES II.
But to consider some of the furniture of this period in detail. Until the sixteenth century was well advanced the word "table" in our language meant an index or pocket book (tablets), or a list, not an article of furniture. The table was, as we have noticed in the time of Elizabeth, composed of boards generally hinged in the middle for convenience of storage, and supported on trestles which were sometimes ornamented by carved work. The word trestle, by the way, is said to be derived from the "threstule," i.e., three-footed supports, and these three-legged stools and benches formed in those days the seats for everyone except the master of the house. Chairs were, as we have seen, scarce articles; sometimes there was only one, a throne-like seat for an honoured guest or for the master or mistress of the house, and doubtless our present phrase of "taking the chair" is a survival of the high place a chair then held amongst the household gods of a gentleman's mansion.[105] Shakespeare possibly had the boards and trestles in his mind when, about 1596, he wrote in "Romeo and Juliet"—
And as the scene in "King Henry the Fourth" is placed some years earlier than that of "Romeo and Juliet," it is probable that "table" had then its earlier meaning, for the Archbishop of York is made to say:—
Mr. Maskell, in his handbook on "Ivories," tells us that the word "table" was also used, in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, to denote the religious carvings and paintings in churches; and he quotes Chaucer to show that the word was also used to describe the game of draughts.
Now, however, at the time of which we are writing, chairs were becoming more plentiful and the table was a definite article of furniture. In inventories of the time and for some twenty years previous, as has been already noticed in the preceding chapter, we find mention of "joyned table," framed table, "standing" and "dormant" table, and the word "board" had gradually disappeared. It remains to us, however, as a souvenir of the past, in the name we still give to a body of men meeting for the transaction of business, and, in connection with social life, in the phrase "the festive board." The width of these earlier tables had been about 30 inches, and guests sat on one side only, with their backs to the wall, in order, it may be supposed, to be the more ready to resist any sudden raid which might be made on the house during the relaxation of the supper hour, and this custom remained in use long after there was any necessity for its observance.
In the time of Charles the First the width was increased, and a contrivance was introduced for doubling the area of the top when required, by drawing out two flaps from either end, and by means of a wedge-shaped arrangement, the centre or main table top was lowered, and the whole table, thus increased, became level. Illustrations taken from Mr. G. T. Robinson's article on furniture in the "Art Journal" of 1881, represent a "Drawinge table," which was the name by which these "latest improvements" were known. The black lines were of stained pear tree, let into the oak: the acorn shaped member of the leg is an imported Dutch design, which became very common about this time, and was applied to the supports of cabinets, sometimes as in the[106] illustration, plainly turned, but frequently carved. Another table of this period was the "folding table," which was made with twelve, sixteen, or with twenty legs, is shewn in the illustration of this example, and which, as its name implies, would shut up into about one third of its extended size. There is one of these tables in the Stationers' Hall.
FOLDING TABLE AT PENSHURST PLACE.
PERIOD: CHARLES II. TO JAMES II.
"DRAWINGE" TABLE WITH BLACK LINES INLAID.
PERIOD: CHARLES II.
It was probably in the early part of the seventeenth century that the Couch became known in England. It was not common, nor quite in the form in which we now recognize that luxurious article of furniture, but was probably a carved oak settle, with cushions so arranged as to form a resting lounge by day. Shakespeare speaks of the "branch'd velvet gown" of Malvolio having come from a "day bed," and there is also an allusion to one in Richard III.[10]
THEODORE HOOK'S CHAIR.

SCROWLED CHAIR IN CARVED OAK.
In a volume of "Notes and Queries" there is a note which would shew that the lady's wardrobe of this time (1622) was a very primitive article of furniture. Mention is made there of a list of articles of[108] wearing apparel belonging to a certain Lady Elizabeth Morgan, sister to Sir Nathaniel Rich, which, according to the old document there quoted, dated the 13th day of November, 1622, "are to be found in a great bar'd chest in my Ladie's Bedchamber." To judge from this list, Lady Morgan was a person of fashion in those days. We may also take it for granted that beyond the bedstead, a prie-dieu chair, a bench, some chests, and the indispensable mirror, there was not much else with which to furnish a lady's bedroom in the reign of James I. or that of his successor.
CHAIR USED BY KING CHARLES I. DURING HIS TRIAL.
The "long settle" and "scrowled chair" were two other kinds of seats in use from the time of Charles I. to that of James II. The illustrations are taken from authenticated specimens in the collection of Mr. Dalton, of Scarborough. They are most probably of Yorkshire manufacture, about the middle of the seventeenth century. The ornament in the panel of the back of the chair is inlaid with box or ash, stained to a greenish black to represent green ebony, and with a few small pieces of rich red wood then in great favour. Mr. G. T. Robinson, to whose article mentioned above we are indebted for the description, says that this wood was "probably brought by some buccaneer from the West." He also mentions another chair of the Stuart period, which formed a table, and subsequently became the property of Theodore Hook, who carefully preserved its pedigree. It was purchased by its late owner, Mr. Godwin, editor of "The Builder." A woodcut of this chair is on page 107.

SETTLE OF CARVED OAK.
Probably made in Yorkshire.
PERIOD: CHARLES II.
Another chair to which there is an historical interest attached is that in which Charles I. sat during his trial; this was exhibited in the Stuart Exhibition in London in 1889. The illustration on page 108 is taken from a print in "The Illustrated London News" of the time.
In addition to the chairs of oak, carved, inlaid, and plain, which were in some cases rendered more comfortable by having cushions tied to the backs and seats, the upholstered chair, which we have seen had been brought from Venice in the early part of the reign of James I., now came into general use. Few have survived, but there are still to be seen in pictures of the period, chairs represented as covered with crimson velvet, studded with brass nails, the seat being trimmed with fringe, similar to that at Knole, illustrated on page 100.
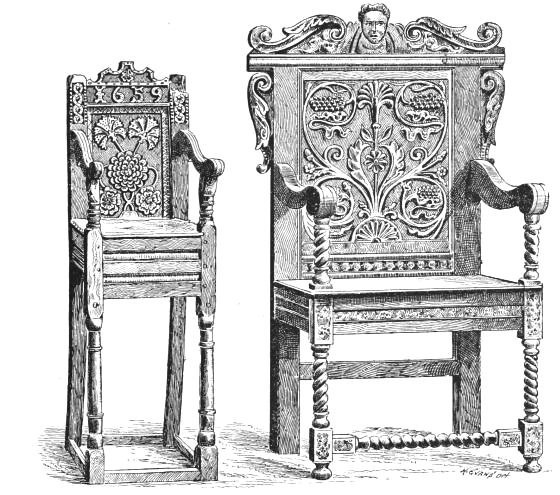

CARVED OAK CHAIR. CARVED OAK CHAIR, JACOBEAN STYLE.
Said to have been used by some of Cromwell's family. (The original in the Author's possession.)
(The original in the possession of T. Knowles Parr, Esq.)
There is in the Historical Portrait Gallery in Bethnal Green Museum, a painting by an unknown artist, but dated 1642, of Sir William Lenthall, who was Speaker of the House of Commons on the memorable occasion when, on the 4th of January in that year, Charles I. entered the House to demand the surrender of the five members. The chair on which Sir[110] William is seated answers this description, and is very similar to the one used by Charles I. (illustrated on page 108).
The importation of scarce foreign woods gave an impetus to inlaid work in England, which had been crude and rough in the time of Elizabeth. In the marqueterie of Italy, France, Holland, Germany, and Spain, considerable excellence had already been attained. Mahogany had been discovered by Raleigh as early as 1595, but did not come into general use until the middle of the eighteenth century.
During the year 1891, owing to the extension of the Great Eastern Railway premises at Bishopsgate Street, an old house of antiquarian interest was pulled down, and generously presented by the Company to the South Kensington Museum. This has been erected so as to enable the visitor to see a good example of the exterior as well as some of the interior woodwork of a quaint house of the middle of the seventeenth century. It was the residence of Sir Paul Pindar, during the time of Charles I., and it contained a carved oak chimneypiece, with some other good ornamental woodwork of this period.

STAIRCASE IN GENERAL IRETON'S HOUSE, DATED 1630.
In the illustration of a child's chair, which is said to have been used by some of Cromwell's family, can be seen an example of carved oak of this time; it was lent to the writer by its present owner, in whose family it is an heirloom, one of his ancestors having married the[111] Protector's daughter. The ornament has no particular style, and it may be taken for granted that the period of the Commonwealth was not marked by any progress in decorative Art. The illustration of a staircase on p. 110 proves that there were exceptions to the prevalent Puritan objection to figure ornament. In one of Mrs. S. C. Hall's papers, "Pilgrimages to English Shrines," contributed in 1849 to "The Art Journal," she describes the interior of the house which was built for Bridget, the Protector's daughter, who married General Ireton. The handsome oak staircase had the newels surmounted by carved figures, representing different grades of men in the General's army—a captain, common soldier, piper, drummer, etc., etc., while the spaces between the balustrades were filled in with devices emblematical of warfare, the ceiling being decorated in the fashion of the period. At the time Mrs. Hall wrote, the house bore Cromwell's name and the date 1630.

SETTEE AND CHAIR.
In carved ebony, part of the Indo-Portuguese Suite at Penshurst Place, with Flemish Folding Chair.
PERIOD: CHARLES II.
We may date from the Commonwealth the more general use of chairs; people sat as they chose, and no longer regarded the chair as the lord's place. A style of chair we still recognise as Cromwellian was imported from Holland about this time—plain square backs and seats covered with brown leather, studded with brass nails. The legs, which are now generally turned with a spiral twist, were in Cromwell's time plain and simple.
The residence of Charles II. abroad had accustomed him and his friends to the much more luxurious furniture of France and Holland. With the Restoration came a foreign Queen, a foreign Court, French manners, and French literature. Cabinets, chairs, tables, and couches were imported into England from the Netherlands, France, Spain, and Portugal; and our craftsmen profited by new ideas and new patterns, and what was of equal consequence, an increased demand for decorative articles of furniture. The King of Portugal had ceded Bombay, one of the Portuguese Indian Stations, to the new Queen of England, and there is a chair of this Indo-Portuguese work, carved in ebony, now in the Museum at Oxford, which was given by Charles II. either to Elias Ashmole or to Evelyn. The chair is very similar to one at Penshurst; it is grouped with a settee of like design, together with a small folding chair which Mr. G. T. Robinson, in his article on "Seats," has described as Italian, but which we take the liberty of pronouncing to be Flemish, judging by a similar one now in the South Kensington Museum.
In connection with this Indo-Portuguese furniture, it would seem that spiral turning became known and fashionable in England during the reign of Charles II., and in some chairs of English make, which have come under the writer's notice, the legs have been carved to imitate the effects of spiral turning—an amount of superfluous labour which[112] would scarcely have been incurred, but for the fact that the country house-carpenter of this time had an imported model, which he copied, without knowing how to produce by means of the lathe the effect which had just come into fashion. There are, too, in certain illustrations in "Shaw's Ancient Furniture," some lamp-holders, in which this spiral turning is overdone, a fault which is frequently to be met with when any particular kind of ornament comes into vogue.
The suite of furniture at Penshurst Place (illustrated), which comprises thirteen pieces, was probably imported about this time; two of the smaller chairs appear to have their original cushions, the others have been re-covered by the late Lord de l'Isle and Dudley. The spindles of the backs of two of the chairs are of ivory; the carving, which is in solid ebony, is much finer on some than on others.
We gather a good deal of information about the furniture of this period from the famous diary of Evelyn. He thus describes Hampton Court Palace, as it appeared to him at the time of its preparation for the reception of Catherine of Braganza, the bride of Charles II., who spent the royal honeymoon in this historic building, which had in its time sheltered for their brief spans of favour the six wives of Henry VIII., and the sickly boyhood of Edward VI.:—
"It is as noble and uniform a pile as Gothic architecture can make it. There is incomparable furniture in it, especially hangings designed by Raphael, very rich with gold. Of the tapestries I believe the world can show nothing nobler of the kind than the stories of Abraham and Tobit.[11]... The Queen's bed was an embroidery of silver on crimson velvet, and cost £8,000, being a present made by the States of Holland when his Majesty returned. The great looking-glass and toilet of beaten massive gold were given by the Queen Mother. The Queen brought over with her from Portugal such Indian cabinets as had never before been seen here." Evelyn wrote, of course, before Wren made his Renaissance additions to the Palace.
After the Great Fire, which occurred in 1666, and destroyed some 13,000 houses, and no less than 89 churches, Sir Christopher Wren was given an opportunity, unprecedented in history, of displaying his power of design and reconstruction. Writing of this great architect, Macaulay says, "The austere beauty of the Athenian portico, the gloomy sublimity of the Gothic arcade, he was, like most of his contemporaries, incapable of emulating, and perhaps incapable of appreciating; but no man born on our side of the Alps has imitated with so much success the magnificence of the palace churches of Italy. Even the superb Louis XIV. has left to posterity no work which can bear a comparison with St. Paul's."
Sedes, ecce tibi! quæ tot produxit alumnos,
Quot gremio nutrit Granta, quot Isis habet.
From the Original by Sir Peter Lely, presented to Dᴿ. Busby by King Charles.
"SEDES BUSBIANA."
From a Print in the possession of J. C. THYNNE, Esq.
PERIOD: CHARLES II.
Wren's great masterpiece was commenced in 1675, and completed in 1710, and its building therefore covers a period of 35 years, carrying us through the reigns of James II., William III. and Mary, and well on to the end of Anne's reign. The admirable work which he did during this time, and which has effected so much for the adornment of our Metropolis, had a marked influence on the ornamental woodwork of the second half of the seventeenth century: in the additions which he made to Hampton Court Palace, in Bow Church, in the Hospitals of Greenwich and of Chelsea, there is a sumptuousness of ornament in stone and marble, which shew the influence exercised on his mind by the desire to rival the grandeur of Louis XIV., the Fountain Court at Hampton being in direct imitation of the Palace of Versailles. The carved woodwork of the choir of St. Paul's, with fluted columns supporting a carved frieze; the richly carved panels, and the beautiful figure work on both organ lofts, afford evidence that the oak enrichments followed the marble and stone ornament. The swags of fruit and flowers, the cherubs' heads with folded wings, and other details in Wren's work, closely resemble the designs executed by Gibbons, whose carving will be noticed later on.
It may be mentioned here that amongst the few churches in the city which escaped the Great Fire, and contained woodwork of particular note, are St. Helen's, Bishopsgate, and the Charterhouse Chapel, which contain the original pulpits of about the sixteenth century.
The famous Dr. Busby, who for 55 years was head master of Westminster School, was a great favourite of King Charles, and a picture, painted by Sir Peter Lely, is said to have been presented to the Doctor by His Majesty; it is called "Sedes Busbiana." Prints from this old picture are scarce, and the writer is indebted to Mr. John C. Thynne for the loan of his copy, from which the illustration is taken. The portrait in the centre, of the Pedagogue aspiring to the mitre, is that of Dr. South, who succeeded Busby, and whose monument in Westminster Abbey is next to his. The illustration is interesting, as although it may not have been actually taken from a chair itself, it shews a design in the mind of a contemporary artist.
Of the Halls of the City Guilds, there is none more quaint, and in greater contrast to the bustle of the neighbourhood, than the Hall of the Brewers' Company, in Addle Street, City. This was partially destroyed, like most of the older Halls, by the Great Fire, but was one of the first to be restored and refurnished. In the kitchen are still to be seen the remains of an old trestle, and other relics of an earlier period, but[114] the hall or dining room, and the Court Room, are complete, with very slight additions, since the date of their interior equipment in 1670 to 1673. The Court Room has a richly carved chimney piece in oak, nearly black with age, the design of which is a shield with a winged head, palms, and swags of fruit and flowers, while on the shield itself is an inscription, stating that this room was wainscoted by Alderman Knight, Master of the Company, and Lord Mayor of the City of London, in the year 1670. The room itself is exceedingly quaint with its high wainscoting and windows, reminding one of the portholes of a ship's cabin, while the chief window looks out on to the old-fashioned garden, giving the beholder altogether a pleasing illusion, carrying him back to the days of Charles II.
The chief room or Hall is still more handsomely decorated with carved oak of this time. The actual date, 1673, is over the doorway on a tablet which bears the names, in the letters of the period, of the master, "James Reading, Esq.," and the wardens, "Mr. Robert Lawrence," "Mr. Samuel Barber," and "Mr. Henry Sell."
The names of other masters and wardens are also written over the carved escutcheons of their respective arms, and the whole room is one of the best specimens in existence of the oak carving of this date. At the western end is the Master's chair, of which by the courtesy of Mr. Higgins, Clerk to the Company, we are able to give an illustration on page 115; the shield-shaped back, the carved drapery, and the coat-of-arms with the company's motto, are all characteristic features, as are also the Corinthian columns and arched pediments in the oak decorations of the room. The broken swan-necked pediment, which surmounts the cornice of the room over the chair, is probably a more recent addition, this ornament having come in about thirty years later.
There are also the old dining tables and benches: these are as plain and simple as possible. In the Court Room is a table, which was formerly in the Company's barge; it has some good inlaid work in the arcading which connects the two end standards, and some old carved lions' feet; the top and other parts have been renewed. There is also an old oak fire-screen of about the end of the seventeenth century.
Another city hall, the interior woodwork of which dates from just after the Great Fire, is that of the Stationers' Company, in Ave Maria Lane, close to Ludgate Hill. Mr. Charles Robert Rivington, the present Clerk to the Company, has written a pamphlet, full of very interesting records of this ancient and worshipful corporation, from which the following paragraph is a quotation:—"The first meeting of the court after the fire, was held at Cook's Hall, and the subsequent courts, until the hall was[115] re-built, at the Lame Hospital Hall, i.e., St. Bartholomew's Hospital. In 1670 a committee was appointed to re-build the hall; and in 1674 the Court agreed with Stephen Colledge (the famous Protestant joiner, who was afterwards hanged at Oxford in 1681) to wainscot the hall 'with well-seasoned and well-matched wainscot, according to a model delivered in for the sum of £300.' His work is now to be seen in excellent condition."

THE MASTER'S CHAIR.
Hall of the Brewers' Company. (From a pen and ink sketch by H. Evans.)
Mr. Rivington read his paper to the London and Middlesex Archæological Society in 1881; and the writer can with pleasure confirm his statement as to the condition, in 1899, of this fine specimen of seventeenth century work. Less ornate and elaborate than the Brewers' Hall, the panels are only slightly relieved with carved mouldings; but the[116] end of the room, or main entrance, opposite the place of the old daïs (long since removed), is somewhat similar to that in the Brewers' Hall, and presents a fine architectural effect, which will be observed in the illustration on page 117.
CARVED OAK LIVERY CUPBOARD.
In the Hall of the Stationers' Company. Made in 1674, the curved pediment added later, probably in 1788.
There is above an illustration of one of the two livery cupboards, which formerly stood on the daïs, and these are good examples of the cupboards for display of plate of this period. The lower part was formerly the receptacle for unused viands, which were distributed to the poor after the feast. In their original state these livery cupboards finished with a straight cornice, the broken pediments with the eagle (the Company's crest) having most probably been added when the Hall was, to quote an inscription on a shield, "repaired and beautified in the mayoralty of the Right Honourable William Gill, in the year 1788," when Mr. Thomas Hooke was Master, and Mr. Field and Mr. Rivington (the present Clerk's grandfather) Wardens.

ARM CHAIRS.
Chair upholstered in Spitalfields silk. Carved and upholstered Chair. Chair upholstered in Spitalfields silk.
HAMPTON COURT PALACE. HARDWICK HALL. KNOLE, SEVENOAKS.
PERIOD: WILLIAM III. TO QUEEN ANNE.
There is still preserved in a lumber room one of the old benches of seventeenth century work—now replaced in the hall by modern folding chairs. This is of oak, with turned skittle-shaped legs slanting outwards, and connected and strengthened by plain stretchers. The old tables are still in their original places.
CARVED OAK SCREEN.
In the Hall of the Stationers' Company, erected in 1674: the Royal Coat of Arms has been since added.
Another example of seventeenth century oak panelling is the handsome chapel of the Mercers' Hall—the only city Company possessing their own chapel—but only the lining of the walls and the reredos are of the original work, the remainder having been added some ten or twelve years ago, when some of the original carving was made use of in the new work. Indeed, in this magnificent hall, about the most spacious of the old City Corporation Palaces, there is a great deal of new work mixed with old—new chimney pieces and old overmantels—some of Grinling Gibbons' carved enrichments, so painted and varnished as to have lost much of their character; these have been applied to the oak panels in the large dining hall.
The woodwork lining of living rooms had been undergoing changes since the commencement of the period of which we are now writing. In[118] 1638 a man named Christopher had taken out a patent for enamelling and gilding leather, which was used as a wall decoration over the oak panelling. This decorated leather had hitherto been imported from Holland and Spain; when this was not used, and tapestry, which was very expensive, was not obtainable, the plaster was roughly ornamented. Somewhat later than this, pictures were let into the wainscot to form part of the decoration, for in 1669 Evelyn, when writing of the house of the "Earl of Norwich," in Epping Forest, says, "A good many pictures put into the wainscot which Mr. Baker, his lordship's predecessor, brought from Spaine." Indeed, subsequently the wainscot became simply the frame for pictures, and the same writer deplores the disuse of timber, and expresses his opinion that a sumptuary law ought to be passed to restore the "ancient use of timber." Although no law was enacted on the subject, yet, some twenty years later, the whirligig of fashion brought about the revival of the custom of lining rooms with oak panelling.
It is said that about 1670 Evelyn found Grinling Gibbons in a small thatched house on the outskirts of Deptford, and introduced him to the King, who gave him an appointment on the Board of Works, and patronised him with extensive orders. The character of his carving is well known; generally using lime-tree as the vehicle of his designs, his life-like birds and flowers, groups of fruit, and heads of cherubs, are easily recognised. One of the rooms in Windsor Castle is decorated with the work of his chisel, which can also be seen in St. Paul's Cathedral, Hampton Court Palace, Chatsworth, Burleigh, and perhaps his best, in Petworth House, in Sussex. He also sculptured in stone. The base of King Charles' statue at Windsor, the font of St. James', Piccadilly (round the base of which are figures of Adam and Eve), are his work, as is also the lime-tree border of festoon work over the Communion table. Gibbons was an Englishman, but appears to have spent his boyhood in Holland, where he was christened "Grinling." He died in 1721. His pupils were Samuel Watson, a Derbyshire man, who did much of the carved work at Chatsworth, Drevot of Brussels, and Lawreans of Mechlin. Gibbons and his pupils founded a school of carving in England which has been continued by tradition to the present day.
SILVER FURNITURE AT KNOLE.
(From a Photo by Mr. Corke, of Sevenoaks.)
A somewhat important immigration of French workmen occurred about this time, owing to the persecutions of Protestants in France, which followed the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685, by Louis XIV., and these refugees bringing with them their skill, their patterns and ideas, influenced the carving of our ornamental frames, and the designs of some of our furniture. This influence is to be traced in some of the contents of Hampton Court Palace, particularly in the carved and gilt centre tables and the torchères of French design but of English workmanship. It is said that no less than 50,000 families left France, some thousands of whom belonged to the industrial classes, and settled in England and Germany, where their descendants still remain. They introduced the manufacture of crystal chandeliers, and founded our Spitalfields silk industry, and other trades till then little practised in England.
The beautiful silver furniture at Knole belongs to this time, having been made for one of the Earls of Dorset, in the reign of James II. The illustration is from a photograph taken by Mr. Corke, of Sevenoaks. Electrotypes of the originals are in the South Kensington Museum. From two other suites at Knole, consisting of a looking glass, a table, and a pair of torchères, in the one case of plain walnut wood, and in the other of ebony with silver mountings, it would appear that a toilet suite of furniture of the time of James II. generally consisted of articles more or less costly, according to circumstances, but of a similar pattern to those shewn in the illustration. The silver table bears the English Hall mark of the reign.
Specimens of English furniture, dating from about 1680 to 1700, distinctly shew the influence of Flemish design. The Stadtholder, King William III., with his Dutch friends, imported many of their household gods, and our English craftsmen seem to have copied these very closely. The chairs and settees in the South Kensington Museum, and at Hampton Court Palace, have the shaped back, with a wide inlaid or carved upright bar; the cabriole leg and the carved shell ornament on the knee of the leg, and on the top of the back, which are still to be seen in many of the old Dutch houses.
There are a few examples of furniture of this date, which it is almost impossible to distinguish from Flemish, but in some others there is a characteristic decoration in marqueterie, which may be described as a seaweed scroll in holly or box wood, inlaid on a pale walnut ground. A good example of this is to be seen in the upright "grandfather's clock" in the South Kensington Museum, the effect being a pleasing harmony of color.
In the same collection there is also a walnut wood centre table, dating from about 1700, which has twisted legs and a stretcher, the top being inlaid with intersecting circles, relieved by the inlay of some stars in ivory.
As we have observed with regard to French furniture of this time, mirrors came more generally into use, and the frames were both carved and inlaid. There are several of these at Hampton Court Palace, all with bevelled edged plate glass; some have frames entirely of glass, the short lengths which make the frame having, in some cases, the joints covered[121] by rosettes of blue glass, and in others a narrow moulding of gilt work on each side of the frame. In one room (the Queen's Gallery) the frames are painted in colors and relieved by a little gilding.
The taste for importing old Dutch furniture, also lacquer cabinets from Japan, not only gave relief to the appearance of a well furnished apartment of this time, but also brought new ideas to our designers and workmen. Our collectors, too, were at this time appreciating the Oriental china, both blue and white, and colored, which had a good market in Holland, so that with the excellent silversmith's work then obtainable, it was possible in the time of William and Mary to arrange a room with more artistic effect than at an earlier period, when the tapestry and panelling of the the walls, a table, the livery cupboard previously described, and some three or four chairs, had formed almost the whole furniture of reception rooms.
The first mention of corner cupboards appears to have been made in an advertisement of a Dutch joiner in "The Postman" of March 8th, 1711; these cupboards, with their carved pediments, being part of the modern fittings of a room of the time of Queen Anne.
The oak presses common to this and earlier times are formed of an upper and lower part, the former sometimes being three sides of an octagon with the top supported by columns, while the lower half is straight, and the whole is carved with incised ornament. These useful articles of furniture, in the absence of wardrobes, are described in inventories of the time (1680-1720) as "press cupboards," "great cupboards," "wainscot," and "joyned cupboards."
The first mention of a "Buerow," as our modern word "Bureau" was then spelt, is said by Dr. Lyon, in his American book, "The Colonial Furniture of New England," to have occurred in an advertisement in "The Daily Post" of January 4th, 1727. The same author quotes Bailey's Dictionarium Britannicum, published in London, 1736, as defining the word "bureau" as "a cabinet or chest of drawers, or 'scrutoir' for depositing papers or accounts."
In the latter half of the eighteenth century these convenient pieces of furniture came into more general use, and illustrations of them as designed and made by Chippendale and his contemporaries will be found in the chapter dealing with that period.
Dr. Lyon also quotes from an American newspaper, "The Boston News Letter" of April 16th, 1716, an advertisement which was evidently published when the tall clocks, which we now call "grandfathers' clocks," were a novelty, and as such were being introduced to the American public. We have already referred to one of those which is in the South[122] Kensington Museum (date 1700), and no doubt the manufacture of similar clocks became more general during the first years of the eighteenth century. The advertisement alluded to runs, "Lately come from London, a parcel of very fine clocks—they go a week and repeat the hour when pulled" (a string caused the same action as the pressing of the handle of a repeating watch) "in Japan cases or walnut."
The style of decoration in furniture and woodwork which we recognise as "Queen Anne," apart from the marqueterie just described, appears, so far as the writer's investigations have gone, to be due to the designs of some eminent architects of the time. Sir James Vanbrugh was building Blenheim Place for the Queen's victorious general, and also Castle Howard. Nicholas Hawksmoor had erected St. George's, Bloomsbury, and James Gibbs, a Scotch architect and antiquary, St. Martin's-in-the-Fields, and the Royal Library at Oxford: a ponderous style characterises the woodwork interior of these buildings. We give an illustration of three designs for chimney pieces and overmantels by James Gibbs, the centre one of which illustrates the curved or "swan-necked" pediment, which became a favourite ornament about this time, until supplanted by the heavier triangular pediment which came in with "the Georges."
The contents of Hampton Court Palace afford evidence of the transition which took place in the design of woodwork and furniture from the time of William III. until that of George II. There is the Dutch chair with cabriole leg, the plain walnut card table also of Dutch design, which probably came over with the Stadtholder; then, there are the heavy draperies, and chairs almost completely covered by Spitalfields silk velvet, to be seen in the bedroom furniture of Queen Anne. Later on, as the heavy Georgian style predominated, there is the stiff ungainly gilt furniture, console tables with legs ornamented with the Greek key pattern badly applied, and finally, as the French school of design influenced our carvers, an improvement may be noticed in the tables and torchères, which, but for being a trifle clumsy, might pass for the work of French craftsmen of the same time. The state chairs, the bedstead, and some stools, which are said to have belonged to Queen Caroline, are further examples of the adoption of French fashion.
Nearly all writers on the subject of furniture and woodwork are agreed in considering that the earlier part of the period discussed in this chapter—namely, the seventeenth century, gives us the best examples of English work. As we have seen in noticing some of the earlier Jacobean examples already illustrated and described, it was a period marked by increased refinement of design, through the abandonment of the more grotesque and often coarse work of Elizabethan carving, and by soundness of construction and thorough workmanship.
THREE CHIMNEYPIECES.
DESIGNED BY JAMES GIBBS, ARCHITECT, IN 1739.
Oak furniture made in England during the seventeenth century, is still a credit to the painstaking craftsmen of those days, and even upholstered furniture, like the couches and chairs at Knole, after more than 250 years' service, are fit for use. When we come to deal with furniture of the present day, and the methods of production which are now in practice, a comparison will be made which must be to the credit of the Jacobean period.
In the foregoing chapters an attempt has been made to preserve, as far as possible, a certain continuity in the history of the subject matter of this work from the earliest times until after the Renaissance had been generally adopted in Europe. In this endeavour a greater amount of attention has been bestowed upon the furniture of a comparatively short period of English history, than upon that of other countries, but it is hoped that this fault will be forgiven by English readers.
It has now become necessary to interrupt this plan, and before returning to the consideration of European design and work, to devote a short chapter to those branches of the Industrial Arts connected with furniture, which flourished in China and Japan, in India, Persia, and Arabia, at a time anterior and subsequent to the Renaissance period in Europe.

PATTERN OF A CHINESE LAC SCREEN.
(In the South Kensington Museum.)
CHINESE FURNITURE: Probable source of artistic taste—Sir William Chambers quoted—Racinet's "Le Costume Historique"—Dutch Influence—The South Kensington and the late Duke of Edinburgh Collections—Processes of making Lacquer—Screens in the Kensington Museum. JAPANESE FURNITURE: Early History—Sir Rutherford Alcock and Lord Elgin—The Collection of the Shôgun—Famous Collections—Action of the present Government of Japan—Special characteristics. INDIAN FURNITURE: Early European influence—Furniture of the Moguls—Racinet's Work—Bombay Furniture—Ivory Chairs and Tables—Specimens in the India Museum. PERSIAN WOODWORK: Collection of Objets d'Art formed by General Murdoch Smith, R.E.—Industrial Arts of the Persians—Arab influence—South Kensington Specimens. SARACENIC WOODWORK: Oriental customs—Specimens in the South Kensington Museum of Arab Work—M. d'Aveune's Work.
 E have been unable to discover when the
Chinese first began to use state or domestic
furniture. Whether, like the ancient Assyrians
and Egyptians, there was an early civilization
which included the arts of joining, carving,
and upholstering, we do not know; most
probably there was; and from the plaster
casts which one sees in our Indian Museum,
of the ornamental stone gateways of Sanchi
Tope, in Bhopal, Central India, it would
appear that, in the early part of our
Christian era, the carvings in wood of their
neighbours and co-religionists, the Hindoos,
represented figures of men and animals in
the woodwork of sacred buildings or palaces.
The marvellous dexterity in manipulating
wood, ivory and stone which we recognize in
the Chinese of to-day, is probably inherited from their early ancestors.
E have been unable to discover when the
Chinese first began to use state or domestic
furniture. Whether, like the ancient Assyrians
and Egyptians, there was an early civilization
which included the arts of joining, carving,
and upholstering, we do not know; most
probably there was; and from the plaster
casts which one sees in our Indian Museum,
of the ornamental stone gateways of Sanchi
Tope, in Bhopal, Central India, it would
appear that, in the early part of our
Christian era, the carvings in wood of their
neighbours and co-religionists, the Hindoos,
represented figures of men and animals in
the woodwork of sacred buildings or palaces.
The marvellous dexterity in manipulating
wood, ivory and stone which we recognize in
the Chinese of to-day, is probably inherited from their early ancestors.
Sir William Chambers travelled in China in the early part of the eighteenth century. It was he who introduced "the Chinese style" into furniture and decoration, which was adopted by Chippendale and other[126] makers, as will be noticed in the chapter dealing with that period of English furniture. He gives us the following description of the furniture he found in "The Flowery Land."
"The movables of the saloon consist of chairs, stools, and tables; made sometimes of rosewood, ebony, or lacquered work, and sometimes of bamboo only, which is cheap, and, nevertheless, very neat. When the movables are of wood, the seats of the stools are often of marble or porcelain, which, though hard to sit on, are far from unpleasant in a climate where the summer heats are so excessive. In the corners of the rooms are stands four or five feet high, on which they set plates of citrons, and other fragrant fruits, or branches of coral in vases of porcelain, and glass globes containing goldfish, together with a certain weed somewhat resembling fennel; on such tables as are intended for ornament only they also place the little landscapes, composed of rocks, shrubs, and a kind of lily that grows among pebbles covered with water. Sometimes, also, they have artificial landscapes made of ivory, crystal, amber, pearls, and various stones. I have seen some of these that cost over 300 guineas, but they are at least mere baubles, and miserable imitations of Nature. Besides these landscapes they adorn their tables with several vases of porcelain, and little vases of copper, which are held in great esteem. These are generally of simple and pleasing forms. The Chinese say they were made two thousand years ago, by some of their celebrated artists, and such as are real antiques (for there are many counterfeits) they buy at an extravagant price, giving sometimes no less than £300 sterling for one of them.
"The bedroom is divided from the saloon by a partition of folding doors, which, when the weather is hot, are in the night thrown open to admit the air. It is very small, and contains no other furniture than the bed, and some varnished chests in which they keep their apparel. The beds are very magnificent; the bedsteads are made much like ours in Europe—of rosewood, carved, or lacquered work; the curtains are of taffeta or gauze, sometimes flowered with gold, and commonly either blue or purple. About the top a slip of white satin, a foot in breadth, runs all round, on which are painted, in panels, different figures—flower pieces, landscapes, and conversation pieces, interspersed with moral sentences and fables written in Indian ink and vermilion."
From old paintings and engravings which date from about the fourteenth or fifteenth century, one gathers an idea of such furniture as existed in China and Japan in earlier times. In one of these, which is reproduced in Racinet's "Le Costume Historique," there is a Chinese princess reclining on a sofa which has a frame of black wood, visible,[127] and slightly ornamented; it is upholstered with rich embroidery, for which these artistic people seem to have been famous from a very early period. A servant stands by her side to hand her the pipe of opium with which the monotony of the day was varied—one arm rests on a small wooden table or stand which is placed on the sofa, and which holds a flower vase and a pipe stand. On another old painting two figures are seated on mats playing a game which resembles draughts, the pieces being moved about on a little table with black and white squares like a modern chessboard, with shaped feet to raise it a convenient height for the players; on the floor, cups of tea stand ready at hand. Such pictures are generally ascribed to the fifteenth century, the period of the great Ming dynasty, which appears to have been the time of an improved culture and taste in China.
From this time and a century later (the sixteenth) also date those beautiful cabinets of lacquered wood enriched with ivory, mother-of-pearl, with silver and even with gold, which have been brought to England occasionally; but genuine specimens of this, and of the seventeenth century, are very scarce and extremely valuable.
The older Chinese furniture which one sees generally in Europe dates from the eighteenth century, and was made to order and imported by the Dutch; this explains the curious combination to be found of Oriental and European designs; thus there are screens with views of Amsterdam and other cities copied from paintings sent out for the purpose, while the frames of the panels are of carved rosewood of the fretted bamboo pattern, characteristic of the Chinese. Elaborate bedsteads, tables, and cabinets were also made, with panels of ash stained a dark color, and ornamented with hunting scenes, in which the representations of men and horses are of ivory, or sometimes with ivory faces and limbs, and the clothes chiefly of a brown colored wood.
In a beautiful table in the South Kensington Museum, which is said to have been made in Cochin-China, mother-of-pearl is largely used and produces a rich effect.
The furniture brought back by the late Duke of Edinburgh from China and Japan is of the usual character imported, and the remarks hereafter made on Indian or Bombay furniture apply equally to this adaptation of Chinese detail to European designs.
The most highly prized work of China and Japan in the way of decorative furniture is the beautiful lacquer work, and in the notice on French furniture of the eighteenth century, in a subsequent chapter, we shall see that the process was adopted in Holland, France, and England with more or less success.
It is worth while, however, to allude to it here a little more fully.
The process as practised in China is thus described by M. Jacquemart:—
"The wood when smoothly planed is covered with a sheet of thin paper or silk gauze, over which is spread a thick coating made of powdered red sandstone and buffalo's gall. This is allowed to dry, after which it is polished and rubbed with wax, or else receives a wash of gum water, holding chalk in solution. The varnish is laid on with a flat brush, and the article is placed in a damp drying room, whence it passes into the hands of a workman, who moistens and again polishes it with a piece of very fine grained soft clay slate, or with the stalks of the horse-tail or shave grass. It then receives a second coating of lacquer, and when dry is once more polished. These operations are repeated until the surface becomes perfectly smooth and lustrous. There are never applied less than three coatings and seldom more than eighteen, though some old Chinese and some Japan ware are said to have received upwards of twenty. As regards China, this seems quite exceptional, for there is in the Louvre a piece with the legend 'lou-tinsg,' i.e., six coatings, implying that even so many are unusual enough to be worthy of special mention."
There is as much difference between different kinds and qualities of lac as between different classes of marqueterie. The most highly prized is the LACQUER ON GOLD GROUND, and the first specimens of this work which reached Europe during the time of Louis XV. were presentation pieces from the Japanese Princes to some of the Dutch officials. This lacquer on gold ground is rarely found in furniture, and only as a rule in some of those charming little boxes, in which the luminous effect of the lac is heightened by the introduction of silver foliage on a minute scale, or of tiny landscape work and figures charmingly treated, partly with dull gold, and partly with gold highly burnished. Small placques of this beautiful ware were used for some of the choicest pieces of furniture made for Marie Antoinette, and mounted by Gouthière.
AVANTURINE lacquer closely imitates in color the sparkling mineral from which it takes its name, and a less highly finished preparation of it is used as a lining for the small drawers of cabinets. Another lacquer has a black ground, on which landscapes delicately traced in gold stand out in charming relief. Such pieces also were used by Riesener and mounted by Gouthière in some of the most costly furniture made for Marie Antoinette; specimens of such furniture are in the Louvre. It is this kind of lacquer, in varying qualities, that is usually found in cabinets, folding screens, coffers, tables, étagéres, and other ornamental articles. Enriched with inlay[129] of mother-of-pearl, the effect of which is in some cases heightened and rendered more effective by transparent coloring on its reverse side, as in the case of a bird's plumage or of those beautiful blossoms which both Chinese and Japanese artists can represent so faithfully.
A very remarkable screen in Chinese lacquer of later date is in the South Kensington Museum; it is composed of twelve folds, each ten feet high, and measuring when fully extended twenty-one feet. This screen is very beautifully decorated on both sides with incised and raised ornaments painted and gilt on black ground, with a rich border ornamented with representations of sacred symbols and various other objects. The price paid for it was £1,000. There are also in the Museum some very rich chairs of modern Chinese work, in brown wood, probably teak, very elaborately inlaid with mother-of-pearl; they were exhibited in Paris in 1867.
Of the very early history of Japanese industrial arts we know but little. We have no record of the kind of furniture which Marco Polo found when he travelled in Japan in the thirteenth century; and until the Jesuit missionaries obtained a footing in the sixteenth century, and sent home specimens of native work, there was probably very little of Japanese manufacture which found its way to Europe. The beautiful lacquer work of Japan, which dates from the end of the sixteenth and the following century, leads us to suppose that a long period of probation must have occurred before these processes, which were probably learned from the Chinese, could have been so thoroughly mastered.
Of furniture—with the exception of the cabinets, chests, and boxes, large and small—of this famous lac, there appears to have been little. Until the Japanese developed a taste for copying European customs and manners, the habit seems to have been to sit on mats and to use small tables raised a few inches from the ground. Even the bedrooms contained no bedsteads, but a light mattress served for bed and bedstead.
The process of lacquering has already been described, and in the chapter on French furniture of the eighteenth century it will be seen how specimens of this decorative material reached France by way of Holland, and were mounted into the "meubles de luxe" of that time. With this exception, and that of the famous collection of porcelain in the Japan Palace at Dresden, probably but little of the Art products of this artistic people had been exported until the country was opened up by the expedition of Lord Elgin and Commodore Perry, in 1858-9, and subsequently by the antiquarian knowledge and research of Sir Rutherford Alcock, who has contributed so much to our knowledge of Japanese Industrial Art; indeed, it is scarcely too much to say, that so far as[130] England is concerned, he was the first to introduce the products of the Empire of Japan.

JAPANESE CABINET OF RED CHASED LACQUER-WORK.
XVII. TO XVIII. CENTURY.
The Revolution, and the break up of the feudal system which had existed in that country for some eight hundred years, ended by placing the Mikado on the throne. There was a sale in Paris, in 1867, of the famous collection of the Shôgun, who had sent his treasures there to raise funds for the civil war in which he was then engaged with the Daimio. This was followed by the exportation of other fine native productions to Paris and London; but the supply of old and really fine specimens has, since about 1874, almost ceased, and, in default, the European markets have become flooded with articles of cheap and inferior workmanship, imported to meet the modern demand. The present Government of Japan, anxious to recover many of the masterpieces which were[131] produced in the best time, under the patronage of the native princes of the old régime, have established a museum at Tokio, where many examples of fine lacquer work, which had been sent to Europe for sale, have been placed after repurchase, to serve as examples for native artists to copy, and to assist in the restoration of the ancient reputation of Japan.
There is in the South Kensington Museum a very beautiful Japanese chest of lacquer work made about the beginning of the seventeenth century, the best time for Japanese Art; it formerly belonged to Napoleon I., and was purchased at the Hamilton Palace Sale for £722: it is some 3ft. 3in. long and 2ft. 1in. high, and was intended originally as a receptacle for sacred Buddhist books. There are, most delicately worked on to its surface, views of the interior of one of the Imperial Palaces of Japan, and a hunting scene. Mother-of-pearl, gold, silver, and avanturine, are all used in the enrichment of this beautiful specimen of inlaid work, and the lock plate is a representative example of the best kind of metal work as applied to this purpose.
The late Duke of Saxe-Coburg had several fine specimens of Chinese and Japanese lacquer work in his collection, about the arrangement of which the writer had the honour of advising His Royal Highness, when it arrived some years ago at Clarence House. The earliest specimen is a reading desk, presented to him by the Mikado, with a slope for a book, much resembling an ordinary bookrest, but charmingly decorated with lacquer in landscape subjects on the flat surfaces, while the smaller parts are diapered with flowers and quatrefoils in relief of lac and gold. This is of the sixteenth century. The collections of the Earl of Elgin and Kincardine, Sir Rutherford Alcock, K.C.B., Mr. Salting, Viscount Gough, and other well-known amateurs, contain some excellent examples of the best periods of Japanese Art work of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.
The grotesque carving of the wonderful dragons and marvellous monsters introduced into furniture made by the Chinese and Japanese, and especially in the ornamental woodwork of the Old Temples, is thoroughly peculiar to those masters of elaborate design and skilful manipulation: and the low rate of remuneration, compared with our European notions of wages, enables work to be produced that would be impracticable under any other conditions. In comparing the ornamentation on Chinese with that of Japanese furniture, it may be said that more eccentricity is effected by the latter than by the former in their designs and general decoration. The Japanese joiner is unsurpassed, and much of the lattice work, admirable in design and workmanship, is so quaint and intricate that only by close examination can it be distinguished from finely cut fret work.
European influence upon Indian Art and manufactures has been of long duration. It was first exercised by the Portuguese and Dutch in the early days of the United East India Company, afterwards by the French, who established a trading company there in 1664, and lastly by the English, the first charter of the old East India Company dating as far back as 1600. Thus European taste dominated almost everything of an ornamental character until it became difficult to find a decorative article the design of which did not in some way or other shew the predominance of European influence over native conception. Therefore it becomes important to ascertain what kind of furniture, limited as it was, existed in India during the period of the Mogul Empire, which lasted from 1505 to 1739, when the invasion of the Persians under Kouli Khan destroyed the power of the Moguls. The country formerly subject to them was then divided among sundry petty princes.
The throne and State chairs used by the Moguls were rich with elaborate gilding; the legs or supports were sometimes of turned wood, with some of the members carved; the chair was formed like an hour glass, or rather like two bowls reversed, with the upper part extended to form a higher back to the seat. In M. Racinet's sumptuous work, "Le Costume Historique," published in Paris in 20 volumes (1876), there are reproduced some old miniatures from the collection of M. Ambroise Didot. These represent—with all the advantages of the most highly finished printing in gold, silver, and colours—portraits of these native sovereigns seated on their State chairs, with the umbrella, as a sign of royalty. The panels and ornaments of the thrones are picked out with patterns of flowers, sometimes detached blossoms, sometimes the whole plant; the colors are generally bright red and green, while the ground of a panel or the back of a chair is in silver, with arabesque tracery, the rest of the chair being entirely gilt. The couches are rectangular, with four turned and carved supports, some eight or ten inches high, and also gilt. With the exception of small tables, which could be carried into the room by slaves, and used for the light refreshments customary to the country, there was no other furniture. The ladies of the harem are represented as being seated on sumptuous carpets, and the walls are ornamented with gold and silver and color, a style of decoration very well suited to the arched openings, carved and gilt doors, and brilliant costumes of the occupants of these Indian palaces.
After the break up of the Mogul power, the influence of Holland, France, and England brought about a mixture of taste and design which[133] with the concurrent alterations in manners and customs, gradually led to the production of what is now known as the "Bombay Furniture." The patient, minute carving of Indian design applied to utterly uncongenial Portuguese or French shapes of chairs and sofas, or to the familiar round or oval table, carved almost beyond recognition, are instances of this style. One sees these occasionally in the house of an Anglo-Indian, who has employed native workmen to make some of this furniture for him; the European chairs and tables having been given as models, while the details of the ornament have been left to native taste. There are in the Indian Museum at South Kensington several examples of this Bombay furniture, and also some of Cingalese manufacture.
It is scarcely part of our subject to allude to the same kind of influence which has spoiled the quaint bizarre effect of native design and workmanship in silver, in jewellery, in carpets, embroideries, and in pottery, which was so manifest in the contributions sent to South Kensington at the Colonial Exhibition, 1886.
In the Jones Collection at South Kensington Museum, there are two carved ivory chairs and a table, the latter gilded, the former partly gilded, which are a portion of a set taken from Tippo Sahib at the storming of Seringapatam. Warren Hastings brought them to England, and they were given to Queen Charlotte. After her death the set was divided: Lord Londesborough purchased part of it, and this portion is now on loan at the Bethnal Green Museum.
Queen Victoria had also amongst her numerous Jubilee presents some very handsome ivory furniture of Indian workmanship, which may be seen at Windsor Castle. These, however, as well as the Jones Collection examples, though thoroughly Indian in character as regards the treatment of scrolls, flowers, and foliage, shew unmistakably the influence of French taste in their general form and composition. Articles, such as boxes, stands for gongs, etc., are to be found carved in sandal wood, and in dalburgia, or black wood, with rosewood mouldings; and a peculiar characteristic of this Indian decoration, sometimes applied to such small articles of furniture, is the coating of the surface of the wood with red lacquer, the plain parts taking a high polish while the carved enrichment remains dull. The effect of this is precisely that of the article being made of red sealing wax, and frequently the minute pattern of the carved ornament and its general treatment tend to give an idea of an impression made in the wax by an elaborately cut die. The casket illustrated on page 134 is an example of this treatment. It was exhibited in 1851.
The larger examples of Indian carved woodwork are of teak; the finest and most characteristic specimens within the writer's knowledge[134] are the two folding doors which were sent as a present to the Indian Government, and are in the Indian Museum. They are of seventeenth century work, and are said to have enclosed a library at Kerowlee. While the door frames are of teak, with the outer frames carved with bands of foliage in high relief, the doors themselves are divided into panels of fantastic shapes, and yet so arranged that there is just sufficient regularity to please the eve. Some of these panels are carved and enriched with ivory flowers, others have a rosette of carved ivory in the centre, and pieces of talc with green and red color underneath, a decoration also found in some Arabian work. It is almost impossible to convey by words an adequate description of these doors; they should be carefully examined as examples of genuine native design and workmanship. Mr. Pollen has concluded a somewhat detailed account of them by saying:—"For elegance of shape and proportion, and the propriety of the composition of the frame and sub-divisions of these doors, their mouldings and their panel carvings and ornaments, we can for the present name no other example so instructive. We are much reminded by this decoration of the pierced lattices at the S. Marco in Venice."
CASKET OF INDIAN LACQUER WORK.
There is in the Indian Museum another remarkable specimen of native furniture—namely, a chair of the purest beaten gold of octagonal shape, and formed of two bowls reversed, decorated with acanthus and lotus in repousée ornament. This is of eighteenth century workmanship, and was formerly the property of Runjeet Sing. The precious metal is thinly laid on, according to the Eastern method, the wood underneath the gold taking all the weight. This throne was to have been used at the opening of the Imperial Institute by Queen Victoria, but at the last moment another seat was selected.
There is also a collection of plaster casts of portions of temples and palaces from a very early period until the present time, several having been sent over as a loan to the Indian and Colonial Exhibition of 1886.
A careful observation of the ornamental details of these casts leads us to the conclusion that the Byzantine style, which was dominant throughout the more civilized portion of Asia during the power of the Romans, had survived the great changes of the Middle Ages. As native work became subject more or less to the influence of the Indo-Chinese carvers of deities on the one side, and of the European notions of the Portuguese pioneers of discovery on the other, a fashion of decorative woodwork was arrived at which can scarcely be dignified by the name of a style, and which it is difficult to describe. Sir George Birdwood, in his work on Indian Art, points out that, about a hundred years ago, Indian designs were affected by the immigration of Persian designers and workmen. The result of this influence is to be seen in the examples in the Museum, a short notice of which will conclude these remarks on Indian work.
The copy in shishem wood of a carved window at Amritzar, in the Punjaub, with its overhanging cornice, ornamental arches, supported by pillars, and the surface, covered with small details of ornament, is a good example of the sixteenth and seventeenth century work. The façades of dwelling houses in teak wood, carved, and still bearing the remains of paint with which part of the carving was picked out, represent the work of the contemporary carvers of Ahmedabad, famous for its woodwork.
Portions of a lacquer work screen similar in appearance to embossed gilt leather, with the pattern in gold, on a ground of black or red, and the singular Cashmere work, called "mirror mosaic," give us a good idea of the Indian decoration of the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries. This effective decoration is produced by little pieces of looking glass being introduced into the small geometrical patterns of the panels; these, when joined together, form a very rich ceiling.
The bedstead of King Theebaw, brought from Mandalay, is an example of this mixture of glass and wood, which can be made extremely[136] effective. The wood is carved and gilt to represent the gold setting of numerous precious stones, which are counterfeited by small pieces of looking-glass and variously-colored pieces of transparent glass.
Some of King Edward's (at the time Prince of Wales) presents—namely, chairs with carved lions forming arms; tables of shishem wood, inlaid with ebony and ivory, shew the European influence we have alluded to.
Amongst the modern ornamental articles in the Museum are many boxes, pen trays, writing cases, and even photographic albums, of wood and ivory mosaic work, the inlaid patterns being produced by placing together strips of tin wire, sandal wood, ebony, and of ivory, white, or stained green: these strips, when bound into a rod, either triangular or hexagonal, are cut into small sections, and then inlaid into the surface of the article to be decorated.
Papier maché and lacquer work are also frequently found in small articles of furniture; and the collection of drawings by native artists attest the high skill in design and execution attained by Indian craftsmen.
The Persians have from time immemorial been an artistic people, and their style of Art throughout successive generations has varied but little.
Major-General Murdoch Smith, R.E., the present Director of the branch of the South Kensington Museum in Edinburgh, who resided for some years in Persia, and had the assistance when there of M. Richard (a well-known French antiquary), made a collection of objets d'art some years ago for the Science and Art Department, which is now in the Kensington Museum, but it contains comparatively little that can be actually termed furniture; and it is extremely difficult to meet with important specimens of ornamental woodwork of native workmanship. Those in the Museum, and in other collections, are generally small ornamental articles. The chief reason for this is, doubtless, that little timber is to be found in Persia, except in the Caspian provinces, where, as Mr. Benjamin has told us in "Persia and the Persians," wood is abundant; and the Persian architect, taking advantage of his opportunity, has designed his houses with wooden piazzas—not found elsewhere—and with "beams, lintels, and eaves quaintly, sometimes elegantly, carved, and tinted with brilliant hues." Another feature of the decorative woodwork in this part of Persia is that produced by the large latticed windows, which are well adapted to the climate.
DOOR.
Of carved sandal wood, from Travancore. Indian Museum, South Kensington.
PERIOD: PROBABLY LATE XVIII. CENTURY.
In the manufacture of textile fabrics—notably, their famous carpets of Yezd and Ispahan, and their embroidered cloths in hammered and engraved metal work, and formerly in beautiful pottery and porcelain—they have excelled, and good examples will be found in the South Kensington Museum. It is difficult to find a representative specimen of Persian furniture except a box or a stool; and the illustration of a brass incense burner is, therefore, given to mark the method of native design, which was adopted in a modified form by the Persians from their Arab conquerors.

INCENSE BURNER OF ENGRAVED BRASS.
In the South Kensington Museum.
This method of design has one or two special characteristics which are worth noticing. One of these was due to the teaching of Mahomet forbidding animal representation in design—a rule which in later work has[138] been relaxed; another was the introduction of mathematics into Persia by the Saracens, which led to the adoption of geometrical patterns in design; and a third, the development of "Caligraphy" into a fine art, which has resulted in the introduction of a text, or motto, into so many of the Persian designs of decorative work. The combination of these three characteristics was the origin of the "Arabesque" form of ornament, which, in artistic nomenclature, occurs so frequently.
The general method of decorating woodwork is similar to the Indian method, and consists in either inlaying brown wood (generally teak) with ivory or pearl in geometrical patterns, or in covering the wooden box, or manuscript case, with a coating of lacquer, somewhat similar to the Chinese or Japanese preparations. On this groundwork some good miniature painting was executed, the colors being, as a rule, red, green, and gold, with black lines to give force to the design.
The author of "Persia and the Persians," already quoted, had, during his residence in the country, as American Minister, great opportunities of observation, and in his chapter entitled "A Glance at the Arts of Persia," he has said a good deal of this mosaic work. Referring to the scarcity of wood in Persia, he says: "For the above reason one is astonished at the marvellous ingenuity, skill and taste developed by the art of inlaid work, or mosaic in wood. It would be impossible to exceed the results achieved by the Persian artisans, especially those of Shiraz, in this wonderful and difficult art.... Chairs, tables, sofas, boxes, violins, guitars, canes, picture frames, almost every conceivable object, in fact, which is made of wood, may be found overlaid with an exquisite casing of inlaid work, so minute sometimes that thirty-five or forty pieces may be counted in the space of a square eighth of an inch. I have counted four hundred and twenty-eight distinct pieces on a square inch of a violin, which is completely covered by this exquisite detail of geometric designs, in mosaic."
Mr. Benjamin—who, it will be noticed, is somewhat too enthusiastic over this kind of mechanical decoration—also observes that, while the details will stand the test of a magnifying glass, there is a general breadth in the design which renders it harmonious and pleasing if looked at from a distance.
In the South Kensington Museum there are several specimens of Persian lacquer work, which have very much the appearance of those papier maché articles that used to be so common in England some forty years ago, save that the decoration is, of course, of Eastern character.
Of seventeenth century work, there is also a fine coffer, richly inlaid with ivory, of the best description of Persian design and[139] workmanship of this period, which was about the zenith of Persian Art during the reign of Shah Abbas. The numerous small articles of what is termed Persian marqueterie, are inlaid with tin wire and stained ivory, on a ground of cedar wood, very similar to the same kind of ornamental work already described in the Indian section of this chapter. These were purchased at the Paris Exhibition in 1867.
Persian Art of the present day may be said to be in a state of transition, owing to the introduction and assimilation of European ideas.
The changes of fashion in Western, as contrasted with Eastern, countries are comparatively rapid. In the former, the record of two or three centuries presents a history of great and well-defined alterations in manners, customs, and, therefore, in furniture: while the more conservative Oriental has been content to reproduce, from generation to generation, the traditions of his forefathers; and we find that, from the time of the Moorish conquest and spread of Arabesque design, no radical change in Saracenic Art occurred until French and English energy and enterprise forced European fashions into Egypt. As a consequence, the original quaintness and orientalism natural to the country, are being gradually replaced by buildings, decoration, and furniture of European fashion.
The carved pulpit, from a mosque in Cairo, which is in the South Kensington Museum, was made for Sultan Kaitbeg, 1468-96. The side panels, of geometrical pattern, though much injured by time and wear, shew signs of ebony inlaid with ivory, and of painting and gilding; they are good specimens of the kind of work. The two doors, also from Cairo, the oldest parts of which are just two hundred years earlier than the pulpit, are exactly of the same style, and, so far as appearances go, might just as well be taken for two hundred years later, so conservative was the Saracenic treatment of decorative woodwork for some four or five centuries. Pentagonal and hexagonal mosaics of ivory, with little mouldings, of ebony dividing the different panels, the centres of eccentric shapes of ivory or rosewood carved with minute scrolls, combine to give these elaborate doors a very rich effect, and remind one of the work still to be seen at the Alhambra, in Granada.
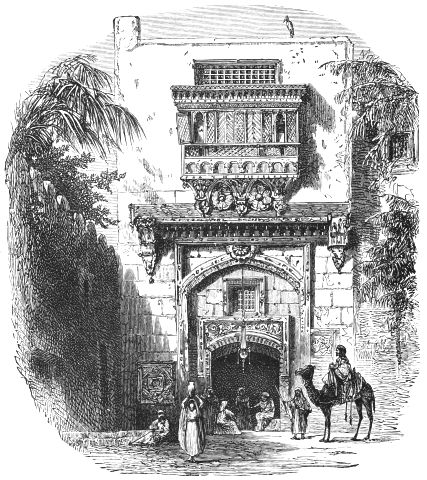

GOVERNOR'S PALACE, MANFALÛT.
Shewing a Window of Arab Lattice Work, similar to that of the Damascus Room in the South Kensington Museum.
The Science and Art Department has been fortunate in securing from the St. Maurice and Dr. Meymar Collections, a great many specimens which are well worth examination. The most remarkable is a complete room brought from a house in Damascus, which is fitted up in the Oriental style, and gives one a good idea of an Eastern interior. The walls are decorated in color and gold; the spaces are divided by flat pilasters; and there are recesses, or cupboards, for the reception of pottery, quaintly formed vessels, and pots of brass. Oriental carpets, octagonal tables, such as the one which ornaments the initial letter of this chapter, hookas, incense burners, and cushions furnish the apartment; while the lattice window is an excellent representation of the "Mesherabijeh," or lattice work with which we are familiar since so much has been imported by Egyptian travellers. In the upper panels of the lattice there are inserted pieces of colored glass, and, looking outwards towards the light, the effect is very pretty. The date of this room is 1756, which appears at the foot of an Arabic inscription, of which a translation is appended to the exhibit. It commences:—"In the Name[141] of God, the Merciful, the Compassionate," and concludes, "Pray, therefore, to Him morning and evening."
A number of bosses and panels, detached from their original framework, are also to be seen, and are good specimens of Saracenic design. A bedstead, with inlay of ivory and numerous small squares of glass, under which are paper flowers, is also a fair sample of native work.
SPECIMEN OF SARACENIC PANELLING OF CEDAR, EBONY, AND IVORY.
(In the South Kensington Museum.)
The illustration on page 142 is of a carved wood door from Cairo, considered by the South Kensington authorities to be of Syrian work. It shews the turned spindles, which the Arabs generally introduce into their ornamental woodwork; and the carving of the vase of flowers is a good specimen of its kind. The date is about the seventeenth century.
For those who would gain an extended knowledge of Saracenic or Arabian Art industry, "L'Art Arabe," by M. Prisse d'Aveunes, should be consulted. There will be found in this work many carefully-prepared illustrations of the cushioned seats, the projecting balconies of the lattice work already alluded to, of octagonal inlaid tables, and such other articles of furniture as were used by the Arabs. The South Kensington Handbook, "Persian Art," by Major-General Murdoch Smith, R.E., is also a very handy and useful work in a small compass.
While discussing Saracenic or Arab furniture, it is worth noticing that our word "sofa" is of Arab derivation, the word "suffah" meaning "a place or couch for reclining before the door of Eastern houses." In Skeat's Dictionary the word is said to have first occurred in the "Guardian," in the year 1713, and the phrase is quoted from No. 167 of that old periodical of the day—"He leapt off from the sofa on which he sat."

A CARVED DOOR OF SYRIAN WORK.
(South Kensington Museum.)
From the same source the word "ottoman," which Webster defines as "a stuffed seat without a back, first used in Turkey," is obviously obtained, and the modern low-seated upholsterer's chair of to-day is[143] doubtless the development of a French adaptation of the Eastern cushion or "divan," this latter word having become applied to the seats which furnished the hall or council chamber in an Eastern palace, although its original meaning was probably the council or "court" itself, or the hall in which such was held.
Thus do the habits and tastes of different nations act and re-act upon each other. Western peoples have carried eastward their civilization and their fashions, influencing Arts and industries with their restless energy, and breaking up the crust of Oriental apathy and indolence; and have brought back in return the ideas gained from an observation of the associations and accessories of Eastern life, to adapt them to the requirements and refinements of European luxury.
SHAPED PANEL OF SARACENIC WORK IN CARVED BONE OR IVORY.

BOULE ARMOIRE.
Designed by Le Brun, formerly in the "Hamilton Palace" Collection, and purchased (Wertheimer) for £12,075 the pair.
PERIOD: LOUIS XIV.
PALACE OF VERSAILLES: "Grand" and "Petit Trianon"—The three Styles of Louis XIV., XV., and XVI.—Colbert and Lebrun—André Charles Boule and his Work—Carved and Gilt Furniture—The Regency and its Influence—Alteration in Condition of French Society—Watteau, Lancret, and Boucher. LOUIS XV. FURNITURE: Famous Ébenistes—Vernis Martin Furniture—Caffieri and Gouthière Mountings—Sêvres Porcelain introduced into Cabinets—Gobelins Tapestry—The "Bureau du Roi." LOUIS XVI. AND MARIE ANTOINETTE: The Queen's Influence—The Painters Chardin and Greuze—More simple Designs—Characteristic Ornaments of Louis XVI. Furniture—Riesener's Work—Gouthière's Mountings—Specimens in the Louvre—The Hamilton Palace Sale—French influence upon the design of furniture in other countries—The Jones Collection—Extract from the "Times."
 HERE is something so distinct in the
development of taste in furniture, marked
out by the three styles to which the three
monarchs have given the names of "Louis
Quatorze," "Louis Quinze," and "Louis
Seize," that it affords a fitting point for a
new departure.
HERE is something so distinct in the
development of taste in furniture, marked
out by the three styles to which the three
monarchs have given the names of "Louis
Quatorze," "Louis Quinze," and "Louis
Seize," that it affords a fitting point for a
new departure.
This will be evident to anyone who will visit, first the Palace of Versailles,[12] then the Grand Trianon, and afterwards the Petit Trianon. By the help of a few illustrations, such a visit in the order given, would greatly interest anyone having even a smattering of knowledge of the characteristic ornaments of these different periods. A careful examination would demonstrate how the one style gradually merged into that of its successor. Thus the massiveness and grandeur of the best Louis Quatorze meubles de luxe became, in their later development, too ornate and effeminate, with an elaboration of enrichment, culminating in the rococo style of Louis Quinze.
Then we find in the "Petit Trianon," and also in the Château of Fontainebleau, the purer taste of Marie Antoinette dominating the Art productions of her time, which reached their zenith, with regard to furniture, in the production of such elegant and costly examples as have been preserved to us in the beautiful work-table and secretaire—sold some years since at the dispersion of the Hamilton Palace Collection—and in some other specimens which may be seen in the Musée du Louvre, in the Jones Collection in the South Kensington Museum, and in other public and private Collections. Several illustrations of these examples will be found in this chapter.
We have to recollect that the reign of Louis XIV. was the time of the artists Berain, Lebrun, and, later in the reign, of Watteau, also of André Charles Boule, ciseleur et doreur du roi, and of Colbert, that admirable Minister of Finance, who knew so well how to second his royal master's taste for grandeur and magnificence. The Palace of Versailles bears throughout the stamp and impress of the majesty of le Grande Monarque; and the rich architectural ornament of the interior, with moulded, gilded, and painted ceilings, required the furnishing to be carried to an extent which had never been attempted previously.
Louis XIV. had judgment in his taste, and he knew that, to carry out his ideas of a royal palace, he must not only select suitable artists capable of control, but he must centralize their efforts. In 1664 Colbert founded the Royal Academy of Painting, Architecture, and Sculpture, into which designs of furniture were admitted. The celebrated Gobelins tapestry factory was also established; and it was here that the King collected together, and suitably housed, the different skilled producers of his furniture, placing them all under the control of his favourite artist, Lebrun, who was appointed director in 1667.
The most remarkable furniture artist of this time, for surely he merits such title, was Andre Charles Boulle, generally spelt Boule. He was born in 1642, and, therefore, was 25 years of age when Lebrun was appointed Art-director. He appears to have originated the method of ornamenting furniture which has since been associated with his name. This was to veneer his cabinets, pedestals, armoires, encoignures, clocks, and brackets with tortoise-shell, into which a cutting of brass was laid, the latter being cut out from a design, in which were harmoniously arranged scrolls, vases of flowers, satyrs, animals, cupids, swags of fruit and draperies. Fantastic compositions of a free Renaissance character constituted the panels; to which bold scrolls in ormolu formed fitting frames; while handsome mouldings of the same material gave a finish to the extremities. These ormolu mountings were gilt by an old-fashioned[147] process,[13] which left upon the metal a thick deposit of gold, and were cunningly chiselled by the skilful hands of Caffieri or his contemporaries.

BOULE ARMOIRE.
In the "Jones" Collection, S. Kensington Museum.
PERIOD: LOUIS XIV.
Boule subsequently learned to economise labour by adopting a similar process to that used by the marqueterie cutter; and by glueing together two sheets of brass, or white metal, and two of shell, and placing over them his design, he was then able to pierce the four layers by one cut of the bandsaw; this gave four exact copies of the design. The same process would be repeated for the reverse side, if, as with an armoire or a large cabinet, two panels, one for each door, right and left, were required; and then, when the brass, or white metal cutting was fitted into the shell so that the joins were imperceptible, he would have two right-hand and two left-hand panels. These would be positive and negative: in the former pair the metal would represent the figured design with the shell as groundwork, and the latter would have the shell as a design, with a ground of metal. The terms positive and negative are the writer's to explain the difference, but the technical terms are "first part" and "second part," or "Boule" and "counter." The former would be selected for the best part of the cabinet; for instance, the panels of the front doors, while the latter would be used for the ends or sides. An illustration of this plan of using all four cuttings of one design, occurs in the armoire No. 1026 in the Jones Collection, and in a great many other excellent specimens. The brass, or the white metal in the design, was then carefully and most artistically engraved; and the beauty of the engraving of Boule's finest productions is a great point of excellence, giving, as it does, a character to the design, and emphasizing its details. The mounting of the furniture in ormolu, of a rich and highly-finished character, completed the design. The Musée du Louvre is rich in examples of Boule's work: and there are some very good pieces in the Jones Collection, at Hertford House, and at Windsor Castle.
The illustration on page 144 is the representation of an armoire, which was, undoubtedly, executed by Boule from a design by Lebrun: it is one of a pair which was sold in 1882, at the Hamilton Palace sale, by Messrs. Christie, for £12,075. Another small cabinet, in the same collection, realised £2,310. The pedestal cabinet illustrated on page 148, from the Jones Collection, is very similar to the latter, and cost Mr. Jones £3,000. When specimens, of the genuineness of which there is no doubt, are offered for sale, they are sure to realize very high prices. The armoire in the Jones Collection, already alluded to (No. 1026), of which there is an illustration, cost Mr. Jones between £4,000 and £5,000.
In some of the best of Boule's cabinets, as, for instance, in the Hamilton Palace armoire (illustrated), the bronze gilt ornaments stand out in bold relief from the surface. In the Louvre there is one which has a figure of le Grand Monarque, clad in armour, with a Roman toga, and wearing the full bottomed wig of the time, which scarcely accords with the costume of a Roman general. The absurd combination which characterizes this affectation of the classic costume is also found in portraits of our George II.

PEDESTAL CABINET.
By Boule, formerly in Mr. Baring's Collection. Purchased by Mr. Jones for £3,000.
(South Kensington Museum.)
The masks, satyrs, and rams' heads, the scrolls of the foliage, are also very bold in specimens of this class of Boule's work; and the "sun"[149] (that is, a mask with rays of light radiating from it) is a very favourite ornament of this period.
Boule had four sons and several pupils; and he may be said to have founded a school of decorative furniture, which had its votaries and imitators now, as it had in its own time. The word one frequently finds misspelt "Buhl," and the term has come to represent any similar mode of decoration of furniture, no matter how meretricious or common it may be.
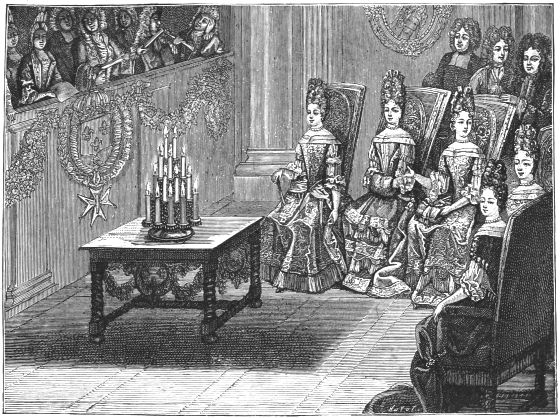

A CONCERT DURING THE REIGN OF LOUIS XIV.
(From a Miniature dated 1696.)
Later in the reign of Louis XIV., as other influences were brought to bear upon the taste and fashion of the day, this style of furniture became more ornate and showy. Instead of the natural color of the shell, either vermilion or gold leaf was placed underneath the transparent shell; the gilt mounts became less severe, and abounded with the curled endive ornament, which afterwards became thoroughly characteristic of the fashion of the succeeding reign; and the forms of the furniture itself followed the taste for a more free and flowing treatment; and it should be mentioned, in justice to Lebrun, that from the time of his death and the appointment of his successor, Mignard, a distinct decline in merit can be traced.
Contemporary with Boule's work, were the richly-mounted tables, having slabs of Egyptian porphyry, or Florentine marble mosaic; and marqueterie cabinets with beautiful mountings of ormolu, or gilt bronze. Commodes and screens were ornamented with Chinese lacquer, which had been imported by the Dutch and taken to Paris, after the French invasion of the Netherlands.
BOUDOIR FURNISHED IN THE TASTE THE LOUIS XIV. PERIOD.
About this time—that is, towards the end of the seventeenth century—the resources of designers and makers of decorative furniture were reinforced by the introduction of glass in larger plates than had been possible previously. Mirrors of considerable size were first made in Venice; these were engraved with figures and scrolls, and mounted in richly carved and gilt wood frames. Soon afterwards manufactories of mirrors, and of glass, in larger plates than before, were set up in England, near Battersea, and in France, at Tour la Ville, near Paris.[151] This novelty not only gave a new departure to the design of suitable frames in carved wood (generally gilt), but also to that of Boule work and marqueterie. It also led to a greater variety of the design for cabinets; and from this time we may date the first appearance of the "Vitrine," or cabinet with glass panels in the doors and sides, for the display of smaller objets d'art.
DECORATION OF A SALON IN LOUIS XIV. STYLE.
The chairs and sofas of the latter half of the reign of Louis Quatorze are exceedingly grand and rich. The suite of furniture for the state apartment of a prince, or wealthy nobleman, comprised a canapé, or sofa, and six fauteuils, or arm chairs, the frames carved with much spirit, or with "feeling," as it is technically termed, and richly gilt. The backs and seats were upholstered and covered with the already famous tapestry of Gobelins or Beauvais. A short account of these factories will be found in the Appendix.
Such a suite of furniture, in bad condition and requiring careful and very expensive restoration, was sold at Christie's some time ago for about £1,400, and it is no exaggeration to say that a really perfect suite, with carving and gilding at the best, and the tapestry not too much worn, if offered for public competition, would probably realize between £3,000 and £4,000.[14]
In the Appendix will be found the names of many artists in furniture of this time, and in the Jones Collection we have several very excellent specimens which can be easily referred to, and compared with others of the two succeeding reigns, whose furniture we are now going to consider.
As an example of the difference in both outline and detail which took place in design, let the reader notice the form of the Louis Quatorze commode vignetted for the initial letter of this chapter, and then turn to the lighter and more fanciful cabinets of somewhat similar shape, which will be found illustrated in the "Louis Quinze" section which follows this. In the Louis Quatorze cabinets the decorative effect, so far as the woodwork is concerned, was obtained first by the careful choice of suitable veneers, and then by joining four pieces in a panel, so that the natural figure of the wood runs from the centre, and then a banding of a darker wood forms a frame. An instance of this will also be found in the above-mentioned vignette.
When the old King died, at the ripe age of 77, the crown devolved on his great-grandson, then a child five years old, and therefore, a Regency became necessary; and this period of some eight years, until the death of Philip, Duke of Orleans, in 1723, when the King was declared to have attained his majority at the age of 13, is known as l'Epoch de la Régence, and is a landmark in the history of furniture.

BOULE COMMODE.
Probably made during the period of the Regency.
(Musée du Louvre.)
There was a great change about this period of French history in the social condition of the upper classes in France. The pomp and extravagance of the late monarch had emptied the coffers of the noblesse, and in order to recruit their finances, marriages became common which a decade or two before that time would hardly have been thought possible. Nobles of ancient lineage married the daughters of bankers and speculators, in order to supply themselves with the means of following the extravagant fashions of the day, and we find the wives of ministers of departments of State using their influence and power for the purpose of making money by gambling in stocks, and accepting bribes for concessions and contracts.

FRENCH SEDAN CHAIR.
(From an Engraving in the South Kensington Art Library.)
PERIOD: LOUIS XV.
PANEL FOR A SCREEN.
Painted by Watteau. PERIOD OF THE REGENCY.
It was a time of corruption, extravagance, licentiousness, and intrigue, and although one might ask what bearing this has upon the history of furniture, a little reflection shows that the abandonment of the great State receptions of the late King, and the pompous and gorgeous entertainments of his time, gave way to a state of society in which the boudoir became of far more importance than the salon, in the artistic furnishing of a fashionable house. Instead of the majestic grandeur of immense reception rooms and stately galleries, we have the elegance and prettiness of the boudoir; and as the reign of the young King advances, we find the structural enrichment of rooms more free, and busy with redundant ornament. The curved endive decoration, so common in carved woodwork and its imitation in "compo." of this period is seen everywhere; in the architraves, in the panel mouldings, in the frame of an overdoor, in the design of a mirror frame; doves, wreaths, Arcadian fountains, flowing scrolls, Cupids, and heads and busts of women terminating in foliage, are carved or moulded in relief, on the walls, the doors, and the alcoved recesses of the reception rooms, either gilded or[154] painted white; and pictures by Watteau, Lancret, or Boucher, and their schools, are appropriate accompaniments.[15]
CONSOLE TABLE, CARVED AND GILT.
(Collection of M. Double, Paris.)
The furniture was made to agree with this decorative treatment; couches and easy chairs were designed in more sweeping curves and on a smaller scale, the woodwork wholly or partially gilt and upholstered, not only with the tapestry of Gobelins, Beauvais, and Aubusson, but with soft colored silk brocades and brocatelles; light occasional chairs were enriched with mother-of-pearl or marqueterie; screens were painted with love scenes and representations of ladies and gentlemen who look as if they passed their entire existence in the elaboration of their toilettes or the exchange of compliments; the stately cabinet is modified into the bombé fronted commode, the ends of which curve outwards with a graceful sweep; and the bureau is made in a much smaller size, more highly decorated with marqueterie, and more fancifully mounted to suit the smaller and more effeminate apartment. The elegant cabinet, called Bouheur du jour (a little cabinet mounted on a table); the small round occasional table, called a guéridon; the encoignure, or corner cabinet; the étagère, or ornamental hanging cabinet with shelves; the three-fold screen, with each leaf a different height, and with shaped top, all date from this time. The chaise à porteur, or Sedan chair, on which so much work and taste were expended, became more ornate, so as to fall in with the prevailing fashion. Marqueterie became more fanciful.
The Louis Quinze cabinets were inlaid, not only with natural woods, but with veneers stained in different tints; and landscapes, interiors, baskets of flowers, birds, trophies, emblems of all kinds, and quaint fanciful conceits are pressed into the service of marqueterie decoration. The most famous artists in this decorative woodwork were Riesener, David Roentgen (generally spoken of as David), Pasquier, Carlin, Leleu, and others, whose names will be found in a list in the Appendix.

LOUIS XV. CARVED AND GILT "FAUTEUIL."
Upholstered with Beauvais tapestry. Subject from La Fontaine's Fables.
During the preceding reign, the Chinese lacquer-work then in use was imported from the East, the fashion for collecting which had set in ever since the Dutch had established a trade with China; and subsequently as the demand arose for smaller pieces of meubles de luxe, collectors had these articles taken to pieces, and the slabs of lacquer[156] mounted in panels to decorate the table, or cabinet, and to display the lacquer. Ébenistes, too, prepared such parts of woodwork as were desired to be ornamented in this manlier, and sent them to China to be coated with lacquer, a process which was then only known to the Chinese; but this delay and expense quickened the inventive genius of the European, and it was found that a preparation of gum and other ingredients applied again and again, and each time carefully rubbed down, produced a surface which was almost as lustrous and suitable for decoration as the original article. A Dutchman named Huygens was the first successful inventor of this preparation; and owing to the adroitness of his work, and of those who followed him and improved his process, one can only detect European lacquer from Chinese by noting certain trifling details in the costumes and foliage of decoration, not strictly Oriental in character.
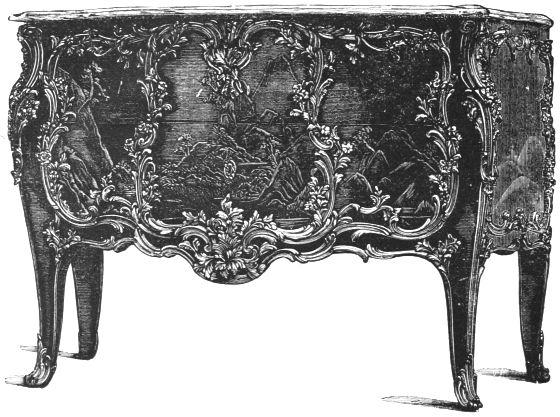

COMMODE.
With Panels of fine old Lacquer and Mountings by Caffieri.
(Jones Collection, S. Kensington Museum.)
PERIOD OF LOUIS XV.
About 1740-4 the Martin family had three manufactories of this peculiar and fashionable work, which became known as Vernis-Martin, or Martins' Varnish; and it is a singular coincidence that one of these was in the district of Paris then and now known as Faubourg Saint Martin. By a special decree a monopoly was granted in 1744 to Sieur Simon Etienne Martin[157] the younger, "To manufacture all sorts of work in relief and in the style of Japan and China." This was to last for twenty years; and we shall see that in the latter part of the reign of Louis XV., and in that of his successor, the decoration was not confined to the imitation of Chinese and Japanese subjects, but the surface was painted in the style of the decorative artist of the day, both in monochrome and in natural colors; such subjects as "Cupid Awakening Venus," "The Triumph of Galatea," "Nymphs and Goddesses," "Garden Scenes," and "Fêtes Champêtres," being represented in accordance with the taste of the period. It may be remarked in passing, that lacquer work was also made previous to this time in England. Several cabinets of "Old" English lac are included in the Strawberry Hill sale catalogue; and they were richly mounted with ormolu, in the French style; this sale took place in 1842. George Robins, so well known for his flowery descriptions, was the auctioneer; the introduction to the catalogue was written by Harrison Ainsworth.

COMMODE.
In Parqueterie, with massive mountings of Gilt Bronze, probably by Caffieri.
(Formerly in the Hamilton Palace Collection. Purchased (Wertheimer) £6,247 10s.)
LOUIS XV. PERIOD.
PART OF A SALON.
Decorated in the Louis Quinze style, shewing the carved and gilt Console Table and Mirror, with other enrichments, en suite.
The gilt bronze mountings of the furniture of this time became less massive and much more elaborate; the curled endive ornament was very much in vogue; the acanthus foliage followed the curves of the commode; busts and heads of women, cupids, satyrs terminating in foliage, suited the design and decoration of the more fanciful shapes; and Caffieri, who is the great master of this beautiful and highly ornate enrichment, introduced Chinese figures and dragons into his designs. The amount of spirit imparted into the chasing of this ormolu is simply marvellous—it has never been equalled, and could not be excelled. Time has now mellowed the color of the woodwork it adorns; and the tint of the gold with which it is overlaid, improved by the lights and shadows caused by the high relief of the work and the consequent darkening of the parts more depressed, while the more prominent ornaments have been rubbed bright from time to time, produces an effect which is exceedingly elegant and rich. One cannot wonder that connoisseurs are prepared to pay such large sums for genuine specimens, or that clever imitations are extremely costly to produce.
BUREAU DU ROI.
Made for Louis XV. by Riesener. Collection of "Mobilier National."
(From a pen and ink drawing by H. Evans.)
PERIOD: LOUIS XV.
Illustrations are given from some of the more notable examples of decorative furniture of this period, which were sold in 1882 at the celebrated Hamilton Palace sale, together with the sums they realised; also of specimens in the South Kensington Museum, in the Jones Collection.
We must also remember, in considering the meubles de luxe of this time, that in 1753 Louis XI. had made the Sêvres Porcelain Manufactory a State enterprise; and later, as that celebrated undertaking progressed, tables and cabinets were ornamented with plaques of the beautiful and choice páte tendre, the delicacy of which was admirably adapted to enrich the light and frivolous furnishing of the dainty boudoir of a Madame du Barri or a Madame Pompadour.
Another famous artist in the delicate bronze mountings of the day was Pierre Gouthière. He commenced work some years later than Caffieri, being born in 1740; and, like his senior fellow craftsman, did not confine his attention to furniture, but exercised his fertility of design, and his passion for detail, in mounting bowls and vases of jasper, of Sêvres and of Oriental porcelain. The character of his work is less forcible than that of Caffieri, and comes nearer to what we shall presently recognise as the Louis Seize or Marie Antoinette style, to which period his work more properly belongs. In careful finish of minute details, it more resembles the fine goldsmith's work of the Renaissance.
Gouthière was employed extensively by Madame du Barri; and at her execution, in 1793, he lost the enormous balance of 756,000 francs, which was due to him, but which debt the State repudiated, and the unfortunate man died in extreme poverty, the inmate of an almshouse.
The designs of the celebrated tapestry of Gobelins and of Beauvais, used for the covering of the finest furniture of this time, also underwent a change; and instead of the representation of the chase, with a bold and vigorous rendering, we find shepherds and shepherdesses, nymphs and satyrs, the illustrations of La Fontaine's fables or renderings of Boucher's pictures. The arm chair, or fauteuil, with upholstered instead of open sides, was introduced into the suite of tapestry furniture, and the term by which it is known, "chaise bergère," seems to be a sign of the fashion of the day.
Without doubt, the most important examples of meubles de luxe of this reign is the famous "Bureau du Roi," made for Louis XV. in 1769, and which is fully described in the inventory of the "Garde Meuble" in[160] the year 1775, under No. 2541. The description is very minute, and is fully quoted by M. Williamson in his valuable work, "Les Meubles d'Art du Mobilier National," occupying in space no less than thirty-seven lines of printed matter. Its size is five and a half feet long and three feet deep; the lines are the perfection of grace and symmetry; the marqueterie is in Riesener's best manner; the mountings are magnificent—reclining figures, foliage, laurel wreaths, and swags, chased with rare skill. The back of this famous bureau is as fully decorated as the front: it is signed, "Riesener, f. e., 1769, á l'arsenal de Paris." Riesener is said to have received the order for this celebrated piece of furniture—of which a full-page illustration is given—from the King in 1767, upon the occasion of the marriage of this favourite Court ébeniste with the widow of his former master Oeben. Its production, therefore, would seem to have occupied about two years.
This celebrated chef d'œuvre was in the Tuileries in 1807, and was included in the inventory found in the cabinet of Napoleon I. It was moved by Napoleon III. to the Palace of St. Cloud, and was only saved from capture by the Germans by its removal to its present home in the Louvre in August, 1870. It is said that it would probably realise, if now offered for sale, between fifteen and twenty thousand pounds.
A similar bureau is in the Hertford Wallace collection, which was made to the order of Stanilaus, King of Poland; and a copy of it, executed by Zwiener, a very clever ébeniste of the present day in Paris, at a cost of some three thousand pounds, is in the same collection. Between the publishing of the third and fourth editions of this book, this valuable collection, under the will of the late Lady Wallace, passed into the possession of the English nation, and the fine specimens of furniture which it contains are now available for reference.
It is probable that for some little time previous to the death of Louis XV., the influence of the beautiful daughter of Maria Theresa on the fashions of the day was manifested in furniture and its accessories. We know that Marie Antoinette disliked the pomp and ceremony of Court functions, and preferred a simpler way of living at the favourite farm house which was given to her husband as a residence, on his marriage, four years before his accession to the throne; and here she delighted to mix with the bourgeoisie on the terrace at Versailles, or donning a simple dress of white muslin, would busy herself in the garden or dairy. There was, doubtless, something of the affectation of a woman spoiled by admiration, in thus playing the rustic: still, one can understand that the best French society, weary of the domination of the late King's mistresses, with their intrigues, their extravagances, and their creatures, looked forward, at the death of Louis, with hope and anticipation to the accession of his grandson and the beautiful young queen.

PART OF A SALON.
Decorated and Furnished in the Louis XVI. Style.
Gradually, under the new régime, architecture became more simple. Broken scrolls were replaced by straight lines, curves and arches were introduced when justified, and columns and pilasters reappeared in the ornamental façade of public buildings. Interior decoration necessarily followed suit: instead of the curled endive scrolls enclosing the irregular panel, and the superabundant foliage in ornament, we find rectangular panels formed by simpler mouldings, with broken corners, having a patera or rosette in each, and between the upright panels there is a pilaster of refined Renaissance design. In the oval medallions supported by cupids, is found a domestic scene by Fragonard or Chardin; and portraits of innocent children by Greuze replaced the courting shepherds and mythological goddesses of Boucher and Lancret. Sculpture, too, became more refined and decorous in its representations.
As with architecture, decoration, painting and sculpture, so also with furniture. The designs became more simple, but were relieved from severity by the amount of ornament, which, except in some cases where it was over-elaborate, was properly subordinate to the design and did not control it.
Mr. Hungerford Pollen attributes this revival of classic taste to the discoveries of ancient treasures in Herculaneum and Pompeii, but, as these occurred in the former city so long before the time we are discussing as the year 1711, and in the latter as 1750, they can scarcely be the immediate cause; the reason most probably is that a return to simpler and purer lines came as a relief and reaction from the over-ornamentation of the previous period. There are not wanting, however, in some of the decorated ornaments of the time distinct signs of the influence of these discoveries. Drawings and reproductions from frescoes, found in these old Italian cities, were in the possession of the draughtsmen and designers of the time; and an instance in point of their adaptation is to be seen in the small boudoir of the Marquise de Serilly, one of the maids of honour to Marie Antoinette. The decorative woodwork of this boudoir is fitted up in the Kensington Museum.
A notable feature in the ornament of woodwork and in metal mountings of this time, is a fluted pilaster with quills or husks filling the flutings some distance from the base, or starting from both base and top and leaving an interval of the fluting plain and without ornament. An example of this will be seen in the next woodcut[162] of a cabinet in the Jones Collection, which has also the familiar "Louis Seize" riband, surmounting the two oval Sêvres china plaques. When the flutings are in oak, in rich mahogany, or painted white, these husks are gilt, and the effect is chaste and pleasing. Variation was introduced into the gilding of frames by mixing silver with some portion of the gold, so as to produce two tints, red gold and green gold: the latter would be used for wreaths and accessories, while the former, or ordinary gilding, was applied to the general surface. The legs of tables were generally fluted, as noted above, tapering towards the feet, and were relieved from a stilted appearance by being connected by a stretcher.
MARQUETERIE CABINET.
With Plaques of Sêvres China.
(In the Jones Collection, South Kensington Museum.)

WRITING TABLE.
Made by Riesener for Marie Antoinette. Collection "Mobilier National."
(From a pen and ink drawing by H. Evans.)
PERIOD: LATE LOUIS XV.
There occurs in M. Williamson's valuable contribution to the literature of our subject ("Les Meubles d'Art du Mobilier National,") an interesting illustration of the gradual alterations which we are noticing as having taken place in the design of furniture. This is a small writing table, some 3ft. 6in. long, made during the reign of Louis XV., but quite in the Marie Antoinette style, the legs tapering and fluted, the frieze having in the centre a plaque of bronze doré, the subject being a group of cupids, representing the triumph of Poetry, and having on each side a scroll with a head and foliage (the only ornament characteristic of Louis Quinze style) connecting leg and frieze. It was made for the Trianon, and the date is just one year after Marie Antoinette's marriage. M. Williamson quotes verbatim the memorandum of which it was the subject:—"Memoire des ouvrages faits et livrés, par les ordres de Monsieur le Chevalier de Fontanieu, pour le garde meuble du Roy par Riesener, ébeniste a l'arsenal Paris," savoir Sept. 21, 1771; and then follows a fully detailed description of the table, with its price, which was 6,000 francs, or £240. An illustration of this table precedes this page.
The maker of this piece of furniture was the same Riesener whose masterpiece is the magnificent Bureau du Roi in the Louvre, to which we have already alluded. This celebrated ébeniste continued to work for Marie Antoinette for about twenty years, until she quitted Versailles, and he probably lived quite to the end of the century, for during the Revolution we find that he served on the Special Commission appointed by the National Convention to decide which works of Art should be retained, and which should be sold, out of the mass of treasure confiscated after the deposition and execution of the King.
Riesener's designs do not shew much variety, but his work is highly finished and elaborate. His method was generally to make the centre panel of a commode front, or the frieze of a table, a tour de force, the marqueterie picture being wonderfully delicate. The subject was generally a vase with fruits and flowers; the surface of the side panels was inlaid with diamond-shaped lozenges, or a small diaper pattern in marqueterie; and then a framework of rich ormolu would separate the panels. The centre panel had sometimes a richer frame. His famous commode, made for the Château of Fontainebleau, which cost a million francs (£4,000)—an enormous sum in those days—is one of his chefs d'œuvres, and is an excellent example of his style. A similar commode was sold in the Hamilton Palace sale for £4,305. An upright secretaire, en suite with the commode, was also sold at the same time for £4,620, and the writing table for £6,000. An illustration of the latter is on the following page, but the details of this elaborate gem of cabinet maker's work, and of[164] Gouthière's skill in mounting, are almost impossible to represent in a woodcut. It is described as follows in Christie's catalogue:—
"Lot 303. An oblong writing table en suite, with drawer fitted with inkstand, writing slide and shelf beneath; an oval medallion of a trophy and flowers on the top, and trophies with four medallions round the sides: stamped T. Riesener and branded underneath with cypher of Marie Antoinette, and Garde Meuble de la Reine." There is no date on the table, but the secretaire is stamped 1790, and the commode 1791. If we assume that the table was produced in 1792, then these three specimens, which have always been regarded as amongst the most beautiful work of the reign, were almost the last which the unfortunate Queen lived to see completed.

THE "MARIE ANTOINETTE" WRITING TABLE.
(Formerly in the Hamilton Palace Collection.)
The fine work of Riesener required to be mounted by an artist of equal merit, and in Gouthière he was most fortunate. There is a famous clock case in the Hertford or Wallace collection, fully signed "Gouthière, ciseleur et doreur du roi à Paris Quai Pelletier, á la Boucle d'or, 1771." Gouthière worked, however, chiefly in conjunction with Riesener and David Roentgen for the adornment of their marqueterie.
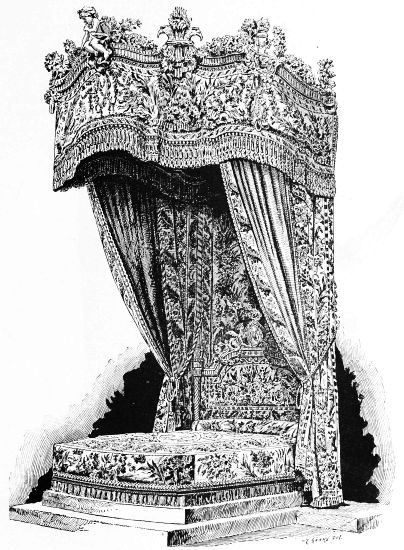

BEDSTEAD OF MARIE ANTOINETTE.
From Fontainebleau. Collection "Mobilier National."
(From a pen and ink drawing by H. Evans.)
PERIOD: LOUIS XVI.
In the Louvre are some beautiful examples of this co-operative work; and also of cabinets, in which plaques of very fine black and gold lacquer take the place of marqueterie; the centre panel being a finely chased oval medallion of Gouthière's gilt bronze, with caryatides figures of the same material at the ends supporting the cornice.
CYLINDER SECRETAIRE.
In Marqueterie, with Bronze Gilt Mountings, by Gouthière.
(Mr. Alfred de Rothschild's Collection.)
PERIOD: LOUIS XVI.
A specimen of this kind of work (an upright secretaire, of which we have not been able to obtain a satisfactory representation) formed part of the Hamilton Palace Collection, and realised £9,450, the highest price which the writer has ever seen a single piece of furniture bring by auction; it may be regarded as the chef d'œuvre of Gouthière.
In the Jones Collection, at South Kensington, there are also several charming examples of Louis Seize meubles de luxe. Some of these are enriched with plaques of Sêvres porcelain, to which the more jewel-like[166] mounting of this time is better adapted than the rococo style which was in vogue during the preceding reign.

ARM CHAIR OF LOUIS XVI. STYLE.
The upholstered furniture became simpler in design; the sofas and chairs have generally, but not invariably, straight fluted tapering legs, which sometimes have the flutings spiral instead of perpendicular: the backs are either oval or rectangular, and ornamented with a carved riband which is represented as tied at the top in a lover's knot. Gobelins, Beauvais, and Aubusson tapestry are used for covering, the subjects being in harmony with the taste of the time. A sofa in this style, with settees at the ends, the frame elaborately carved with trophies of arrows and flowers in high relief, and covered with fine old Gobelins tapestry, was sold at the Hamilton Palace Sale for £1,176. This was formerly at Versailles. Beautiful silks and brocades were also extensively used, both for chairs and for the screens, which, at this period, were varied in design and extremely pretty. Small two-tier tables of tulip wood with delicate mountings were quite the rage. The legs of small occasional pieces, like those of the chairs, are occasionally carved. An excellent example of a piece with cabriole legs is the charming little "Marie Antoinette" cylinder-fronted marqueterie escritoire in the Jones Collection (illustrated below). The marqueterie is attributed to Riesener, but from its treatment being so different from that which, as an almost invariable rule, he adopted, it is more probably the work of David.
CARVED AND GILT CAUSEUSE OR SETTEE, AND FAUTEUIL OR ARM CHAIR.
Covered with Beauvais Tapestry. (Collection "Mobilier National.")
(From a pen and ink drawing by H. Evans.)
PERIOD: END OF LOUIS XVI.

CARVED AND GILT CANAPÉ OR SOFA.
Covered with Beauvais tapestry. Collection "Mobilier National."
PERIOD: END OF LOUIS XVI.
Another fine specimen, illustrated on page 170, is the small cabinet made of kingwood, with fine ormolu mounts, and some beautiful Sêvres plaques.
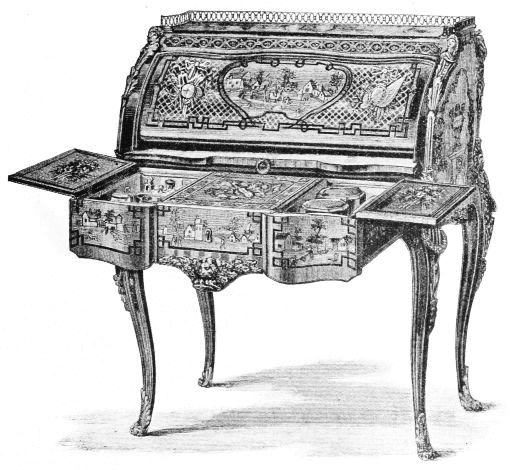

MARQUETERIE ESCRITOIRE.
By David, said to have belonged to Marie Antoinette.
(Jones Collection, South Kensington Museum.)
The influence exercised by the splendour of the Court of Louis Quatorze, and by the bringing together of artists and skilled handi-craftsmen for the adornment of the palaces of France, which we have seen took place during the latter half of the seventeenth century, was not without its effect upon the Industrial Arts of other countries. Macaulay mentions the "bales of tapestry" and other accessories which were sent to Holland to fit up the camp quarters of Louis le Grand[168] when he went there to take the command of his army against William III., and he also tells us of the sumptuous furnishing of the apartments at St. Germains when James II., during his exile, was the guest of Louis. The grandeur of the French King impressed itself upon his contemporaries, and war with Germany, as well as with Holland and England, helped to spread this influence. We have noticed how Wren designed the additions to Hampton Court Palace in imitation of Versailles: and in the chapter which follows this, it will be seen that the designs of Chippendale were really reproductions of French furniture of the time of Louis Quinze. The King of Sweden, Charles XII., "the Madman of the North," as he was called, imitated his great French contemporary, and in the palace at Stockholm there are still to be seen traces of the Louis Quatorze style in decoration and in furniture; such adornments are out of keeping with the simplicity of the habits of the present Royal family of Sweden.
A Bourbon Prince, too, succeeded to the throne of Spain in 1700, and there are still in the palaces and picture galleries of Madrid some fine specimens of French furniture of the three reigns which have just been discussed. It may be taken, therefore, that for a period dating from the latter part of the seventeenth century, the dominant influence upon the design of decorative furniture was of French origin.
There is evidence of this influence in a great many examples of the work of Flemish, German, English, and Spanish cabinet makers. Some of these are worthy of mention, and will repay a careful examination. One of them is a corner cupboard of rosewood, inlaid with engraved silver, part of the design being a shield with the arms of an Elector of Cologne; there is also a pair of somewhat similar cabinets from the Bishop's Palace at Salzburg. These are of German work, early eighteenth century, and have evidently been designed after Boule's productions. The shape and the gilt mounts of a secretaire of walnutwood with inlay of ebony and ivory, and some other furniture also, which, with the specimens just described, may be seen in the Bethnal Green Museum, all manifest the influence of the French school, when the bombé-fronted commodes and the curved lines of chairs and tables came into fashion.
Having described somewhat in detail the styles which prevailed and some of the changes which occurred in France, from the time of Louis XIV. until the Revolution, it is unnecessary, for the purposes of this sketch, to do more than briefly refer to the work of those countries which may be said to have adopted, to a greater or less extent, French designs. For reasons already stated, an exception is made in the case of our own country; and the following chapter will be devoted to the[169] furniture designed and made by some of the English craftsmen of the latter half of the eighteenth century. Of Italy it may be observed generally that the Renaissance of Raffaelle, Leonardo da Vinci, and Michael Angelo, which we have seen became degenerate towards the end of the sixteenth century, relapsed still further during the period which we have just been discussing; and, although the freedom and grace of the Italian carving, and the elaboration of inlaid arabesques, must always have some merit of their own, the work of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries in Italy will compare very unfavourably with that of the earlier period of the Renaissance.
A NORSE INTERIOR, SHEWING CHAIRS OF DUTCH DESIGN.
PERIOD: LATE XVII. OR EARLY XVIII. CENTURY.
There are many other museum specimens which might be referred to, proving the influence of French design of the seventeenth and subsequent centuries on that of other countries. The above illustration of a Norse interior shews that this influence penetrated as far as Scandinavia; the old-fashioned box-like bedsteads which the Norwegians had retained[170] from early times, and which in a ruder form are still to be found in the cottages of many Scottish counties, especially of those where the Scandinavian connection existed, are characteristic of the country. The design of the chairs in the preceding illustration is an evidence of the innovations which had been made upon native fashions. These chairs are in style thoroughly Dutch, of about the end of the seventeenth, or early in the eighteenth century; the cabriole legs and shell ornaments were probably the direct result of the influence of the French on the Dutch. The woodcut is from a drawing of an old house in Norway.

SECRETAIRE.
In King and Tulip Wood, with Sêvres Plaques and Ormolu Mountings.
PERIOD: EARLY LOUIS XVI.
It would be unfitting to close this chapter on French furniture without paying tribute to the munificence and public spirit of Mr. John Jones, whose bequest to the South Kensington Museum constitutes in itself a representative Museum of this class of decorative furniture. Several of the illustrations in this chapter have been taken from this collection.
The money value alone of this collection of furniture, porcelain, bronzes, and articles de vertû, mostly of the period embraced within the limits of this chapter, amounts to about £400,000, and exceeds the value of any bequest the nation has ever had. Perhaps the references contained in these few pages, to the French furniture of this time, may stimulate the interest of the public in, and its appreciation of, this valuable national property.

CLOCK.
By Robin, in Marqueterie Case, with Mountings of Gilt Bronze.
(Jones Collection, South Kensington Museum.)
LOUIS XVI. PERIOD.
Soon after this generous bequest was placed in the South Kensington Museum, for the benefit of the public, a leading article appeared in the[172] Times, from which the following extract will very appropriately conclude this chapter:—"As the visitor passes by the cases where these curious objects are displayed, he asks himself what is to be said on behalf of the art of which they are such notable examples. Tables, chairs, commodes, secretaires, wardrobes, porcelain vases, marble statuettes, they represent in a singularly complete way the mind and the work of the ancien régime. Like Eisen's vignettes, or the contes of innumerable story-tellers, they bring back to us the grace, the luxury, the prettiness, the frivolity of that Court which believed itself, till the rude awakening came, to contain all that was precious in the life of France. A piece of furniture like the little Sêvres-inlaid writing table of Marie Antoinette is, to employ a figure of Balzac's, a document which reveals as much to the social historian as the skeleton of an ichthyosaurus reveals to the palæontologist. It sums up an epoch. A whole world can be inferred from it. Pretty, elegant, irrational, and entirely useless, this exquisite and costly toy might stand as a symbol for the life which the Revolution swept away."
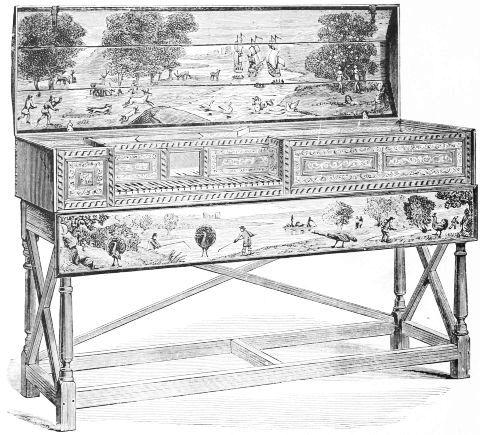
HARPSICHORD, from the Permanent Collection belonging to South Kensington Museum.
DATE ABOUT 1750. See Appendix, p. 266.
Chinese Styles—Sir William Chambers—The Brothers Adams' work—Pergolesi, Cipriani, and Angelica Kauffmann—Architects of the time—Wedgwood and Flaxman—Chippendale's Work and his Contemporaries—Chair in the Barbers' Hall—Lock, Shearer, Hepplewhite, Ince, Mayhew, Sheraton—Introduction of Satinwood and Mahogany—Gillows, of Lancaster and London—History of the Sideboard—The Dining Room—Furniture of the time.
 OON after the second half of the eighteenth
century had set in, during the latter days of the
second George, and the early part of his successor's
long reign, there is a distinct change in the
design of English decorative furniture.
OON after the second half of the eighteenth
century had set in, during the latter days of the
second George, and the early part of his successor's
long reign, there is a distinct change in the
design of English decorative furniture.
Sir William Chambers, R.A., an architect, who has left us Somerset House as a lasting monument of his talent, appears to have been the first to impart to the interior decoration of houses what was termed "the Chinese style," as the result of his visit to China, of which a notice was made in the chapter on Eastern furniture; and as he was considered an "oracle of taste" about this time, his influence was very powerful. Chair backs consequently have the peculiar irregular lattice work which is seen in the fretwork of Chinese and Japanese ornaments; and Pagodas, Chinamen and monsters occur in his designs for cabinets. The overmantel which had hitherto been designed with some architectural pretension, now gave way to the larger mirrors which were introduced by the improved manufacture of plate glass; and the chimney piece became lower. During his travels in Italy, Chambers had found some Italian sculptors, and had brought them to England, to carve in marble his designs; they were generally of a free Italian character, with scrolls of foliage and figure ornaments: but being of stone instead of woodwork, they scarcely belong to our subject, save to indicate the change in fashion of the chimney piece, the vicissitudes of which we have already noticed. Chimney pieces were now no longer specially designed by architects, as part of the interior fittings, but were made and sold with the grates, to suit the taste of the purchaser, often quite irrespective of[174] the rooms for which they were intended. It may be said that Dignity gave way to Elegance.
Robert Adam, having returned from his travels in France and Italy, had designed and built, in conjunction with his brother James, Adelphi Terrace, about 1769, and subsequently Portland Place, and other streets and houses of a like character; the furniture being made under the direction of Robert, to suit the interiors. There is much interest attaching to No. 25, Portland Place, because this was the house built, decorated and furnished by Robert Adam for his own residence, and, fortunately, the chief reception rooms remain to show the style then in vogue. The brothers Adam introduced into England the application of composition ornaments to woodwork. Festoons of drapery, wreaths of flowers caught up with rams' heads, or of husks tied with a knot of riband, and oval patent to mark divisions in a frieze, or to emphasize a break in the design, are ornaments characteristic of what was termed the Adams style.
Robert Adam published between 1778 and 1822, in three magnificent volumes, "Works in Architecture." One of these was dedicated to King George III., to whom he was appointed Architect. Many of his designs for furniture was carried cut by Gillows; there is a good collection of his original drawings in the Soane Museum, Lincoln's Inn Fields.
The decoration was generally in low relief, with fluted pilasters, and sometimes a rather stiff Renaissance ornament decorating the panel; the effect was neat and chaste, and a distinct change from the rococo style which had preceded it.
The design of furniture was modified to harmonize with such decoration. The sideboard had a straight and not infrequently a serpentine-shaped front, with square tapering legs, and was surmounted by a pair of urn-shaped knife cases, the wood used being almost invariably mahogany with the inlay generally of plain flutings relieved by fans or oval paterœ in satin wood.
Piranesi, Cipriani and Angelica Kauffmann had been attracted to England by the promise of lucrative employment, and not only decorated the panels of ceilings and walls which were enriched by Adams's "compo." (in reality a revival of the old Italian gesso work), but also painted the ornamental cabinets, occasional tables, and chairs of the time. Some of the work of Angelica Kauffmann as a decorative artist may still be seen in several houses in Adelphi Terrace, in the Arts Club, and in many private residences, of which there is a very useful list in Miss Frances Gerard's biography of the artist, published in 1892.
FAC-SIMILE OF ORIGINAL DRAWINGS BY ROBERT ADAM (REDUCED).
Towards the end of the century, satin wood was introduced into England from the East Indies; it became very fashionable, and was[176] a favourite ground-work for decoration, the medallions of figure subjects, generally of cupids, wood-nymphs, or illustrations of mythological fables, on darker colored wood, formed an effective relief to the yellow satin wood. Sometimes the cabinet, writing table, or spindle-legged occasional piece was made entirely of this wood, having no other decoration beyond the beautiful marking of carefully-chosen veneers; sometimes it was banded with tulipwood or harewood (a name given to sycamore artificially stained), and at other times painted as just described. A very beautiful example of this last-named treatment is the dressing table in the South Kensington Museum, which we give as an illustration on the opposite page.
Besides Chambers, there were several other architects who designed furniture about this time who have been almost forgotten. Abraham Swan, some of whose designs for wooden chimney pieces in the quasi-classic style are given, flourished about 1758. John Carter, who published "Specimens of Ancient Sculpture and Painting"; Nicholas Revitt and James Stewart, who jointly published "Antiquities of Athens" in 1762; J. C. Kraft, who designed in Robert Adam's style; W. Thomas, M.S.A., and others, have left us many drawings of interior decorations, chiefly chimney pieces and the ornamental architraves of doors, all of them in low relief and of a classical character, as was the fashion towards the end of the eighteenth century.
Josiah Wedgwood, too, turned his attention to the production of plaques in relief, for adaptation to chimney pieces of this character. In a letter written from London to Mr. Bentley, his partner, at the works, he deplores the lack of encouragement in this direction which he received from the architects of his day; he, however, persevered, and by the aid of Flaxman's inimitable artistic skill as a modeller, made several plaques of his beautiful jasper ware, which were let in to the friezes of chimney pieces, and also into other woodwork. There can be seen in the South Kensington Museum a pair of pedestals of this period (1770-1790) so ornamented.
It is now necessary to consider the work of a group of English cabinet makers, who not only produced a great deal of excellent furniture, but who also published a large number of designs drawn with extreme care and a considerable degree of artistic skill.
The first of these, and the best known, was Thomas Chippendale, who is said to have been born in Worcester. He appears to have succeeded his father, a chair maker, and to have carried on a large and successful business in St. Martin's Lane, London, which was at this time an important Art centre, and close to the newly-founded Royal Academy.

ENGLISH SATINWOOD DRESSING TABLE.
With Painted Decoration.
END OF XVIII. CENTURY.
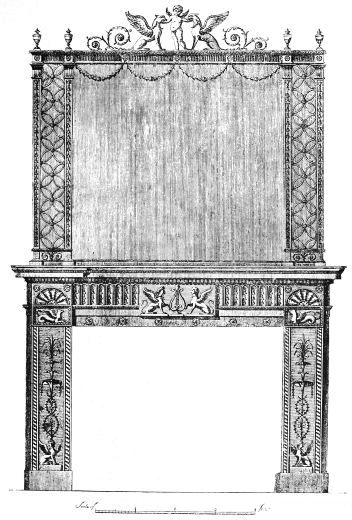
CHIMNEYPIECE AND OVERMANTEL.
DESIGNED BY W. THOMAS, ARCHITECT. 1783.
Very similar to Robert Adam's work.
Chippendale published "The Gentleman and Cabinet Maker's Director," not, as stated in the introduction to the catalogue to the South Kensington Museum, in 1769, but some years previously, as is testified by a copy of the "third edition" of the work, which is in the writer's possession and bears date 1762, the first edition having appeared in 1754. The title page of this edition is reproduced in fac-simile on page 178.
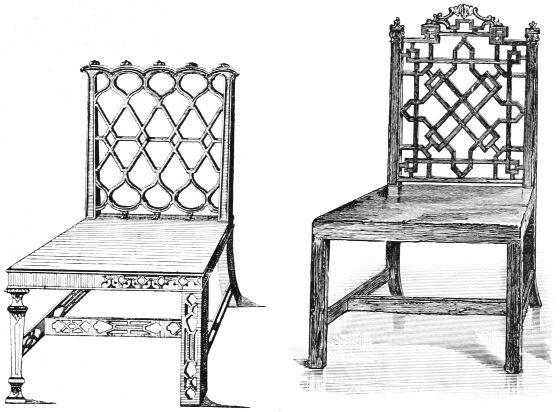
CHAIRS,
With ornament in the Chinese style, by Thomas Chippendale.
This valuable work of reference contains over two hundred copper-plate engravings of chairs, sofas, bedsteads, mirror frames, girandoles, torchères or lamp stands, dressing tables, cabinets, chimney pieces, organs, jardinières, console tables, brackets, and other useful and decorative articles, of which some examples are given. It will be observed from these that the designs of Chippendale are very different from those popularly ascribed to him. Indeed it would appear that this maker has become better known than any other, from the fact of the designs in his book having been recently republished in various forms; his popularity has thus been revived, while the names of his contemporaries are forgotten. For the last fifteen or twenty years, therefore, during which time the fashion has obtained of collecting the furniture of a bygone century, almost every cabinet, table, or mirror frame, presumably of English manufacture, which[178] is slightly removed from the ordinary type of domestic furniture, has been, for want of a better title, called "Chippendale." As a matter of fact, he appears to have adopted from Chambers the fanciful Chinese ornament, and the rococo style of that time, which was superseded some five-and-twenty years later by the quiet and more classic designs of Adam and his contemporaries.

Fac-simile of the Title Page of Chippendale's "Director."
(Reduced by Photography.) The original is folio size.
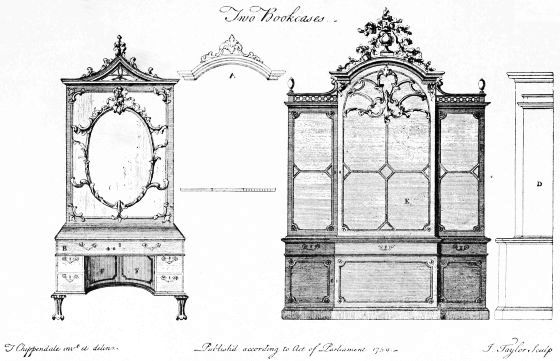
N. LXXXVII.
T. Chippendale invᵗ. et delins. Publish'd according to Act of Parliament 1769. J Taylor Sculp
FAC-SIMILE OF A PAGE IN CHIPPENDALE'S "DIRECTOR." (The original is folio size.)
TEA CADDY,
Carved in the French style. (From Chippendale's "Director.")
In the chapter on Louis XV. and Louis XVI. furniture, it has been shewn how French fashion went through a similar change about this same period. In Chippendale's chairs and console tables, in his state bedsteads and his lamp-stands, one can recognize the broken scrolls and curved lines, so familiar in the bronze mountings of Caffieri. The influence of the change which had occurred in France during the Louis Seize period is equally evident in Adam's treatment. It was helped forward by the migration into this country of skilled workmen from France, during the troubles of the revolution at the end of the century. Some of Chippendale's designs bear such titles as "French chairs" or a "Bombé-fronted Commode." These might have appeared as illustrations in a contemporary book on French furniture, so identical are they in every detail with the carved woodwork of Picau, of Canner, or of Nilson, who designed the flamboyant frames of the time of Louis XV. Other designs have more individuality. In his mirror frames he introduced a peculiar bird with a long snipe-like beak and rather impossible wings, an imitation of rockwork and dripping water, Chinese figures with pagodas and umbrellas; and sometimes the illustration of Æsop's fables interspersed with scrolls and flowers. By dividing the glass unequally, by the introduction into his design of bevelled pillars with carved capitals and bases, he produced a quaint and pleasing effect, very suitable to the rather effeminate fashion of his time, and in harmony with three-cornered hats, wigs and patches, embroidered waistcoats, knee breeches, silk stockings, and enamelled snuff-boxes. In some of the designs there is a fanciful Gothic, to which he makes[180] special allusion in his preface, as likely to be considered by his critics as impracticable, but which he undertakes to produce if desired—
"Though some of the profession have been diligent enough to represent them (espescially those after the Gothick and Chinese manner) as so many specious drawings impossible to be worked off by any mechanick whatsoever. I will not scruple to attribute this to Malice, Ignorance, and Inability; and I am confident I can convince all Noblemen, Gentlemen, or others who will honour me with their Commands, that every design in the book can be improved, both as to Beauty and Enrichment, in the execution of it, by
"Their most obedient servant,
"THOMAS CHIPPENDALE."
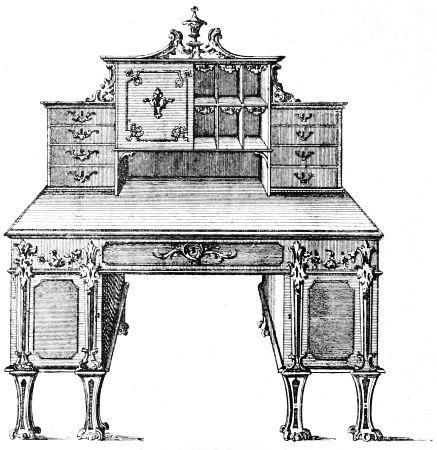
A BUREAU.
(From Chippendale's "Director.")
The reader will notice that in the examples selected from Chippendale's book there are none of those fretwork tables and cabinets which are generally termed "Chippendale." We know, however, that besides the designs which have just been described, and which were intended for gilding, he also made mahogany furniture, and in the "Director" there are drawings of chairs, washstands, writing-tables and cabinets of this description. Fretwork is seldom seen, but the carved ornament is generally a foliated or curled endive scroll; sometimes the top of a cabinet is finished in the form of a Chinese pagoda. Upon examining a piece of furniture that may reasonably be ascribed to him, it will be found to be of excellent workmanship, and the wood, always mahogany without any inlay, is richly marked, shewing a careful selection of material.
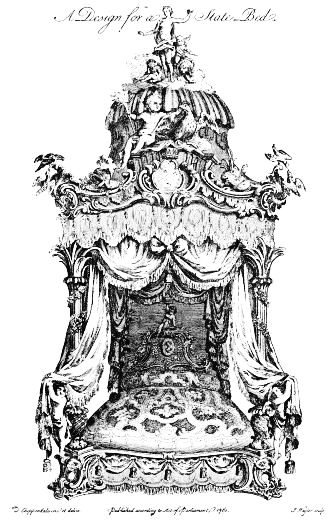
Nᵒ. XIXII.
A Chippendale Design. Published according to Act of Parliament 1765. J. Taylor sculp.
FAC-SIMILE OF A PAGE IN CHIPPENDALE'S "DIRECTOR."
(The original is folio size.)

"FRENCH" COMMODE AND LAMP STANDS.
DESIGNED BY T. CHIPPENDALE, AND PUBLISHED IN HIS "DIRECTOR."
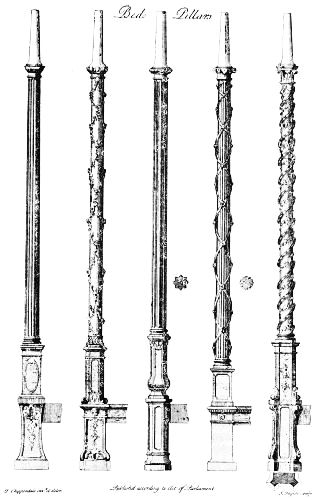
Pl. XXXV.
A Chippendale invᵗ et delves. Published according to Act of Parliament. J. Taylor sculp.
FAC-SIMILE OF A PAGE IN CHIPPENDALE'S "DIRECTOR."
(The original is folio size.)
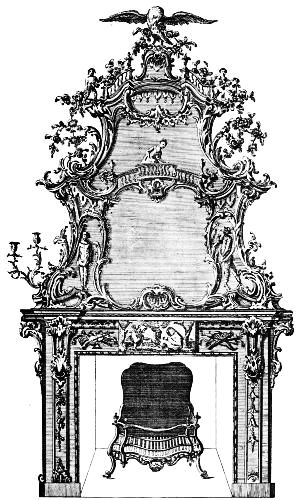
CHIMNEYPIECE AND MIRROR.
DESIGNED BY T. CHIPPENDALE, AND PUBLISHED IN HIS "DIRECTOR."
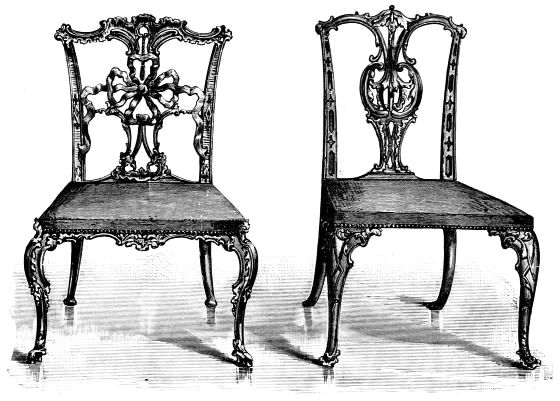

PARLOUR CHAIRS, BY CHIPPENDALE.
The chairs of Chippendale and his school are very characteristic. If the outline of the back of some of them be compared with the stuffed back of the chair from Hardwick Hall (illustrated in Chap. IV.) it will be seen that the same lines occur, but instead of the frame of the back being covered with silk, tapestry, or other material—as in William III.'s time—Chippendale's are cut open into fanciful patterns; and in his more highly ornate work, the twisted ribands of his design are scarcely to be reconciled with the use for which a dining room chair is intended. The well-moulded sweep of his lines, however, counter-balances this defect to some extent, and a good Chippendale mahogany chair will ever be an elegant article of furniture.
One of the most graceful chairs of about the middle of the century, in the style of Chippendale's best productions, is the Master's Chair in the Hall of the Barbers' Company. It is carved in rich Spanish mahogany, and upholstered in morocco leather; the ornament consists of scrolls and cornucopiæ with flowers charmingly disposed, the arms and motto of the Company being introduced. Unfortunately, there is no certain record[182] as to the designer and maker of this beautiful chair, and it is to be regretted that the date (1865), the year when the Hall was redecorated, should have been placed in prominent gold letters on this interesting relic of a past century.
CLOCK CASE, BY CHIPPENDALE.
Apart from the several books of design noticed in this chapter, there were published two editions of a work, undated, containing many of the drawings found in Chippendale's book. This book was entitled, "Upwards of One Hundred New and Genteel Designs, being all the most approved patterns of household furniture in the French taste. By a Society of Upholders and Cabinet makers." It is probable that Chippendale was a member of this Society, and that some of the designs were his, but that he severed himself from it, and published his own book, preferring[183] to advance his individual reputation. The "sideboard" which one so generally hears called "Chippendale" scarcely existed in his time. If it did it must have been quite at the end of his career. There were side tables, sometimes called "Side-Boards," but they contained neither cellaret nor cupboard; only a drawer for table linen.
The name of Robert Manwaring should not be omitted as one of Chippendale's contemporaries. He published "The Chairmaker's Guide" in 1766, which included "upwards of two hundred new and genteel designs, both decorative and plain, of all the most approved patterns for burjairs, toillets, cornishes and lanthorns, etc."
The patterns of his chair-backs are very similar to those of his contemporaries, and four of his designs which were reproduced in "Furniture and Decoration," two years ago, only differ in detail from those illustrated here as the work of Ince and Mayhew. Manwaring also designed china cabinets, fenders, balconies, and other decorative items, and he is believed to have been a leading member of the Society of Upholders and Cabinet Makers, alluded to in page 182.
Two other designers and makers of mahogany ornamental furniture, who also deserve special mention in the discussion of eighteenth century English furniture, are W. Ince and J. Mayhew, who were partners in business in Broad Street, Golden Square, and contemporary with Chippendale. They also published a book of designs,[16] which is alluded to by Thomas Sheraton in the preface to his "Cabinet Maker and Upholsterer's Drawing Book," published in 1793. A few examples from Ince and Mayhew's "Cabinet Maker's Real Friend and Companion" are given, from which it is evident that, without any distinguishing brand, or without the identification of any particular piece of furniture with one of their designs, it is difficult to distinguish between their work and that of Chippendale and other contemporary makers.
It is, however, noticeable, after careful comparison of the work of Chippendale with that of Ince and Mayhew, that the furniture designed and made by the latter has many more of the characteristic details and ornaments which are now generally looked upon as denoting the work of Chippendale; for instance, the fretwork ornaments finished by the carver, and then applied to the plain mahogany; the open-worked scroll shaped backs to encoignures or china shelves; and the carved Chinaman with the pagoda. Some of the frames of chimney glasses and pictures made by Ince and Mayhew are almost identical with those attributed to Chippendale.
CHINA SHELVES, DESIGNED BY W. INCE.
(Reproduced by Photography from an old Print in the Author's possession.)
Other well known designers and manufacturers of this time were Hepplewhite, who published a book of designs very similar to those of his contemporaries, and Matthias Lock, some of whose original drawings were on view in the Exhibition of 1862,[17] with interesting memoranda attached, giving the names of his workmen and the wages paid: from these it would appear that five shillings a day was at that time sufficient remuneration for a skilful wood carver.

GIRANDOLES AND PIER TABLE, DESIGNED BY W. THOMAS, ARCHITECT, 1783.
(Reproduced by Photography from an old Print in the Author's possession.)
Another good designer and maker of much excellent furniture of this time was "Shearer," who has been unnoticed by nearly all writers on the subject. In an old book of designs in the author's possession, "Shearer delin" and "published according to Act of Parliament, 1788," appears underneath the representations of sideboards, tables, bookcases, dressing tables, which are very similar in every way to those of Sheraton, his contemporary. George Richardson and Matthias Darly should also be mentioned as notable designers of furniture and decorative details of this time.
A copy of Hepplewhite's Book, in the author's possession (published in 1789), contains 300 designs "of every article of household furniture in the newest and most approved taste," and it is worth while to quote from his preface to illustrate the high esteem in which English cabinet work was held at this time.
"English taste and workmanship have of late years been much sought for by surrounding nations; and the mutability of all things, but more especially of fashions, has rendered the labours of our predecessors in this line of little use; nay, in this day can only tend to mislead those foreigners who seek a knowledge of English taste in the various articles of household furniture."
It is amusing to think how soon the "mutabilities of fashion" did for a time supersede many of his designs.
A selection of drawings from his book is given, and it will be useful to compare them with those of other contemporary makers. From such a comparison it will be seen that in the progress from the rococo of Chippendale to the more severe lines of Sheraton, Hepplewhite forms a connecting link between the two.
The names given to some of these designs appear curious; for instance:
"Rudd's table or reflecting dressing table," so called from the first one having been invented for a popular character of that time.
"Knife cases," for the reception of the knives which were kept in them and used to "garnish" the sideboards.
"Cabriole chair," implying a stuffed back, and not having reference, as it does now, to the curved form of the leg.
"Bar backed sofa," being what we should now term a three or four chair settee, i.e., like so many chairs joined and having an arm at either end.
"Library case" instead of Bookcase.
"Confidante" and "Duchesse," which were sofas of the time.
"Gouty stool," a stool having an adjustable top.
"Tea chest," "Urn stand," and other names which have now disappeared from ordinary use in describing similar articles.
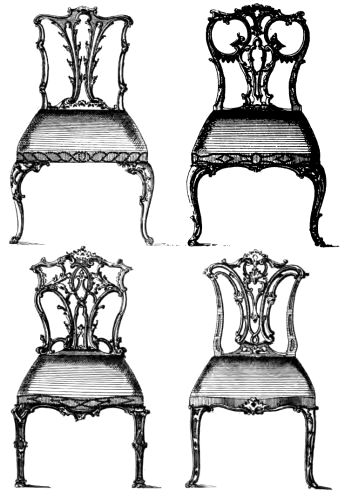
PARLOUR CHAIRS, DESIGNED BY W. INCE.
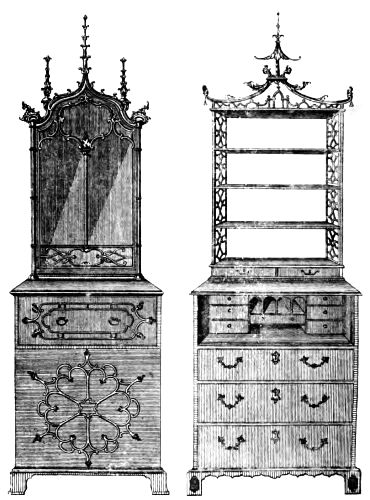
LADIES' SECRETAIRES, DESIGNED BY W. INCE.
(Reproduced by Photography from an old print in the Author's possession.)
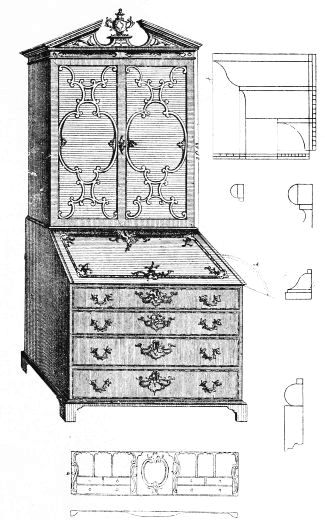
DESK AND BOOKCASE, DESIGNED BY W. INCE.
(Reproduced by Photography from an old Print in the Author's possession.)
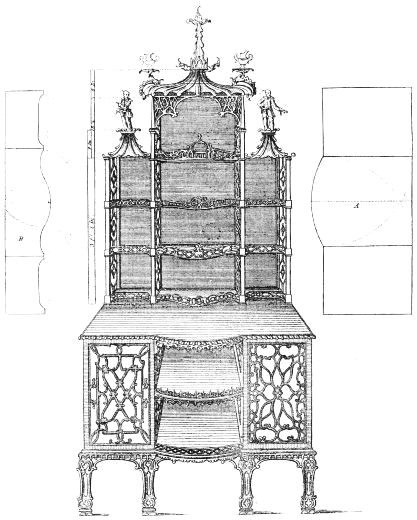
CHINA CABINET, DESIGNED BY J. MAYHEW.
(Reproduced from an old Print in the Author's possession.)
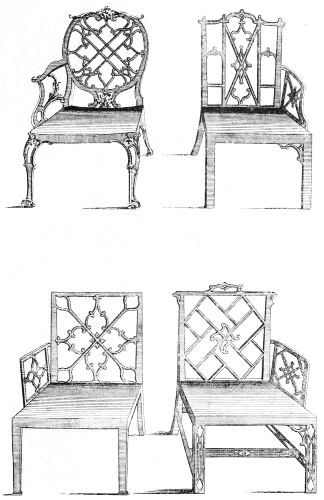
"DRESSING CHAIRS," DESIGNED BY J. MAYHEW.
These shew the influence of Sir W. Chambers' Chinese style.
Hepplewhite had a "specialité," to which he alludes in his book, and of which he gives several designs. This was his japanned or painted furniture; the wood was coated with a preparation after the manner of Chinese or Japanese lacquer, and then decorated, generally with gold on a black ground, the designs being in fruits and flowers: and also medallions painted in the style of Cipriani and Angelica Kauffmann. Subsequently, furniture of this character, instead of being japanned, was only painted white. It is probable that many of the chairs of this time which one now sees to be of wood of inferior quality, and with scarcely any ornament, were originally decorated in the manner just described, and therefore the "carving" of details would have been superfluous. Injury to the enamelling, by wear and tear, was most likely the cause of their being stripped of their rubbed and partly obliterated decorations, and they were then stained and polished, presenting an appearance which is scarcely just to the designer and manufacturer.
In some of Hepplewhite's chairs, too, as in those of Sheraton, one may fancy he sees evidence of the squabbles of two fashionable factions of this time, "the Court party" and the "Prince's party," the latter having the well-known Prince of Wales' plumes very prominent, and forming the ornamental support of the back of the chair. Another noticeable enrichment is the carving of wheat ears on the shield shape backs of the chairs.
To convey an idea of the fashion of the day, "the plan of a room shewing the proper distribution of the furniture," appears on page 193. It is evident from the large looking glass which overhangs the sideboard that the fashion had now set in to use these mirrors. Some thirty or forty years later this mirror became part of the sideboard, and, in some large and pretentious designs which we have seen, the sideboard itself was little better than the support of a huge glass in a heavily carved frame.
The dining tables of this period deserve a passing notice as a step in the development of that important member of our "Lares and Penates." What was, and is still, called the "pillar and claw" table, came into fashion towards the end of the last century. It consisted of a round or square top supported by an upright cylinder, which rested on a plinth having three, or sometimes four, feet carved as claws. In order to extend these tables for a larger number of guests, an arrangement was made for placing several together. When apart, they served as pier or side tables, and some of these—the two end ones, being semi-circular—may still be found in some of our old inns.[18]
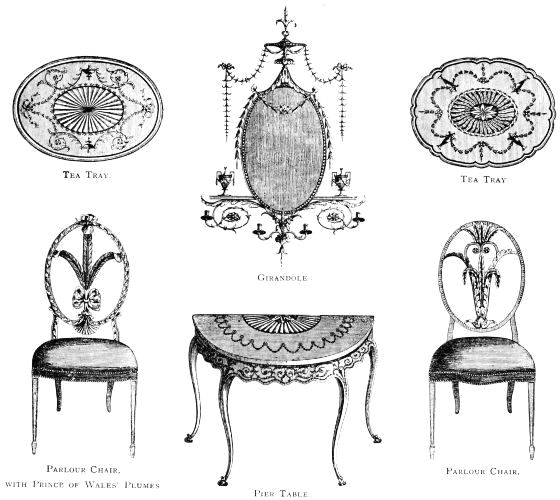
DESIGNS OF FURNITURE.
FROM HEPPLEWHITE'S "GUIDE," PUBLISHED 1787.
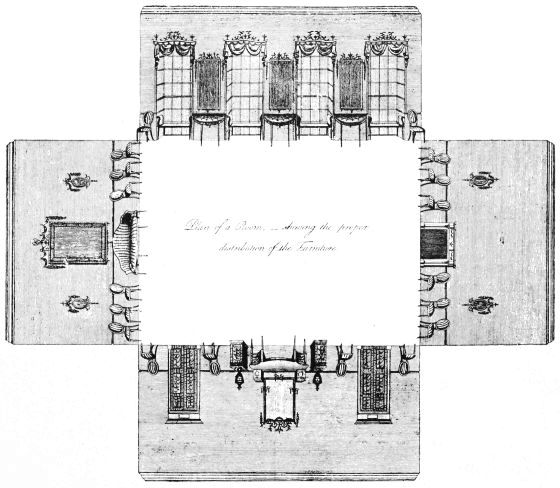
FAC-SIMILE OF PAGE IN HEPPLEWHITE'S "CABINET MAKER'S GUIDE," PUBLISHED IN 1787.
Plan of a Room,—shewing the proper
distribution of the Furniture.
It was not until the year 1800 that Richard Gillow, of the well-known firm in Oxford Street, invented and patented the convenient telescopic contrivance which, with slight improvements, has given us the table of the present day. The term still used by auctioneers in describing a modern extending table as a "set of dining tables," is, probably, a survival of the older method of providing for a dinner party. Gillow's patent is described[194] as "an improvement in the method of constructing dining and other tables calculated to reduce the number of legs, pillars, and claws, and to facilitate and render easy, their enlargement and reduction."
INLAID TEA CADDY AND TOP OF PIER TABLES.
(From "Hepplewhite's Guide.")
As an interesting link between the present and the past, it may be useful here to introduce a slight notice of this well-known firm of furniture manufacturers, for which the writer is indebted to Mr. Clarke, one of the present partners of Gillows. "We have an unbroken record of books dating from 1724, but we existed long anterior to this: all records were destroyed during the Scottish Rebellion in 1745. The house originated in Lancaster, which was then the chief port in the north, Liverpool not being in existence at the time, and Gillows exported furniture largely to the West Indies, importing rum as payment, for which privilege they held a special charter. The house opened in London in 1765, and for some time the Lancaster books bore the heading and inscription, 'Adventure to London.' On the architect's plans for the premises now so well known in Oxford Street, occur these words, 'This is the way to Uxbridge.'" Mr. Clarke's information may be supplemented by adding that from Dr. Gillow, whom the writer had the pleasure of meeting some years ago, and who was the thirteenth child of the Richard Gillow before mentioned, he learnt that this same Richard Gillow retired in 1830, and died as lately as 1866 at the age of 90. Dowbiggin, founder of the firm of Holland and Sons, was an apprentice to Richard Gillow.
Mahogany may be said to have come into general use subsequent to 1720, and its introduction is asserted to have been due to the tenacity of purpose of a Dr. Gibbon, whose wife wanted a candle box, an article of common domestic use of the time. The Doctor, who had laid by in the garden of his house in King Street, Covent Garden, some planks sent to him by his brother, a West Indian captain, asked a joiner to use a part of the wood for this purpose; it was found too tough and hard for the tools of the period, but the Doctor was not to be thwarted, and insisted on harder-tempered tools being found, and the task was completed; the result was the production of a candle box which was admired by every one. He then ordered a bureau of the same material, and when it was finished, he invited his friends to see the new work; amongst others, the Duchess of Buckingham begged a small piece of the precious wood, and it soon became the fashion. On account of its toughness, and peculiarity of grain, it was capable of treatment impossible with oak, and the high polish it took by oil and rubbing (not French polish, a later invention), caused it to come into great request. The term "putting one's knees under a friend's mahogany," probably dates from about this time.
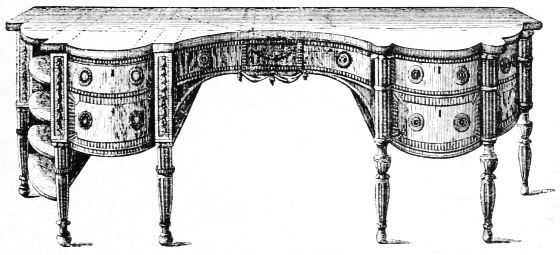
KNEEHOLE TABLE, BY SHERATON.
Thomas Sheraton, who commenced work some twenty years later than Chippendale, and continued in business until the early part of the nineteenth century, accomplished much excellent work in English furniture.
CHAIRS, BY SHERATON
The fashion had now changed; instead of the rococo—literally, rock work and shell (roequaille et coquaille)—ornament, which had gone out, a simpler and more severe taste had come in. In Sheraton's cabinets, chairs, writing tables, and occasional pieces, we have therefore no longer the cabriole leg or the carved ornament; but, as in the case of the brothers Adam, and the furniture designed by them for such houses as those in Portland Place, we have now square tapering legs, severe lines, and quiet ornament. Sheraton trusted almost entirely for decoration to his marqueterie. Some of this is very delicate and of excellent workmanship. He introduced occasionally into his scrolls animals with foliated extremities, and he also inlaid marqueterie trophies of musical instruments;[197] but as a rule the decoration was in wreaths of flowers, husks, or drapery, in strict adherence to the fashion of the decorations to which allusion has been made. A characteristic feature of his cabinets was the swan-necked pediment surmounting the cornice, being a revival of an ornament fashionable during Queen Anne's reign. It was then chiefly found in stone, marble, or cut brickwork, but subsequently became prevalent in inlaid woodwork.
A CHINA CABINET AND A BOOKCASE WITH SECRETAIRE.
Designed by T. Sheraton, and published in his "Cabinet Maker and Upholsterer's Drawing Book," 1793.
Sheraton was apparently a man very well educated for his time, whether self taught or not one cannot say; but that he was an excellent draughtsman, and had a complete knowledge of geometry, is evident from the skilful drawings in his book, and the careful though rather verbose directions he gives for perspective drawing. Many of his numerous designs for furniture and ornamental items are drawn to a scale with the geometrical nicety of an engineer's or architect's plan. He has drawn in elevation, plan, and minute detail, each of the five architectural orders.
CHAIR BACKS, FROM SHERATON'S "CABINET MAKER."
The selection made here from his designs for the purposes of illustration, is not taken from his later work, which properly belongs to a future chapter, when we come to consider the influence of the French Revolution, and the translation of the "Empire" style to England. Sheraton published "The Cabinet Maker and Upholsterer's Drawing Book" in 1793, and the list of subscribers whose names and addresses are given, throws much light on the subject of the furniture of his time.[19] Amongst these are many of his aristocratic patrons and no less than 450 names and addresses of cabinet makers, chair makers, and carvers, exclusive of harpsichord manufacturers, musical instrument makers, upholsterers, and other kindred trades. Included with these we find the names of firms who, from the appointments they held, it may be inferred, had a high reputation for good work, and a leading position in the trade, but who, perhaps from the absence of a taste for "getting into print" and from the lack of any brand or mark by which their work can be identified, have passed into oblivion while their contemporaries are still famous. The following names taken from this list are probably those of men who had for many years conducted well known and old established businesses, but would now be but poor ones to "conjure" with: while those of Chippendale, Sheraton, or Hepplewhite, are a ready passport for a doubtful specimen. For instance:—France, Cabinet Maker to His Majesty, St. Martin's Lane; Charles Elliott, Upholder to His Majesty and Cabinet Maker to the Duke of York, Bond Street; Campbell and Sons, Cabinet Makers to the Prince of Wales, Mary-le-bone Street, London. Besides those who held Royal appointments, there were other manufacturers of decorative furniture—Thomas Johnson, Copeland, Robert[199] Davy, a French carver named Nicholas Collet, who settled in England, and many others.
In Mr. J. H. Pollen's larger work on furniture and woodwork, which includes a catalogue of the different examples in the South Kensington Museum, there is a list of the various artists and craftsmen who have been identified with the production of artistic furniture either as designers or manufacturers, and the writer has found this of considerable service. In the Appendix to this work, this list has been reproduced, with the addition of several names (particularly those of the French school) omitted by Mr. Pollen, and it will, it is hoped, prove a useful reference to the reader.
Although in deference to the prevailing taste for our National manufacture of the latter half of the last century, this chapter is somewhat long, on account of the endeavour to give more detailed information about English furniture of that period, still, in concluding it, a few remarks about the "Sideboard" may be allowed.
The changes in form and fashion of this important article of domestic furniture are interesting, and to explain them a slight retrospect is necessary. The word "Buffet," sometimes translated "Sideboard," which was used to describe continental pieces of furniture of the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, does not designate our Sideboard, which may be said to have been introduced by William III., and of which kind there is a fair specimen in the South Kensington Museum; an illustration of it has been given in the chapter dealing with that period.
The term "stately sideboard" occurs in Milton's "Paradise Regained," which was published in 1671; and Dryden, in his translation of "Juvenal," published in 1693, when contrasting the furniture of the classical period of which he was writing, with that of his own time, uses the following line:—
"No sideboards then with gilded plate were dressed."
The fashion in those days of having symmetrical doors in a room, that is, false doors to correspond with the door used for exit, which one still finds in many old houses in the neighbourhood of Portland Place, and particularly in the Palaces of St. James' and of Kensington, enabled our ancestors to have good cupboards for the storage of glass, crockery, and reserve wine. After the middle of the eighteenth century,[200] however, these extra doors and the cupboard enclosed by them, gradually disappeared; and soon after the mahogany side table came into fashion, it became the custom to supplement this article of furniture by an independent pedestal cupboard on either side (instead of the cupboards alluded to), one for hot plates and the other for wine. Then, as the thin legs gave the table rather a lanky appearance, the garde de vin, or cellaret, was added in the form of an oval tub of mahogany, with bands of brass, sometimes raised on low feet with castors for convenience, which was used as a wine cooler. A pair of urn-shaped mahogany vases stood on the pedestals, and these contained—the one hot water for the servants' use in washing the knives, forks, and spoons, which being then much more valuable were limited in quantity, and the other held iced water for the guests' use. To understand this arrangement the reader is referred to the illustration on page 193.
A brass rail at the back of the side table, with ornamented pillars and branches for candles, was used, partly to enrich the furniture, and partly to form a support to the handsome pair of knife and spoon cases, which completed the garniture of a gentleman's sideboard of this period. It would therefore seem that the modern sideboard is the combination of these separate articles into one piece of furniture—at different times and in different fashions—first the pedestals joined to the table produced our "pedestal sideboard," then the mirror was joined to the back, the cellaret made part of the interior fittings, and the banishment of knife cases and urns to the realms of the curiosity hunter, or for conversion into spirit cases and stationery holders. The sarcophagus, often richly carved, of course succeeded the simple cellaret of Sheraton's period.
Before we dismiss the furniture of the "dining room" of this period, it may interest some of our readers to know that until the first edition of "Johnson's Dictionary" was published in 1755, the term was not to be found in the vocabularies of our language designating its present use. In Barrat's "Alvearic," published in 1580, "parloir," or "parler," was described as "a place to sup in." Later, "Minsheu's Guide unto Tongues," in 1617, gave it as "an inner room to dine or to suppe in," but Johnson's definition is "a room in houses on the first floor, elegantly furnished for reception or entertainment."
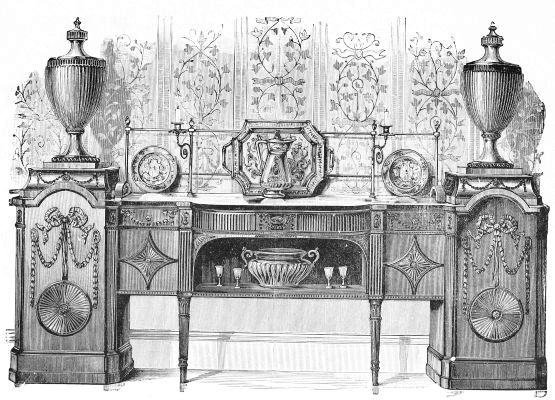

A SIDEBOARD IN MAHOGANY WITH INLAY OF SATINWOOD.
IN THE STYLE OF ROBERT ADAM.
To the latter part of the eighteenth century—the English furniture of which time has been discussed in this Chapter—belong the quaint little "urn stands" which were made to hold the urn with boiling water, while the tea pot was placed on a little slide which is drawn out from underneath the top. In those days tea was an expensive[201] luxury, and urn stands (illustrated below) were inlaid in the fashion of the time. These, together with the old mahogany or marqueterie tea caddies, which were sometimes the object of considerable skill and care, are dainty relics of the past. One of these, designed by Chippendale, as illustrated on page 179, and another by Hepplewhite will be found on page 194. They were fitted with two and sometimes three bottles or tea poys of silver or Battersea enamel, to hold the black and green teas, and when really good examples of these daintily-fitted tea caddies are offered for sale they bring large sums.
URN STAND. TOILET GLASS. URN STAND.
The "wine table" of this time deserves a word. These are now somewhat rare, and are only to be found in a few old houses, and in some of the Colleges at Oxford and Cambridge. These are fitted with revolving tops, which had circles turned out to a slight depth for each glass to stand in, and they were sometimes shaped like the half of a flat ring. These latter were for placing in front of the fire, when the outer side of the table formed a convivial circle, round which the sitters gathered after they had left the dinner table.
One of these old tables is still to be seen in the Hall of Gray's Inn, and the writer was told that its fellow was broken and had been "sent away." They are nearly always of good rich mahogany, and have legs more or less ornamental according to circumstances.
A distinguishing feature of English furniture of the eighteenth century was the partiality for secret drawers and contrivances for hiding away papers or valued articles; and in old secretaires and writing tables we find a great many ingenious designs which remind us of the days when there were but few banks, and people kept money and deeds in their own custody.
The reader who would make a careful study of English furniture of the period discussed in this chapter, is referred to the exhaustive work[202] edited by Mr. John Aldam Heaton, and published by Mr. Bumpus in parts:—"Furniture and Decoration in England during the 18th Century, being facsimile reproductions of the choicest examples from the works of Chippendale, Adam, G. Richardson, Hepplewhite, Sheraton, Piranesi, and others."

CARVED JARDINIERE, BY CHIPPENDALE.
The French Revolution and the First Empire—Influence on design of Napoleon's Campaigns—The Cabinet presented to Marie Louise—Dutch Furniture of the time—English Furniture—-Sheraton's later work—Thomas Hope, architect—George Smith's designs—Fashion during the Regency—Gothic revival—Seddon's furniture—Other makers—Influence on design of the Restoration in France—Furniture of William IV. and early part of Queen Victoria's reign—Baroque and Rococo styles—The panelling of rooms, dado, and skirting—The Art Union—The Society of Arts—Sir Charles Barry and the new Palace of Westminster—Pugin's designs—Auction Prices of Furniture—Christie's—The London Club Houses—Steam—Different Trade Customs—Exhibitions in France and England—Harry Rogers work—The Queen's cradle—State of Art in England during the first part of Queen Victoria's reign—Continental designs—Italian carving—Cabinet work—General remarks.
EMPIRE FURNITURE.
 HERE are great crises in the history of a nation
which stand out in prominent relief. One of
these is the French Revolution, which commenced
in 1792, and wrought such dire havoc amongst
the aristocracy, with so much misery and distress
throughout that country. It was an event of
great importance, whether we consider the religion,
the politics, or the manners and customs of a
people, as affecting the changes in the style of
the decoration of their homes. The horrors of
the Revolution are matters of common knowledge
to every schoolboy, and there is no need to dwell
either upon them or their consequences, which are
so thoroughly apparent. To the confiscation of
the property of those who had fled the country,
was added the general dislocation of everything
connected with the work of the industrial arts.
HERE are great crises in the history of a nation
which stand out in prominent relief. One of
these is the French Revolution, which commenced
in 1792, and wrought such dire havoc amongst
the aristocracy, with so much misery and distress
throughout that country. It was an event of
great importance, whether we consider the religion,
the politics, or the manners and customs of a
people, as affecting the changes in the style of
the decoration of their homes. The horrors of
the Revolution are matters of common knowledge
to every schoolboy, and there is no need to dwell
either upon them or their consequences, which are
so thoroughly apparent. To the confiscation of
the property of those who had fled the country,
was added the general dislocation of everything
connected with the work of the industrial arts.
Nevertheless it should be borne in mind that amongst the anarchy and disorder of this terrible time in France, the National Convention had sufficient foresight to appoint a Commission, composed of competent men in different branches of Art, to determine what State property in artistic objects should be sold, and what was of sufficient historical interest to be retained as a national possession. Riesener, the celebrated ébeniste, whose work we have described in the chapter on Louis Seize furniture, and David, the famous painter of the time, both served on this Commission, of which they must have been valuable members.
There is a passage in an article on "Art," by a democratic French writer, as early as 1790—when the great storm cloud was already threatening to burst—which is quoted by Mr. C. Perkins, the American translator of Dr. Falke's German work, "Kunst im Hause," and gives us the keynote to the great change which took place in the fashion of furniture about the time of the Revolution:—"We have changed everything; freedom, now consolidated in France, has restored the pure taste for the antique! Farewell to your marqueterie and Boule, your ribbons, festoons, and rosettes of gilded bronze; the hour has come when objects must be made to harmonize with circumstances."
Thus it is hardly too much to say that designs were governed by the politics and philosophy of the day; and one finds in furniture of this period, the reproduction of ancient Greek forms for chairs and couches; ladies' work tables, too, are fashioned somewhat after the old drawings of sacrificial altars; and the classical tripod is a favourite support. The mountings represent antique Roman fasces with an axe in the centre; trophies of lances, surmounted by a Phrygian cap of liberty; winged figures, emblematic of freedom; and antique heads of helmeted warriors arranged like cameo medallions.
After the execution of Robespierre, and the abolition of the Revolutionary Tribunal in 1794, came the establishment of the Directory; and then, after Buonaparte's brilliant success in Italy, and the famous expeditions to Syria and Egypt two years later, came his proclamation as First Consul in 1799, which, in 1802, was confirmed as a life appointment.
We have only to refer to the portrait of the great soldier, represented with the crown of bay leaves and other attributes of the old Roman imperialism, to see that in his mind was the ambition of reviving much of the splendour and of the surroundings of the Cæsars, whom he took, to some extent, as his models; and that in founding on the ashes of the Revolution a new fabric, with new people about him, all influenced by his energetic personality, he desired to mark his victories by stamping the new order of things with his powerful and assertive individualism.
The cabinet which was designed and made for Marie Louise, on his marriage with her in 1810, is an excellent example of the Napoleonic furniture. The wood used for this style of furniture was almost invariably rich mahogany, the color of which made a good ground for the bronze gilt mounts which were applied. The full-page illustration shews these mountings, which are all classical in character; and though there is no particular grace in the outline or form of the cabinet, there is a certain dignity and solemnity, relieved from oppressiveness by the fine chasing and gilding of the metal enrichments, and the excellent color and figuring of the rich Spanish mahogany used. This cabinet, and several other more or less ornate pieces of Napoleonic furniture, may still be seen in the Chateau of Fontainebleau.
CABINET IN MAHOGANY WITH BRONZE GILT MOUNTINGS.
Presented by Napoleon I. to Marie Louise on his Marriage with her in 1810.
PERIOD: NAPOLEON I.
On secretaires and tables, a common ornament of this description of furniture, is a column of mahogany, with a capital and base of bronze (either gilt, part gilt, or green), in the form of the head of a sphinx with the foot of an animal; console tables are supported by sphinxes and griffins: and candelabra and wall brackets for candles, have winged figures of females, stiff in modelling and constrained in attitude, but almost invariably of good material with careful finish.
TABOURET, OR STOOL. ARM CHAIR.
Carved and Gilt. In Mahogany, with Gilt Bronze Mountings.
PERIOD OF NAPOLEON I.
The bas-reliefs in metal which ornament the panels of the friezes of cabinets, or the marble bases of clocks, are either reproductions of mythological subjects from old Italian gems and seals, or represent the battles of the Emperor, in which Napoleon is portrayed as a Roman general. There was plenty of room to replace so much that had disappeared during the Revolution, and a vast quantity of decorative furniture was made during the few years which elapsed before the disaster of Waterloo caused the disappearance of a power which had been almost meteoric in its career.
One of the best authorities on "Empire Furniture" is the book of designs published in 1809 by the architects Percier and Fontaine. It is the more valuable, as a work of reference, from the fact that every design represented was actually carried out, and is not a mere exercise of fancy, as is the case with many such books. In the preface the authors[206] modestly state that they are entirely indebted to the antique for the reproduction of the different ornaments; and the originals, from which some of the designs were taken, are still preserved in a fragmentary form in the Museum of the Vatican.
The illustration on page 205 of an arm chair and a stool, together with that of the tripod table which ornaments the initial letter of this chapter, are favourable examples of the richly-mounted and more decorative furniture of this style. While they are not free from the stiffness and constraint which are inseparable from classic designs as applied to furniture, the rich color of the mahogany, the high finish and good gilding of the bronze mounts, and the costly silk with which they are covered, render them attractive and give them a value of their own.
The more ordinary furniture, however, of the same style, but without these decorative accessories, is stiff, ungainly, and uncomfortable, and seems to remind us of a period in the history of France when political and social disturbance deprived the artistic and pleasure-loving Frenchman of his peace of mind, distracting his attention from the careful consideration of his work. It may be mentioned here that, in order to supply a demand which has lately arisen, chiefly in New York, but also to some extent in England, for the best "Empire" furniture, the French dealers have bought up some of the old undecorated pieces, and by ornamenting them with gilt bronze mounts, cast from good old patterns, have sold them as original examples of the meubles de luxe of the period.
In Dutch furniture of this time one sees the reproduction of the Napoleonic fashion—the continuation of the Revolutionists' classicalism. Many marqueterie secretaires, tables, chairs, and other like articles, are mounted with the heads and feet of animals, with lion's heads and sphinxes, designs which could have been derived from no other source; and the general design of the furniture loses its bombé form, and becomes rectangular and severe. Whatever difficulty there may be in sometimes deciding between the designs of the Louis XIV. period, towards its close, and that of Louis XV., there can be no mistake about l'epoch de la Directoire and le style de l'Empire. These are marked and branded with the Egyptian expedition, and the Syrian campaign, as legibly as if they all bore the familiar plain Roman N, surrounded by a laurel wreath, or the Imperial eagle which had so often led the French legions to victory.
It is curious to notice how England, though so bitterly opposed to Napoleon, caught the infection of the dominant features of design which were prevalent in France about this time.
NELSON'S CHAIRS.
DESIGNS PUBLISHED BY T. SHERATON, OCTOBER, 1806.
DRAWING ROOM CHAIR.
Design published by T. Sheraton, April, 1804.
Thus, in Sheraton's Book on Furniture, to which allusion has been made, and from which illustrations have been given in the chapter on "Chippendale and his Contemporaries," there is evidence that, as in France during the influence of Marie Antoinette, there was a classical revival, and the lines became straighter and more severe for furniture, so this alteration was adopted by Sheraton, Shearer and other English designers at the end of the century. But if we refer to Sheraton's later drawings, which are dated about 1804 to 1806, we see the constrained figures and heads and feet of animals, all brought into the designs as shewn in the "drawing room" chairs here illustrated. These shew unmistakable signs of the French "Empire" influence, the chief difference between the French and English work being, that, whereas in French Empire furniture the excellence of the metal work redeems it from heaviness or ugliness,[208] such merit was wanting in England, where we have never excelled in bronze work, the ornament being generally carved in wood, either gilt or colored bronze-green. When metal was used it was brass, cast and fairly finished by the chaser, but much more clumsy than the French work. Therefore, the English furniture of the first years of the nineteenth century is stiff, massive, and heavy, equally with its French contemporary wanting in gracefulness, and not having the compensating attractions of fine mounting, or the originality and individuality which must always add an interest to Napoleonic furniture.
DRAWING ROOM CHAIR.
Design published by T. Sheraton, April 1, 1804.
There was, however, made about this time by Gillow, to whose earlier work reference has been made in the previous chapter, some excellent furniture, which, while to some extent following the fashion of the day, did so more reasonably. The rosewood and mahogany tables, chairs, cabinets, and sideboards of his make, inlaid with scrolls and lines of flat brass, and mounted with handles and feet of brass, generally representing the heads and claws of lions, do great credit to the English work of this time. The sofa table and sideboard, illustrated on the previous page, are of this class, and shew that Sheraton, too, designed furniture of a less pronounced character, as well as the heavier kind to which reference has been made.
"CANOPY BED."
DESIGN PUBLISHED BY T. SHERATON, NOVEMBER 9TH, 1803.
"SISTERS' CYLINDER BOOKCASE."
DESIGNED BY T. SHERATON, 1802.

SIDEBOARD.
In Mahogany, with Brass Rail and Convex Mirror at back.
Design published by T. Sheraton, 1802.

SOFA TABLE.
Design published by T. Sheraton, 1804.
A very favourable example of the craze in England for classic design in furniture and decoration, is shewn in the reproduction of a drawing by Thomas Hope (known as "Anastasius Hope"), in 1807, a well-known architect of the time, in which it will be observed that the forms and fashions of some of the chairs and tables described and illustrated in the chapter on "Ancient Furniture" have been taken as models.
There were several makers of first-class furniture, of whom the names of some still survive in the "style and title" of firms of the present day, who are their successors, while those of others have been forgotten, save by some of our older manufacturers and auctioneers, who, at the request of the writer, have been good enough to look up old records and revive the memories of fifty years ago. Of these the best known was Thomas Seddon, who came from Manchester and settled in Aldersgate Street. His two sons succeeded to the business, became cabinet makers to George IV., and furnished and decorated Windsor Castle. At the King's death their account was disputed, and £30,000 was struck off, a loss which necessitated an arrangement with their creditors. Shortly after this, however, they took the Barracks of the London Light Horse Volunteers in the Gray's Inn Road (now the Hospital), and carried on there for a time a very extensive business. Seddon's work ranked with Gillow's, and they shared with that house the best orders for furniture.
Thomas Seddon, painter of Oriental subjects, who died in 1856, and P. Seddon, a well-known architect, were grandsons of the original founder of the firm. On the death of the elder brother, Thomas, the younger one then transferred his connection to the firm of Johnstone and Jeanes, in Bond Street, another old house which until recently carried on business as "Johnstone and Norman," and who some few years ago executed a very extravagant order for an American millionaire. This was a reproduction of Byzantine designs in furniture of cedar, ebony, ivory, and pearl, made from drawings by the late Sir Alma Tadema, R.A.
Snell, of Albemarle Street, was established early in the century, and had obtained an excellent reputation; his specialité was well-made birch bedroom suites, but he also made furniture of a general description. The predecessor of the present firm of Howard and Son, who commenced business in Whitechapel as early as 1800, and the first Morant, may all be mentioned as manufacturers in the first quarter of the century.
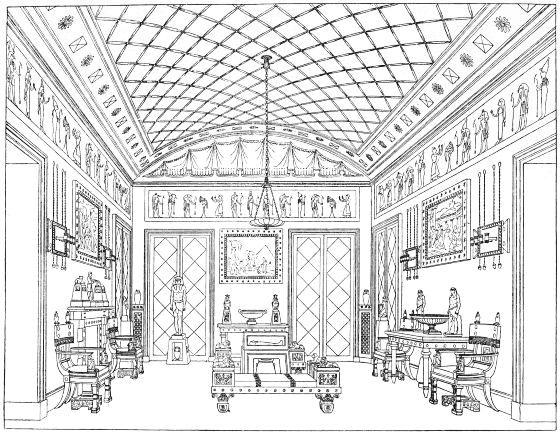
DESIGN OF A ROOM IN THE CLASSIC STYLE, BY THOMAS HOPE, ARCHITECT, IN 1807.
Somewhat later, Trollopes, of Parliament Street; Holland, who had succeeded Dowbiggin (Gillow's apprentice), first in Great Pulteney Street, and subsequently at the firm's present address; Wilkinson, of Ludgate Hill, founder of the present firm of upholsterers in Bond Street; Aspinwall, of Grosvenor Street; the second Morant, of whom the great Duke of Wellington made a personal friend; and Crace, a prominent decorator of great taste, who carried out many of Pugin's Gothic designs, were all men of good reputation. Miles and Edwards, of Oxford Street, whom Hindleys succeeded, were also well known for good middle-class furniture. These are some of the best known manufacturers of the first half of the present century, and though until after the Great Exhibition there was, as a rule, little in the designs to render their productions remarkable, the work of those named will be found sound in construction, and free from the faults which accompany the cheap and showy reproductions of more pretentious styles, which mark so much of the furniture of the present day. With regard to this, more will be said in the next chapter.
There was then a very limited market for any but the most commonplace furniture. Our wealthy people bought the productions of French cabinet makers, either made in Paris or by Frenchmen who came over to England, and the middle classes were content with the most ordinary and useful articles. If they had possessed the means, they certainly had neither the taste nor the education to furnish more ambitiously. The great extent of suburbs which now surround the Metropolis, and which include such numbers of expensive and extravagantly-fitted residences of merchants and tradesmen, did not then exist. The latter lived over their shops or warehouses, and the former only aspired to a dull house in Bloomsbury, or like David Copperfield's father-in-law, Mr. Spenlow, a villa at Norwood, or perhaps a country residence at Hampstead or Highgate.
In 1808 a designer and maker of furniture, George Smith by name, who held the appointment of "Upholder extraordinary to H.R.H. the Prince of Wales," and carried on business at "Princess" Street, Cavendish Square, produced a book of designs, 158 in number, published by "Wm. Taylor," of Holborn. These include cornices, window drapery, bedsteads, tables, chairs, bookcases, commodes, and other furniture, the titles of some of which occur for about the first time in our vocabularies, having been adapted from the French. "Escritoire, jardinière, dejuné-tables, chiffoniers" (the spelling copied from Smith's book), all bear the impress of the pseudo-classic taste; and his designs, some of which are[213] here reproduced, show the fashion of our so-called artistic furniture in England at the time of the Regency. Mr. Smith, in the "Preliminary Remarks" prefacing his illustrations, gives us an idea of the prevailing taste, which, looking back now some three-quarters of a century, it is instructive to peruse:—

"LIBRARY FAUTEUIL."
Reproduced from Smith's Book of Designs, published in 1804.
"The following practical observations on the various woods employed in cabinet work may be useful. Mahogany, when used in houses of consequence, should be confined to the parlour and the bedchamber floors. In furniture for these apartments the less inlay of other woods, the more chaste will be the style of work. If the wood be of a fine, compact, and[214] bright quality, the ornaments may be carved clean in the mahogany. Where it may be requisite to make out panelling by an inlay of lines, let those lines be of brass or ebony. In drawing-rooms, boudoirs, ante-rooms, East and West India satin woods, rosewood, tulip wood, and the other varieties of woods brought from the East, may be used; with satin and light coloured woods the decorations may be of ebony or rosewood; with rosewood let the decorations be ormolu, and the inlay of brass. Bronze metal, though sometimes used with satin wood, has a cold and poor effect: it suits better on gilt work, and will answer well enough on mahogany."
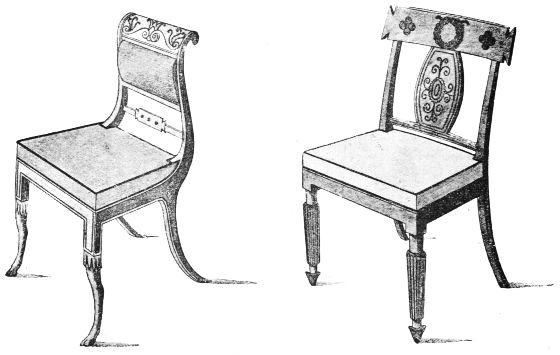
"PARLOR CHAIRS."
Shewing the inlay of Brass referred to. From Smith's Book of Designs, published in 1808.
Amongst the designs published by him are some few of a subdued Gothic character; these are generally carved in light oak, or painted light stone color, and have, in some cases, heraldic shields, with crests and coats of arms picked out in color. There are window seats painted to imitate marble, with the Roman or Greco-Roman ornaments painted green to represent bronze. The least objectionable are those of mahogany with bronze green ornaments.
Of the furniture of this period there are several pieces in the Mansion House, in the City of London, which apparently was partly refurnished about the commencement of the century.
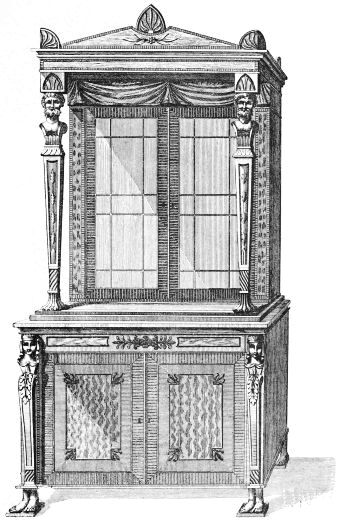
BOOKCASE.
DESIGN PUBLISHED BY T. SHERATON, JUNE 12th, 1806.
Note.—Very similar bookcases are in the London Mansion House.
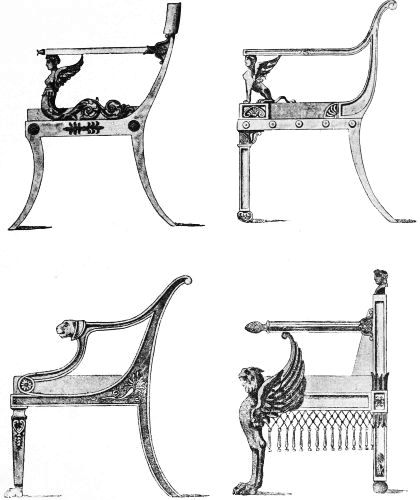
"DRAWING ROOM CHAIRS IN PROFILE."
From G. Smith's Book, published in 1808.
In the Court Room of the Skinners' Company there are tables which are now fitted with extensions, so as to form a horseshoe table for committee meetings. They are good examples of the heavy and solid carving in mahogany, early in the century before the fashion of representing the heads and feet of animals in the designs of furniture had gone out. These tables have massive legs, with lions' heads and claws, carved with great skill and shewing much spirit, the wood being of the best quality and rich in color.
In the work of the manufacturers just enumerated may be traced the influence of the "Empire" style. With the restoration, however, of the Monarchy in France, came the inevitable change in fashions, and "Le style de l'Empire" was condemned. In its place came a revival of the Louis Quinze scrolls and curves, but with less character and restraint, until the style we know as "baroque,"[20] or debased "rococo" came in. Ornament of a florid and incongruous character was lavished on decorative furniture, indicative of a taste for display, rather than for appropriate enrichment.
It had been our English custom for some long period to take our fashions from France, and, therefore, about the time of William IV. and during the early part of Queen Victoria's reign, the furniture for our best houses was designed and made in the French style. In the "Music" Room at Chatsworth are some chairs and footstools used at the time of the Coronation of William IV. and Queen Adelaide, which have quite the appearance of French furniture.
The old fashion of lining rooms with oak panelling, which has been noticed in the earlier chapter, had undergone a change worth recording. If the illustration of the Elizabethan oak panelling, as given in the English section of Chapter III., be referred to, it will be seen that the oak lining reaches from the floor to within about two or three feet of the cornice. Subsequently this panelling was divided into an upper and a lower part, the former commencing about the height of the back of an ordinary chair, a moulding or chair-rail forming a capping to the lower part. Then pictures came to be let into the panelling: and presently the upper part was discarded and the lower wainscoting remained, properly termed the Dado,[21] which we have seen revived both in wood and in various decorative materials of the present day. During the period we are now discussing, this arrangement lost favour in the eyes of our grandfathers, and the lowest member, or base, of the Dado only was retained, which is now termed the "skirting board."
As we approach a period that our older contemporaries can remember, it is very interesting to turn over the leaves of the back numbers of such magazines and newspapers as treated of the Industrial Arts. The Art Union, which changed its title to the Art Journal in 1849, had then been in existence for about ten years, and had done good work in promoting the encouragement of Art and manufactures. The "Society of Arts" had been formed in London as long ago as 1756, and had given prizes for designs and methods of improving different processes of manufacture. Exhibitions of the specimens sent in for competition for the awards were, and are still, held at their house in Adelphi Buildings. Old volumes of "Transactions of the Society" are quaint works of reference with regard to these exhibitions.
About 1840, Mr., afterwards Sir, Charles Barry, R.A., had designed and commenced the present, or, as it was then called, the New Palace of Westminster, and following the Gothic character of the building, the furniture and fittings were naturally of a design to harmonize with what was then quite a departure from the heavy architectural taste of the day. Mr. Barry was the first in the last century to leave the beaten track, although the Reform and Travellers' Clubs had already been designed by him on more classic lines. The Speaker's chair in the House of Commons is evidently designed after one of the fifteenth century "canopied seats," which have been noticed and illustrated in the second chapter; and the "linen scroll pattern" panels can be counted by the thousand in the Houses of Parliament and the different official residences which form part of the Palace. The character of the work is subdued and not flamboyant, is excellent in design and workmanship, and is highly creditable, when we take into consideration the very low state of Art in England fifty years ago.
This want of taste was very much discussed in the periodicals of the day, and, yielding to expressed public opinion, Government had in 1840-1 appointed a Select Committee to take into consideration the promotion of the Fine Arts in the country. Mr. Charles Barry, Mr. Eastlake, and Sir Martin Shee, R.A., were amongst the witnesses examined. The report of this Committee, in 1841, contained the opinion "That such an important and National work as the erection of the two Houses of Parliament affords an opportunity, which ought not to be neglected, of encouraging, not only the higher, but every subordinate branch of Fine Art in this country."
Mr. Augustus Welby Pugin was a well-known designer of the Gothic style of furniture of this time. Born in 1811, he had published in 1835 his "Designs for Gothic Furniture," and subsequently his "Glossary of[218] Ecclesiastical Ornament and Costume"; and by skilful application of his knowledge to the decorations of the different ecclesiastical buildings he designed, his reputation became established. One of his designs is here reproduced. Pugin's work and reputation have survived, notwithstanding the furious opposition he met with at the time. In a review of one of his books, in the Art Union of 1839, the following sentence completes the criticism:—"As it is a common occurrence in life to find genius mistaken for madness, so does it sometimes happen that a madman is mistaken for a genius. Mr. Welby Pugin has oftentimes appeared to us to be a case in point."

PRIE-DIEU.
In Carved Oak, enriched with Painting and Gilding.
Designed by Mr. Pugin, and manufactured by Mr. Crace, London.
At this time furniture design and manufacture, as an Industrial Art in England, seems to have attracted no attention whatever. There are[219] but few allusions to the design of decorative woodwork in the periodicals of the day; and the auctioneers' advertisements—with a few notable exceptions, like that of the Strawberry Hill Collection of Horace Walpole, gave no descriptions; no particular interest in the subject appears to have been manifested, save by a very limited number of the dilettanti, who, like Walpole, collected the curios and cabinets of two or three hundred years ago.

SECRETAIRE AND BOOKCASE.
In Carved Oak, in style of German Gothic.
(From a Drawing by Professor Heideloff. Published in the "Art Union," 1846.)
York House was redecorated and furnished about this time, and as it is described as "Excelling any other dwelling of its own class in regal magnificence and vieing with the Royal Palaces of Europe," we may take note of an account of its re-equipment, written in 1841, for the Art Union. This notice speaks little for the taste of the period, and less for the knowledge and grasp of the subject by the writer of an Art critique of the day:—"The furniture generally is of no particular style, but, on the whole, there is to be found a mingling of everything, in the best manner of the best epochs of taste." Writing further on of the ottoman[220] couches, "causeses," etc., the critic goes on to tell of an alteration in fashion which had evidently just taken place: "Some of them, in place of plain or carved rosewood or mahogany, are ornamented in white enamel, with classic subjects in bas-relief of perfect execution."
Towards the close of the period embraced in the limits of this chapter, the eminent firm of Jackson and Graham was making headway. A French designer named Prignot was of considerable assistance in establishing their reputation for taste; and in the Exhibition which was soon to take place this firm took a very prominent position. Collinson and Lock,[22] who afterwards acquired this firm's premises and business, were both brought up in the house as young men, and left some thirty odd years ago for Herrings, of Fleet Street, whom they succeeded about 1870.
Another well-known decorator who designed and manufactured furniture of good quality was Leonard William Collmann, first of Bouverie Street, and later of George Street, Portman Square. He was a pupil of Sydney Smirke, R.A. (who designed and built the Carlton and the Conservative Clubs), and was himself an excellent draughtsman, and carried out the decoration and furnishing of many public buildings, London Clubs, and mansions of the nobility and gentry. His son is at present Director of Decorations to the King at Windsor Castle. Collmann's designs were occasionally Gothic, but generally classic.
There is evidence of the want of interest in the subject of furniture in the auctioneers' catalogues of the day. By the courtesy of Messrs. Christie, Manson and Woods, the writer has had access to the records of this old firm, and two or three instances of sales of furniture may be given. While the catalogues of the Picture sales of 1830-40 were printed on paper of quarto size, and the subjects described at length, those of "Furniture" are of the old-fashioned small octavo size, resembling the catalogue of a small country auctioneer of the present day, and the printed descriptions rarely exceed a single line. The prices seldom amounted to more than £10; the whole proceeds of the day's sale were often less than £100, and sometimes did not reach £50. At the sale of "Rosslyn House," Hampstead, in 1830, a mansion of considerable importance, the highest-priced article was "A capital mahogany pedestal sideboard, with hot closet, cellaret, 2 plate drawers, and fluted legs," which brought £32. At the sale of the property of "A Man of Fashion," "a marqueterie cabinet, inlaid with trophies, the panels of Sêvres china, mounted in ormolu," sold for twenty guineas; and a "Reisener (sic) table, beautifully inlaid with flowers, and drawers," which appears to have been reserved at nine guineas, was bought in at eight-and-a-half guineas.[221] Frequenters of Christie's of the present day who have seen such furniture realise as many pounds as the shillings included in such sums, will appreciate the enormously increased value of really good old French furniture.
Perhaps the most noticeable comparison between the present day and that of half-a-century ago may be made in reading through the prices given at the great sale at Stowe House, in 1848, when the financial difficulties of the Duke of Buckingham caused the sale by auction which lasted thirty-seven days, and realised upwards of £71,000; the proceeds of the furniture amounted to £27,152. We have seen in the notice of French furniture that armoires by Boule have, during the past few years, brought from £4,000 to £6,000 each, under the hammer, and the want of appreciation of this work, probably the most artistic ever produced by designer and craftsman, is sufficiently exemplified by the statement that at the Stowe sale two of Boule's famous armoires, of similar proportions to those in the Hamilton Palace and Jones Collections, were sold for £21 and £19 8s. 6d. respectively.
We are accustomed now to see the bids at Christie's advance by guineas, by fives, tens and fifties; and it is amusing to read in these old catalogues of marqueterie tables, satin wood cabinets, rosewood pier tables, and other articles of "ornamental furniture," as it was termed, being knocked down to Town and Emanuel, Webb, Morant, Hitchcock Baldock, Forrest, Redfearn, Litchfield (the writer's father), and others who were the buyers and regular attendants at "Christie's" (afterwards Christie and Manson) of 1830 to 1845, for such sums as 6s., 15s., and occasionally £10 or £15.
A single quotation is given, but many such are to be found:—
Sale on February 25th and 26th, 1841. Lot 31. "A small oval table, with a piece of Sêvres porcelain painted with flowers. 6s."
It is pleasant to remember, as some exception to this general want of interest in the subject, that in 1843 there was held at Gore House, Kensington, then the fashionable residence of Lady Blessington, an exhibition of old furniture; and a series of lectures, illustrated by the contributions, was given by Mr., now Sir, J. C. Robinson. The Venetian State chair, illustrated on page 57, was amongst the examples lent by the Queen on that occasion. Specimens of Boule's work and some good pieces of Italian Renaissance were also exhibited.
A great many of the older Club Houses of London were built and furnished between 1813 and 1851, the Guards' being of the earlier date, and the Army and Navy of the latter; and during the intervening thirty odd years the United Service, Travellers', Union, United University[222] Athenæum, Oriental, Wyndham, Oxford and Cambridge, Reform, Carlton, Garrick, Conservative, and some others were erected and fitted up. Many of these still retain much of the furniture of Gillows, Seddons, and some of the other manufacturers of the time whose work has been alluded to, and these are favourable examples of the best kind of cabinet work done in England during the reign of George IV., William IV., and that of the early part of Queen Victoria. It is worth recording, too, that during this period, steam power, which had been first applied to machinery about 1815, came into more general use in the manufacture of furniture. With its adoption there seems to have been a gradual abandonment of the apprenticeship system in the factories and workshops of our country; and the present "piece-work" arrangement, which had obtained more or less since the English cabinet makers had brought out their "Book of Prices" some years previously, became generally the custom of the trade, in place of the older "day work" of a former generation.
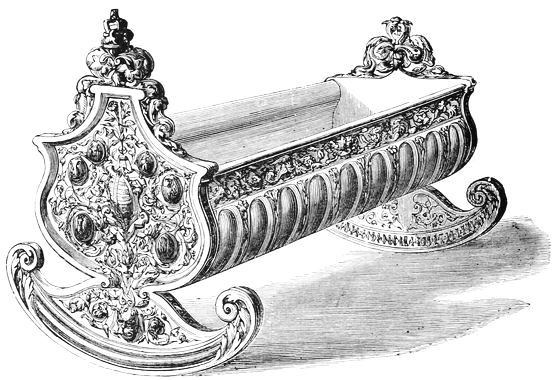
CRADLE.
In Boxwood, for H.M. Queen Victoria. Designed and Carved by H. Rogers, London.
In France the success of national exhibitions had become assured, the exhibitors having increased from only 110, when the first experiment was tried in 1798, by leaps and bounds, until at the eleventh exhibition, in 1849, there were 4,494 entries. The Art Journal of that year gives us a good illustrated notice of some of the exhibits, and devotes an article to pointing out the advantages to be gained by something of the kind taking place in England.
From 1827 onwards we had established local exhibitions in Dublin, Leeds, and Manchester. The first time a special building was devoted to the exhibition of manufactures was at Birmingham in 1849; and from the illustrated review of this in the Art Journal, one can see that there was a desire on the part of our designers and manufacturers to strike out in new directions and make progress.
We are able to reproduce some of the designs of furniture of this period; and in the cradle designed and carved in Turkey-boxwood, for Queen Victoria, by Mr. Harry Rogers, we have a fine piece of work, which would not have disgraced the latter period of the Renaissance. Indeed, Mr. Rogers was a very notable designer and carver of this time; he had introduced his famous boxwood carving about seven years previously.

DESIGN FOR A TEA CADDY.
By J. Strudwick, for Inlaying in Ivory.
Published as one of the "Original Designs for Manufacturers" in the Art Journal, 1849.
This cradle was also, by Queen Victoria's command, sent to the Exhibition, and it may be worth while quoting the artist's description of the carving:—"In making the design for the cradle it was my intention that the entire object should symbolize the union of the Royal Houses of England with that of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, and with this view, I[224] arranged that one end should exhibit the arms and national motto of England, and the other those of H.R.H. Prince Albert. The inscription, 'Anno, 1850,' was placed between the dolphins by Her Majesty's special command."

DESIGN FOR ONE OF THE WINGS OF A SIDEBOARD.
By W. Holmes. Exhibited at the "Society of Arts" in 1848, and published in the Art Journal, in 1849.
In a criticism of this excellent specimen of work, the Art Journal of the time said:—"We believe the cradle to be one of the most important examples of the art of wood carving ever executed in this country."
Rogers was also a writer of considerable ability on the styles of ornament: and there are several contributions from his pen to the[225] periodicals of the day, besides designs which were published in the Art Journal under the heading of "Original Designs for Manufacturers." These articles appeared occasionally, and contained many excellent suggestions for manufacturers and carvers, amongst others the drawings of H. Fitzcook, one of whose designs for a work table is here reproduced. Others more or less constant contributors of the original designs for furniture were J. Strudwick and W. Holmes, a design from the pencil of each of whom is given.

DESIGN FOR A WORK TABLE.
By H. Fitzcook. Published as one of the "Original Designs for Manufacturers," in the Art Journal, 1850.
But though here and there in England good designers came to the front, as a general rule the art of design in furniture and decorative woodwork was at a very low ebb about this time.
In furniture, straight lines and simple curves may be plain and uninteresting, but they are by no means so objectionable as the over ornamentation of the debased rococo style, which obtained in this country about forty years ago; and if the scrolls and flowers, the shells and rockwork which ornamented mirror frames, sideboard backs, sofas, and[226] chairs, were debased in style, even when carefully carved in wood, the effect was infinitely worse when, for the sake of economy, as was the case with the houses of the middle classes, this elaborate and laboured enrichment was executed in the fashionable stucco of the day.
Large mirrors, with gilt frames of this material, held the places of honor on the marble chimney piece, and on the console, or pier table, which was also of gilt stucco, with a marble slab. The chiffonier, with its shelves having scroll supports like an elaborate S, and a mirror at the back, with a scrolled frame, was a favourite article of furniture.
Carpets were badly designed, and loud and vulgar in coloring; chairs, on account of the shape and ornament in vogue, were unfitted for their purpose, on account of the wood being cut across the grain; the fire-screen, in a carved rosewood frame, contained the caricature, in needlework, of a spaniel, or a family group of the time, ugly enough to be in keeping with its surroundings.
The dining room was sombre and heavy. The pedestal sideboard, with a large mirror with a scrolled frame at the back, had come in; the chairs were massive and ugly survivals of the earlier reproductions of the Greek patterns, and though solid and substantial, the effect was neither cheering nor refining.
In the bedrooms were winged wardrobes and chests of drawers; dressing tables and washstands, with scrolled legs, nearly always in mahogany; the old four-poster had given way to the Arabian or French bedstead, and this was being gradually replaced by the iron or brass bedsteads, which came in after the "Exhibition of 1851" had shewn people the advantages of the lightness and cleanliness of these materials.
In a word, from the early part of the last century, until the impetus given to Art by this great Exhibition had had time to take effect, the general taste in furnishing houses of all but a very few persons was at about its worst.
In other countries the rococo taste had also taken hold. France maintained a higher standard than England, and such figure work as was introduced into her furniture, was better executed, though her joinery was inferior. In Italy, old models of the Renaissance still served as examples for reproduction, but the ornament was more carelessly carved and the decoration less considered. Ivory inlaying was largely practised in Milan and Venice; mosaics of marble were specialités of Rome and of Florence, and were much used in the decoration of cabinets; Venice was busy manufacturing carved walnutwood furniture, in buffets, cabinets, negro page boys elaborately painted and gilt; and carved mirror frames, the chief ornaments of which were cupids and foliage.
Italian carving has always been free and spirited, the figures have never been wanting in grace, and though by comparison with the best time of the Renaissance there is a great falling off, still, the work executed in Italy during the nineteenth century has been of considerable merit as regards ornament, though this has been overdone. In construction, and joinery, however, the Italian work was and still is, for the most part, very inferior. Cabinets of great pretension and elaborate ornament, inlaid perhaps with ivory, lapislazuli, or marbles, are so imperfectly made that one would think ornament, and certainly not durability, had been the object of the producer.
In Antwerp, Brussels, Liege, and other Flemish Art centres, the School of Wood Carving, which came in with the Renaissance, appears to have been maintained with more or less excellence. With the increased quality of the carved woodwork manufactured, there was a proportion of ill-finished and over-ornamented work produced; and although, as has been before observed, the manufacture of cheap marqueterie in Amsterdam, and other Dutch cities was bringing the name of Dutch furniture into ill-repute—still, so far as the writer's observations have gone, the Flemish wood-carver appears to have been, at the time now under consideration, ahead of his fellow craftsmen in Europe; and when, in the ensuing chapter, we shall notice some of the representative exhibits in the great International Competition of 1851, it will be seen that the Antwerp designer and carver was certainly in the foremost rank.
In Austria, too, some good cabinet work was being carried out, M. Leistler, of Vienna, having at the time a high reputation.
In Paris, the house of Fourdinois was making a name which, in subsequent exhibitions, we shall see took a leading place among the designers and manufacturers of decorative furniture.
England, it has been observed, was suffering from languor in Art industry. The excellent designs of the Adams and their school, which obtained early in the century, had been supplanted, and a meaningless rococo style succeeded the heavy imitations of French pseudo-classic furniture. Instead of, as in the earlier and more tasteful periods, when architects had designed woodwork and furniture to accord with the style of their buildings, they appear to have then, as a general rule, abandoned the control of the decoration of interiors, and the result was one which—when we examine our National furniture of half a century ago—has not left us much to be proud of as an artistic and industrious people.
Some notice has been taken of the appreciation of this unsatisfactory state of things by the Government of the time, and by the Press; and, as with a knowledge of our deficiency, came the desire and the energy to[228] bring about its remedy, we shall see that, with the Exhibition of 1851, and the intercourse and the desire to improve, which naturally followed that great and successful effort, our designers and craftsmen profited by the great stimulus which Art and Industry then received.

VENETIAN STOOL OF CARVED WALNUT WOOD.
SIDEBOARD IN CARVED OAK, WITH CELLARET.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY MR. GILLOW, LONDON. 1851 EXHIBITION.
CHIMNEYPIECE AND BOOKCASE.
In carved walnut wood, with colored marbles inlaid, and doors of perforated brass.
DESIGNED BY MR. T. R. MACQUOID, ARCHITECT, AND MANUFACTURED BY MESSRS. HOLLAND & SONS, LONDON. 1851 EXHIBITION.
CABINET IN THE MEDIÆVAL STYLE.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY MR. CRACE, LONDON. 1851 EXHIBITION.
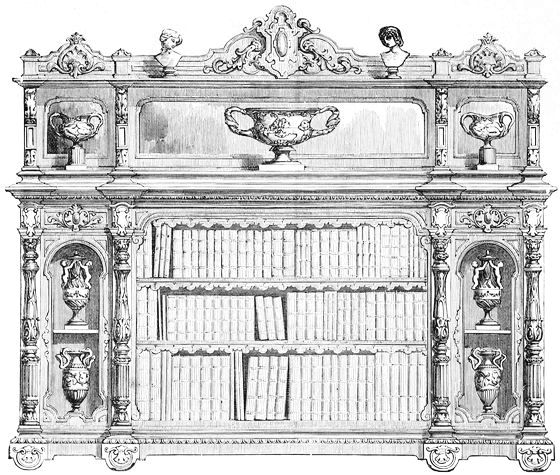
BOOKCASE IN CARVED WOOD.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY MESSRS. JACKSON & GRAHAM, LONDON. 1851 EXHIBITION.
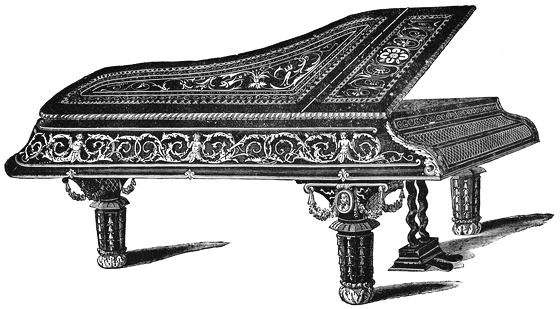
GRAND PIANOFORTE.
In Ebony inlaid, and enriched with Gold in relief.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY MESSRS. BROADWOOD, LONDON. 1851 EXHIBITION.
THE GREAT EXHIBITION:—Exhibitors and contemporary Cabinet Makers—Exhibition of 1862, London; 1867, Paris; and subsequently—Description of Illustrations—Fourdinois, Wright and Mansfield—The South Kensington Museum—Talbert's Work—Revival of Marquetry—Comparison of Present Day with that of a Hundred Years Ago—Æstheticism—Traditions—Trades-Unionism—The Arts and Crafts Exhibition Society—Kensington School of Wood-carving—Independence of Furniture—Present Fashions—Writers on Design—The New Renaissance—"Trade" Journals—Modern Furniture in other Countries—Concluding Remarks.
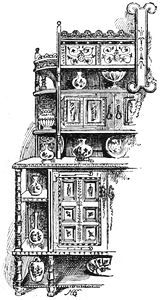 N the previous chapter, attention has been taken
of the success of the National Exhibition in Paris
of 1849; in the same year the competition of our
manufacturers at Birmingham gave an impetus
to Industrial Art in England, and there was about
this time a general forward movement, with a
desire for an International Exhibition on a grand
scale. Articles advocating such a step appeared
in newspapers and periodicals of the time, and,
after much difficulty, and many delays, a committee
for the promotion of this object was formed.
This resulted in the appointment of a Royal Commission,
and the Prince Consort, as President of
this Commission, took a keen personal interest
in every arrangement for this great enterprise.
Indeed, there can be no doubt that the success
which crowned the work was, in a great measure, due to his taste,
patience, and excellent business capacity. It is no part of our task to
record all the details of an undertaking which, at the time, was a
burning question of the day; still, as we cannot but look upon this
Exhibition of 1851 as one of the landmarks in the history of furniture,
it is worth while to record some particulars of its genesis and accomplishment.
N the previous chapter, attention has been taken
of the success of the National Exhibition in Paris
of 1849; in the same year the competition of our
manufacturers at Birmingham gave an impetus
to Industrial Art in England, and there was about
this time a general forward movement, with a
desire for an International Exhibition on a grand
scale. Articles advocating such a step appeared
in newspapers and periodicals of the time, and,
after much difficulty, and many delays, a committee
for the promotion of this object was formed.
This resulted in the appointment of a Royal Commission,
and the Prince Consort, as President of
this Commission, took a keen personal interest
in every arrangement for this great enterprise.
Indeed, there can be no doubt that the success
which crowned the work was, in a great measure, due to his taste,
patience, and excellent business capacity. It is no part of our task to
record all the details of an undertaking which, at the time, was a
burning question of the day; still, as we cannot but look upon this
Exhibition of 1851 as one of the landmarks in the history of furniture,
it is worth while to record some particulars of its genesis and accomplishment.
The idea of the Exhibition of 1851 is said to have been originally due to Mr. F. Whishaw, Secretary of the Society of Arts, as early as 1844, but no active steps were taken until 1849, when the Prince Consort, who was President of the Society, took the matter up very warmly. His speech at one of the meetings contained the following sentence:—
"Now is the time to prepare for a great Exhibition—an Exhibition worthy of the greatness of this country, not merely national in its scope and benefits, but comprehensive of the whole world; and I offer myself to the public as their leader, if they are willing to assist in the undertaking."

LADY'S ESCRITOIRE.
In White Wood, Carved with Rustic Figures. Designed and Manufactured by M. Wettli, Berne, Switzerland. 1851 Exhibition, London.
To Mr. (afterwards Sir) Joseph Paxton, then head gardener to the Duke of Devonshire, the general idea of the famous glass and iron building is due. An enterprising firm of contractors, Messrs. Fox and Henderson, were entrusted with the work; a guarantee fund of some £230,000 was raised by public subscriptions; and the great Exhibition was opened by Queen Victoria on the 1st of May, 1851. At a civic banquet in honor of[231] the event, the Prince Consort very aptly described the object of the great experiment:—"The Exhibition of 1851 would afford a true test of the point of development at which the whole of mankind had arrived in this great task, and a new starting point from which all nations would be able to direct their further exertions."
The number of exhibitors was some 17,000, of whom over 3,000 received prize and council medals; and the official catalogue, compiled by Mr. Scott Russell, the secretary, contains a great many particulars which are instructive reading, when we compare the work of many of the firms of manufacturers, whose exhibits are therein described, with their work of the present day.
The Art Journal published a special volume, entitled "The Art Journal Illustrated Catalogue," with woodcuts of the more important exhibits, and, by the courtesy of the proprietors, a small selection is reproduced, which will give the reader an idea of the design of furniture, both in England and the chief Continental industrial centres at that time.
They have been selected as being fairly representative of the work of the time, and not on account of their own intrinsic excellence.
With regard to the exhibits of English firms, of which these illustrations include examples, little requires to be said, in addition to the remarks already made in the preceding chapter, of their work previous to the Exhibition. One of the illustrations, however, may in passing be further alluded to, since the changes in form and character of the Pianoforte is of some importance in the consideration of the design of furniture. Messrs. Broadwood's Grand Pianoforte (illustrated) was a rich example of decorative woodwork in ebony and gold, and may be compared with the illustration on page 172 of a harpsichord, which the Piano had replaced about 1767; and this supplies evidence of the increased attention devoted to decorative furniture at and since the time of the 1851 Exhibition. In the Appendix will be found a short notice of the different phases through which the ever-present piano has passed, from the virginal, or spinette—of which an illustration will be found in "A Sixteenth Century Room" in Chapter III.—down to the latest development of the decoration of the case of the instrument by leading artists of the present day. Mr. Algernon Rose, of Messrs. Broadwood, whose firm was established at their present address in 1732, has been good enough to supply the author with the particulars for this notice.
It will be seen from the illustrations of these exhibits that, so far as figure carving and composition are concerned, our foreign rivals, the Italians, Belgians, Austrians, and French, were far ahead of us. In mere construction and excellence of work, we have ever been able to hold our[232] own, and, so long as our designers have kept to beaten tracks, the effect is satisfactory. It is only when an attempt has been made to soar above the conventional, that the effort is not so successful.

LADY'S WORK TABLE AND SCREEN.
In Papier-maché. 1851 Exhibition, London.
In looking over the list of exhibits, one finds evidence of the fickleness of fashions. The manufacture of decorative articles of furniture of papier-maché was then very extensive, and there are several specimens of this class of work executed, both by French and English firms. The drawing-room of 1850 to 1860 was apparently incomplete without occasional chairs, a screen with painted panel, a work table, or some small cabinet or casket of this decorative but somewhat flimsy material.
The design and execution of mountings of cabinets in metal work, particularly of the highly-chased and gilt bronzes for the enrichment of meubles de luxe, was then, as it still to a great extent remains, the specialité of the Parisian craftsman, and almost the only English exhibits of such work were those of foreigners who had settled amongst us.
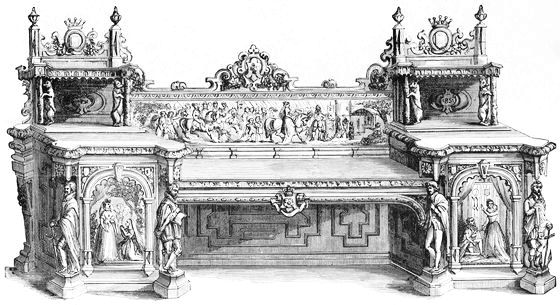
SIDEBOARD.
In Carved Oak, with subjects taken from Sir Walter Scott's "Kenilworth."
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY MESSRS. COOKES, WARWICK. 1851 EXHIBITION, LONDON.

A STATE CHAIR.
Carved and Gilt Frame, Upholstered in Ruby Silk, Embroidered with the Royal Coat of Arms and the Prince of Wales' Plumes.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY M. JANCOWSKI, YORK. 1851 EXHIBITION, LONDON.

SIDEBOARD IN CARVED OAK.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY M. DURAND, PARIS. 1851 EXHIBITION, LONDON.

BEDSTEAD IN CARVED EBONY.
RENAISSANCE STYLE. DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY M. ROULÉ, ANTWERP. 1851 EXHIBITION, LONDON.

PIANOFORTE
In Rosewood, inlaid with Boulework, in Gold, Silver, and Copper.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY M. LEISTLER, VIENNA. 1851 EXHIBITION, LONDON.
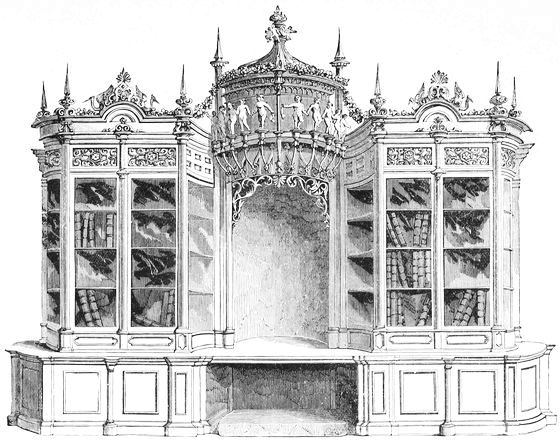
BOOKCASE.
In Carved Lime Tree, with Panels of Satinwood.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY M. LEISTLER, VIENNA. 1851 EXHIBITION, LONDON.
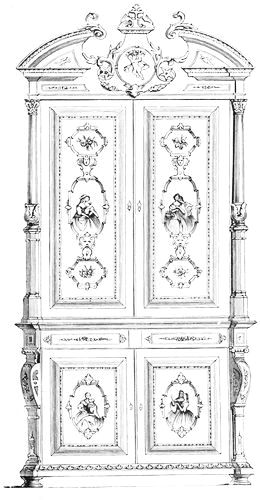
CABINET.
In Tulipwood, ornamented with Bronze, and inlaid with Porcelain.
MANUFACTURED BY M. GAMBS, ST. PETERSBURG. 1851 EXHIBITION.
Amongst the latter was Monbro, a Frenchman, who established himself in Berners Street, London, and made furniture of an ornamental character in the style of his countrymen, reproducing the older designs of "Boule" and marqueterie furniture. The present house of Mellier and Cie. are his successors, Mellier having been in his employ. The late Samson Wertheimer, father of Messrs. Charles and Asher Wertheimer, now so well known in the Art world, then in Greek Street, Soho, was steadily making a reputation by the excellence of the metal mountings of his own design and workmanship, which he applied to caskets of French style. Furniture of a decorative character and of excellent quality was also made some forty years ago by Town and Emanuel, of Bond Street, and many of this firm's "Old French" tables and cabinets were so carefully finished with regard to style and detail, that, with the "tone" which time has given them, it is not always easy to distinguish them from the models from which they were taken. Toms was assistant to Town and Emanuel, and afterwards purchased and carried on the business of "Toms and Luscombe," a firm well known as manufacturers of excellent and expensive "French" furniture, until their retirement from business over twenty years ago.

CASKET OF IVORY.
With Ormolu Mountings. Designed and Manufactured by M. Matifat, Paris. 1851 Exhibition, London.
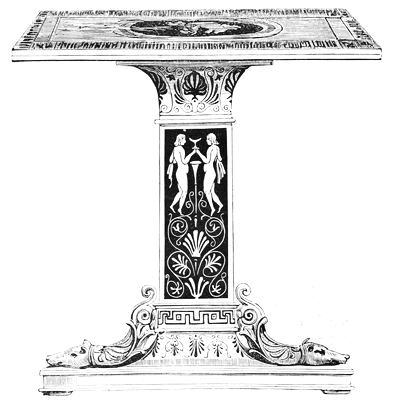

TABLE.
In the Classic Style, inlaid with Ivory. Manufactured for the King of Sardinia by M. G. Capello, Turin. 1851 Exhibition, London.

CHAIR.
In the Classic Style, inlaid with Ivory. Manufactured for the King of Sardinia by M. G. Capello, Turin. 1851 Exhibition, London.
Webb, of Old Bond Street, succeeded by Annoot, and subsequently by Radley,[23] was a manufacturer of this class of furniture; he employed a considerable number of workmen, and carried on a very successful business.
The name of "Blake," too, is one that will be remembered by some of our older readers who were interested in marqueterie furniture of forty years ago. He made an inlaid centre table for the late Duke of Northumberland, from a design by Mr. C. P. Slocombe, of South Kensington Museum; he also made excellent copies of Louis XIV. furniture.
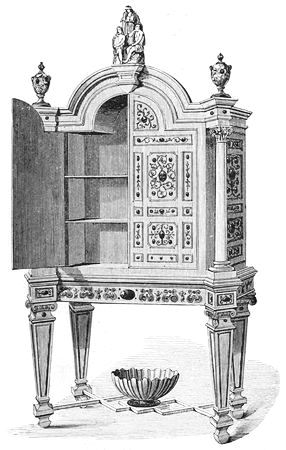
CABINET OF EBONY IN THE RENAISSANCE STYLE.
With Carnelions inserted. Litchfield and Radclyffe. 1862 Exhibition.
The next International Exhibition held in London was in the year 1862, and, though its success was somewhat impaired by the great calamity this country sustained in the death of the Prince Consort on 14th December, 1861, and also by the breaking out of the Civil War in the United States of America, the exhibitors had increased from 17,000 in '51 to some 29,000 in '62, the foreign entries being 16,456, as against 6,566.
Exhibitions of a National and International character had also been held in many of the Continental capitals. There was in 1855 a successful one in Paris, which was followed by one still greater in 1867, and, as every one knows, they have been lately of almost annual occurrence in various countries, affording the enterprising manufacturer better and more frequent opportunities of placing his productions before the public, and of teaching both producer and consumer to appreciate and profit by every improvement in taste, and by the greater demand for artistic objects.
The few illustrations from these more recent Exhibitions of 1862 and 1867 deserve a passing notice. The cabinet of carved ebony with enrichments of carnelion and other richly-colored minerals (illustrated on previous page), was made by the firm in which the author's father was senior partner; it received a good deal of notice, and was purchased by William, third Earl of Craven, a well-known virtuoso of some forty years ago.
The work of Fourdinois, of Paris, has already been alluded to, and in the 1867 Exhibition his furniture acquired a still higher reputation for good taste and attention to detail. The full page illustration of a cabinet of ebony, with carvings of boxwood, represents a remarkably rich piece of work of its kind; the effect is produced by carving the boxwood figures and ornamental scroll work in separate pieces, and then inserting these bodily into the ebony. By this means the more intricate work is able to be more carefully executed, and the close grain and rich tint of Turkey boxwood (perhaps next to ivory the best medium for rendering fine carving) tells out in relief against the ebony of which the body of the cabinet is constructed. This excellent example of modern cabinet work by Fourdinois was purchased for the South Kensington Museum for £1,200, and no one who has a knowledge of the cost of executing minute carved work in boxwood and ebony, will consider the price excessive.
The house of Fourdinois no longer exists; the names of the foremost makers of French meubles de luxe, in Paris, of this time were Beurdely, Dasson, Roux, Sormani, Durand, and Zwiener. Some mention has already been made of Zwiener, as the maker of a famous bureau in the Hertford Collection,[24] and a sideboard exhibited by Durand in the '51 Exhibition is amongst the illustrations selected as representative of cabinet work at that time.
The illustration of Wright and Mansfield's satinwood cabinet, with Wedgwood plaques inserted, and with wreaths and swags of marqueterie inlaid, is in the Adams style, a class of design of which this firm made a specialité. Both Wright and Mansfield had been assistants at Jackson and Graham's, and after a short term in Great Portland Street, they removed to Bond Street, and carried on a successful business of a high class and somewhat exclusive character, until their retirement some years ago. This cabinet was exhibited in Paris in 1867, and was purchased by our South Kensington authorities. Perhaps it is not generally known that a grant is made to the Department for the purchase of suitable specimens of furniture and woodwork for the Museum. This expenditure is made with great care and discrimination. It may be observed here that the South Kensington Museum, which was founded in 1851, was, at the time of which we are writing, playing an important part in the Art education of the country. The literature of the day also contributed many useful works of instruction and reference for the designer of furniture and woodwork.
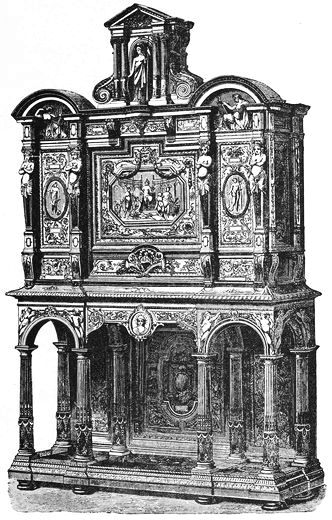
CABINET OF EBONY WITH CARVINGS OF BOXWOOD.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY M. FOURDINOIS, PARIS. 1867 EXHIBITION, PARIS.
(PURCHASED BY S. KENSINGTON MUSEUM FOR £1,200.)

CABINET IN SATINWOOD.
With Wedgwood plaques and inlay of various woods in the Adams style.
DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED BY MESSRS. WRIGHT & MANSFIELD, LONDON. 1867 EXHIBITION, PARIS.
(PURCHASED BY THE SOUTH KENSINGTON MUSEUM.)

EBONY AND IVORY CABINET.
In the Style of Italian Renaissance by ANDREA PICCHI, Florence.
EXHIBITED PARIS, 1867.
Note.—A marked similarity in this design to that of a 17th Century cabinet, illustrated in the Italian section of Chapter iii., will be observed.
The work of Mr. Bruce J. Talbert deserves mention here, and should not have been omitted in the first edition. His designs for furniture, conceived on the basis of modified Gothic, adapted to modern requirements, were appreciated by a considerable following; and the dining room and library furniture especially, made from his drawings, stand the test of time. He published a book of designs in 1868, entitled "Gothic Forms applied to Furniture, Metal Work, and Decoration for Domestic Purposes," and, subsequently, in 1876, "Examples of Ancient and Modern Furniture, Tapestries, Metal Work, Decoration, &c." In this latter work he reproduced several of his drawings, which had been exhibited in the Royal Academy in 1870 and five following years; and he compiled a reference table of the dates when the various periods of architecture came in, with marginal notes, which will be found very useful to the reader in connection with our subject. We have, by permission of Mr. Talbert's publisher (Mr. Batsford, of Holborn), been able to give here a full-page illustration of part of a design for a dining room, from his Academy drawing of 1870, which will convey a fair idea of the character of his work. Talbert made designs for furniture exhibited in Paris in 1867, one of which, that of a Sideboard, made by Gillows, was purchased for the South Kensington Museum. Shortly before his death he turned his attention to Renaissance designs.
One noticeable feature of modern design in furniture, is the revival of marquetry. Like all mosaic work, to which branch of Industrial Art it properly belongs, this kind of decoration should be quite subordinate to the general design; but, with a rage for novelty which seized public attention some forty years ago, it developed into the production of all kinds of fantastic patterns in different veneers. A kind of minute mosaic work in wood, which was called "Tunbridge Wells work," became fashionable for small articles. Within the last twenty-five years, the reproductions of what is termed "Chippendale," and also of Adam, and Sheraton, designs in marqueterie furniture, have been manufactured to an enormous extent. Partly on account of the difficulty in obtaining the[238] richly-marked and figured old mahogany and satin-wood, of a hundred years ago, which needed little or no inlay as ornament, and partly to meet the public fancy, by covering up bad construction with veneers of marquetry decoration, a great deal more inlay has been given to these reproductions than ever appeared in the original work of the eighteenth century cabinet makers. Simplicity was sacrificed, and veneers, thus used and abused, came to be a term of contempt, implying sham or superficial ornament. Dickens, in one of his novels, has introduced the "Veneer" family, thus stamping the term more strongly on the popular imagination.
The method now practised in using marquetry to decorate furniture is very similar to the one explained in the description of "Boule" furniture given in Chapter VI., except that instead of shell, the marquetry cutter uses the veneer, which he intends to be the groundwork of his design, and as in some cases these veneers are cut to the thickness of 1⁄16 of an inch, several layers can be sawn through at once. Sometimes, instead of using so many different kinds of wood, when a polychromatic effect is required, holly wood and sycamore are stained different colors, and the marquetry thus prepared, is glued on to the body of the furniture, and subsequently prepared, engraved, and polished.
This kind of work is done to a great extent in England, but still more extensively and elaborately in France and Italy, where ivory and brass, marble, and other materials are also used to enrich the effect. This effect is either satisfactory or the reverse, according as the work is well or ill-considered and executed.
It must be obvious, too, that in the production of marquetry the processes are obtainable by machinery, which saves labour and cheapens productions of the commoner kinds; this tends to produce a decorative effect which is often inappropriate and superabundant.
Perhaps it is allowable to add here that marquetry, or marqueterie, its French equivalent, is the more modern survival of "Tarsia" work, to which allusion has been made in previous chapters. Webster defines the word as "Work inlaid with pieces of wood, shells, ivory, and the like," derived from the French word marqueter, to checker, and marque (a sign), of German origin. It is distinguished from parquetry (which is derived from "parc," an enclosure, of which it is a diminutive), and signifies a kind of joinery in geometrical patterns, generally used for flooring. When, however, the marquetry assumes geometrical patterns (frequently a number of cubes shaded in perspective), the design is often termed in Art catalogues a "parquetry" design.
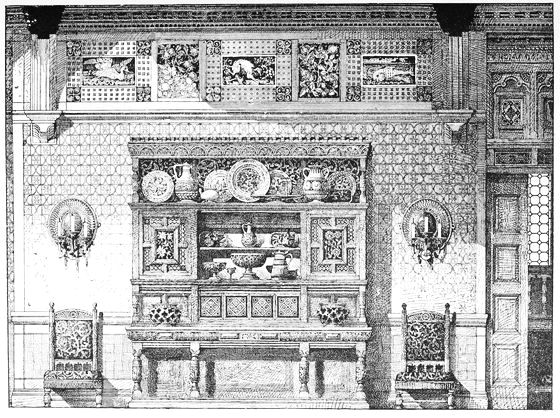
DESIGN FOR A DINING ROOM.
BY BRUCE J. TALBERT. EXHIBITED IN THE ROYAL ACADEMY IN 1870.
In considering the design and manufacture of furniture of the present day, as compared with that of, say, a hundred years ago, there are[239] two or three main factors to be taken into account. Of these the most important is the enormously increased demand, by the multiplication of purchasers, for some classes of furniture, which formerly had but a limited sale. This enables machinery to be used to advantage in economising labour, and therefore one finds in the so-called "Queen Anne" and "Jacobean" cabinet work of the well-furnished house of the present time, rather too prominent evidence of the lathe and the steam plane. Mouldings are machined by the length, then cut into cornices, mitred round panels, or affixed to the edge of a plain slab of wood, giving it the effect of carving. The everlasting spindle, turning rapidly by the lathe, is introduced with wearisome redundance, to ornament the stretcher and the edge of a shelf; the busy fret or band-saw produces fanciful patterns which form a cheap enrichment when applied to a drawer-front, a panel, or a frieze; and carving machines can copy any design, which a century ago were the careful and painstaking result of a practised craftsman's skill.
Again, as the manufacture of furniture is now chiefly carried on in large factories, both in England and on the Continent, the sub-division of labour causes the article to pass through different hands, in successive stages, and the wholesale manufacture of furniture by steam, has taken the place of the personal supervision by the master's eye, of the task of the few men who were in the old days the occupants of his workshop. As a writer on the subject has well said, "the chisel and the knife are no longer in such cases controlled by the sensitive touch of the human hand." In connection with this we are reminded of Ruskin's precept that "the first condition of a work of Art is that it should be conceived and carried out by one person."
Instead of the carved ornament being the outcome of the artist's educated taste, which places on the article the stamp of individuality—instead of the furniture being, as it was in the seventeenth century in England, and some hundred years earlier in Italy and in France, the craftsman's pride—it is now the result of the rapid multiplication of some pattern which had caught the popular fancy, generally a design in which there is a good deal of decorative effect, for a comparatively small price.
The difficulty of altering this unsatisfactory state of things is evident. On the one side, the manufacturers or the large furnishing firms have a strong case in their contention, that the public will go to the market it considers the best: and when decoration is pitted against simplicity, though the construction which accompanies the former be ever so faulty, the more pretentious article will be selected. When a successful pattern has been produced, and arrangements and sub-contracts have been made[240] for its repetition in large quantities, any considerable variation made in the details (even if it be the suppression of ornament) will cause an addition to the cost which those only who understand something of a manufacturer's business can appreciate.
During the present generation an Art movement has sprung up called Æstheticism, which has been defined as the "Science of the Beautiful and the Philosophy of the Fine Arts," and aims at carrying a love of the beautiful into all the relations of life. The fantastical developments which accompanied the movement brought its devotees into much ridicule about twenty years ago, and the pages of Punch of that time will be found to happily travesty its more amusing and extravagant aspects. The great success of Gilbert and Sullivan's operetta, "Patience," produced in 1881, was also to some extent due to the humorous allusions to the extravagance of the "Æsthetes." In support of what may be termed a higher Æstheticism, Mr. Ruskin has written much to give expression to his ideas and principles for rendering our surroundings more beautiful. The names of the late Sir Frederic Leighton and of Sir Alma Tadema are conspicuous amongst those who have in their houses carried such principles into effect, and among others who have been and are, more or less, associated with this movement, may be named Rossetti, Burne Jones, Holman Hunt, and William Morris. As a writer on Æstheticism has observed:—"When the extravagances attending the movement have been purged away, there may be still left an educating influence, which will impress the lofty and undying principles of Art upon the minds of the people."
For a time, in spite of ridicule, this so-called Æstheticism was the vogue, and considerably affected the design and decoration of furniture of the time. Woodwork was painted olive green; the panels of cabinets, painted in sombre colors, had pictures of sad-looking maidens, and there was an attempt at a "dim religious" effect in our rooms, quite inappropriate to such a climate as that of England. The reaction, however, from the garish and ill-considered colorings of a previous decade or two, has left behind it much good, and with the catholicity of taste which marks the furniture of the present day, people see some merit in every style, and are endeavouring to select that which is desirable without running to the extreme of eccentricity.
Perhaps the advantage thus gained is counterbalanced by the loss of our old "traditions," for amongst the wilderness of reproductions of French furniture, more or less frivolous—of Chippendale, as that master is generally understood—of what is termed "Jacobean" and "Queen Anne"—to say nothing of a quantity of so-called "antique furniture," we are bewildered in attempting to identify the latter end[241] of the nineteenth century with any particular style of furniture. By "tradition" it is intended to allude to the old-fashioned manner of handing down from father to son, or master to apprentice, for successive generations, the knowledge and skill to produce any particular class of object of Art or manufacture. Surely Ruskin had something of this in his mind when he said, "Now, when the powers of fancy, stimulated by this triumphant precision of manual dexterity, descend from generation to generation, you have at last what is not so much a trained artist, as a new species of animal, with whose instinctive gifts you have no chance of contending."
Tradition may be said to still survive in the country cartwright, who produces the farmer's wagon in accordance with custom and tradition, modifying the method of construction somewhat perhaps to meet altered conditions of circumstances, and then ornamenting his work by no particular set design or rule, but partly from inherited aptitude and partly from playfulness or fancy. In the house-carpenter attached to some of our old English family estates, there will also be found, here and there, surviving representatives of the traditional "joyner" of the seventeenth century; and in Eastern countries, particularly in Japan, we find the dexterous joiner or carver of to-day is a descendant of a long line of more or less excellent mechanics.
It must be obvious, too, that "Trade Unionism" of the present day cannot but be, in many of its effects, prejudicial to the industrial Arts. A movement which aims at reducing men of different intelligence and ability to a common standard, and which controls the amount of work done, and the price paid for it, whatever are its social or economical advantages, must have a deleterious influence upon the Art products of our time.
Writers on Art and manufactures, of varying eminence and opinion, are unanimous in pointing out the serious drawbacks to progress which will exist, so long as there is a demand for cheap and meretricious imitations of old furniture, as opposed to more simply made articles, designed in accordance with the purposes for which they are intended. Within the past few years a great many well directed endeavours have been made in England to improve design in furniture, and to revive something of the feeling of pride and ambition in his craft, which, in the old days of the Trade Guilds, animated our Jacobean joiner. One of the best directed of these enterprises is that of the "Arts and Crafts Exhibition Society," of which Mr. Walter Crane, A.R.W.S., is president, and which includes, in its committee and supporters, a great many influential names. As suggested on the "cover" of their Exhibition Catalogue, designed by the President, one chief aim of the Society is to link arm and arm "Design[242] and Handicraft," by exhibiting only such articles as bear the names of individuals who, respectively, drew the design and carried it out: each craftsman has thus the credit and responsibility of his own part of the work, instead of the whole appearing as the production of Messrs. A. B. or C. D., who may have known nothing personally of the matter beyond generally directing the affairs of a large manufacturing or furnishing business.
In the catalogue published by this Society there are several short and useful essays in which furniture is treated, generally and specifically, by capable writers, amongst whom are Mr. Walter Crane, Mr. Edward Prior, Mr. Halsey Ricardo, Mr. Reginald T. Blomfield, Mr. W. R. Letharby, Mr. J. H. Pollen, Mr. Stephen Webb, and Mr. T. G. Jackson, R.A., the order of names being that in which the several essays are arranged. This small but valuable contribution to the subject of design and manufacture of furniture, is full of interest, and points out the defects of our present system. Amongst other regrets, one of the writers (Mr. Halsey Ricardo) complains that the "transient tenure that most of us have in our dwellings, and the absorbing nature of the struggle that most of us have to make to win the necessary provisions of life, prevent our encouraging the manufacture of well wrought furniture. We mean to outgrow our houses—our lease expires after so many years, and then we shall want an entirely different class of furniture—consequently we purchase articles that have only sufficient life in them to last the brief period of our occupation, and are content to abide by the want of appropriateness or beauty, in the clear intention of some day surrounding ourselves with objects that shall be joys to us for the remainder of our life."
The School of Art Woodcarving at South Kensington, which was established some twenty years ago at "the City and Guilds Institute," is also doing a useful and practical work. With a very moderate grant from the City Guilds and the use of free quarters, the School maintains itself, and is the means of educating, either free or at reduced terms, a great many students who go out into the world the better prepared to compete with their foreign rivals. The Committee of Management, under the presidency of Major-General Sir J. F. D. Donelly, K.C.B., is composed of artists and architects of note and others who not only give their moral support to the institution but bring some of their ornamental woodwork to the School for execution under their direction.
The management of Miss Rowe[25] is evidence of the success which attends the effort of an intelligent and enthusiastic lady, and the[243] instructors, Messrs. Grimwood and Ross, are practical carvers, who can not only correct but can design and cut the patterns set for their pupils. After the first year probation the professional students receive a fair proportion of the value of their work, which is assessed by the instructors.
It is by the maintenance of such technical schools, which with more or less success are now being started by our local authorities in different parts of England, that we can to some extent replace the advantages which the old system of apprenticeship gave to the learners of a craft.

THE ELLESMERE CABINET.
In the collection of the late Lady Marian Alford.
Many other societies, guilds, and Art schools have been established with more or less success, with a view of improving the design and manufacture of furniture, and providing suitable models for our young[244] woodcarvers to copy. The Ellesmere Cabinet (illustrated on page 243) was one of the productions of the "Home Arts and Industries Association," founded in 1883 by the late Lady Marian Alford, a well known connoisseur and Art patron. It will be seen that this is virtually a Jacobean design.
In the earlier chapters of this book, it has been observed that as Architecture became a settled Art or Science, it was accompanied by a corresponding development in the design of the room and its furniture, under, as it were, one impulse of design, and this appropriate concord may be said to have obtained in England until nearly the middle of the last century, when, after the artificial Greek style in furniture and woodwork which had been attempted by Wilkins, Soane, and other contemporary architects, had fallen into disfavour, there was first a reaction, and then an interregnum, as has been noticed in the previous chapter. The Great Exhibition marked a fresh departure, and quickened, as we have seen, industrial enterprise in this country: and though, upon the whole, good results have been produced by the impetus given by these international competitions, they have not been exempt from unfavourable accompaniments. One of these was the eager desire for novelty, without the necessary judgment to discriminate between good and bad. For a time, nothing satisfied the purchaser of so-called "artistic" products, whether of decorative furniture, carpets, curtains, or merely ornamental articles, unless the design was "new." The natural result was the production either of heavy, or ugly, or flimsy and inappropriate furniture, which has been condemned by every competent writer on the subject. In some of the designs selected from the exhibits of '51 this desire to leave the beaten track of conventionality will be evident; and for a considerable time after the Exhibition, we can see, in our designs, the result of too many opportunities for imitation, acting upon minds insufficiently trained to exercise careful judgment and selection.
About the early part of the nineteenth century, the custom of employing architects to design the interior fittings and the furniture of their buildings, so as to harmonize, appears to have been abandoned; this was probably due, partly to some indifference to this subsidiary portion of their work, but also to the change of taste which led people to prefer the cheapness of painted and artificially grained pine-wood, with decorative effects produced by wall-papers, to the more solid but expensive though less showy wood-panelling, architectural mouldings, well-made panelled doors and chimney pieces, which one finds, down to quite the end of the previous century, even in houses of moderate rentals. Furniture therefore became independent, and, "beginning to account herself an Art, trangressed her limits" ... and "grew to the conceit that it could stand by itself,[245] and, as well as its betters, went a way of its own."[26] The effect of this is to be seen in "interiors" of our own time which are handed over from the builder, as it were, in blank, to be filled up from the upholsterer's store, the curiosity shop, and the auction room, while a large contribution from the conservatory or the nearest florist, gives a finishing touch to a mixture, which characterises the present taste for furnishing a boudoir or a drawing room.
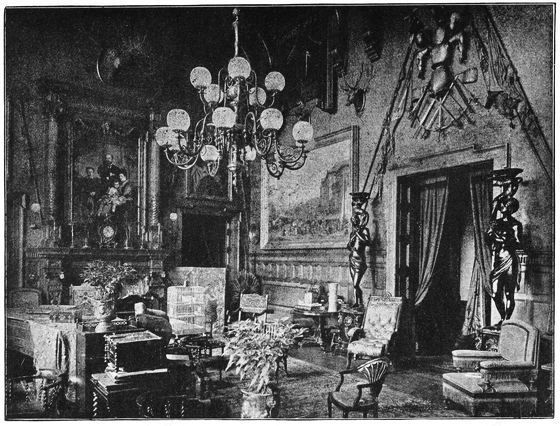

THE SALOON AT SANDRINGHAM HOUSE.
(From a Photo by Bedford Lemére & Co., by permission of H.M. The King.)
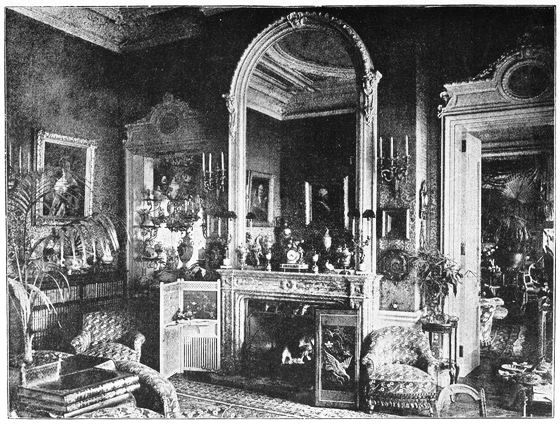

THE DRAWING ROOM AT SANDRINGHAM HOUSE.
(From a Photo by Bedford Lemére & Co., by permission of H.M. The King.)
There is, of course, in very many cases, an individuality gained by the "omnium gatherum" of such a mode of furnishing. The cabinet which reminds its owner of a tour in Italy, the quaint stool from Tangier, and the embroidered piano-cover from Spain, are to those who are in the habit of travelling, pleasant souvenirs; as are also the presents from friends (when they have taste and judgment), the screens and flower-stands and the photographs, which are reminiscences of the forms and faces separated from us by distance or removed by death. The test of the whole question of such an arrangement of furniture in our living rooms, is the amount of judgment and discretion displayed. Two favourable examples of the present fashion, representing the interior of the Saloon and Drawing Room at Sandringham House, are here reproduced.
There is at the present time an ambition on the part of many well-to-do persons to imitate the effect produced in houses of old families, where, for generations, valuable and memorable articles of decorative furniture have been accumulated, just as pictures, plate and china have been preserved; and failing the inheritance of such household gods, it is the practice to acquire, or as the modern term goes, "to collect," old furniture of different styles and periods, until the room becomes incongruous and overcrowded, an evidence of the wealth, rather than of the taste, of the owner. As it frequently happens that such collections are made very hastily, and in the brief intervals of a busy commercial or political life, the selections are not the best or most suitable; and where so much is required in a short space of time, it becomes impossible to devote a sufficient sum of money to procure really valuable specimens; in their place, effective and low-priced reproductions of an old pattern (with all the faults inseparable from such conditions) are added to the conglomeration of articles requiring attention, and taking up space. The limited accommodation of houses built on ground which is too valuable to allow spacious halls and large apartments, makes this want of discretion and judgment the more objectionable. There can be no doubt that want of care and restraint in the selection of furniture, by the purchasing public, affects its character, both as to design and workmanship.
These are some of the faults in the modern style of furnishing, which have been pointed out by recent writers and lecturers on the subject. In "Hints on Household Taste,"[27] Mr. Eastlake has scolded us severely for running after novelties and fashions, instead of cultivating suitability and simplicity, in the selection and ordering of our furniture; and he has contrasted descriptions and drawings of well designed and constructed pieces of furniture of the Jacobean period with those of last century's productions. Col. Robert Edis, in "Decoration and Furniture of Town Houses," has published designs which are both simple and economical, with regard to space and money, while suitable to the specified purpose of the furniture or "fitment."
The ruling principle in the majority of these designs has been to avoid over-ornamentation, and pretentions to display, and to encourage good solid work, in hard, durable, and (on account of the increased labour) expensive woods, or, when economy is required, in light soft woods, painted or enamelled. Some manufacturing firms, whose high reputation renders them independent of any recommendation, have adopted this principle, and, as a result, there is now no difficulty in obtaining well designed and soundly well constructed furniture, which is simple, unpretentious, and worth the price charged for it. Unfortunately for the complete success of these sounder principles, really good and appropriate furniture meets with a fierce competition from more showy and ornate productions, made to sell rather than to last: furniture which seems to have upon it the stamp of our "three years' agreement," or "seven years' lease." Of this it may be said, speaking not only from an artistic, but from a moral and humane standpoint, it is made so cheaply, that it seems a pity it is made at all.
A revival in taste, which has been not inappropriately termed "The New Renaissance," and has produced many excellent results, has been brought about by several well-known architects and designers. Mr. Street, R.A.; Messrs. Norman Shaw, R.A.; Waterhouse, R.A.; Sir Alma Tadema, R.A.; T. G. Jackson, R.A.; W. Burges, R.A.; Walter Crane, Thomas Cutler, E. W. Godwin, W. Morris, B. J. Talbert, S. Webb, and many others, have devoted a considerable amount of attention to the design of furniture; but it is scarcely within the writer's province to attempt a description of the character of their respective work.
The "Trade" Journals, too, have contributed their influence by publishing drawings of work completed, suggestions for their readers to carry out, and also by illustrated notices of the different exhibitions which take place from time to time.
The "Cabinet Maker and Art Furnisher," edited by Mr. J. Williams Berm, M.P., L.C.C., contains "Pen and Ink Notes by the Editor," which should be useful, as they are certainly instructive; and a number of good designs are published month by month, in "Furniture and Decoration." These are contributed by J. W. Bliss, R. A. Briggs, A.R.I.B.A., H. L. Chalmers, Owen W. Davis, Lewis F. Day, Edwin Foley, Christopher Gill, Bertram Goodhue, Ernest George and Peto, A. Jonquet, Felix Lenoir, Letharby, Wilbert Rattray, Stenhouse, John Turner, Frank Ward, A. H. Wolf, and the editors themselves—Timms and Webb.
In the "American Sketches" published in this Journal, we see the kind of work which is being designed and carried out in the United States. Designs of furniture and interior fittings of the houses of American millionaires, drawn by Cauffmann; Frank Colburn, of Morristown, New Jersey; Sanford Phipps, and James Thompson, of Boston; Ross and Marvin, of New York, shew that there is no distinctive American style, but that the revival in taste, which has been alluded to in England, has found its way to America, and from the number of articles of furniture still called after Mr. Eastlake, it is evident that the teachings of that gentleman had considerable effect. The "Furniture Gazette," "The Builder," and "Building News" also publish designs of furniture and woodwork.
The disadvantages, inseparable from our present state of society, which we have noticed as prejudicial to English design and workmanship, and which check the production of really satisfactory furniture, are also to be observed in other countries; and as the English, and English-speaking people, are probably the largest purchasers of foreign manufactures, these disadvantages act and re-act on the furniture of different nations.
In France, the cabinet maker has ever excelled in the production of ornamental furniture; and by constant reference to older specimens in the Museums and Palaces of his country, he is far better acquainted with what may be called the traditions of his craft than his English brother. To him the styles of François Premier, of Henri Deux, and the "three Louis" are "classic," and in the beautiful chasing and finishing of the mounts with which the French bronziste ornaments the best meubles de luxe, it is almost impossible to surpass his best efforts, provided the requisite price be paid; but these amounts are, in many cases, so considerable as hardly to be credible to those who have but little knowledge of the subject. As a simple instance, the "copy" of the "Bureau du Louvre" (described in Chapter vi.) in the Hertford House collection, cost the late Sir Richard Wallace a sum of £4,000.

CARVED FRAME, BY RADSPIELER, MUNICH.
As, however, in France, and in countries which import French furniture, there are many who desire to obtain the effect of this[249] beautiful but expensive furniture, but are unable to spend several thousand pounds in the decoration of a single room. To meet this demand, the industrious and ingenious Frenchman manufactures vast quantities of furniture which affects, without attaining, the merits of the better made and more highly finished articles.
In Holland, Belgium, and Germany, as has already been pointed out, the manufacturer of ornamental oak furniture, on the lines of the Renaissance models, still prevails, and such furniture is largely imported into this country.
The illustration of a carved frame in the rococo style of Chippendale with a Chinaman in a canopy, represents an important school of wood-carving which has been developed in Munich; and in the "Künst Gewerberein," or "Workman's Exhibition," in that city, the Bavarians have a very similar arrangement to that of the Arts and Crafts Exhibition Society of this country, of which mention has already been made, each article being labelled with the name of the designer and maker.
Italian carved furniture of modern times has already been noticed; and in the selections made from the 1851 Exhibition, some productions of different countries have been illustrated, which tend to shew that, speaking generally, the furniture most suitable for display is produced abroad, while none can excel English cabinet makers in the production of useful furniture and woodwork, when it is the result of design and handicraft, unfettered by the detrimental, but too popular, condition that the article when finished shall appear to be more costly than it really is.
In conclusion, it seems evident that, with all the faults and shortcomings of the latter part of the nineteenth century—and no doubt they were many, both of commission and of omission—still, speaking generally, there was no lack of men with ability to design, and no want of well trained patient craftsmen to produce, furniture which would equal the finest examples of the Renaissance and Jacobean periods. With the improved means of inter-communication between England and her Colonies, and with the chief industrial centres of Europe united for the purposes of commerce, the whole civilised world is, as it were, one kingdom: merchants and manufacturers can select the best and most suitable materials, can obtain photographs or drawings of the most distant examples, or copies of the most expensive designs, while the public Art Libraries of London, and Paris, contain valuable works of reference, which are easily accessible to the student or to the workman. It is very pleasant to bear testimony to the courtesy and assistance which the student or workman invariably receives from those who are in charge of our public reference libraries.
There needs, however, an important condition to be taken into account. Good work, requiring educated thought to design, and skilled labour to produce, must be paid for at a very different rate to the furniture of machined mouldings, stamped ornament, and other numerous and inexpensive substitutes for handwork, which our present civilization has enabled our manufacturers to produce, and which, for the present, seems to find favour with the multitude. It has been well said that "Decorated or sumptuous furniture is not merely furniture that is expensive to buy, but that which has been elaborated with much thought, knowledge, and skill. Such furniture cannot he cheap certainly, but the real cost is sometimes borne by the artist who produces, rather than by the man who may happen to buy it."[28] It is often forgotten that the price paid is that of the lives and health of the workers and their families.
A point has now been reached at which our task must be brought to its natural conclusion: for although many collectors and others interested in the subject, have invited the writer's attention to numerous descriptions and examples, from an examination of which much information could, without doubt, be obtained, still, the exigencies of a busy life, and the limits of a single volume of moderate dimensions, forbid the attempt to add to a story which, it is feared, may perhaps have already overtaxed the reader's patience.
As has already been suggested in the preface, this book is not intended to be a guide to "collecting," or "furnishing"; nevertheless, it is possible that, in the course of recording some of the changes which have taken place in designs and fashions, and of bringing into notice, here and there, the opinions of those who have thought and written upon the subject, some indirect assistance may have been given in both these directions. If this should be the case, and if an increased interest has been thereby excited in the surroundings of the Home, or in some of those Art collections—the work of by-gone years—which form part of our National property, the writer's aim and object will have been attained, and his humble efforts amply rewarded.
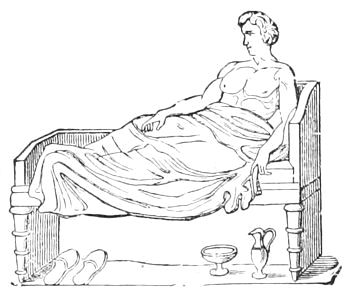
THE following List of the Names of some Artists and Manufacturers of past times, in alphabetical order, will be useful for reference. The Author is indebted to Mr. J. Hungerford Pollen for some additions to his list in "Ancient and Modern Furniture." (published in 1874). The names of existing firms are not included, partly on account of the large number who might fairly claim a place amongst the makers of furniture of the present time, and partly because any selection of names by a contemporary would appear to be invidious and arbitrary:—
| Names of Artists or Manufacturers. |
Country and time in which they worked. |
Remarks and References. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | |||
| Adam, J. (and R.) | England | 1728-1792 | Chapter vii. |
| Agnolo, B. d' | Italy | 1460-1563 | Architect who designed much intarsia work, also carved church work. |
| Agnolo, D. d' | " | 16th century | Son of above. |
| Agnolo, J. d' | " | " " | Ditto. |
| Ambrogio, G. | " | 17th " | |
| Annoot, — | England | 19th " | Chapter ix., p. 235 (French style). |
| Ards, W. | Flanders | 15th " | Executed carvings in the roof of Hotel de Ville, Malines. |
| Armand, Jean | France | 18th " | Marquetry. |
| Asinelis, A. | Italy | 16th " | |
| Aubiche, Jacques d' | France | 18th " | Faubourg, Ste. Antoine. |
| B | |||
| Bachelier, — | France | 16th century | |
| Baerze, J. de | Flanders | 14th " | Carved figure work, preserved in Museum of Dijon. |
| Baker, — | England | 18th " | Flower painter. |
| Balthazar, Lieutand | France | " " | |
| Barili, A. | Italy | 16th " | Carved woodwork for Cathedral of Siena. |
| Barili, G. (Florence) | " | " " | Carved doors in the Vatican. |
| Barili, S. | " | " " | Carved work for Cathedral of Siena. |
| Barry, Sir Charles (architect) | England | 19th " | Chapter viii., woodwork of Houses of Parliament. |
| Baumgartner, U. | Germany | 17th century | Made the celebrated Pomeranian Art Cabinet in Berlin Museum.[252] |
| Beaugreant, G. de | Flanders | 16th " | One of the designers of the chimney-piece at Bruges, see p. 63. |
| Beck, S. | Germany | " " | |
| Belli, A. A. | Italy | " " | |
| Belli, G. | " | " " | |
| Beneman, G. | France | 18th " | "Maitre ébeniste" in 1785, worked at Fontainebleau. |
| Berain, J. | " | 1636-1711 | Chapter vi., designed for Boule. |
| Bergamo, D. da | Italy | 1490-1550 | Intarsia work in Church of S. Dominic in Bologno. |
| Bergamo, S. da | " | 16th century | Brother and assistant. |
| Bernardo, — | " | " " | |
| Berruguete, — | Spain | 1480-1561 | Chapter iii. (Spanish section), pupil of M. Angelo. |
| Bertolina, B. J. | Italy | 16th century | |
| Beyaert, J. | Flanders | 15th " | Carvings in roof of Salle de Marriage, Hotel de Ville, Louvain. |
| Binson, Andrieu de | France | 18th " | Furniture and carriage decorator, worked in 1736. |
| Blake, S. | England | 19th " | Marqueterie furniture (French style) p. 235. |
| Blondeel, L. | Flanders | 1495-1560 | Designed the chimney-piece at Bruges, see p. 63. |
| Bolgié, G. | Italy | 18th century | |
| Bonzanigo, G. M. | " | " " | |
| Borello, F. | " | 16th " | |
| Borgona, F. de | Spain | " " | |
| Botto, B. | Italy | " " | Famous wood carver. |
| Botto, G. B. | " | " " | |
| Botto, P. | " | " " | |
| Botto, S. A. | " | " " | |
| Boulle, A. C. (generally spelt "Boule") | France | 1642-1732 | Chapter vi. |
| Boulle, P. | " | 17th century | Born 1619, premier ébeniste to Louis XIII. |
| Bourdin, M. | " | 16th " | Chapter iii., pp. 60, 63. |
| Brandri, — | " | 17th " | An Italian, worked with Goletti at "Pietra Dura" under Colbert. |
| Brescia, R. da | Italy | 16th " | |
| Bross, — de | France | 17th " | |
| Bruggeman, H. | Germany | 15th " | Carver. |
| Bruhl, A. | Flanders | 16th and 17th centuries |
Carved stalls of centuries San Giorgio Maggiore in Venice. |
| Brunelleschi, F. | Italy | 1377-1446 | |
| Brustolone, A. | " | 1670-1732 | |
| Buontalenti, B. T. | " | 16th century | |
| Burb, — | France | 18th century | Said to have worked for M. de Pompadour (Vernis Martin style).[253] |
| Names of Artists or Manufacturers. |
Country and time in which they worked. |
Remarks and References. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | |||
| Caffieri, Ph. | France | 17th and 18th centuries |
Chap. vi. (worked with Riesener) famous mounter. |
| Campbell and Sons | England | 18th century | Chapter vii., p. 198. |
| Canabas, Joseph | France | " " | Made mechanical tables, Rue du fg. St. Antoine. |
| Cano, A. | Spain | 17th " | |
| Canavo, J. de. | Italy | 16th " | |
| Canozii, C. | " | " " | Executed intarsia work in S. Marco, Venice. |
| Canozii, G. M. | " | " " } | Carvers of church |
| Canozii, L. | " | " " } | decorative work. |
| Capitsoldi, — | England | 18th " | Louis Seize style of furniture. |
| Capo di Ferro, Brothers | Italy | 16th " | |
| Carlin, E. | France | 18th " | Stamped on table in Jones Collection. |
| Carlin, Martin | " | " " | Ebony with porcelain plaques, lac, and "Pietra Dura." |
| Carlone, J. | Italy | " " | |
| Carnicero, A. | Spain | 1693-1756 | Sculptor, carved in convent of Valladolid. |
| Carter, — (architect) | England | 18th century | Chapter vii. |
| Castelli, Q. | Italy | 16th " | |
| Cauner, — | France | 18th " | Chapter vii. (frames in Louis XV. style). |
| Cauvet, G. P. | " | 1731-1788 | |
| Ceracci, G. | England | 18th century | Italian, modelled for R. Adam. |
| Cervelliera, B. del | Italy | " " | |
| Chambers, Sir W. | England | 1726-1796 | Chapter vii., introduced Chinese style in furniture. |
| Chippendale, T. | " | 18th century | Chapter vii. |
| Cipriani, G. B. | " | " " | Chapter vii., employed by Chambers and others to paint furniture. |
| Claude, Charles S. | France | " " | Faubourg Ste. Antoine, 1752, good plain work with metal mounts. |
| Claude, Lebesque | " | " " | Worked in Paris, 1771. |
| Cleyn, F. R. | England | 17th " | Worked for Charles II. |
| Coech, P. | Flanders | 16th " | Chapter iii., p. 63. |
| Coit, — | England | 18th " | Chaser of metal mounts. |
| Collett, A. | " | " " | Chapter vii., carver. |
| Collmann, L. W. | " | 19th " | Chapter viii., p. 220 |
| Copeland, — | " | 18th " | |
| Cosson, J. L. | France | " " | Stamped on the table in Jones Collection. |
| Cotte, J. de | " | " "[254] | |
| Cotte, R. D. | France | 1656-1735 | |
| Cotton, C. | England | 18th century | |
| Couet, L. Jaques | France | " " | Rue de Bussy in 1774. |
| Cramer, M. G. | " | " " } | Stamped on tables in Bethnal |
| Cressent, — | " | " " } | Green Museum (Mainwaring Collection). |
| D | |||
| Darly, Mathias | England | 18th century | Chapter vii., p. 186, designer. |
| David, — (see Roentgen) | France | " " | Chapter vi., famous for marqueterie. |
| Davy, R. | England | 1750-1794 | Wood carving, p. 198. |
| Dello Delli | Italy | 14th & 15th centuries |
|
| Deloose, — | France | 18th century | Stamped on table in Jones Collection. |
| Delorme, — | " | " " } | Stamped on table in Bethnal |
| Denizot, — | " | " " } | Green Museum (Mainwaring Collection). |
| Dolen, — van | Flanders | 18th century | Carvings in Church of S. Gudule, Brussels. |
| Donatello, — | Italy | 1380-1466 | |
| Dorsient, A. C.; C. Oc. | Flanders | 10th century | Signed on carved door in South Kensington Museum, dated 1580. |
| Dowbiggin, — | England | 18th and 19th centuries |
Chapter vii. and viii. (Gillow's apprentice). |
| Ducereau, A. | France | 1515-1518 | |
| Dugar, E. | Italy | 16th century | |
| Dugourc | France late | 18th " | Designed for Beneman, Swerdficher, and others. |
| Duplessis, — | " | " " | Famous mounter of furniture. |
| Du Quefnoy, F. H. and J. | Flanders | 17th " | |
| E | |||
| Ellaume, Jean C. | France | 18th century | Worked in Paris, 1754. |
| Elliott, Charles | England | " " | Chapter vii., p. 198. |
| Etienne, Avril | France | Lived at the Rue Charenton in 1774, good plain work with metal mounts. | |
| F | |||
| Faydherbe, L. (artist and architect) | Flanders | 1627-1694 | Chapter iii. |
| Feucheré, — (mounter) | France | 18th century | Chapter vi. |
| Flaxman, — | England and Italy | " " | Chapter vii. |
| Filipo, D. di | Italy | 16th " | |
| Fitzcook, H. | England | 19th " | Chapter viii., designed for manufacturers. |
| Flörein, J. | Flanders. | 15th " | |
| Floris, C. | Netherlands | 16th " | Chapter iii. [255] |
| Flötner, P. | Germany | 16th century | Designs for furniture in the Berlin Museum. |
| Forestier, — | France | 18th " | Mounter of mahogany furniture. |
| Fourdinois, — | " | 19th " | Chapters viii. and ix., exhibited '51, '67. |
| France, — | England | 18th " | Chapter vii., p. 198. |
| Names of Artists or Manufacturers. |
Country and time in which they worked. |
Remarks and References. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| G | |||
| Gabler, M. | Germany | 17th century | |
| Gaine, — | France | 18th " | |
| Gallé, — | Holland | 17th " | Ebony, with metal and hard pebbles. |
| Galletti, G. | Italy | 18th " | |
| Gallieux, — (mounter) | France | " " | Stamped on tables in Jones Collection. |
| Garnier, P. | " | " " | Stamped on table, and on marquetry encoignures in the Duke of Westminster's Collection. |
| Genfer, M. | Germany | 17th " | |
| Gervasius, — | England | " " | |
| Gettich, P. | Germany | " " | |
| Geuser, M. | " | " " | |
| Gheel, F. van | Flanders | 18th " | |
| Gibbons, G. | England | 17th " | Chapter iv., worked for Charles II. |
| Gillet, Louis | France | 18th " | Worked in Paris, 1776. |
| Gillow, R. | England | 18th and 19th centuries |
Chapters vii., viii., ix. |
| Giovanni, Fra | Italy | 16th century | |
| Glosencamp, H. | Flanders | " " | Chapter iii. (Bruges chimney-piece). |
| Goletti, — | France | 17th " | "Pietra Dura," worked under Colbert. |
| Goujon, J. | " | 16th " | Sculptor, designed much furniture. |
| Gouthière, P. | " | 18th " | Chapter vi., born 1740, worked with Riesener, famous mounter. |
| H | |||
| Habermann, — | France | 18th century | Rococo or Pompadour style. |
| Habert, — | Italy | 16th to 17th " |
Stamped on examples in Hamilton Palace Collection. |
| Haeghen, — van der | Flanders | 18th " | |
| Heckinger, J. | Germany | 17th " | |
| Hedom, J. B. | France | 18th " | |
| Heinhofer, Ph. | " | 16th and 17th centuries |
Designed the celebrated Pomerian Art Cabinet in Berlin Museum. |
| Helmont, — van | Flanders | 18th century | Carved pulpits in St. John Baptist, Cologne.[256] |
| Henrieux, — | France | " " | Famous mounter. |
| Hepplewhite, A. | England | " " | Chapter vii. |
| Hernandez, G. | Spain | 1586-1646. | |
| Herring, — | England | 19th century | Chapter viii. |
| Holbein, — | " early | 16th " | Chapter (iii.) (English section). |
| Holthausen, H. J. | France | 18th " | Stamped on table in Bethnal Green Museum (Mainwaring Collection). |
| Holmes, W. | England | 19th " | Chapter viii. (designer). |
| Hool, J. B. van | Flanders | 18th " | |
| Hope, T. (architect) | " early | 19th " | Chapter viii., classical style. |
| Huet, — | France | 18th " | |
| Huygens — (lacquer) | France & Holland | 17th century | Chapter vi. |
| Hyman, F. | England | 18th century | |
| I | |||
| Ince, W. | England | 18th century | Chapter vii., contemporary with Chippendale. |
| J | |||
| Jackson and Graham | England | 19th century | Chapters viii. and ix., exhibited '51. |
| Jansen, G. | France | 18th " | Stamped on table in Jones Collection. |
| John of St. Omer (Frenchman) | " | 13th " | Court painter & house decorator to Henry III. |
| John of Padua | " | 15th " | Chapter iii., employed by Henry VIII. |
| Johnson, T. | " | 18th " | Chapter vii., p. 198. |
| Jones, Inigo (architect) | " early | 17th " | Chapter iv. |
| Juni, (J. D.) | Spain | 16th and 17th centuries |
|
| K | |||
| Kampen, Lambert van | Germany | 16th century | Carved the Chapter House panels in Münster, Westfalen. |
| Kauffmann, A. (artist) | England | 18th " | Chapter vii. (painted furniture). |
| Kiskner, U. | Germany | 17th " | |
| Kraft, J. C. (architect) | England | 18th " | Chapter vii. |
| Kuenlin, J. | Germany | 17th " | |
| L | |||
| Ladetto, F. | Italy | 18th century | |
| Lalonde, — | France | " " | Furniture with mechanical contrivances (Louis XVI.). |
| Lardant, Jacques | " | 16th " | Chapter iii., p. 60. |
| Lathille, Pierre | France | 18th century | Worked in Paris, 1737.[257] |
| Lawreans, — | England | 17th " | Pupil of G. Gibbons (chapter iv.) |
| Le Brun, — (artist) | France | " " | Chapter vi., designed for Boule. |
| Lecreux, N. A. J. | Flanders | 1757-1836 | Carved pulpits. |
| Lelu, — | France | 18th century | Chapter vi., stamped on specimen in Jones Collection. Worked for Madame DuBarri. |
| Le Moyne | " | 1645-1718 | |
| Leopardi, A. | Italy | 1450-1525 | |
| Le Pautre, J. | France | 1617-1682 | |
| Le Roux, J. B. | " | 18th century | Chimney-pieces and room decorations. Worked in 1777. |
| Levasseur, — | " | " " | Chapter vi. |
| Lieutand, — | " | " " | Stamped on specimens in collection "National Mobilier," Paris. |
| Linnell, J. | England | 18th " | Furniture in Chippendale style |
| Lock, M. | " | " " | Chapter viii., carver and gilder, "Mobilier National," Paris. |
| Loir, A. | France | 1630-1713 | |
| L'Orme, Ph. de | " | 16th century | |
| Lunigia, A. da | Italy | " " | |
| Names of Artists or Manufacturers. |
Country and time in which they worked. |
Remarks and References. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M | |||
| Macé, J. | France | 17th century | "Menuisier en ébéne," was lodged in the Louvre to work, in 1644. |
| Claud, Isaac, Louis (?) sons of the above Macé |
|||
| Maffeis, P. di | Italy | 15th " | |
| Maggiolino, — | " | 18th " | A Milanese cabinet maker (marquetry chests of drawers), contemporary with Riesener. |
| Magister, O. | " | 16th " | |
| Majano, B. da | " | 15th " | Coffer maker to Matthias Corvinus, King of Hungary. |
| Majano, G. da | " | 1432-1490 | |
| Manwaring, Robert | England | 18th century | Chair maker (chap. vii., p. 173). |
| Magaritome, — | Italy | 1236-1313 | |
| Marot, D. | France | 1650-1700? | |
| Marot, G. | " | 17th century | |
| Marot, J. | " | 1625-1679 | |
| Martin, R. | " | 1706-1765 | Chapter vi., introduced Vernis-Martin. |
| Martincourt, — | " | 18th century | Bronze chaser. |
| Mayhew, — | England | " " | Chapter vii., contemporary with Chippendale. |
| Meissonnier, J. A. | France | 1693-1750 | Introduced broken shell-shaped curves and the more rococo style of Louis XIV. to XV. |
| Mendeler, G. | Germany | 17th century | [258] |
| Meulen, R. van der | Flanders | 1645-1717 | Carved chimney-pieces (G. Gibbon's style). |
| Miglionné, Ferdinand Filippo de |
France | 17th century | Invited to France by Colbert. |
| Minore, G. | Italy | 15th " | |
| Modena, P. da | " | " " | Chair of S. Francesco in Trevisco in 1486. |
| Moenart, M. | Flanders | 17th " | Carved the stalls in St. James', Bruges. |
| Monbro, — | England | 19th " | Chapter ix., p. 233. |
| Montepulciano, G. da | Italy | 16th " | |
| Morand, de Pont de Vaux | France | Stamped on a clock case at Versailles, with date 1706. | |
| Morant, — | England | 19th " | Chapter viii. |
| Moser, L. | Germany | 15th " | |
| Müller, D. | " | 17th " | |
| Müller, J. | " | " " | |
| N | |||
| Newrone, G. C. | Italy | 16th century | |
| Nilson, — | France | 18th " | Chapter vii., carver. |
| Nys, L. de | Flanders | " " } | Carved confessionals, work dated 1768. |
| Nys, P. de | " | " " } | |
| O | |||
| Oeben, Jean Francis | France | 18th century | Chapter vi., stamped on secretaire in Jones Collection. In 1751 ébenistes were bound to stamp their work. This Oeben died in 1765. |
| Oeben, Simon (probably son of the above) |
" | " " | Called the "inventor" of cylinder secretaires. |
| Oost, P. van. | Flanders | 14th " | |
| Oppen, Oorde Jean | Holland and France | 18th " | |
| P | |||
| Pacher, M. | Germany | 15th century | |
| Padova, Z. da | Italy | 16th " | |
| Pafrat, — | France | 18th " | On tables in Jones Collection at Bethnal Green Museum. |
| Panturmo, J. di | Italy | 1492-1556 | |
| Pardo, G. | Spain | 16th century | |
| Pareta, G. di | Italy | " " | |
| Passe, C. de | France | " " | Chapter iii. |
| Passe, C. de, the younger | " | " " | Chapter iii. |
| Percier and Fontaine (architects) |
France | 18th and 19th centuries. |
Chapter viii., p. 205, Empire furniture. |
| Pergolesi, — (artist) | England | 18th century | Chapter vii., employed by Robert Adam.[259] |
| Perreal, J. | France | 15th " | |
| Pettitt (otherwise Petit), Nicholas |
" | 18th " | Stamped on specimens in Jones Collection and in Bethnal Green Museum, "1761." |
| Philippon, A. | France | 16th " | |
| Picau, — | " | 18th " | Chapter vii., carver of frames (Louis XV. style). |
| Picq, J. | Flanders | 17th " | |
| Piffetti, A. P. | Italy | 1700-1777 | Furnished Royal Palace of Tusin (Boule style). |
| Pigalle, — | England | 18th century | French sculptor. |
| Pillon, G. | France | late 16th " | Chapter iii. |
| Pinodo, — | Spain | 18th " | Signature on painted cabinet in Bethnal Green Museum. |
| Pioniez, — | France | " " | Stamped on secretaire in Jones Collection. |
| Plumier, P. D. | Flanders | 1688-1721 | |
| Poitou, Phillipe | France | 18th century | "Ébeniste de France." |
| Porfirio, B. di | Italy | 16th " | |
| Prignot, — | England | 19th " | Designed for Jackson and Graham. |
| Puget, — | France | 18th " | Furniture and ship decorator. |
| Q | |||
| Quellin, A. | Flanders | 1609-1668 | |
| Quellin, A., the younger | " | 1625-1700 | |
| Quellin, E. | " | 17th century | |
| R | |||
| Raephorst, B. van | Flanders | 15th century | Carver of church reredos in 1740. |
| Ramello, F. | Italy | 16th " | |
| Ranson, — | France | 18th " | |
| Rasch, A. | Flanders | 15th " | Chapter iii. Chimney-piece in Palais de Justice, Bruges. |
| Revitt, N. (architect) | England | 18th " | Chapter vii. |
| Richardson, George | " | " " | Chapter vii., p. 186. Designer |
| Richter, C. | France | " " | Stamped on cabinet in the Jones Collection. |
| Riesener, — | " | " " | Born 1730. Chapter vi., ébeniste to M. Antoinette, came from Gladbeck, near Cologne. Died in 1806. |
| Roentgen, D. (see also David) |
" | " " | Chapter vi., contemporary with Riesener. Was living in 1780. |
| Rogers, H. | England | 19th " | Carved in boxwood, Chapter viii. |
| Rohan, J. de. | " | 16th " } | "Maitre Menuisiers" of Lyons, |
| Rohan, J. de. | " | " " } | 1548. |
| [260] | |||
| Rosch, J. | Germany | 15th " | |
| Rossi, P. de | Italy | 15th & 16th centuries | Lady artist of Bologna, carved minute work on peach stones. |
| Rovezzano, B. da | England | 16th century | Employed by Cardinal Wolsey. |
| Ruckera, Th. | Augsburg | " " | Chapter iii. (German section), steel chair, Longford Castle. |
| Names of Artists or Manufacturers. |
Country and time in which they worked. |
Remarks and References. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | |||
| Saint-Germain | France | 18th century | |
| Saint Yues, Antoine de | " | " " | |
| Salambier, — | " | 18th & 19th centuries | Designed room decorations, mirror frames, etc. |
| Sangher, J. de | Flanders | 17th century | |
| Schelden, P. van der | " | 16th " | |
| Schwanhard, H. | Germany | 17th " | Invented the "Wavy" mouldings used in Dutch and German furniture. |
| Seddon, Thomas | England | 19th " | Chapter viii., contemporary with early Gillow. |
| Seddon, Thomas & George (sons of above) |
" | " " | Chapter viii., furnished Windsor |
| Serlius, S. | France | 16th " | |
| Servellino, G. del | Italy | 15th " | |
| Shearer, — | England | 18th " | Chapter vii. |
| Sheraton, Th. | " | " " | Chapter vii. |
| Slocombe, P. | " | 19th " | Chapter ix., p. 245, designer. |
| Smet, R. de | Flanders | 16th " | Chapter iii. (Bruges chimney piece). |
| Smith, G. | England | 18th " | Chapter viii. (published book of designs). |
| Snell, — | " | 19th " | |
| Somer, Jacques | France | 18th " | |
| Stewart, Jas. (architect) | England | " " | Chapter vii. |
| Stobre, Laurent | France | 17th " | |
| Stockel, Joseph | " | 18th " | Worked at Fontainebleau. |
| Stoss, V. | Germany | 1438-1533 | |
| Street, Sir G., R. A, | England | 19th century | The New Law Courts (mediæval woodwork). |
| Swan, Abraham (architect) | " | 18th " | Chapter vii. |
| Swerdficher, F. | France | " " | Made the jewel cabinet of M. Antoinette, now in the "Garde Meuble." |
| Syrlin, J. | Germany | 15th " | |
| Syrlin, J., the younger | " | 15th and 16th centuries |
Chap. iii. (choir stalls, Ulm |
| T | |||
| Taillebert, U. | Flanders | 16th century | |
| Talbert, B. J. (architect) | England | 19th " | Chapter ix. Designed furniture in Gothic style. |
| Tasso, D. | Italy | 15th & 16th centr's.} | Known as wood carvers in |
| Tasso, G. | " | " " " } | Florence. Worked from M. |
| Tasso, G. B. | " | " " " } | Angelo's designs. |
| Tasso, M. D. | Italy | 15th century[261] | |
| Tatham, C. H. (architect) | England | 18th " | Designed interior decorations, &c., for the Duke of York. |
| Taurini, R. | Italy | 16th " | Pupil of A. Durer (stalls of Milan Cathedral). |
| Thomas, — (architect) | England | 18th " | Chapter vii. |
| Thomire, P. Ph. (mounter) | France | 1751-1843 | Museum of "Mobilier National," Paris. |
| Tolfo, G. | Italy | 16th century | |
| Toms and Luscombe | England | 19th " | Chapter ix., p. 235 (French style). |
| Topino, G. | France | 18th " | On examples in Jones Collection. |
| Toro, — | " | 18th " | Style of Boule (made for Palace of Versailles). |
| Torrigiano, — | England | 1472-1522 | Designed shrine of Henry VII. (Westminster Abbey). |
| Toto, — | " | 1331-1351 | |
| Town and Emanuel | " | 19th century | Chapter xi., pp. 233-5 (French style). |
| Travers, R. | France | 18th " | Worked in Paris, 1774. |
| Trevigi, G. da | England | 1503-44 | Court painter and decorator to Henry VIII. |
| Triard, J. B. | France | 18th century | |
| Tuart, — | " | 18th " | Lacquer work. |
| U | |||
| Uccello, P. | Italy | 1396-1479 | |
| Ugliengo, C. | " | 18th century | |
| V | |||
| Vasson, — | France | 18th century | A Mounter, or Bronziste. |
| Venasca, G. P. | Italy | 18th " | |
| Verbruggen, P. | Flanders | 17th " | Chapter iii.} Carved church ornamental work. |
| Verbruggen, P. the younger | " | 1660-1724 | Chapter iii.} Pulpit of Jesuits' College, Antwerp. |
| Verhaegen, Th. | " | 18th century | Carved work in several Mechlin Churches. |
| Vincenzo, Fra | Italy | Worked at Verona (intarsia). | |
| Vion, — | France | 18th century | A Mounter, or Bronzister. |
| Voyers, — | England | 18th " | Louis Seize style of furniture. |
| Vriesse, V. de | France | 17th " | Chapter iii. |
| W | |||
| Waldron, — | England | 18th century | Originally carver, afterwards actor. |
| Walker, H. | " | 16th " | |
| Watson, — | " | 17th and 18th centuries | Chapter iv., pupil of G. Gibbons. |
| Webb, — | " | 19th century | Chapter ix., p. 235. |
| Wedgwood, Josiah | England | 18th century | Chapter vii., introduced his plaques for furniture.[262] |
| Weinkopf, W. | Germany | 16th " | Worked in Nuremberg, temp. A. Durer. |
| Wertheimer, S. | England | 19th " | Chapter ix., p 233. |
| Wilkinson, — | " | " " | Chapter viii. |
| Willemfens, L. | Flanders | 1635-1702 | |
| William the Florentine | England | 13th century | Court painter and house decorator to Henry III. |
| Wilton, J. | England | 18th " | Employed by Sir W. Chambers. |
| Wren, Sir C. | " | 16th to 17th centuries | Chapter iv. |
| Wright and Mansfield | " | 19th century | Adams style of furniture. |
| Z | |||
| Zabello, F. | Italy | 16th century | Stalls in Cathedral of Bergamo. |
| Zorn, G. | Germany | 17th " | |
NOTE.—The Monogram "ME," branded on some of the old eighteenth century French cabinets, stands for "Menuisier Ébeniste," and generally accompanies the name or initials of the maker.
The following different kinds of wood are used in the manufacture of Furniture.
FOR THE BEST FURNITURE.
For Common Furniture and Interior Fittings.
Also some selections of Honduras mahogany when finely marked, and different varieties of the Eucalyptus.
The most expensive of these are used in veneers; and in the more ornamental and polychromatic marquetry, holly, horse chestnut, sycamore, pear tree and plum tree are used, being woods easily stained.
Amongst some of the rarer and more beautifully marked woods, used in small quantities, are the following:—
TEAK is an extremely strong East India wood; there is also an African teak (Sierra Leone), called African oak.
SHISHAM or BLACKWOOD (Dalbergia Sps) is a heavy close-grained wood, dark brown in color, resembling ebony when polished, and is much used for furniture in India.
SANDAL WOOD, TEAK, MANGO WOOD.—Sir George Birdwood, in "Indian Arts," gives a complete list of these Indian woods, with their botanical names and other valuable information.
For a more complete list of the different woods used by cabinet makers, the reader is referred to Mr. J. Hungerford Pollen's "Introduction to the South Kensington Collection"; to many of these he has been able, after much research, to give their botanical names, a task rendered somewhat difficult owing to the popular name of the wood being derived from some peculiar marking or colouring but giving no clue to its botanical status. Amongst these are tulip wood, rose wood, king wood, pheasant wood, partridge wood, and snake wood. It is worthy of remark that, whereas in England the terms "king wood" and "tulip wood" represent the former, a wood of rich dark reddish-brown color, or "purple madder," and the latter one of a yellowish-red, prettily-streaked, in France these terms have exactly the reverse equivalents. These were very favourite veneers in the best French marqueterie furniture described in Chapter VI., and are frequently found, the one as bordering to relieve the panel or drawer front of the other.
In the Museum at Kew Gardens, and also in the Colonial Galleries of the Imperial Institute, are excellent collections of many rare woods well worth examination.
Some particulars of the different woods mentioned in the Bible, from which examples of Ancient Furniture were manufactured, and to which reference has been made in Chapter I.
These notes have been kindly supplied by Dr. Edward Clapton, whose collection of specimens of these scarce woods is of great interest.
SHITTIM WOOD is the wood of the Shittah tree, or Acacia Seyal. This spiny tree especially abounded in the peninsula of Sinai and around the Dead Sea, but was also found in various parts of Syria, Arabia, and Africa. In the present day the shittah trees are very few and small, but in the time of Moses there were forests of them, and of a size sufficient to form long and wide planks. It is, as Jerome says, "a very strong wood of incredible lightness and beauty," and, he adds, "it is not subject to decay." This corresponds to the translation of the Hebrew term for shittim wood in the Septuagint, which is "incorruptible wood." Though light, it is hard, strong, and durable. As a proof of this, the Ark, and other furniture of the Tabernacle, which were made of shittim wood, must have lasted for a period of some 500 years before all traces of them were lost. Dean Stanley remarks that the plural word shittim was given to the wood of the shittah tree from the tangled thickets into which the stems of the trees expand.
ALMUG.—The wood of the Pterocarpus Santalinus, a large tree of the order "Leguminosœ."—The wood is very hard, has a reddish color, and takes a fine polish. It is a native of India and Ceylon, whence it was in Solomon's time conveyed to Ophir, on the east coast of Africa, and from Ophir to Palestine; "and the navy also of Hiram, that brought gold from Ophir, brought in great plenty of almug trees, and the king made of the almug trees pillars for the house of the Lord, and for the king's house, harps also and psalteries for singers." 1 Kings x. 11, 12. Almug is not the same as Algum, which grew on Lebanon with the cedar and fir. 2 Chron. ii. 8.
THYINE WOOD.—The wood of the Thuja Articulata, now named Callitris Quadrivalvis, a tree of the cypress sub-order of coniferæ, from 20 to 30 feet high. It is a native of Algiers and the Atlas range of North Africa. The wood is dark colored, hard, and fragrant, taking a fine polish; it yields an odoriferous resin called Sanderach, which was much used by the Romans for incense in the worship of their gods. Thyine takes its name from "to burn incense." It was much prized[264] by the ancient Greeks and Romans, not only because it was considered sacred but also on account of the beauty of the wood for various ornamental purposes. Pliny speaks of the mania of his countrymen for ornaments made of this wood, and tells us that when Roman ladies were upbraided by their husbands for their extravagance in pearls, they retorted upon them for their excessive fondness for tables made of thyine wood. So great a rage was there for ornamental cabinet work in ancient Rome that Cicero had a table made of it that cost £9,000. Ornaments made of this wood can be seen in the Museum at Kew, presented by the late Jerome Napoleon. The ceiling and floor of the celebrated Mosque of Cordova are of thyine wood, and it is also referred to in the Bible.
GOBELINS, BEAUVAIS, AND AUBUSSON TAPESTRY.—The famous factory of Gobelins originated in the establishment of some dye works in the Faubourg St. Marcel of Paris, by two brothers, Gilles and Jean Gobelin, who had introduced from Venice the art of dyeing scarlet; they also produced some other excellent colors, and this enterprise—at first considered foolish, and acquiring the name of Folie Gobelin—afterwards became most successful. This was in the reign of François I.; they subsequently added a tapestry factory to their dye works. Either in 1662 or in 1667, as different authorities state, Colbert, who had succeeded Cardinal Mazarin as Chief Adviser and Minister of Louis XIV., purchased the factory from the Gobelin family, and reorganised the establishment as the Royal Upholstery Works, employing the artists Lebrun, Berain, Simon Vouet, and others, to furnish subjects for the cartoons, the former artist being appointed Director of the Works. Since 1697 the manufacture of tapestry only has been carried on, and the product of these celebrated looms has become known as Gobelins tapestry. Previous to this time, however, namely, 1669, Colbert ordered the manufacture at Gobelins of what is termed the "low warp" tapestry suitable for furniture—a branch of manufacture which had been transferred to the State works of Beauvais, where the special mode of making tapestry, suitable for the covering of chairs and sofas, has since been carried on, the looms of Gobelins being more generally employed to produce larger panels for hangings. The fine texture, the brilliant colorings of the famous tapestry, are world famous; and enormous sums are commanded by some of the older panels, the tints of which are softened by age, while the condition remains good. Besides the tapestry for furniture, sometimes made at Gobelins, and more generally at Beauvais, a great deal has been produced by the looms at Aubusson, a factory said to have been originated by the immigration of some Flemish workmen into La March during the fourteenth century. Owing, however, to the difficulty in obtaining good patterns and the quality of wool required, their tapestry did not acquire a very high reputation. Colbert granted these manufactories a Charter in 1669, and also gave them protection against foreign rivals; and the looms of Aubusson became busy and their proprietors prosperous. The productions of Gobelins and Beauvais being monopolised by the Court, the works of Aubusson had to provide for the more general requirements of the people, and, therefore, though good of its kind, and occasionally excellent, this tapestry has never attained the reputation of its more famous contemporaries. To those who would learn more of Tapestry, its history, methods of production, and many instructive details, the little South Kensington handbook, "Tapestry," is highly commended; it was written for the Science and Art Department by M. Alfred de Champeaux, and translated by Mrs. R. F. Sketchley.
WOOD GILDING.—The processes of applying gold to wood and to metal are entirely different. In the former the gold, which has been supplied to the gilder in extremely thin layers, generally placed between the leaves of a little paper book to prevent them sticking together, is transferred therefrom to the surface to be gilt, by a dexterous movement of a flat gilder's camel's hair brush, or "tip," as it is termed, the wood having been previously prepared by successive coatings of whitening and thin glue, a thicker body of preparations being required for those parts which are to be burnished. A great deal depends upon the care and time bestowed on the preparation of the work, sometimes as many as ten coatings being given to the wood, and these are successively rubbed down with pumice stone and glass paper, care being taken not to lose the sharpness of carved ornaments. This application of gold leaf is termed mechanical gilding, and is used for gilt furniture, picture frames, or other decorations. Within the last ten years the gold has been applied to the more richly carved furniture in a powder. This preparation of gold is very expensive, costing about £7 the ounce, and is only used for the more costly chairs and couches, etc., generally of old French make, which require re-gilding.
METAL GILDING.—The process of gilding metal which was practised by the mounters of the fine old French furniture described in Chapter VI., consisted in applying to the "ormolu" an amalgam of gold and mercury; the latter was evaporated by heat, and the gold remained firmly adhered to the metal mount, and was afterwards colored as desired, a slightly greenish tinge being effected by such masters as Caffieri, Gouthière, and others. This kind of gilding requires a considerable quantity of the precious metal to be used, and is therefore very costly, but is rich in effect, and, under favourable conditions, permanent. It is, however, very injurious to the workers, on account of the fumes of the mercury poisoning the system; and it has generally been abandoned in favour of the much quicker and far cheaper process of electro-gilding, by which an effect can be produced by an infinitesimal coating of gold. The water gilding process is still used to a moderate extent by the makers of the more expensive reproductions of old furniture in Paris. There is a very cheap and effective process of lacquering which sometimes is termed "gilding," used to give ormolu mounts the color of gold; this is done by applying a solution of shellac and spirits of wine to the metal when heated, and, as with water-gilding, the volatile spirit evaporates and leaves a thin coating of the shellac, which may also be treated so as to have very much the appearance of gold, to the inexperienced eye. It should be mentioned that where mounts are gilt, it is usual to make the material more like the color of gold than ordinary brass would be; this is done by the admixture of a considerable amount of copper, the amalgam being generally termed "or-molu."
POLISHING.—The older method of polishing woodwork consisted in the application of a mixture of turpentine and beeswax to the surface; this would be repeated again and again, and then well rubbed down with a hard brush, when a very durable polish was obtained. For flat surfaces, and particularly for the tops of dining tables which were formerly uncovered to show the wood, oil polishing was the fashion; this was effected by rubbing the table-top with a heavy weight backwards and forwards, using oil as a lubricant. Good housewives used to polish up their dining tables very frequently. Oil polishing had the great advantage, too, of producing a surface which hot plates did not easily mark. The cost, time, and trouble, however, caused these older processes to be abandoned in favour of "French" polishing, which is the application on a prepared surface of shellac dissolved in methylated spirits, and often other ingredients to give poor-looking wood a richer color. This polish is quicker, and therefore, cheaper than the old-fashioned method. It has come into general adoption since the Great Exhibition of 1851.
The Pianoforte is such an important article in the furniture of the present time, that a few notes about its development, from a decorative point of view, may be acceptable. In "Musical Instruments," one of the South Kensington handbooks, Carl Engel traces the Pianoforte from the "Clavicembalo," which he tells us, "was, in fact, nothing but a Cembalo or Dulcimer, with a key board attached to it." Our present Grand Piano was, however, more immediately a development of the Harpsichord[29] and Spinet, which had succeeded the Virginal of the 16th century. These were made of oblong shape and supported on stands, which were simply supports for the instrument, and did not form a part of it as do the legs of a modern "grand." In an original play bill, which is still preserved at Messrs. Broadwoods', there is an announcement that at the Theatre Royal, Covent Garden, on the 16th of May, 1767, at the end of Act I. (of the Beggars' Opera), "Miss Brickler will sing a favourite song from 'Judith,' accompanied by Mr. Dibden, on a new Instrument, called Pianoforte."
There is an illustration on p. 172 of a Harpsichord which is in the South Kensington Museum, and in the same collection are others, varying in types as instruments, and of different decorations. The one which belonged to Handel is a good specimen of the decoration bestowed on these instruments. Others of about the middle of the eighteenth century, were covered with a coating of lacquer, like some of the furniture referred to in Chapter VI., the parts of the cases to be so decorated having been sent to China, and returned when coated with the preparation, then only known to the Chinese, but afterwards imitated in Europe. Some of these lacquered cases are very beautiful, and those which were elaborately painted in the Vernis Martin style, are finished with the care of cabinet pictures or miniatures. They have, as a rule, the fine subject painting, or landscape, inside the lid of the case, as in the illustration on p. 172, while the outside of the case is decorated with arabesques of gold on a dark colored ground. Such an Instrument was sold at the sale of Lord Lonsdale's furniture, a few years ago, for some three hundred pounds.
The rectangular shape appears to have been partially abandoned for the "Wing form," of which the modern "Grand" is a development, about the time of Queen Anne, and was, in some cases, adapted to the Harpsichord of the time. The earlier pianofortes were rectangular in form, with the idea of preventing the unequal appearance produced by the bent treble side of the Grand, and the writer has in his possession such an instrument, without pedals, which bears the inscription:—"By Royal Patent. Longman and Broderip, Musical Instrument makers, 13, Haymarket, and 26, Cheapside, London." Collard and Collard are the successors of this firm, and still retain the same premises in Cheapside. The oldest Broadwood piano, at present on exhibition in Vienna, bears the name of "Schudi and Broadwood," with date 1780. It is square and without pedals.
Towards the end of the last century pianos were made to harmonize with the Adam, Hepplewhite, and Sheraton furniture of the day, and some were elaborately inlaid with small plaques of Wedgwood's Jasper ware.
There are also instruments in existence, and designs, which shew that as the style of furniture changed during the time of the French Revolution, and subsequently to the Classic Greek, the Piano followed the new fashion. There is in St. James's Palace the instrument made by Broadwood for the Princess Charlotte, who died early in the nineteenth century. This is square in form, and is veneered with a single sheet of ivory, the elephant's tusk having been first softened by acid, and then cut circular fashion.
In France, the older Harpsichord and the later Pianoforte have followed the different styles which have affected the decorative furniture of that country, and the same remark applies to the more limited productions of such instruments in other countries.
During the period of had taste which prevailed in England thirty or forty years ago, those who made and those who purchased pianos were content to have either the instrument in the most ordinary and commonplace case of mahogany, walnut, or the rosewood which about 1840 came into great favour, or else the cases were designed in an extravagant fashion, and covered with a superabundance of ornament, quite out of keeping with the use of a musical instrument.
Two illustrations in Chapter IX., one of Broadwood's Grand, and the other of an upright in Bottle's style of work, by Leistler, of Vienna, may be taken as the most favourable examples of pinaoforte decorations at the time of the 1851 Exhibition.
Latterly there has been amongst leading manufacturers, especially those of our own country, a marked improvement, and the cases are made of rare and carefully chosen woods, and the style adapted, in many instances to the furniture of the room. Sir Alma Tadema designed cases in the Byzantine style. Mr. Burne-Jones painted one with an elaborate design of figures and scrolls; another with a shower of roses right across the sounding board, and he also revived the old-fashioned trestle support, formerly used for harpsichords. Mr. Waterhouse, R.A., Mr. John Birnie Philip, who executed the podium of the Albert Memorial, Mr. T. G. Jackson, R.A., and others, have also designed piano cases for friends and clients.
In the "Inventions" Exhibition, a few years since, there was a very good opportunity of noticing the advance in design of the Pianoforte. In nearly every instance the old fashioned fretwork front had been abandoned for a painting or a marquetry panel. Some were enamelled white, and relieved by gilding; others had a kind of gesso-work decoration, and the different fashionable styles of furniture were reproduced with various modifications. Amongst others, Kirkmans exhibited a grand and an upright made from designs by Col. Edis, and Hopkinson a boudoir grand and some small cottage pianos in satinwood and marquetry, and also in satinwood painted in the old English style, and having silk panels in front with copies of Bartolozzi prints. The designs were in the latter case made by the author. Broadwoods, and other English firms, also produced special designs.
Since this Exhibition, if there has not been improvement, there has been endless variety, and the piano case is now designed and decorated to please the taste of the most fastidious or the most eccentric.
NOTE.—The Names of several Designers and Makers, omitted from the Index, will be found in the list in the Appendix, with references.
[1] Gopher is supposed to mean cypress wood. See Notes on Woods (Appendix).
[2] See also Notes on Woods (Appendix).
[3] Those who would read a very interesting account of the history of this stone are referred to the late Dean Stanley's "Historical Memorials of Westminster Abbey."
[4] The sous, which was but nominal money, may be reckoned as representing 20 francs, the denier 1 franc, but allowance must be made for the enormous difference in the value of silver, which would make 20 francs in the thirteenth century represent upwards of 200 francs in the present century.
[5] The panels of the high screen or back to the stalls in "La Certosa di Pavia" (a Carthusian Monastery suppressed by Joseph II.) are famous examples of early intarsia. In an essay on the subject written by Mr. T. G. Jackson, A.R.A., they are said to be the work of one Bartolommeo, an Istrian artist, and to date from 1486. The same writer mentions still more elaborate examples of pictorial "intarsia" in the choir stalls of Sta. Maria, Maggiore, in Bergamo.
[6] Writers of authority on architecture have noticed that the chief characteristic in style of the French Renaissance, as contrasted with the Italian, is that in the latter the details and ornament of the new school were imposed on the old foundations of the Gothic character. The Chateau of Chambord is given as an instance of this combination.
[7] "Meubles en bois sculpté ayant figuré à l'exposition rétrospective de Lyon en 1877," par J. B. Giraud.
[8] Dr. Jacob von Falké states that the first mention of glass as an extraordinary product occurs in a register of 1239.
[9] The present decorations of the room were painted either actually by Watts or under his directions, when, as favourite artist to the fourth Lord Holland, he did so much to beautify the house and made so many additions to its store of portraits. His work is fully described in "Holland House," by Princess Marie Liechtenstein. London, 1874.
[10] The following passage occurs in one of Beaumont and Fletcher's plays:—
"Is the great Couch up, the Duke of Medina sent?" to which the duenna replies, "'Tis up, and ready;" and then Marguerite asks, "And day beds in all chambers?" receiving in answer, "In all, lady."
[11] This tapestry is still in the Great Hall at Hampton Court Palace.
[12] The present decorations of the Palace of Versailles were carried out about 1830, under Louis Phillipe. "Versailles Galeries Historiques," par C. Gavard, is a work of 13 vols. devoted to the illustration of the pictures, portraits, statues, busts, and various decorative contents of the Palace.
[13] For description of method of gilding the mounts of furniture, see Appendix.
[14] NOTE.—Since the first edition of this book was published in 1892, the value of really fine old French furniture has considerably risen, and the above-named estimate of the auction price of such a suite of furniture as is described would have to be doubled.
[15] Watteau, 1684-1721. Lancret, b. 1690, d. 1743. Boucher, b. 1703, d. 1770.
[16] "The universal system of Household Furniture, 300 designs on 95 plates, folio. London. N.D. (circa 1770)"
[17] Matthias Lock published "A new book of pier frames, ovals, girandoles, tables, etc." Imp. 8vo., 1769.
[18] The Court room of the Stationers' Hall contains an excellent set of tables of this kind.
[19] The late Mr. Adam Black, senior partner in the publishing firm of A. and C. Black, and Lord Macaulay's colleague in Parliament, when quite a young man, assisted Sheraton in the production of this book; at that time the famous designer of furniture was in poor circumstances.
[20] The word baroque, which became a generic term, was derived from the Portuguese "barrocco," meaning a large irregular-shaped pearl. At first a jeweller's technical term, it came later, like "rococo," to be used to describe the kind of ornament which prevailed in design of the nineteenth century, after the disappearance of the classic.
[21] Mr. Parker defines Dado as "The solid block, or cube, forming the body of a pedestal in classical architecture, between the base mouldings and the cornice: an architectural arrangement of mouldings, etc., round the lower parts of the wall of a room, resembling a continuous pedestal."
[22] Collinson and Lock amalgamated with Warings in 1897.
[23] The present firm is Radley, Robson and Mackay.
[24] This Collection, now better known as the Wallace Collection, has been bequeathed to the Nation.
[25] Miss Rowe, who has made some valuable contributions to the literature of Woodwork, has written hand-books for young woodcarvers, which are published under the sanction of the South Kensington authorities.
[26] Essay by Mr. Edward S. Prior, "Of Furniture and the Room."
[27] Published in 1868, when the craze for novelties was at its height.
[28] Essay on "Decorated Furniture," by J. H. Pollen.
[29] The Harpsichord made for Frederick the Great, by Burkardt-Tschudi, whose son-in-law was the first John Broadwood, was in the style of German Renaissance.
Transcriber notes:
P. xi. Chapter VIII. is on p. 203, not p. 201, changed.
P. 53. Footnote 5: 'Maggoire' changed to 'Maggiore' as noted in other edition.
P. 122. 'wallnut' changed to 'walnut.'
P. 254. 'Green Musuem', changed 'Musuem. to 'Museum'.
P. 272. 'Sta ioners', changed to 'Stationers'.